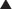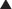Chapter 24 Pulmonary System
Beta 2 (β2) Agonists (Bronchodilators)
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
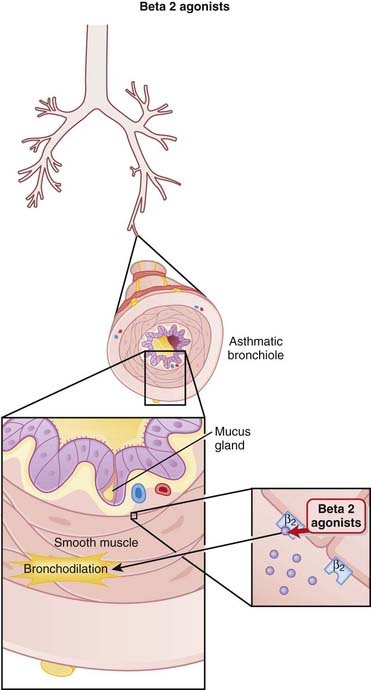
 Stimulation of β2 receptors in bronchial smooth muscle results in relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle. This results in a larger diameter airway, resulting in lower resistance to airflow in and out of the lungs (Figure 24-1).
Stimulation of β2 receptors in bronchial smooth muscle results in relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle. This results in a larger diameter airway, resulting in lower resistance to airflow in and out of the lungs (Figure 24-1).Pharmacokinetics
 These drugs are all typically administered via inhalation: via metered dose inhaler (MDI), dry powder inhaler, or nebulizer (atomizes liquid drug into a mist). Inhalation delivers the drug to the lungs, where the highest concentrations are desired, thereby reducing the probability of side effects.
These drugs are all typically administered via inhalation: via metered dose inhaler (MDI), dry powder inhaler, or nebulizer (atomizes liquid drug into a mist). Inhalation delivers the drug to the lungs, where the highest concentrations are desired, thereby reducing the probability of side effects. Response to SABAs is rapid (response time 5 minutes) compared with inhaled anticholinergics (30 minutes).
Response to SABAs is rapid (response time 5 minutes) compared with inhaled anticholinergics (30 minutes). For LABAs, the response time of formoterol is similar to that of SABAs (5 minutes), but the onset of action of salmeterol is longer (15 to 20 minutes).
For LABAs, the response time of formoterol is similar to that of SABAs (5 minutes), but the onset of action of salmeterol is longer (15 to 20 minutes).Contraindications
Side Effects
Important Notes
 SABAs as required may be used as sole therapy in mild episodic asthma. Neither SABAs nor LABAs should be used as sole therapy in persistent asthma but should be combined with antiinflammatory therapy.
SABAs as required may be used as sole therapy in mild episodic asthma. Neither SABAs nor LABAs should be used as sole therapy in persistent asthma but should be combined with antiinflammatory therapy. The combination of LABAs and ICSs has become standard therapy in the management of asthma. There are two reasons why this combination is believed to be so effective. First, the use of a bronchodilator is believed to open up the airways to improve distribution of the steroid. Second, it appears that chronic ICS use up-regulates β2 receptors in the lungs. This is important because chronic use of β2 agonists is believed to lead to a down-regulation of β2 receptors in the lungs. Some available drugs are combinations of a bronchodilator and steroid together in one inhaler (Table 24-1).
The combination of LABAs and ICSs has become standard therapy in the management of asthma. There are two reasons why this combination is believed to be so effective. First, the use of a bronchodilator is believed to open up the airways to improve distribution of the steroid. Second, it appears that chronic ICS use up-regulates β2 receptors in the lungs. This is important because chronic use of β2 agonists is believed to lead to a down-regulation of β2 receptors in the lungs. Some available drugs are combinations of a bronchodilator and steroid together in one inhaler (Table 24-1). Although use of ICS-LABA combinations is now a routine practice, the use of LABAs as monotherapy has prompted a lingering safety concern that has plagued these agents since their introduction into the market.
Although use of ICS-LABA combinations is now a routine practice, the use of LABAs as monotherapy has prompted a lingering safety concern that has plagued these agents since their introduction into the market.| Salmeterol + fluticasone | Advair |
| Formoterol + budesonide | Symbicort |
| Salbutamol + ipratropium | Combivent |
Evidence
Long-Acting β Agonists with or without Inhaled Corticosteroids in Adults or Children with Asthma
 A 2007 Cochrane review (67 studies, 42,333 participants) examined the use of LABAs (salmeterol, 50 studies; formoterol, 17 studies) versus placebo. In these studies, patients were followed for 4 to 52 weeks. Patients were allowed to combine inhaled corticosteroids (ICSs) with LABAs in 40 studies, 24 studies did not permit ICSs, and three studies were unclear about ICS use. Use of LABAs, with or without ICSs, was associated with improvements in pulmonary function, symptoms, rescue medication use, and quality-of-life scores.
A 2007 Cochrane review (67 studies, 42,333 participants) examined the use of LABAs (salmeterol, 50 studies; formoterol, 17 studies) versus placebo. In these studies, patients were followed for 4 to 52 weeks. Patients were allowed to combine inhaled corticosteroids (ICSs) with LABAs in 40 studies, 24 studies did not permit ICSs, and three studies were unclear about ICS use. Use of LABAs, with or without ICSs, was associated with improvements in pulmonary function, symptoms, rescue medication use, and quality-of-life scores.Formoterol Plus Inhaled Corticosteroids in Asthma
 A 2009 Cochrane review (3 studies, N = 5905 patients) compared combinations of formoterol and ICSs with SABAs alone for relief of asthma symptoms. No clinically important advantages were found for the combination in patients with mild asthma. However, in more severe asthma, one study found that patients not well controlled on high-dose ICSs and who had had an exacerbation in the prior year had a reduced risk of exacerbations requiring oral steroids when using the combination versus terbutaline or formoterol monotherapy for relief. A study in children also found less serious adverse events with the combination of budesonide and formoterol for maintenance and relief.
A 2009 Cochrane review (3 studies, N = 5905 patients) compared combinations of formoterol and ICSs with SABAs alone for relief of asthma symptoms. No clinically important advantages were found for the combination in patients with mild asthma. However, in more severe asthma, one study found that patients not well controlled on high-dose ICSs and who had had an exacerbation in the prior year had a reduced risk of exacerbations requiring oral steroids when using the combination versus terbutaline or formoterol monotherapy for relief. A study in children also found less serious adverse events with the combination of budesonide and formoterol for maintenance and relief.Regular Formoterol versus Placebo or Short-Acting β Agonists in Chronic Asthma
 A 2008 Cochrane review (22 studies, 8032 patients) compared serious adverse event rates for regular formoterol use with placebo or SABAs in chronic asthma. Nonfatal serious adverse events were increased versus placebo (odds ratio [OR] 1.57), but no increase was detected versus salbutamol or terbutaline. The increased risk over placebo was also seen in patients taking ICSs.
