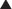Chapter 23 Psychiatry
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 The monoamine hypothesis suggests that depression is caused by a deficiency of synaptic neurotransmitters such as serotonin (5-HT), norepinephrine, and dopamine. Serotonin, in particular, is associated with mood.
The monoamine hypothesis suggests that depression is caused by a deficiency of synaptic neurotransmitters such as serotonin (5-HT), norepinephrine, and dopamine. Serotonin, in particular, is associated with mood. Normally, 5-HT is released from presynaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft, where it travels to postsynaptic receptors.
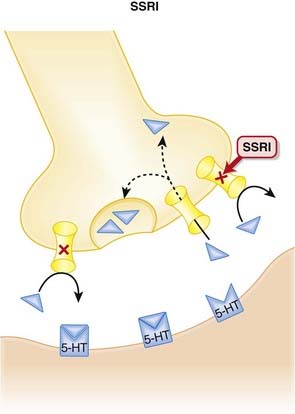
Normally, 5-HT is released from presynaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft, where it travels to postsynaptic receptors. Once released from these postsynaptic receptors, 5-HT is removed from the synaptic cleft by reuptake transporters located on the presynapse. Once it is taken up presynaptically, it is degraded (Figure 23-1).
Once released from these postsynaptic receptors, 5-HT is removed from the synaptic cleft by reuptake transporters located on the presynapse. Once it is taken up presynaptically, it is degraded (Figure 23-1). SSRIs bind to this reuptake transporter, preventing the removal of 5-HT and leading to increased 5-HT available to bind to postsynaptic receptors.
SSRIs bind to this reuptake transporter, preventing the removal of 5-HT and leading to increased 5-HT available to bind to postsynaptic receptors. The clinical efficacy of antidepressants is delayed a few weeks when compared with their pharmacological actions. It is therefore hypothesized that the efficacy of these agents in the treatment of depression is related to a downstream effect.
The clinical efficacy of antidepressants is delayed a few weeks when compared with their pharmacological actions. It is therefore hypothesized that the efficacy of these agents in the treatment of depression is related to a downstream effect. There are a variety of theories as to what this downstream effect might be, although most involve either a change in receptor density or fundamental changes at the cellular level, including a reorganization of neurons.
There are a variety of theories as to what this downstream effect might be, although most involve either a change in receptor density or fundamental changes at the cellular level, including a reorganization of neurons. One of the examples of altered receptor density occurs with presynaptic 5-HT inhibitory autoreceptors. These autoreceptors reduce 5-HT release when bound by 5-HT. Excess 5-HT in the synapse because of SSRI therapy leads to down-regulation of this inhibitory autoreceptor and enhanced release of 5-HT into the synapse.
One of the examples of altered receptor density occurs with presynaptic 5-HT inhibitory autoreceptors. These autoreceptors reduce 5-HT release when bound by 5-HT. Excess 5-HT in the synapse because of SSRI therapy leads to down-regulation of this inhibitory autoreceptor and enhanced release of 5-HT into the synapse.Pharmacokinetics
Contraindications
 SSRIs and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs): SSRIs increase serotonin concentrations in the synapse, whereas MAOIs inhibit the breakdown of serotonin. Concomitant use can therefore lead to excessive serotonin (see details in Side Effects). When switching from an SSRI to an MAOI, or vice versa, allow for a washout period of at least 1 to 2 weeks.
SSRIs and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs): SSRIs increase serotonin concentrations in the synapse, whereas MAOIs inhibit the breakdown of serotonin. Concomitant use can therefore lead to excessive serotonin (see details in Side Effects). When switching from an SSRI to an MAOI, or vice versa, allow for a washout period of at least 1 to 2 weeks. SSRIs and thioridazine (an antipsychotic): Thioridazine elicits QT interval prolongation, and fluoxetine in particular enhances this effect by inhibiting the metabolism of thioridazine. A washout period of at least 5 weeks should elapse before someone who was on fluoxetine should be started on thioridazine, and fluoxetine should not be initiated for at least 2 weeks after discontinuation of thioridazine. The seriousness of these drug interactions has led to the withdrawal of thioridazine in many markets.
SSRIs and thioridazine (an antipsychotic): Thioridazine elicits QT interval prolongation, and fluoxetine in particular enhances this effect by inhibiting the metabolism of thioridazine. A washout period of at least 5 weeks should elapse before someone who was on fluoxetine should be started on thioridazine, and fluoxetine should not be initiated for at least 2 weeks after discontinuation of thioridazine. The seriousness of these drug interactions has led to the withdrawal of thioridazine in many markets.Side Effects
Serious
Non-Serious
 Sexual dysfunction may be both mechanical, as serotonin inhibits functions such as erections, ejaculation, lubrication, and orgasm, and central, as serotonin has an inhibitory effect on dopamine, a neurotransmitter believed to play an important role in arousal. Note: sexual dysfunction can also accompany depression.
Sexual dysfunction may be both mechanical, as serotonin inhibits functions such as erections, ejaculation, lubrication, and orgasm, and central, as serotonin has an inhibitory effect on dopamine, a neurotransmitter believed to play an important role in arousal. Note: sexual dysfunction can also accompany depression.Important Notes
 As with other antidepressants, when an SSRI is being discontinued, the dose should be tapered gradually in order to avoid discontinuation symptoms, including dizziness, nausea, headache, and others. The incidence and severity appears to vary between SSRI, and longer half-life agents such as fluoxetine appear to be less likely to induce a discontinuation syndrome.
As with other antidepressants, when an SSRI is being discontinued, the dose should be tapered gradually in order to avoid discontinuation symptoms, including dizziness, nausea, headache, and others. The incidence and severity appears to vary between SSRI, and longer half-life agents such as fluoxetine appear to be less likely to induce a discontinuation syndrome. The use of SSRIs and other antidepressants in children is currently under review. The focus of concern is the propensity to elicit behavioral and emotional changes, including an increased risk of self-harm and suicide. All antidepressants thus carry safety warnings for use in pediatrics.
The use of SSRIs and other antidepressants in children is currently under review. The focus of concern is the propensity to elicit behavioral and emotional changes, including an increased risk of self-harm and suicide. All antidepressants thus carry safety warnings for use in pediatrics. Although they all increase serotonin levels, the SSRIs are a heterogeneous class and should not be considered interchangeable. For example, citalopram is considered to be the most serotonin-selective of the SSRIs, although it does have affinity for H1 receptors. Fluoxetine and sertraline have the highest affinity for dopamine D2 receptors, whereas paroxetine has the most potent anticholinergic effects. The clinical consequences of this pharmacologic heterogeneity have yet to be fully characterized.
Although they all increase serotonin levels, the SSRIs are a heterogeneous class and should not be considered interchangeable. For example, citalopram is considered to be the most serotonin-selective of the SSRIs, although it does have affinity for H1 receptors. Fluoxetine and sertraline have the highest affinity for dopamine D2 receptors, whereas paroxetine has the most potent anticholinergic effects. The clinical consequences of this pharmacologic heterogeneity have yet to be fully characterized. SS and neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS), two rare but very serious complications of SSRIs or MAOIs and antipsychotics, respectively, share some common features including fever, increased muscle tone (more hyperreflexia with SS), and autonomic instability.