A 2008 Cochrane review (22 studies, 8032 patients) compared serious adverse event rates for regular formoterol use with placebo or SABAs in chronic asthma. Nonfatal serious adverse events were increased versus placebo (odds ratio [OR] 1.57), but no increase was detected versus salbutamol or terbutaline. The increased risk over placebo was also seen in patients taking ICSs. Parasympathetic stimulation of muscarinic receptors of the bronchioles results in bronchoconstriction and also increased bronchial secretions. These actions are largely mediated through M3 receptors, and to a lesser extent, M1 (Figure 24-2).
Parasympathetic stimulation of muscarinic receptors of the bronchioles results in bronchoconstriction and also increased bronchial secretions. These actions are largely mediated through M3 receptors, and to a lesser extent, M1 (Figure 24-2). Antagonism of these muscarinic receptors prevents bronchoconstriction and reduces secretions. Tiotropium has greater selectivity for M3 receptors than ipratropium, which is considered to be relatively nonspecific for M1, M2, and M3 receptors. The clinical significance of this increased specificity has not been established.
Antagonism of these muscarinic receptors prevents bronchoconstriction and reduces secretions. Tiotropium has greater selectivity for M3 receptors than ipratropium, which is considered to be relatively nonspecific for M1, M2, and M3 receptors. The clinical significance of this increased specificity has not been established. Ipratropium and tiotropium are inhaled. They are quaternary compounds (therefore polarized and not apt to cross hydrophobic cell membranes). They do not readily cross the pulmonary membranes into the blood. Therefore, systemic absorption is low.
Ipratropium and tiotropium are inhaled. They are quaternary compounds (therefore polarized and not apt to cross hydrophobic cell membranes). They do not readily cross the pulmonary membranes into the blood. Therefore, systemic absorption is low. A lot of the drug ends up being swallowed. However, absorption from the gastrointestinal (GI) tract is also very low.
A lot of the drug ends up being swallowed. However, absorption from the gastrointestinal (GI) tract is also very low. Compared with salbutamol, onset and duration of action are prolonged, likely because of minimal absorption from the lung.
Compared with salbutamol, onset and duration of action are prolonged, likely because of minimal absorption from the lung. When anticholinergics are used, caution should be exercised in patients who have conditions that would be exacerbated by cholinergic antagonism, such as glaucoma and urinary retention. However, because inhaled anticholinergics have low systemic absorption, this is typically not an issue in most patients.
When anticholinergics are used, caution should be exercised in patients who have conditions that would be exacerbated by cholinergic antagonism, such as glaucoma and urinary retention. However, because inhaled anticholinergics have low systemic absorption, this is typically not an issue in most patients.Cardiovascular Safety
 A 2008 meta-analysis (17 trials, N = 14,783 patients) found an increased risk of the composite of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction (MI), and stroke in patients on inhaled anticholinergics (1.8%) versus control therapy (1.2%). Specifically, risk of MI and cardiovascular death was increased, whereas risk of stroke was not.
A 2008 meta-analysis (17 trials, N = 14,783 patients) found an increased risk of the composite of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction (MI), and stroke in patients on inhaled anticholinergics (1.8%) versus control therapy (1.2%). Specifically, risk of MI and cardiovascular death was increased, whereas risk of stroke was not.Ipratropium versus Short-Acting β2 Agonists in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 A 2006 Cochrane review (11 studies, N = 3912 patients) found small benefits of ipratropium over SABAs on measures of lung function, quality of life, and the requirement for oral steroids. The combination of ipratropium and SABAs was better than a β2 agonist alone with respect to postbronchodilator lung function and a reduction in the need for oral steroids.
A 2006 Cochrane review (11 studies, N = 3912 patients) found small benefits of ipratropium over SABAs on measures of lung function, quality of life, and the requirement for oral steroids. The combination of ipratropium and SABAs was better than a β2 agonist alone with respect to postbronchodilator lung function and a reduction in the need for oral steroids.Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists
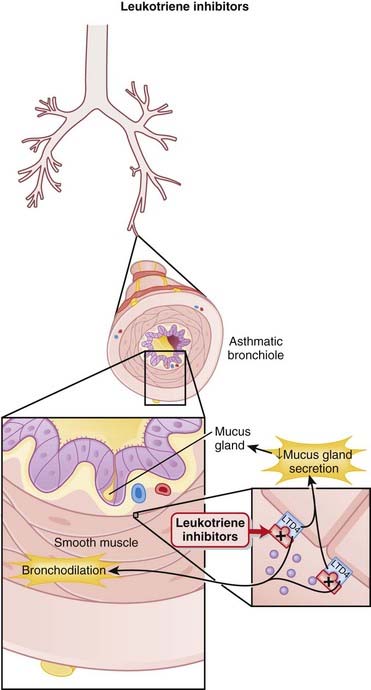
 Leukotrienes are biologically active fatty acids derived from the oxidative metabolism of arachidonic acid, via the enzyme 5-lipoxygenase.
Leukotrienes are biologically active fatty acids derived from the oxidative metabolism of arachidonic acid, via the enzyme 5-lipoxygenase. Leukotriene receptor antagonists competitively and selectively block the LTD4 receptor (Figure 24-3).
Leukotriene receptor antagonists competitively and selectively block the LTD4 receptor (Figure 24-3). These drugs are not indicated for acute exacerbations of the disease. They are recommended for prophylaxis and chronic treatment of asthma.
These drugs are not indicated for acute exacerbations of the disease. They are recommended for prophylaxis and chronic treatment of asthma. LTRAs can be tried when an inhaled steroid cannot be used, or if the inhaled steroid dose cannot be increased.
LTRAs can be tried when an inhaled steroid cannot be used, or if the inhaled steroid dose cannot be increased.LRTAs versus Inhaled Corticosteroids (ICSs) for Chronic Asthma
 A 2000 Cochrane review (27 trials) compared the safety and efficacy of antileukotrienes to ICS in mild to moderate asthma. Patients treated with antileukotrienes were more likely to have an exacerbation requiring systemic steroids (NNH = 26). ICS also improved pulmonary functions (FEV1), symptoms, nocturnal awakenings, rescue medication use, and quality of life to a greater extent than did antileukotrienes. More patients treated with antileukotrienes withdrew due to poor asthma control. The risk of side effects was no different between groups.
A 2000 Cochrane review (27 trials) compared the safety and efficacy of antileukotrienes to ICS in mild to moderate asthma. Patients treated with antileukotrienes were more likely to have an exacerbation requiring systemic steroids (NNH = 26). ICS also improved pulmonary functions (FEV1), symptoms, nocturnal awakenings, rescue medication use, and quality of life to a greater extent than did antileukotrienes. More patients treated with antileukotrienes withdrew due to poor asthma control. The risk of side effects was no different between groups.LTRAs Plus ICSs versus Long-Acting β2 Agonists (LABAs) Plus ICSs for Chronic Asthma
 A 2006 Cochrane review (16 studies) evaluated the effect of adding LTRAs vs. LABAs to ICS in patients with chronic asthma. The findings showed a lower rate of requiring systemic steroids (RR = 0.83) with LABAs. Other endpoints including lung function tests, symptoms, and use of rescue β2 agonists were also superior with LABAs. Withdrawals from treatment and side effects were similar in both groups.
A 2006 Cochrane review (16 studies) evaluated the effect of adding LTRAs vs. LABAs to ICS in patients with chronic asthma. The findings showed a lower rate of requiring systemic steroids (RR = 0.83) with LABAs. Other endpoints including lung function tests, symptoms, and use of rescue β2 agonists were also superior with LABAs. Withdrawals from treatment and side effects were similar in both groups. Zileuton is a 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor approved for use in the United States but not in some other jurisdictions, due to safety concerns.
Zileuton is a 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor approved for use in the United States but not in some other jurisdictions, due to safety concerns. An ene bond is one in which there are two bonds between two carbon atoms (C=C). Leuktrienes have three of these bonds. The ane bond is a single bond (C–C).
An ene bond is one in which there are two bonds between two carbon atoms (C=C). Leuktrienes have three of these bonds. The ane bond is a single bond (C–C). The mechanism of action of methylxanthines is not completely understood. There are three theories on how they work:
The mechanism of action of methylxanthines is not completely understood. There are three theories on how they work:
 Active or symptomatic coronary heart disease is a contraindication. Methylxanthines increase cAMP, which will increase cardiac inotropy. Furthermore, the heart rate will be increased. Both these factors will impair the oxygen supply-demand ratio to the myocardium.
Active or symptomatic coronary heart disease is a contraindication. Methylxanthines increase cAMP, which will increase cardiac inotropy. Furthermore, the heart rate will be increased. Both these factors will impair the oxygen supply-demand ratio to the myocardium. Side effects are common because of the unpredictability of serum levels and the narrow therapeutic index.
Side effects are common because of the unpredictability of serum levels and the narrow therapeutic index.Theophylline versus Long-Acting β Agonists for Chronic Stable Asthma
 A Cochrane review in 2007 (13 studies, N = 1344 patients) found that theophylline and LABAs are equally effective in improving symptoms and lung function (predicted FEV1) in stable asthma. However, there are more side effects with theophylline (relative risk [RR], 2.27).
A Cochrane review in 2007 (13 studies, N = 1344 patients) found that theophylline and LABAs are equally effective in improving symptoms and lung function (predicted FEV1) in stable asthma. However, there are more side effects with theophylline (relative risk [RR], 2.27).Theophylline versus Placebo for Stable COPD
 A Cochrane review in 2002 (20 studies, N = 873 patients) found that in patients with stable COPD, compared with placebo, theophylline caused a small increase of FEV1 (weighted mean difference [WMD] 100 mL) and forced vital capacity (FVC) (WMD 195 mL/min) and slightly improved O2 and CO2 levels. There were no differences for the following endpoints: distance walked (exercise test), symptoms of breathlessness or wheeze, exacerbations, or dropouts. Patients who were surveyed preferred theophylline over placebo. All patients were receiving other medications for COPD in both the placebo and treatment arms.
A Cochrane review in 2002 (20 studies, N = 873 patients) found that in patients with stable COPD, compared with placebo, theophylline caused a small increase of FEV1 (weighted mean difference [WMD] 100 mL) and forced vital capacity (FVC) (WMD 195 mL/min) and slightly improved O2 and CO2 levels. There were no differences for the following endpoints: distance walked (exercise test), symptoms of breathlessness or wheeze, exacerbations, or dropouts. Patients who were surveyed preferred theophylline over placebo. All patients were receiving other medications for COPD in both the placebo and treatment arms.Theophylline versus Placebo for Treatment of COPD Exacerbations
 A Cochrane review in 2003 (4 studies, N = 169 patients) found that the change in FEV1 at 2 hours was similar in both groups but transiently increased with methylxanthines at 3 days (WMD 101 mL). Data on clinical outcomes were sparse. Trends toward improvements in hospitalization and length-of-stay were offset by a trend toward more relapses at 1 week. Changes in symptom scores were not significant. Methylxanthines caused more nausea and vomiting than placebo (OR 4.6) and trended toward more frequent tremor, palpitations, and arrhythmias.
A Cochrane review in 2003 (4 studies, N = 169 patients) found that the change in FEV1 at 2 hours was similar in both groups but transiently increased with methylxanthines at 3 days (WMD 101 mL). Data on clinical outcomes were sparse. Trends toward improvements in hospitalization and length-of-stay were offset by a trend toward more relapses at 1 week. Changes in symptom scores were not significant. Methylxanthines caused more nausea and vomiting than placebo (OR 4.6) and trended toward more frequent tremor, palpitations, and arrhythmias. If you add a methyl (CH3) group to xanthine, you get a methylxanthine. If you add a CH3 group to theophylline, you get caffeine. The similarity to caffeine may explain the stimulatory side effects.
If you add a methyl (CH3) group to xanthine, you get a methylxanthine. If you add a CH3 group to theophylline, you get caffeine. The similarity to caffeine may explain the stimulatory side effects. Aminophylline is a combination mixture of theophylline and ethylenediamine (two amine groups connect by two carbons). It simply dissociates in the body to theophylline.
Aminophylline is a combination mixture of theophylline and ethylenediamine (two amine groups connect by two carbons). It simply dissociates in the body to theophylline. Overall, steroids have a broad antiinflammatory effect. This counteracts the airway inflammation characteristic in asthma. A variety of mechanisms are believed to contribute to the antiinflammatory effects of corticosteroids:
Overall, steroids have a broad antiinflammatory effect. This counteracts the airway inflammation characteristic in asthma. A variety of mechanisms are believed to contribute to the antiinflammatory effects of corticosteroids: Reduced function of phospholipase A2, resulting in reduced mediators of inflammation: prostaglandins (PGs) and leukotrienes (LTs)
Reduced function of phospholipase A2, resulting in reduced mediators of inflammation: prostaglandins (PGs) and leukotrienes (LTs) Steroids exert their actions in a broad range of tissues, and therefore there are many effects of glucocorticoids.