SS and neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS), two rare but very serious complications of SSRIs or MAOIs and antipsychotics, respectively, share some common features including fever, increased muscle tone (more hyperreflexia with SS), and autonomic instability.Advanced
Drug Interactions
 The SSRIs inhibit multiple CYP450 isozymes. Fluoxetine and paroxetine inhibit the CYP2D6 isoenzyme, and this can lead to clinically important drug interactions with drugs such as tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), carbamazepine, or vinblastine. There is also a very serious interaction with thioridazine (see Contraindications).
The SSRIs inhibit multiple CYP450 isozymes. Fluoxetine and paroxetine inhibit the CYP2D6 isoenzyme, and this can lead to clinically important drug interactions with drugs such as tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), carbamazepine, or vinblastine. There is also a very serious interaction with thioridazine (see Contraindications).Evidence
Depression
 A 2005 Cochrane review (132 trials, N = 14,391 participants) compared fluoxetine with other antidepressants. The review found that among SSRIs, sertraline and paroxetine were more efficacious than fluoxetine in improving depression rating scores. Findings related to side effects were as follows:
A 2005 Cochrane review (132 trials, N = 14,391 participants) compared fluoxetine with other antidepressants. The review found that among SSRIs, sertraline and paroxetine were more efficacious than fluoxetine in improving depression rating scores. Findings related to side effects were as follows:
Premenstrual Syndrome
 A 2007 Cochrane review (31 trials, N = 844 participants) found that SSRIs were highly effective in the treatment of premenstrual symptoms, both physical and behavioral, compared with placebo. There were 2.5 times as many withdrawals because of adverse events among SSRI-treated subjects as among placebo-treated subjects.
A 2007 Cochrane review (31 trials, N = 844 participants) found that SSRIs were highly effective in the treatment of premenstrual symptoms, both physical and behavioral, compared with placebo. There were 2.5 times as many withdrawals because of adverse events among SSRI-treated subjects as among placebo-treated subjects.FYI
 The SSRIs were the first class of antidepressants that were discovered using “rational drug design.” The strategy was based on the observation that TCAs inhibited noradrenaline (NA) or 5-HT reuptake to various extents. Scientists then discovered some nontricyclic compounds that were also reuptake inhibitors, acting on either NA or 5-HT to varying degrees. This led to the approval of the first such agent, zimeldine, which was withdrawn from the market after a few years.
The SSRIs were the first class of antidepressants that were discovered using “rational drug design.” The strategy was based on the observation that TCAs inhibited noradrenaline (NA) or 5-HT reuptake to various extents. Scientists then discovered some nontricyclic compounds that were also reuptake inhibitors, acting on either NA or 5-HT to varying degrees. This led to the approval of the first such agent, zimeldine, which was withdrawn from the market after a few years.Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)
Description
TCAs are a class of antidepressants with a common chemical (tricyclic) structure and mode of action.
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 The monoamine hypothesis suggests that depression is caused by a deficiency of synaptic neurotransmitters such as serotonin (5-HT), NA, and dopamine. Serotonin, in particular, is associated with mood.
The monoamine hypothesis suggests that depression is caused by a deficiency of synaptic neurotransmitters such as serotonin (5-HT), NA, and dopamine. Serotonin, in particular, is associated with mood. Normally, 5-HT and NA are released from presynaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft, where they travel to postsynaptic receptors.
Normally, 5-HT and NA are released from presynaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft, where they travel to postsynaptic receptors. Once released from these postsynaptic receptors, 5-HT and NA are removed from the synaptic cleft by reuptake transporters located on the presynapse.
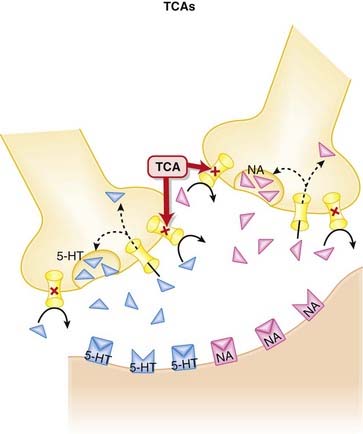
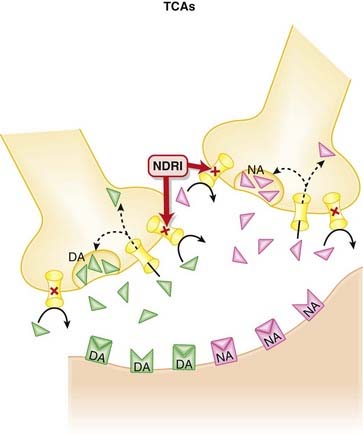
Once released from these postsynaptic receptors, 5-HT and NA are removed from the synaptic cleft by reuptake transporters located on the presynapse. The TCAs inhibit the reuptake of serotonin (5-HT) and NA into the presynaptic cell body, increasing the amount of 5-HT and NA available to bind to postsynaptic receptors (Figure 23-2).
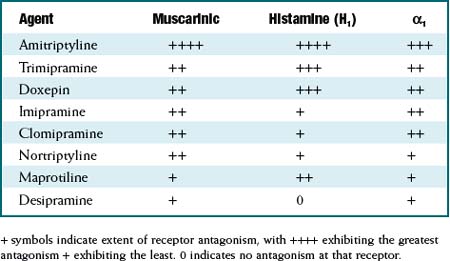
The TCAs inhibit the reuptake of serotonin (5-HT) and NA into the presynaptic cell body, increasing the amount of 5-HT and NA available to bind to postsynaptic receptors (Figure 23-2). TCAs antagonize other receptors: muscarinic, histamine (H1), adrenergic (α1) receptors. This accounts for their extensive list of side effects.
TCAs antagonize other receptors: muscarinic, histamine (H1), adrenergic (α1) receptors. This accounts for their extensive list of side effects. The clinical efficacy of antidepressants is delayed when compared with their pharmacologic actions. It is therefore hypothesized that the efficacy of these agents in the treatment of depression is related to a downstream effect.
The clinical efficacy of antidepressants is delayed when compared with their pharmacologic actions. It is therefore hypothesized that the efficacy of these agents in the treatment of depression is related to a downstream effect.Contraindications
 Avoid concomitant use of TCAs and MAOIs: TCAs increase serotonin concentrations in the synapse, whereas MAOIs inhibit the breakdown of serotonin. Concomitant use can therefore lead to excessive serotonin. When switching from a TCA to an MAOI, or vice versa, allow for a washout period of at least 2 weeks.
Avoid concomitant use of TCAs and MAOIs: TCAs increase serotonin concentrations in the synapse, whereas MAOIs inhibit the breakdown of serotonin. Concomitant use can therefore lead to excessive serotonin. When switching from a TCA to an MAOI, or vice versa, allow for a washout period of at least 2 weeks.Side Effects
Important Notes
 The TCAs are grouped as a class based on their chemical structure. Although as a class they are considered to be 5-HT or noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors, the degree of reuptake inhibition differs markedly among agents. See Table 23-1.
The TCAs are grouped as a class based on their chemical structure. Although as a class they are considered to be 5-HT or noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors, the degree of reuptake inhibition differs markedly among agents. See Table 23-1. Similarly, the affinities for blockade of receptors that mediate the side effects experienced by patients also differ markedly among agents. See Table 23-2.