Steroids exert their actions in a broad range of tissues, and therefore there are many effects of glucocorticoids. Steroids also have a number of other effects, many of which are not beneficial but contribute to many of the harmful effects of these agents. Fortunately, the harmful effects are mitigated by the minimal systemic absorption associated with the inhalational route.
Steroids also have a number of other effects, many of which are not beneficial but contribute to many of the harmful effects of these agents. Fortunately, the harmful effects are mitigated by the minimal systemic absorption associated with the inhalational route. Asthma:
Asthma:
 At higher doses, side effects associated with systemic corticosteroids may develop, most notably osteoporosis. This is rare with inhaled steroids.
At higher doses, side effects associated with systemic corticosteroids may develop, most notably osteoporosis. This is rare with inhaled steroids. ICSs are typically used in combination with inhaled beta agonists, as these bronchodilators help to open the airways and facilitate deposition of the steroid.
ICSs are typically used in combination with inhaled beta agonists, as these bronchodilators help to open the airways and facilitate deposition of the steroid. Because of their potential for extensive systemic side effects, the use of systemic corticosteroids such as prednisone is typically reserved for severe asthma, preferably administered over short courses.
Because of their potential for extensive systemic side effects, the use of systemic corticosteroids such as prednisone is typically reserved for severe asthma, preferably administered over short courses.Long-Acting β2 Agonists with or without ICSs in Adults or Children with Asthma
 A 2007 Cochrane review (67 studies, N = 42,333 participants) examined the use of LABAs (salmeterol, 50 studies; formoterol, 17 studies) versus placebo. In these studies, patients were followed for 4 to 52 weeks. Patients were allowed to combine ICSs with LABA in 40 studies, whereas 24 studies did not permit ICS and three studies were unclear about ICS use. Use of LABAs with or without ICSs was associated with improvements in pulmonary function, symptoms, rescue medication use, and quality-of-life scores.
A 2007 Cochrane review (67 studies, N = 42,333 participants) examined the use of LABAs (salmeterol, 50 studies; formoterol, 17 studies) versus placebo. In these studies, patients were followed for 4 to 52 weeks. Patients were allowed to combine ICSs with LABA in 40 studies, whereas 24 studies did not permit ICS and three studies were unclear about ICS use. Use of LABAs with or without ICSs was associated with improvements in pulmonary function, symptoms, rescue medication use, and quality-of-life scores.ICSs versus Nonsteroid Inhaled Therapy for Treatment of COPD
 A 2008 systematic review (11 trials, N = 14,426 patients) compared ICS therapy for ≥6 months with nonsteroid inhaled therapy in patients with COPD. There was no difference in all-cause mortality, and a higher incidence of pneumonia was found with ICSs (RR 1.34).
A 2008 systematic review (11 trials, N = 14,426 patients) compared ICS therapy for ≥6 months with nonsteroid inhaled therapy in patients with COPD. There was no difference in all-cause mortality, and a higher incidence of pneumonia was found with ICSs (RR 1.34). The chronic use of corticosteroids in children has been a cause for concern owing to the growth-retarding effects of these agents. Determination of a causal relationship between chronic inhaled steroid use and stunted growth is complicated by the fact that asthma itself may also slow growth and development in children.
The chronic use of corticosteroids in children has been a cause for concern owing to the growth-retarding effects of these agents. Determination of a causal relationship between chronic inhaled steroid use and stunted growth is complicated by the fact that asthma itself may also slow growth and development in children. Nasally administered corticosteroids are used for chronic inflammatory problems of the nasal passages and sinuses.
Nasally administered corticosteroids are used for chronic inflammatory problems of the nasal passages and sinuses.Phosphodiesterase-5 Inhibitors
Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitors are vasodilators.
 PDE breaks down intracellular cyclic adenine monophosphate (cAMP) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP).
PDE breaks down intracellular cyclic adenine monophosphate (cAMP) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). PDE inhibitors therefore result in increased intracellular cAMP and cGMP. The cell or tissue type affected will dictate the effect of the PDE inhibitor. Furthermore, different PDE subtypes have different selectivity for cAMP and cGMP. This is important because the two clinically important PDE inhibitors (types 3 and 5) are quite different from each other.
PDE inhibitors therefore result in increased intracellular cAMP and cGMP. The cell or tissue type affected will dictate the effect of the PDE inhibitor. Furthermore, different PDE subtypes have different selectivity for cAMP and cGMP. This is important because the two clinically important PDE inhibitors (types 3 and 5) are quite different from each other. PDE5 is distributed in the body primarily in vascular smooth muscle; thus, its effects primarily influence vascular tone.
PDE5 is distributed in the body primarily in vascular smooth muscle; thus, its effects primarily influence vascular tone. PDE5 is more selective for intracellular cGMP. cGMP interacts with nitric oxide (NO):
PDE5 is more selective for intracellular cGMP. cGMP interacts with nitric oxide (NO):
 PKG acts on a variety of sites; the net effect is to lower intracellular Ca2+, which results in uncoupling of actin and myosin, leading to smooth muscle relaxation and ultimately vasodilation (Figure 24-4).
PKG acts on a variety of sites; the net effect is to lower intracellular Ca2+, which results in uncoupling of actin and myosin, leading to smooth muscle relaxation and ultimately vasodilation (Figure 24-4). Erections occur because the two corpora cavernosa and the single corpus spongiosum become filled with blood and then, under pressure, increase in size and impart resistance to bending. Filling the three corpora requires arterial vasodilation to increase blood flow.
Erections occur because the two corpora cavernosa and the single corpus spongiosum become filled with blood and then, under pressure, increase in size and impart resistance to bending. Filling the three corpora requires arterial vasodilation to increase blood flow. Pulmonary hypertension refers to increased blood pressure in the pulmonary arterial system. There are many different causes, but a common component across many different causes is abnormally increased pulmonary vasoconstriction. Remember that blood pressure is proportional to resistance, and resistance to flow is greatly influenced by vascular tone.
Pulmonary hypertension refers to increased blood pressure in the pulmonary arterial system. There are many different causes, but a common component across many different causes is abnormally increased pulmonary vasoconstriction. Remember that blood pressure is proportional to resistance, and resistance to flow is greatly influenced by vascular tone. Each of the drugs in this class have different onset times and half-lives and thus different durations of action (Table 24-2).