Similarly, the affinities for blockade of receptors that mediate the side effects experienced by patients also differ markedly among agents. See Table 23-2. Because of their prominent antimuscarinic effects, TCAs should be used with caution in conditions that would be exacerbated by cholinergic antagonism: urinary retention, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), glaucoma (closed angle), and increased IOP.
Because of their prominent antimuscarinic effects, TCAs should be used with caution in conditions that would be exacerbated by cholinergic antagonism: urinary retention, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), glaucoma (closed angle), and increased IOP. TCAs are potentially fatal in overdose situations and have one of the highest mortality rates associated with overdose. Cardiac arrhythmias, hypotension, and central nervous system (CNS) involvement are the most common events associated with TCA overdose. TCAs undergo slow absorption; therefore a patient may arrive on his or her own at an emergency department with a fatal dose of TCAs that has not yet been absorbed. This propensity of TCAs to be fatal in overdose is particularly concerning, given the general FDA warning about increased risk of suicidality with antidepressant use.
TCAs are potentially fatal in overdose situations and have one of the highest mortality rates associated with overdose. Cardiac arrhythmias, hypotension, and central nervous system (CNS) involvement are the most common events associated with TCA overdose. TCAs undergo slow absorption; therefore a patient may arrive on his or her own at an emergency department with a fatal dose of TCAs that has not yet been absorbed. This propensity of TCAs to be fatal in overdose is particularly concerning, given the general FDA warning about increased risk of suicidality with antidepressant use.TABLE 23-1 Extent of Serotonin and Noradrenaline Reuptake Inhibition among TCAs
| Agent | Serotonin (5HT) | Noradrenaline(NA) |
|---|---|---|
| Clomipramine | +++ | + |
| Amitriptyline | ++ | ± |
| Imipramine | + | + |
| Trimipramine | 0 | + |
| Doxepin | + | ++ |
| Nortriptyline | ± | ++ |
| Desipramine | 0 | +++ |
+ symbols indicate extent of reuptake inhibition, with +++ exhibiting the greatest reuptake inhibition + exhibiting the least. 0 indicates no inhibition of the reuptake transporter for that neurotransmitter.
Evidence
FYI
 TCAs have been around for 50 years. Imipramine was the first TCA synthesized, and it was based on the tricyclic structure of the antipsychotic chlorpromazine. A study in 1958 found imipramine lacked efficacy in psychosis, but, surprisingly, a subgroup of patients with depression improved on imipramine. TCAs became the drugs of choice for treating depression for the next 30 years.
TCAs have been around for 50 years. Imipramine was the first TCA synthesized, and it was based on the tricyclic structure of the antipsychotic chlorpromazine. A study in 1958 found imipramine lacked efficacy in psychosis, but, surprisingly, a subgroup of patients with depression improved on imipramine. TCAs became the drugs of choice for treating depression for the next 30 years.Serotonin Noradrenaline Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 The monoamine hypothesis suggests that depression is caused by a deficiency of synaptic neurotransmitters such as serotonin (5-HT), NA, and dopamine. Serotonin, in particular, is associated with mood.
The monoamine hypothesis suggests that depression is caused by a deficiency of synaptic neurotransmitters such as serotonin (5-HT), NA, and dopamine. Serotonin, in particular, is associated with mood. Normally, 5-HT and NA are released from presynaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft, where they travel to postsynaptic receptors.
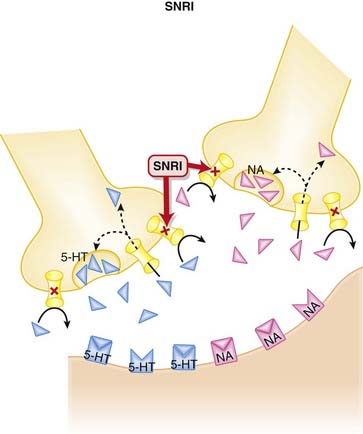
Normally, 5-HT and NA are released from presynaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft, where they travel to postsynaptic receptors. Once released from these postsynaptic receptors, 5-HT and NA are removed from the synaptic cleft by reuptake transporters located on the presynapse. Once they are taken up presynaptically, they are degraded (Figure 23-3).
Once released from these postsynaptic receptors, 5-HT and NA are removed from the synaptic cleft by reuptake transporters located on the presynapse. Once they are taken up presynaptically, they are degraded (Figure 23-3). SNRIs bind to these reuptake transporters, preventing the removal of 5-HT and NA and leading to increased availability to bind to postsynaptic receptors.
SNRIs bind to these reuptake transporters, preventing the removal of 5-HT and NA and leading to increased availability to bind to postsynaptic receptors. Venlafaxine has much higher affinity for the serotonin reuptake transporter, and at low doses acts more like an SSRI. It is not until higher doses are used that it also blocks noradrenaline reuptake.
Venlafaxine has much higher affinity for the serotonin reuptake transporter, and at low doses acts more like an SSRI. It is not until higher doses are used that it also blocks noradrenaline reuptake. Conversely, milnacipran blocks serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake equally, whereas the other agents in this class fall somewhere between these two.
Conversely, milnacipran blocks serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake equally, whereas the other agents in this class fall somewhere between these two. The clinical efficacy of antidepressants is delayed when compared with their pharmacologic actions. It is therefore hypothesized that the efficacy of these agents in the treatment of depression is related to a downstream effect.
The clinical efficacy of antidepressants is delayed when compared with their pharmacologic actions. It is therefore hypothesized that the efficacy of these agents in the treatment of depression is related to a downstream effect.Pharmacokinetics
 Compared with the SSRIs, the SNRIs have shorter elimination half-lives. Venlafaxine is available in an extended-release(ER) dosage form.
Compared with the SSRIs, the SNRIs have shorter elimination half-lives. Venlafaxine is available in an extended-release(ER) dosage form. Venlafaxine has an active metabolite: O-desmethylvenlafaxine. The parent and its metabolites have lower clearance in patients with hepatic cirrhosis and severe renal disease, requiring a dose reduction.
Venlafaxine has an active metabolite: O-desmethylvenlafaxine. The parent and its metabolites have lower clearance in patients with hepatic cirrhosis and severe renal disease, requiring a dose reduction.Side Effects
 Gastrointestinal (GI) distress, attributed to inhibition of serotonin reuptake, appears to be most common with venlafaxine. Stimulation of serotonin receptors in the brain likely mediates nausea. Serotonin receptors are also found in the gut, and serotonin appears to have an effect on GI motility that becomes intolerable in some patients, leading to cramping and diarrhea.
Gastrointestinal (GI) distress, attributed to inhibition of serotonin reuptake, appears to be most common with venlafaxine. Stimulation of serotonin receptors in the brain likely mediates nausea. Serotonin receptors are also found in the gut, and serotonin appears to have an effect on GI motility that becomes intolerable in some patients, leading to cramping and diarrhea. Insomnia may occur due to stimulation of 5-HT receptors in the CNS. Both the length and quality of sleep may be impaired.
Insomnia may occur due to stimulation of 5-HT receptors in the CNS. Both the length and quality of sleep may be impaired. Sexual dysfunction, attributed to inhibition of serotonin reuptake, appears to be most common with venlafaxine. It may be both mechanical, as serotonin inhibits functions such as erections, ejaculation, lubrication, and orgasm, and central, as serotonin has an inhibitory effect on dopamine, a neurotransmitter believed to play an important role in arousal.