Each of the drugs in this class have different onset times and half-lives and thus different durations of action (Table 24-2). Because PDE5 inhibitors are hepatically metabolized and eliminated by the kidney, they can accumulate and result in overdose when given to patients with renal dysfunction. This manifests as excessive vasodilation and hypotension.
Because PDE5 inhibitors are hepatically metabolized and eliminated by the kidney, they can accumulate and result in overdose when given to patients with renal dysfunction. This manifests as excessive vasodilation and hypotension.TABLE 24-2 Onset and Elimination Half-Life of PDE-5 Inhibitors
| Drug | Peak of Onset | Half-Life |
|---|---|---|
| Sildenafil | 60 minutes | 4 hours |
| Vardenafil | 60 minutes | 4.7 hours |
| Tadalafil | 120 minutes | 17.5 hours |
 Renal failure is a relative contraindication because the steady state plasma levels can become dangerously elevated when the drugs are administered by intravenous infusion for pulmonary hypertension.
Renal failure is a relative contraindication because the steady state plasma levels can become dangerously elevated when the drugs are administered by intravenous infusion for pulmonary hypertension. Nitroglycerin coadministration can cause severe and difficult-to-treat hypotension. Coadministration of nitroglycerin is absolutely contraindicated.
Nitroglycerin coadministration can cause severe and difficult-to-treat hypotension. Coadministration of nitroglycerin is absolutely contraindicated. Priapism (prolonged erection) can result in tissue ischemia of the penis. If an erection becomes painful or lasts for >2 hours, emergency medical attention should be obtained immediately.
Priapism (prolonged erection) can result in tissue ischemia of the penis. If an erection becomes painful or lasts for >2 hours, emergency medical attention should be obtained immediately. Sudden hearing loss: The mechanism of injury for this side effect has not yet been established. It is usually unilateral and can be reversible. Associated vertigo has also been documented.
Sudden hearing loss: The mechanism of injury for this side effect has not yet been established. It is usually unilateral and can be reversible. Associated vertigo has also been documented. Visual loss: Nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) is a very rare condition that might be associated with increased risk.
Visual loss: Nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) is a very rare condition that might be associated with increased risk. Coadministration of nitrates to patients with angina in the emergency room can result in profound refractory hypotension. Patients may not be completely forthcoming about the use of medications for erectile dysfunction, and therefore the risks of coadministration (if nitrates are about to be given) must be carefully explained to male patients.
Coadministration of nitrates to patients with angina in the emergency room can result in profound refractory hypotension. Patients may not be completely forthcoming about the use of medications for erectile dysfunction, and therefore the risks of coadministration (if nitrates are about to be given) must be carefully explained to male patients. PDE3 breaks down both cAMP and cGMP. The subtype of PDE determines the ratio of activity against cAMP versus cGMP. PDE3 preferentially acts on cAMP 10 times more than it does cGMP. The changes in cAMP and cGMP in different cells dictate the clinical effects seen in either the heart or the vasculature.
PDE3 breaks down both cAMP and cGMP. The subtype of PDE determines the ratio of activity against cAMP versus cGMP. PDE3 preferentially acts on cAMP 10 times more than it does cGMP. The changes in cAMP and cGMP in different cells dictate the clinical effects seen in either the heart or the vasculature. PDEs are a superfamily. There are 11 subtypes. Currently, the other PDE inhibitor in clinical use is PDE3 (an example is milrinone), used in acute heart failure.
PDEs are a superfamily. There are 11 subtypes. Currently, the other PDE inhibitor in clinical use is PDE3 (an example is milrinone), used in acute heart failure. A systematic review in 2009 of 116 RCTs found that successful intercourse attempts were improved to 69% with sildenafil versus placebo (35%), with very similar findings for tadalafil, vardenafil, mirodenafil, and udenafil. Men with severe erectile dysfunction obtained more benefit than men with mild erectile dysfunction. Men with specific medical conditions (e.g., depression, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, prostate cancer) were also more likely to obtain benefit. Side effects, most commonly headache, flushing, rhinitis, and dyspepsia, were significantly more frequent. Risk of serious cardiovascular events was 0.2% to 0.5% with PDE5 inhibitors and 0.1% to 0.2% with placebo.
A systematic review in 2009 of 116 RCTs found that successful intercourse attempts were improved to 69% with sildenafil versus placebo (35%), with very similar findings for tadalafil, vardenafil, mirodenafil, and udenafil. Men with severe erectile dysfunction obtained more benefit than men with mild erectile dysfunction. Men with specific medical conditions (e.g., depression, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, prostate cancer) were also more likely to obtain benefit. Side effects, most commonly headache, flushing, rhinitis, and dyspepsia, were significantly more frequent. Risk of serious cardiovascular events was 0.2% to 0.5% with PDE5 inhibitors and 0.1% to 0.2% with placebo. Although popularized for the treatment of erectile dysfunction, PDE5 drugs were originally designed to treat pulmonary hypertension; a certain side effect led to the discovery of their more widely known use.
Although popularized for the treatment of erectile dysfunction, PDE5 drugs were originally designed to treat pulmonary hypertension; a certain side effect led to the discovery of their more widely known use. Caffeine is a weak, nonspecific PDE inhibitor. This results in increased heart rate and, paradoxically (compared with PDE5 inhibitors), vasoconstriction.
Caffeine is a weak, nonspecific PDE inhibitor. This results in increased heart rate and, paradoxically (compared with PDE5 inhibitors), vasoconstriction. Theophylline, used in airway disease, is also a PDE inhibitor (see also the discussion of xanthines)
Theophylline, used in airway disease, is also a PDE inhibitor (see also the discussion of xanthines)Endothelin Receptor Antagonists
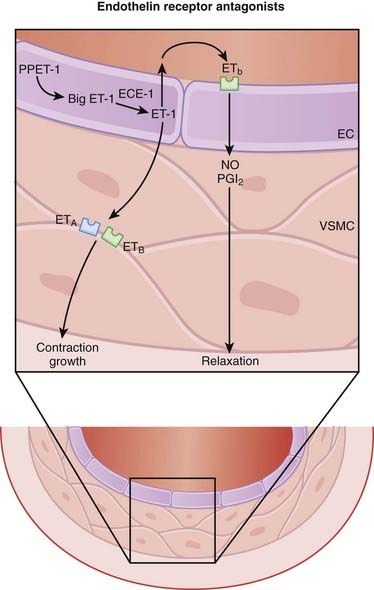
 There are three isoforms of ET (ET-1, ET-2, ET-3) in humans, and two different receptors (ETA and ETB). The ET-1 isoform is the focus of current drug development.
There are three isoforms of ET (ET-1, ET-2, ET-3) in humans, and two different receptors (ETA and ETB). The ET-1 isoform is the focus of current drug development. ETA receptors are found mainly on vascular smooth muscle cells, whereas ETB receptors are found on vascular endothelial cells and to a lesser extent on smooth muscle cells.
ETA receptors are found mainly on vascular smooth muscle cells, whereas ETB receptors are found on vascular endothelial cells and to a lesser extent on smooth muscle cells. ETA and ETB are both G protein–coupled receptors. Binding of ET-1 to the ETA or ETB receptor on vascular smooth muscle cells leads to vasoconstriction, whereas binding to ETB receptors on endothelial cells leads to release of nitric oxide, which then acts on vascular smooth muscle cells to induce a transient vasodilation (Figure 24-5).
ETA and ETB are both G protein–coupled receptors. Binding of ET-1 to the ETA or ETB receptor on vascular smooth muscle cells leads to vasoconstriction, whereas binding to ETB receptors on endothelial cells leads to release of nitric oxide, which then acts on vascular smooth muscle cells to induce a transient vasodilation (Figure 24-5). The vascular actions of ETB receptors on smooth muscle (constriction) and endothelial cells (dilation) therefore oppose each other, meaning that the relative distribution of these receptors within a regional vascular bed will determine the response to nonselective ET antagonists.
The vascular actions of ETB receptors on smooth muscle (constriction) and endothelial cells (dilation) therefore oppose each other, meaning that the relative distribution of these receptors within a regional vascular bed will determine the response to nonselective ET antagonists. It is therefore believed that ETA selective antagonists may have greater ability to dilate blood vessels than nonselective antagonists. However, the clinical impact of selective versus nonselective ET receptor antagonism has yet to be established in well-designed clinical trials.
It is therefore believed that ETA selective antagonists may have greater ability to dilate blood vessels than nonselective antagonists. However, the clinical impact of selective versus nonselective ET receptor antagonism has yet to be established in well-designed clinical trials. ET-1 also has several other effects, most notably in the kidney, and could play a potential role in promoting cell growth and remodeling and in carcinogenesis. Several cells in the kidney release ET-1, and the ETB receptor appears to mediate both natriuresis and diuresis.
ET-1 also has several other effects, most notably in the kidney, and could play a potential role in promoting cell growth and remodeling and in carcinogenesis. Several cells in the kidney release ET-1, and the ETB receptor appears to mediate both natriuresis and diuresis. Vasodilation, resulting in the following effects:
Vasodilation, resulting in the following effects:
 Liver injury: A reversible, asymptomatic increase in liver enzymes can progress to liver failure and death if the drug is not discontinued or the dose adjusted. This is thought to result from impaired transport and subsequent accumulation of toxic bile salts in hepatocytes. For a serious disorder this occurs relatively frequently; therefore liver enzymes should be monitored during therapy.
Liver injury: A reversible, asymptomatic increase in liver enzymes can progress to liver failure and death if the drug is not discontinued or the dose adjusted. This is thought to result from impaired transport and subsequent accumulation of toxic bile salts in hepatocytes. For a serious disorder this occurs relatively frequently; therefore liver enzymes should be monitored during therapy. ET is considered to be the most potent vasoconstrictor found in the human body, and therefore ET antagonists were thought to have great potential as leading antihypertensive agents. However, their major role has been seen in pulmonary hypertension, and they have not gained widespread use in hypertension.
ET is considered to be the most potent vasoconstrictor found in the human body, and therefore ET antagonists were thought to have great potential as leading antihypertensive agents. However, their major role has been seen in pulmonary hypertension, and they have not gained widespread use in hypertension. Given their propensity to cause liver injury, the future role of ETRAs in hypertension may be in treatment-resistant patients or in specific forms of hypertension that may benefit from ET antagonism.
Given their propensity to cause liver injury, the future role of ETRAs in hypertension may be in treatment-resistant patients or in specific forms of hypertension that may benefit from ET antagonism. Patients with various forms of pulmonary hypertension, especially idiopathic, tend to have higher-than-normal ET-1 levels. This is the rationale for their use and success in the management of pulmonary hypertension.
Patients with various forms of pulmonary hypertension, especially idiopathic, tend to have higher-than-normal ET-1 levels. This is the rationale for their use and success in the management of pulmonary hypertension. ETRAs are being investigated in a variety of other disorders in which remodeling and/or vasoconstriction play a role, including connective tissue disorders, Raynaud’s disease, heart failure, erectile dysfunction, and various disorders of cerebral vasoconstriction.
ETRAs are being investigated in a variety of other disorders in which remodeling and/or vasoconstriction play a role, including connective tissue disorders, Raynaud’s disease, heart failure, erectile dysfunction, and various disorders of cerebral vasoconstriction. ET receptors are also located in the following organs: lung, heart, kidney, intestine, and adrenal gland. The receptors are especially dense in the heart and lungs.
ET receptors are also located in the following organs: lung, heart, kidney, intestine, and adrenal gland. The receptors are especially dense in the heart and lungs. A 2009 Cochrane review (11 studies, N = 1457 participants) found that ETRAs (bosentan, sitaxsentan) did not improve mortality but did improve other measurements of pulmonary hypertension, including exercise capacity (improvement of 33.7 m on the 6-minute walk test), New York Heart Association/World Health Organization (NYHA/WHO) functional class, and dyspnea, as well as some measures of cardiopulmonary hemodynamics. These efficacy findings were largely in an idiopathic PH population. Hepatotoxicity was an uncommon side effect.
A 2009 Cochrane review (11 studies, N = 1457 participants) found that ETRAs (bosentan, sitaxsentan) did not improve mortality but did improve other measurements of pulmonary hypertension, including exercise capacity (improvement of 33.7 m on the 6-minute walk test), New York Heart Association/World Health Organization (NYHA/WHO) functional class, and dyspnea, as well as some measures of cardiopulmonary hemodynamics. These efficacy findings were largely in an idiopathic PH population. Hepatotoxicity was an uncommon side effect. The ETRAs are unusually expensive for small molecule drugs (i.e., nonbiologics), typically priced at over $100 per day. Their high price may result in part from the fact that they are primarily used to treat a rare condition, pulmonary hypertension.
The ETRAs are unusually expensive for small molecule drugs (i.e., nonbiologics), typically priced at over $100 per day. Their high price may result in part from the fact that they are primarily used to treat a rare condition, pulmonary hypertension. Given that ET was just discovered in 1988, the development and approval of ETRAs such as bosentan (2001) occurred remarkably fast.