Sexual dysfunction, attributed to inhibition of serotonin reuptake, appears to be most common with venlafaxine. It may be both mechanical, as serotonin inhibits functions such as erections, ejaculation, lubrication, and orgasm, and central, as serotonin has an inhibitory effect on dopamine, a neurotransmitter believed to play an important role in arousal.Important Notes
 When an SNRI is being discontinued, the dose should be tapered gradually in order to avoid discontinuation symptoms, including aggression, agitation, convulsions, dysphoric mood, electric shock sensations, and others. These symptoms have been particularly evident with venlafaxine.
When an SNRI is being discontinued, the dose should be tapered gradually in order to avoid discontinuation symptoms, including aggression, agitation, convulsions, dysphoric mood, electric shock sensations, and others. These symptoms have been particularly evident with venlafaxine. The theory behind the development of the SNRIs was to try and increase the levels of two neurotransmitters (serotonin, noradrenaline) simultaneously, while avoiding many of the bothersome side effects of the TCAs, which also act as reuptake inhibitors of these two neurotransmitters. There is evidence to suggest that dual reuptake inhibition is more efficacious than selective inhibition (see Evidence section).
The theory behind the development of the SNRIs was to try and increase the levels of two neurotransmitters (serotonin, noradrenaline) simultaneously, while avoiding many of the bothersome side effects of the TCAs, which also act as reuptake inhibitors of these two neurotransmitters. There is evidence to suggest that dual reuptake inhibition is more efficacious than selective inhibition (see Evidence section). Reboxetine was the first noradrenaline selective reuptake inhibitor, approved in Europe for treatment of depression. It was rejected by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) because of concerns over poor efficacy.
Reboxetine was the first noradrenaline selective reuptake inhibitor, approved in Europe for treatment of depression. It was rejected by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) because of concerns over poor efficacy. All antidepressants carry an FDA warning about increased suicidality, particularly in younger (<25 years of age) patients. The mechanism has not been established and there is not enough data to determine whether a lower risk exists for some antidepressants compared with others. These concerns must also be balanced against the potential for increased risk of completed suicides in untreated depression.
All antidepressants carry an FDA warning about increased suicidality, particularly in younger (<25 years of age) patients. The mechanism has not been established and there is not enough data to determine whether a lower risk exists for some antidepressants compared with others. These concerns must also be balanced against the potential for increased risk of completed suicides in untreated depression.Evidence
Venlafaxine versus Fluoxetine for Depression
 A 2005 Cochrane review (10 trials, N = 1831 participants) compared fluoxetine with venlafaxine. The authors found venlafaxine to be significantly better than fluoxetine (an SSRI) for improving depression rating scores. Some side effects were more common with venlafaxine than with fluoxetine, including dry mouth, dizziness, sweating, and nausea.
A 2005 Cochrane review (10 trials, N = 1831 participants) compared fluoxetine with venlafaxine. The authors found venlafaxine to be significantly better than fluoxetine (an SSRI) for improving depression rating scores. Some side effects were more common with venlafaxine than with fluoxetine, including dry mouth, dizziness, sweating, and nausea.Venlafaxine for Generalized Anxiety Disorder
 A 2003 Cochrane review (8 trials, N = 2058 participants) examined the efficacy of various antidepressants for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). Based on two trials, the authors found venlafaxine to be statistically better than placebo for treatment response, assessed by Clinical Global Impression (CGI) scores.
A 2003 Cochrane review (8 trials, N = 2058 participants) examined the efficacy of various antidepressants for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). Based on two trials, the authors found venlafaxine to be statistically better than placebo for treatment response, assessed by Clinical Global Impression (CGI) scores.Milnacipran for Depression
 A 2009 Cochrane review (16 trials, N = 2277 participants) compared milnacipran with other antidepressants for depression. Milnacipran was associated with fewer withdrawals because of adverse events (a measure of tolerability) compared with the TCAs (odds ratio [OR] 0.55), and weak evidence suggested fewer adverse events of sleepiness or drowsiness, dry mouth, or constipation versus these agents.
A 2009 Cochrane review (16 trials, N = 2277 participants) compared milnacipran with other antidepressants for depression. Milnacipran was associated with fewer withdrawals because of adverse events (a measure of tolerability) compared with the TCAs (odds ratio [OR] 0.55), and weak evidence suggested fewer adverse events of sleepiness or drowsiness, dry mouth, or constipation versus these agents.Noradrenergic and Specific Serotonergic Antidepressants (NaSSAs)
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
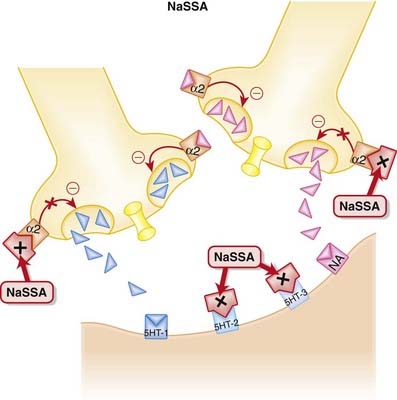
 NaSSAs have a dual mechanism of action:
NaSSAs have a dual mechanism of action:
 Inhibition of α2 autoreceptors and heteroreceptors
Inhibition of α2 autoreceptors and heteroreceptors
Side Effects
 Sedation occurs because of blockade of histamine receptors. It tends to predominate at lower doses, as increasing NA at higher doses counteracts this effect.
Sedation occurs because of blockade of histamine receptors. It tends to predominate at lower doses, as increasing NA at higher doses counteracts this effect.Important Notes
 With its distinct mechanism, mirtazapine is seen as an alternative for patients intolerant to SSRIs. It has the advantage of lower incidence of sexual dysfunction, but it also has greater propensity for weight gain compared with SSRIs.
With its distinct mechanism, mirtazapine is seen as an alternative for patients intolerant to SSRIs. It has the advantage of lower incidence of sexual dysfunction, but it also has greater propensity for weight gain compared with SSRIs. Because of its sedative and appetite-stimulating effects, mirtazapine may theoretically be a more useful antidepressant in the elderly, as these patients often have depression accompanied by insomnia and weight loss.
Because of its sedative and appetite-stimulating effects, mirtazapine may theoretically be a more useful antidepressant in the elderly, as these patients often have depression accompanied by insomnia and weight loss. Although they are not thought of as being in the same class, the “atypical” antidepressants trazodone and nefazodone have some similarities to mirtazapine in their mechanisms of action. Both block 5-HT2 postsynaptic receptors and promote serotonin neurotransmission, although trazodone and nefazodone enhance serotonin by inhibiting its reuptake.
Although they are not thought of as being in the same class, the “atypical” antidepressants trazodone and nefazodone have some similarities to mirtazapine in their mechanisms of action. Both block 5-HT2 postsynaptic receptors and promote serotonin neurotransmission, although trazodone and nefazodone enhance serotonin by inhibiting its reuptake. Nefazodone is also believed to inhibit the reuptake of noradrenaline. Nefazodone was withdrawn from North American markets in the early 2000s for hepatotoxicity, and trazodone, once a very popular antidepressant, has been supplanted by newer agents such as the SSRIs.