Given that ET was just discovered in 1988, the development and approval of ETRAs such as bosentan (2001) occurred remarkably fast. PGs act on a family of receptors that are coupled to G proteins. Some G proteins are stimulatory, and some are inhibitory, depending on the specific receptor type; therefore, the physiologic effect of a given PG depends on the receptor and the tissue type.
PGs act on a family of receptors that are coupled to G proteins. Some G proteins are stimulatory, and some are inhibitory, depending on the specific receptor type; therefore, the physiologic effect of a given PG depends on the receptor and the tissue type. Prostacyclin (PGI2) and its analogues are potent vasodilators and possess antithrombotic and antiproliferative properties.
Prostacyclin (PGI2) and its analogues are potent vasodilators and possess antithrombotic and antiproliferative properties. The endothelial cells are the major source of prostacyclin production. Therefore, endogenous prostacyclins are well positioned to exert their effects on blood cells, endothelial cells, and vascular smooth muscle cells.
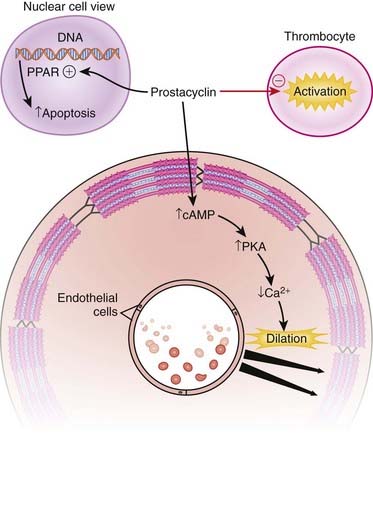
The endothelial cells are the major source of prostacyclin production. Therefore, endogenous prostacyclins are well positioned to exert their effects on blood cells, endothelial cells, and vascular smooth muscle cells. The PGI receptor is expressed in endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, leukocytes, and thrombocytes and is coupled with Gs proteins, which then activate adenylate cyclase, leading to increased cAMP, which activates protein kinase A (PKA), finally leading to vasodilation (Figure 24-6).
The PGI receptor is expressed in endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, leukocytes, and thrombocytes and is coupled with Gs proteins, which then activate adenylate cyclase, leading to increased cAMP, which activates protein kinase A (PKA), finally leading to vasodilation (Figure 24-6). Prostacyclin also couples with Gq proteins and activates vasoconstrictive pathways under certain circumstances in certain tissues, but this effect is overshadowed by the vasodilator effects.
Prostacyclin also couples with Gq proteins and activates vasoconstrictive pathways under certain circumstances in certain tissues, but this effect is overshadowed by the vasodilator effects. Endothelial damage, monocytes, fibroblasts, and the coagulation system all contribute to vascular fibrosis. Iloprost has been shown to inhibit the messenger RNA (mRNA) expression of important mediators of these processes, thereby demonstrating antiproliferative effects.
Endothelial damage, monocytes, fibroblasts, and the coagulation system all contribute to vascular fibrosis. Iloprost has been shown to inhibit the messenger RNA (mRNA) expression of important mediators of these processes, thereby demonstrating antiproliferative effects. Prostacyclin also activates peroxisome proliferator–activated receptors (PPARs) that are located in the nucleus. PPARs activate the apoptosis pathway, leading to accelerated programmed cell death.
Prostacyclin also activates peroxisome proliferator–activated receptors (PPARs) that are located in the nucleus. PPARs activate the apoptosis pathway, leading to accelerated programmed cell death. On the platelet, cyclooxygenase (COX)-1 catalyzes the prothrombotic mediator thromboxane, and COX-2 catalyzes the formation of prostacyclin, which is an antiaggregating agent.
On the platelet, cyclooxygenase (COX)-1 catalyzes the prothrombotic mediator thromboxane, and COX-2 catalyzes the formation of prostacyclin, which is an antiaggregating agent. Manipulating the balance of thromboxane and prostacyclin in favor of prostacyclin results in an antiplatelet effect.
Manipulating the balance of thromboxane and prostacyclin in favor of prostacyclin results in an antiplatelet effect. Pulmonary hypertension is associated with vasoconstriction, thrombosis, and cellular proliferation. The three actions of prostacyclins (vasodilation, antiproliferation, and antiplatelet) all potentially provide benefit to patients with pulmonary hypertension.
Pulmonary hypertension is associated with vasoconstriction, thrombosis, and cellular proliferation. The three actions of prostacyclins (vasodilation, antiproliferation, and antiplatelet) all potentially provide benefit to patients with pulmonary hypertension. A very important benefit of a drug with a short half-life, such as epoprostenol, is that when it is administered by intravenous infusion into the right side of the heart, the pulmonary circulation receives the highest dose of drug and the systemic circulation receives a lower exposure, reducing the probability of systemic side effects.
A very important benefit of a drug with a short half-life, such as epoprostenol, is that when it is administered by intravenous infusion into the right side of the heart, the pulmonary circulation receives the highest dose of drug and the systemic circulation receives a lower exposure, reducing the probability of systemic side effects. Furthermore, about 95% is inactivated after one circulation through the pulmonary circulation via enzymes that are specific for PGs.
Furthermore, about 95% is inactivated after one circulation through the pulmonary circulation via enzymes that are specific for PGs. Severe hypoxia with adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): When inhaled, prostacyclin can selectively cause vasodilation of vessels that are adjacent to the few functioning alveoli (this is where the drug actually reaches the circulation) and helps to improve ventilation-perfusion matching.
Severe hypoxia with adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): When inhaled, prostacyclin can selectively cause vasodilation of vessels that are adjacent to the few functioning alveoli (this is where the drug actually reaches the circulation) and helps to improve ventilation-perfusion matching. Erectile dysfunction: Although now usually treated with a PDE5 inhibitor, PGs can also be used for their vasodilation properties to treat erectile dysfunction.
Erectile dysfunction: Although now usually treated with a PDE5 inhibitor, PGs can also be used for their vasodilation properties to treat erectile dysfunction. Alprostadil can be used to maintain patency of the ductus arteriosus in a newborn who has a duct-dependent congenital cardiac anomaly.
Alprostadil can be used to maintain patency of the ductus arteriosus in a newborn who has a duct-dependent congenital cardiac anomaly. Vasodilation:
Vasodilation:
 Pulmonary hypertension is a progressive disease. The right ventricle is not nearly as strong as the left ventricle, and its ability to work against high resistance is very limited. As the pulmonary resistance and pressures increase through progressive vasoconstriction and endothelial thickening and fibrosis, the right ventricle becomes less able to provide adequate cardiac output to the lungs.