Nefazodone is also believed to inhibit the reuptake of noradrenaline. Nefazodone was withdrawn from North American markets in the early 2000s for hepatotoxicity, and trazodone, once a very popular antidepressant, has been supplanted by newer agents such as the SSRIs. All antidepressants carry an FDA warning about increased suicidality, particularly in younger (<25 years of age) patients. The mechanism has not been established and there is not enough data to determine whether a lower risk exists for some antidepressants compared with others. These concerns must also be balanced against the potential for increased risk of completed suicides in untreated depression.
All antidepressants carry an FDA warning about increased suicidality, particularly in younger (<25 years of age) patients. The mechanism has not been established and there is not enough data to determine whether a lower risk exists for some antidepressants compared with others. These concerns must also be balanced against the potential for increased risk of completed suicides in untreated depression.Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
Description
MAOIs are a heterogeneous group of agents that inhibit the monoamine oxidase (MAO) enzyme.
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
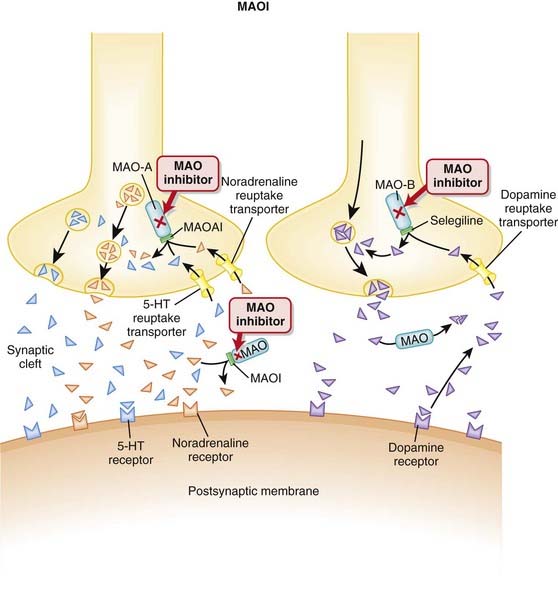
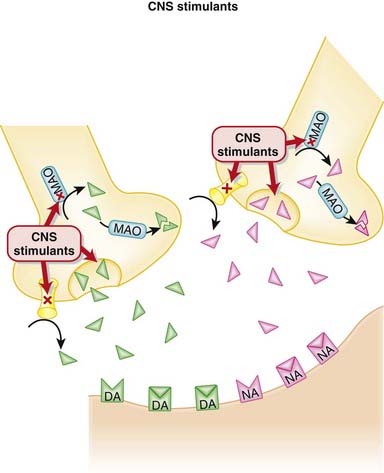
 MAO degrades catecholamines, serotonin, and other endogenous amines in the CNS as well as in the periphery.
MAO degrades catecholamines, serotonin, and other endogenous amines in the CNS as well as in the periphery. The purpose of MAO inhibition is therefore to increase levels of these substances within the body, specifically the CNS. The efficacy of these agents is a result of their actions within the CNS, whereas the side effects are largely mediated by their actions outside of the CNS.
The purpose of MAO inhibition is therefore to increase levels of these substances within the body, specifically the CNS. The efficacy of these agents is a result of their actions within the CNS, whereas the side effects are largely mediated by their actions outside of the CNS. MAO inhibition can be either reversible or irreversible. Irreversible binding leads to a much more prolonged effect (Figure 23-5).
MAO inhibition can be either reversible or irreversible. Irreversible binding leads to a much more prolonged effect (Figure 23-5). The benefits and adverse effects of MAOIs will therefore be determined by their selectivity for these isoenzymes and whether the inhibition is reversible.
The benefits and adverse effects of MAOIs will therefore be determined by their selectivity for these isoenzymes and whether the inhibition is reversible. Therefore MAO-A inhibitors are thought to work by increasing levels of amines such as norepinephrine and serotonin.
Therefore MAO-A inhibitors are thought to work by increasing levels of amines such as norepinephrine and serotonin. Because the MAO-B enzyme has no effect on epinephrine, norepinephrine, or serotonin, at normal doses MAO-B inhibitors increase dopamine levels in the CNS without increasing levels of these other neurotransmitters. Parkinson’s disease is characterized by a relative deficiency of dopamine in the CNS; therefore MAO-B inhibitors are used to treat Parkinson’s disease.
Because the MAO-B enzyme has no effect on epinephrine, norepinephrine, or serotonin, at normal doses MAO-B inhibitors increase dopamine levels in the CNS without increasing levels of these other neurotransmitters. Parkinson’s disease is characterized by a relative deficiency of dopamine in the CNS; therefore MAO-B inhibitors are used to treat Parkinson’s disease. At higher doses, MAO-B inhibitors begin to lose selectivity, and thus begin to inhibit MAO-A as well as MAO-B. Therefore in higher doses, MAO-B inhibitors can also be used to treat depression.
At higher doses, MAO-B inhibitors begin to lose selectivity, and thus begin to inhibit MAO-A as well as MAO-B. Therefore in higher doses, MAO-B inhibitors can also be used to treat depression. It is also believed that byproducts such as peroxide associated with dopamine degradation lead to further CNS damage in Parkinson’s disease. Therefore an additional proposed mechanism of the MAO-B inhibitors is to inhibit the production of these toxic metabolites. There is also some work suggesting that these toxic byproducts may play a role in the pathophysiology of depression, suggesting a potential disease-modifying role for MAO inhibition in this condition, as well.
It is also believed that byproducts such as peroxide associated with dopamine degradation lead to further CNS damage in Parkinson’s disease. Therefore an additional proposed mechanism of the MAO-B inhibitors is to inhibit the production of these toxic metabolites. There is also some work suggesting that these toxic byproducts may play a role in the pathophysiology of depression, suggesting a potential disease-modifying role for MAO inhibition in this condition, as well.Pharmacokinetics
Contraindications
 Drug interaction: with sympathomimetics: nonselective MAOIs may potentiate the hypertensive effects of sympathomimetics, leading to a hypertensive crisis that can be fatal. Methylphenidate, dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine, and similar agents (methyldopa, l-dopa, l-tryptophan, l-tyrosine, phenylalanine) should be avoided.
Drug interaction: with sympathomimetics: nonselective MAOIs may potentiate the hypertensive effects of sympathomimetics, leading to a hypertensive crisis that can be fatal. Methylphenidate, dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine, and similar agents (methyldopa, l-dopa, l-tryptophan, l-tyrosine, phenylalanine) should be avoided.Side Effects
 Sleep disturbances include insomnia and reduction in rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. The insomnia is likely a central stimulatory effect from the increased monoamines, although a mechanism has not been established. Moclobemide, a reversible and selective MAO-A inhibitor, may cause fewer problems with sleep.
Sleep disturbances include insomnia and reduction in rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. The insomnia is likely a central stimulatory effect from the increased monoamines, although a mechanism has not been established. Moclobemide, a reversible and selective MAO-A inhibitor, may cause fewer problems with sleep. Weight gain is a common side effect of antidepressants; likely, increased monoamines play a role, but the mechanism has not been established.
Weight gain is a common side effect of antidepressants; likely, increased monoamines play a role, but the mechanism has not been established. Postural hypotension: The mechanism has not been established. This can be problematic in elderly patients, leading to falls. Note that this side effect is distinct from the hypertensive crisis, described later, which occurs because of an interaction with other agents and has a very specific mechanism.