Pulmonary hypertension is a progressive disease. The right ventricle is not nearly as strong as the left ventricle, and its ability to work against high resistance is very limited. As the pulmonary resistance and pressures increase through progressive vasoconstriction and endothelial thickening and fibrosis, the right ventricle becomes less able to provide adequate cardiac output to the lungs.
 ET antagonists and PDE5 inhibitors are other vasodilators used in treatment of pulmonary hypertension.
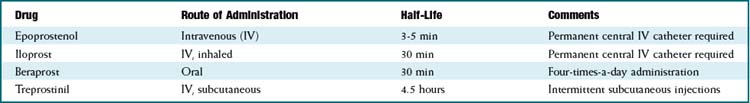
ET antagonists and PDE5 inhibitors are other vasodilators used in treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Epoprostenol and iloprost, when administered long term, require an implanted central venous catheter (surgically placed, it goes into the right atrium via the subclavian or internal jugular vein) and a battery-powered infusion pump. Complications include catheter infections and pump problems; in addition, the route of administration requires much more effort and maintenance than intermittent administration (subcutaneously or oral).
Epoprostenol and iloprost, when administered long term, require an implanted central venous catheter (surgically placed, it goes into the right atrium via the subclavian or internal jugular vein) and a battery-powered infusion pump. Complications include catheter infections and pump problems; in addition, the route of administration requires much more effort and maintenance than intermittent administration (subcutaneously or oral).
 Beraprost is orally administered. Treprostinil has a longer half-life and can be administered subcutaneously a few times a day. Neither of these drugs requires an infusion pump, so administration is much easier.
Beraprost is orally administered. Treprostinil has a longer half-life and can be administered subcutaneously a few times a day. Neither of these drugs requires an infusion pump, so administration is much easier. In critically ill patients, the intravenous administration is more controlled and therefore preferred: doses can be quickly titrated according to the response of the patient.
In critically ill patients, the intravenous administration is more controlled and therefore preferred: doses can be quickly titrated according to the response of the patient. Effects on the airways are different depending on the type of PG:
Effects on the airways are different depending on the type of PG:
 Duct-dependent congenital cardiac abnormalities require an open communication (the ductus arteriosus) from the aorta to the pulmonary artery to allow flow between the pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation. Closure of the ductus in these patients (before urgent corrective surgery) is not compatible with life. One example is pulmonary atresia, a condition in which the pulmonary valve does not form and so there is no connection from the right ventricle to the pulmonary circulation; the only alternate route to the lungs is from the aorta through the ductus. Of course, some blood also continues down the aorta into the systemic circulation. Closure of the ductus would result in complete loss of blood flow to the lungs and death within minutes.
Duct-dependent congenital cardiac abnormalities require an open communication (the ductus arteriosus) from the aorta to the pulmonary artery to allow flow between the pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation. Closure of the ductus in these patients (before urgent corrective surgery) is not compatible with life. One example is pulmonary atresia, a condition in which the pulmonary valve does not form and so there is no connection from the right ventricle to the pulmonary circulation; the only alternate route to the lungs is from the aorta through the ductus. Of course, some blood also continues down the aorta into the systemic circulation. Closure of the ductus would result in complete loss of blood flow to the lungs and death within minutes.
 A Cochrane meta-analysis in 2006 looked at the following:
A Cochrane meta-analysis in 2006 looked at the following:
 Intravenous prostacyclin versus usual care (3 studies, 101 patients): There were significant improvements in walking exercise capacity, cardiopulmonary hemodynamics, and NYHA functional class over a range of 3 days to 12 weeks.
Intravenous prostacyclin versus usual care (3 studies, 101 patients): There were significant improvements in walking exercise capacity, cardiopulmonary hemodynamics, and NYHA functional class over a range of 3 days to 12 weeks. Oral prostacyclin versus placebo (two studies): Short-term data (3 to 6 months) indicated that there was a significant improvement in exercise capacity, but data from one study of 52 weeks reported no significant difference at 12 months. No significant differences were observed for any other outcome.
Oral prostacyclin versus placebo (two studies): Short-term data (3 to 6 months) indicated that there was a significant improvement in exercise capacity, but data from one study of 52 weeks reported no significant difference at 12 months. No significant differences were observed for any other outcome. Subcutaneous treprostinil versus placebo (two studies): One large study reported a significant median improvement in exercise capacity of around 16 meters (over 8 to 12 weeks). Cardiopulmonary hemodynamics and symptom scores favored treprostinil. Infusion site pain and withdrawals because of adverse events were more frequent with treprostinil.
Subcutaneous treprostinil versus placebo (two studies): One large study reported a significant median improvement in exercise capacity of around 16 meters (over 8 to 12 weeks). Cardiopulmonary hemodynamics and symptom scores favored treprostinil. Infusion site pain and withdrawals because of adverse events were more frequent with treprostinil. Inhaled prostacyclin versus placebo (one study): There was a small but statistically significant increase in walking exercise capacity in patients treated with inhaled prostacyclin. Treatment led to better symptom scores and functional class status than with placebo. Side effects and adverse events were common in the studies.
Inhaled prostacyclin versus placebo (one study): There was a small but statistically significant increase in walking exercise capacity in patients treated with inhaled prostacyclin. Treatment led to better symptom scores and functional class status than with placebo. Side effects and adverse events were common in the studies. In 1934 Dr. Ulf von Euler found that extracts of sheep vesicular gland dramatically lowered blood pressure when injected into animals. Human seminal fluid also seemed to possess similar qualities. Von Euler named it prostaglandin, believing that it originated in the prostate gland.
In 1934 Dr. Ulf von Euler found that extracts of sheep vesicular gland dramatically lowered blood pressure when injected into animals. Human seminal fluid also seemed to possess similar qualities. Von Euler named it prostaglandin, believing that it originated in the prostate gland. Nomenclature:
Nomenclature:
 Eicosa is Greek for 20. Eicosanoids have 20 carbon atoms. Eicosanoids include PGs, prostacyclins, LTs, and thromboxane. Arachidonic acid is the most abundant precursor.
Eicosa is Greek for 20. Eicosanoids have 20 carbon atoms. Eicosanoids include PGs, prostacyclins, LTs, and thromboxane. Arachidonic acid is the most abundant precursor. The letter after PG is a historical designation:
The letter after PG is a historical designation:
 The subscripted number refers to the number of double bonds (C=C).
The subscripted number refers to the number of double bonds (C=C).