Postural hypotension: The mechanism has not been established. This can be problematic in elderly patients, leading to falls. Note that this side effect is distinct from the hypertensive crisis, described later, which occurs because of an interaction with other agents and has a very specific mechanism. Sexual disturbances: The mechanism has not been established, although several antidepressants that affect monoamine levels have this side effect, and enhanced serotonin is believed to mediate sexual dysfunction with these agents.
Sexual disturbances: The mechanism has not been established, although several antidepressants that affect monoamine levels have this side effect, and enhanced serotonin is believed to mediate sexual dysfunction with these agents.Important Notes
 MAO-A in the gut breaks down tyramine, a chemical that stimulates the release of norepinephrine. Tyramine is typically found in aged foods such as cheese, wine, beer, yogurt, and yeast. Ingestion of these foods leads to increased tyramine, and because its breakdown is inhibited, there is increased norepinephrine release, leading to hypertensive crisis.
MAO-A in the gut breaks down tyramine, a chemical that stimulates the release of norepinephrine. Tyramine is typically found in aged foods such as cheese, wine, beer, yogurt, and yeast. Ingestion of these foods leads to increased tyramine, and because its breakdown is inhibited, there is increased norepinephrine release, leading to hypertensive crisis. Little MAO-B is found in the gut; therefore an MAO-B selective inhibitor will have minimal effect on the metabolism of dietary tyramine. Although MAO-B selectivity reduces the risk of hypertensive crisis, this selectivity is lost at higher doses.
Little MAO-B is found in the gut; therefore an MAO-B selective inhibitor will have minimal effect on the metabolism of dietary tyramine. Although MAO-B selectivity reduces the risk of hypertensive crisis, this selectivity is lost at higher doses. Reversible MAOIs lead to much less accumulation of tyramine and thus are considered to have minimal risk for hypertensive crisis resulting from the wine-cheese reaction.
Reversible MAOIs lead to much less accumulation of tyramine and thus are considered to have minimal risk for hypertensive crisis resulting from the wine-cheese reaction. A novel approach to avoiding accumulation of dietary tyramine is to bypass the GI MAO-A altogether by use of a patch.
A novel approach to avoiding accumulation of dietary tyramine is to bypass the GI MAO-A altogether by use of a patch. Linezolid, the first in a new class of antibiotics called the oxazolidinones, is also an MAOI. Concomitant use of these agents should therefore be avoided.
Linezolid, the first in a new class of antibiotics called the oxazolidinones, is also an MAOI. Concomitant use of these agents should therefore be avoided. All antidepressants carry an FDA warning about increased suicidality, particularly in younger (<25 years of age) patients. The mechanism has not been established and there is not enough data to determine whether a lower risk exists for some antidepressants compared with others. These concerns must also be balanced against the potential for increased risk of completed suicides in untreated depression.
All antidepressants carry an FDA warning about increased suicidality, particularly in younger (<25 years of age) patients. The mechanism has not been established and there is not enough data to determine whether a lower risk exists for some antidepressants compared with others. These concerns must also be balanced against the potential for increased risk of completed suicides in untreated depression.Evidence
MAO-B Inhibitors versus Dopaminergics for Early Parkinson’s Disease
 A 2009 Cochrane review (two trials, N = 593 patients) compared MAO-B inhibitors with a dopamine agonist or levodopa in patients with early Parkinson’s. No difference in deaths was found between selegiline and either agent, but patients treated with selegiline were more likely to need add-on therapy during follow-up than patients receiving levodopa (OR 12.02) or a dopamine agonist (OR 2.00). Motor fluctuations were reduced by MAO-B inhibitors versus levodopa (OR 0.55) but not dopamine agonists. Withdrawals because of adverse events were less common with MAO-B inhibitors compared with dopamine agonists (OR 0.11).
A 2009 Cochrane review (two trials, N = 593 patients) compared MAO-B inhibitors with a dopamine agonist or levodopa in patients with early Parkinson’s. No difference in deaths was found between selegiline and either agent, but patients treated with selegiline were more likely to need add-on therapy during follow-up than patients receiving levodopa (OR 12.02) or a dopamine agonist (OR 2.00). Motor fluctuations were reduced by MAO-B inhibitors versus levodopa (OR 0.55) but not dopamine agonists. Withdrawals because of adverse events were less common with MAO-B inhibitors compared with dopamine agonists (OR 0.11).Noradrenaline and Dopamine Reuptake Inhibitors (NDRIs)
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 Bupropion inhibits the presynaptic reuptake of both dopamine (DA) and noradrenaline (NA), leading to increased levels of both of these neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft (Figure 23-6).
Bupropion inhibits the presynaptic reuptake of both dopamine (DA) and noradrenaline (NA), leading to increased levels of both of these neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft (Figure 23-6). The clinical efficacy of all antidepressants is delayed a few weeks when compared with their pharmacologic actions. It is therefore hypothesized that the efficacy of these agents in the treatment of depression is related to a downstream effect.
The clinical efficacy of all antidepressants is delayed a few weeks when compared with their pharmacologic actions. It is therefore hypothesized that the efficacy of these agents in the treatment of depression is related to a downstream effect. A variety of theories exist regarding what this downstream effect might be, although most involve either a change in receptor density or fundamental changes at the cellular level, including a reorganization of neurons.
A variety of theories exist regarding what this downstream effect might be, although most involve either a change in receptor density or fundamental changes at the cellular level, including a reorganization of neurons. With respect to smoking cessation, dopamine is believed to be the key neurotransmitter in the reward pathway associated with addiction. It is believed that the increased levels of dopamine in the synapse help to mimic the reward associated with smoking, thus attenuating some of the withdrawal symptoms associated with abstinence.
With respect to smoking cessation, dopamine is believed to be the key neurotransmitter in the reward pathway associated with addiction. It is believed that the increased levels of dopamine in the synapse help to mimic the reward associated with smoking, thus attenuating some of the withdrawal symptoms associated with abstinence.Contraindications
 Seizures: Bupropion may lower the seizure threshold, so it must be avoided in individuals with a history of seizures or who are prone to seizures:
Seizures: Bupropion may lower the seizure threshold, so it must be avoided in individuals with a history of seizures or who are prone to seizures:
Important Notes
 Bupropion is unique among antidepressants as an inhibitor of dopamine reuptake, leading to increased dopamine levels in the synapse. This has lead to its use as a smoking cessation therapy, the indication for which it is most commonly prescribed.
Bupropion is unique among antidepressants as an inhibitor of dopamine reuptake, leading to increased dopamine levels in the synapse. This has lead to its use as a smoking cessation therapy, the indication for which it is most commonly prescribed. Another unique feature of bupropion is its lack of serotonergic effects. Antidepressants are known for eliciting sexual dysfunction, and this side effect has been attributed to their serotonergic properties. In clinical trials bupropion appears to have a lower propensity for sexual side effects compared with SSRIs and other serotonergic antidepressants.
Another unique feature of bupropion is its lack of serotonergic effects. Antidepressants are known for eliciting sexual dysfunction, and this side effect has been attributed to their serotonergic properties. In clinical trials bupropion appears to have a lower propensity for sexual side effects compared with SSRIs and other serotonergic antidepressants. In many jurisdictions, bupropion is marketed under two separate names, Wellbutrin and Zyban. Wellbutrin is prescribed for depression, and Zyban is used for smoking cessation. Because of the risk of overdose signs and symptoms, specifically seizures, care must be taken to ensure that patients do not take Wellbutrin and Zyban concomitantly.
In many jurisdictions, bupropion is marketed under two separate names, Wellbutrin and Zyban. Wellbutrin is prescribed for depression, and Zyban is used for smoking cessation. Because of the risk of overdose signs and symptoms, specifically seizures, care must be taken to ensure that patients do not take Wellbutrin and Zyban concomitantly. Reboxetine is an antidepressant that selectively targets noradrenaline reuptake. It has received marketing approval in Europe but not in the United States because of concerns over poor efficacy.
Reboxetine is an antidepressant that selectively targets noradrenaline reuptake. It has received marketing approval in Europe but not in the United States because of concerns over poor efficacy. All antidepressants carry an FDA warning about increased suicidality, particularly in younger (<25 years of age) patients. The mechanism has not been established and there is not enough data to determine whether a lower risk exists for some antidepressants compared with others. These concerns must also be balanced against the potential for increased risk of completed suicides in untreated depression.
All antidepressants carry an FDA warning about increased suicidality, particularly in younger (<25 years of age) patients. The mechanism has not been established and there is not enough data to determine whether a lower risk exists for some antidepressants compared with others. These concerns must also be balanced against the potential for increased risk of completed suicides in untreated depression.Evidence
Smoking Cessation: Antidepressants versus Placebo
 A 2007 Cochrane review (53 trials) compared antidepressants to placebo or alternative pharmacotherapies for smoking cessation or relapse prevention. The review included 31 RCTs of bupropion versus placebo or no treatment for smoking cessation, finding that bupropion doubled the odds of cessation across these studies (OR 1.94). In four trials, nortriptyline also improved the odds of quitting smoking (OR 2.34).
A 2007 Cochrane review (53 trials) compared antidepressants to placebo or alternative pharmacotherapies for smoking cessation or relapse prevention. The review included 31 RCTs of bupropion versus placebo or no treatment for smoking cessation, finding that bupropion doubled the odds of cessation across these studies (OR 1.94). In four trials, nortriptyline also improved the odds of quitting smoking (OR 2.34).Smoking Cessation: versus Varenicline (Partial Nicotine Agonist)
 A 2007 Cochrane review (7 trials, N = 7267 participants) assessed the efficacy and tolerability of varenicline versus other interventions and placebo for smoking cessation. The authors included three double-blind randomized controlled trials that compared bupropion with varenicline and when the data from these studies were combined, found that more varenicline subjects were abstinent or continuously abstinent from smoking at 12 months compared with bupropion (relative risk [RR] 1.52).
A 2007 Cochrane review (7 trials, N = 7267 participants) assessed the efficacy and tolerability of varenicline versus other interventions and placebo for smoking cessation. The authors included three double-blind randomized controlled trials that compared bupropion with varenicline and when the data from these studies were combined, found that more varenicline subjects were abstinent or continuously abstinent from smoking at 12 months compared with bupropion (relative risk [RR] 1.52).Lithium
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 Decades after the discovery of lithium’s utility in bipolar disorder, the mechanism behind its efficacy is still poorly understood.
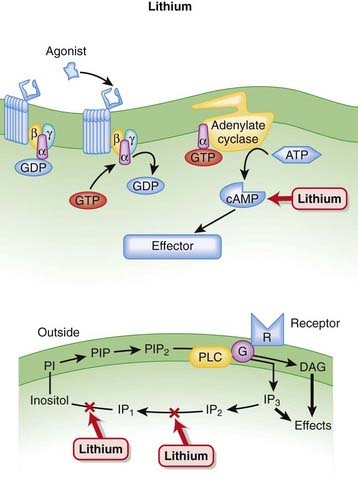
Decades after the discovery of lithium’s utility in bipolar disorder, the mechanism behind its efficacy is still poorly understood. One thing that is clear is that lithium has multiple effects on second messengers (Figure 23-7):
One thing that is clear is that lithium has multiple effects on second messengers (Figure 23-7):
 Increasing evidence suggests that lithium may have a neuroprotective role in the CNS, although the connection between this and its efficacy in mania is unclear at present. Lithium has been reported to increase expression of the antiapoptotic protein bcl-2.
Increasing evidence suggests that lithium may have a neuroprotective role in the CNS, although the connection between this and its efficacy in mania is unclear at present. Lithium has been reported to increase expression of the antiapoptotic protein bcl-2. Another neuroprotective factor thought to mediate the effects of lithium is the enzyme glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3). GSK-3 regulates numerous cellular processes such as gene transcription, synaptic plasticity, apoptosis, and circadian rhythms, among others. Lithium’s inhibition of GSK-3 is believed to have a neuroprotective effect.
Another neuroprotective factor thought to mediate the effects of lithium is the enzyme glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3). GSK-3 regulates numerous cellular processes such as gene transcription, synaptic plasticity, apoptosis, and circadian rhythms, among others. Lithium’s inhibition of GSK-3 is believed to have a neuroprotective effect.Pharmacokinetics
 Lithium has a narrow therapeutic index; therefore, small increases in lithium levels can lead to toxic effects. The effective plasma concentration is 0.6 to 1.25 mEq/L; moderate toxicity can occur starting at 1.5 mEq/L, and severe toxicity at 2 mEq/L.
Lithium has a narrow therapeutic index; therefore, small increases in lithium levels can lead to toxic effects. The effective plasma concentration is 0.6 to 1.25 mEq/L; moderate toxicity can occur starting at 1.5 mEq/L, and severe toxicity at 2 mEq/L. Lithium is almost exclusively excreted in the urine, with <1% in feces and smaller amounts excreted in sweat. Lithium is filtered freely, with 80% being reabsorbed in the nephron. In patients with normal renal function, 50% to 80% of a single dose is excreted in urine within 24 hours. Renal lithium excretion varies among individuals and is generally decreased in older patients and increased in younger patients.
Lithium is almost exclusively excreted in the urine, with <1% in feces and smaller amounts excreted in sweat. Lithium is filtered freely, with 80% being reabsorbed in the nephron. In patients with normal renal function, 50% to 80% of a single dose is excreted in urine within 24 hours. Renal lithium excretion varies among individuals and is generally decreased in older patients and increased in younger patients.Contraindications
 In the presence of the following conditions, lithium should be used only with extreme caution, when other treatments have failed:
In the presence of the following conditions, lithium should be used only with extreme caution, when other treatments have failed:Side Effects
Serious
 Acute lithium toxicity causes nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, renal failure, neuromuscular dysfunction, ataxia, tremor, confusion, delirium, and seizures.
Acute lithium toxicity causes nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, renal failure, neuromuscular dysfunction, ataxia, tremor, confusion, delirium, and seizures. Arrhythmia: Lithium inhibits K+ entry into myocytes, which leads to abnormal repolarization and abnormal T-waves. This can also lead to intracellular K+ depletion, and extracellular hyperkalemia, increasing the risk of sudden cardiac arrest from small changes in potassium levels.
Arrhythmia: Lithium inhibits K+ entry into myocytes, which leads to abnormal repolarization and abnormal T-waves. This can also lead to intracellular K+ depletion, and extracellular hyperkalemia, increasing the risk of sudden cardiac arrest from small changes in potassium levels.Important Notes
 Lithium is unique among all psychotropic agents in that it lacks any sedative, euphoriant, or depressive effects in normal individuals who do not suffer from psychiatric illness.
Lithium is unique among all psychotropic agents in that it lacks any sedative, euphoriant, or depressive effects in normal individuals who do not suffer from psychiatric illness.Advanced
Drug Interactions
 A drug interaction between lithium and diuretics has a unique mechanism. In response to decreased volume secondary to diuretic use, the kidneys will try to retain Na+ in an effort to retain water. When the kidney reabsorbs Na+, it will also reabsorb Li+, as it has a hard time differentiating between these two monovalent cations.
A drug interaction between lithium and diuretics has a unique mechanism. In response to decreased volume secondary to diuretic use, the kidneys will try to retain Na+ in an effort to retain water. When the kidney reabsorbs Na+, it will also reabsorb Li+, as it has a hard time differentiating between these two monovalent cations.Evidence
Bipolar Disorder
 A 2007 Health Technology Assessment (United Kingdom) review (45 trials) compared various mood stabilizers in preventing relapse in bipolar disorder. The authors found that lithium, valproate, lamotrigine, and olanzapine were more efficacious than placebo as maintenance therapy for relapse prevention. Lithium and olanzapine were effective for preventing manic relapses, but not for depressive relapses.
A 2007 Health Technology Assessment (United Kingdom) review (45 trials) compared various mood stabilizers in preventing relapse in bipolar disorder. The authors found that lithium, valproate, lamotrigine, and olanzapine were more efficacious than placebo as maintenance therapy for relapse prevention. Lithium and olanzapine were effective for preventing manic relapses, but not for depressive relapses.Lithium versus Placebo for Maintenance Treatment in Mood Disorders
 A 2001 Cochrane review (nine trials, N = 825 participants) compared lithium to placebo for treatment of mood disorder. Lithium was most beneficial at preventing relapse when used in bipolar disorder (OR 0.29). No significant benefit for relapse prevention was found in unipolar disorder. Because of low event rates, no conclusions could be drawn about the impact of lithium on suicide.
A 2001 Cochrane review (nine trials, N = 825 participants) compared lithium to placebo for treatment of mood disorder. Lithium was most beneficial at preventing relapse when used in bipolar disorder (OR 0.29). No significant benefit for relapse prevention was found in unipolar disorder. Because of low event rates, no conclusions could be drawn about the impact of lithium on suicide.FYI
 The discovery of lithium, one of the most important drugs in psychiatry, is an example of serendipity and scientific acumen. In the late 1940s an Australian scientist was administering lithium salt to guinea pigs to increase the solubility of urates. After noting that lithium made the animals lethargic, he decided to give lithium carbonate to agitated or manic psychiatric patients. Lithium appeared to have a positive effect on mania, paving the way for its use for this indication.
The discovery of lithium, one of the most important drugs in psychiatry, is an example of serendipity and scientific acumen. In the late 1940s an Australian scientist was administering lithium salt to guinea pigs to increase the solubility of urates. After noting that lithium made the animals lethargic, he decided to give lithium carbonate to agitated or manic psychiatric patients. Lithium appeared to have a positive effect on mania, paving the way for its use for this indication.First-Generation Antipsychotics
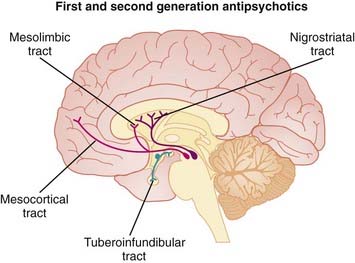
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 Dopamine is believed to play a key role in schizophrenia and thought disorders. Patients with schizophrenia experience hallucinations (visual, auditory, and tactile experiences in the absence of stimulation—for example, seeing something that is not there) and delusions (beliefs that are not true).
Dopamine is believed to play a key role in schizophrenia and thought disorders. Patients with schizophrenia experience hallucinations (visual, auditory, and tactile experiences in the absence of stimulation—for example, seeing something that is not there) and delusions (beliefs that are not true). There are several dopamine pathways in the CNS, but the following are key in both the efficacy and side effects of antipsychotic therapy:
There are several dopamine pathways in the CNS, but the following are key in both the efficacy and side effects of antipsychotic therapy:
 All antipsychotics are antagonists at dopamine D2 receptors. It is the antagonism of D2 receptors in the mesolimbic pathway that is thought to alleviate the positive symptoms of schizophrenia. Blockade of D2 receptors in other pathways is believed to result in many of the side effects of typical antipsychotics.
All antipsychotics are antagonists at dopamine D2 receptors. It is the antagonism of D2 receptors in the mesolimbic pathway that is thought to alleviate the positive symptoms of schizophrenia. Blockade of D2 receptors in other pathways is believed to result in many of the side effects of typical antipsychotics. Recently, subtypes of the D2 receptor have been identified: D3, and D4. Collectively, D2, D3, and D4 receptors are often referred to as the “D2-like receptors.” These receptors all have different distributions in the brain and subtle differences in pharmacology that are still not fully understood.
Recently, subtypes of the D2 receptor have been identified: D3, and D4. Collectively, D2, D3, and D4 receptors are often referred to as the “D2-like receptors.” These receptors all have different distributions in the brain and subtle differences in pharmacology that are still not fully understood. First-generation antipsychotics antagonize numerous other receptors, including adrenergic and cholinergic as well as histamine H1 receptors. Although it is still unclear to what extent, if any, antagonism of these receptors contributes to the efficacy of antipsychotics, they have a clear role in mediating many of the side effects associated with these agents.
First-generation antipsychotics antagonize numerous other receptors, including adrenergic and cholinergic as well as histamine H1 receptors. Although it is still unclear to what extent, if any, antagonism of these receptors contributes to the efficacy of antipsychotics, they have a clear role in mediating many of the side effects associated with these agents.Pharmacokinetics
 Most antipsychotics are highly lipophilic (and therefore easily enter the brain) and accumulate in well-perfused tissues such as brain and lung. Because of their lipophilic nature, most antipsychotics have the potential to cross the placenta and to enter breast milk.
Most antipsychotics are highly lipophilic (and therefore easily enter the brain) and accumulate in well-perfused tissues such as brain and lung. Because of their lipophilic nature, most antipsychotics have the potential to cross the placenta and to enter breast milk. A number of first-generation antipsychotics have active metabolites, including haloperidol, chlorpromazine, and thioridazine. The activity of these active metabolites may complicate the correlation of plasma drug monitoring with clinical efficacy.
A number of first-generation antipsychotics have active metabolites, including haloperidol, chlorpromazine, and thioridazine. The activity of these active metabolites may complicate the correlation of plasma drug monitoring with clinical efficacy. Elimination half-lives are typically in the 12- to 24-hour range, so all first-generation antipsychotics permit once-daily dosing.
Elimination half-lives are typically in the 12- to 24-hour range, so all first-generation antipsychotics permit once-daily dosing. Several first-generation antipsychotics are available in parenteral formulations, both standard intravenous and intramuscular formulations to achieve faster onset, and depot formulations to achieve prolonged effects (Table 23-3).
Several first-generation antipsychotics are available in parenteral formulations, both standard intravenous and intramuscular formulations to achieve faster onset, and depot formulations to achieve prolonged effects (Table 23-3).TABLE 23-3 Onset and Duration of Action of Depot and Intramuscular Formulations of First- Generation Antipsychotics
| Onset | Duration | |
|---|---|---|
| Depot | ||
| Haloperidol decanoate | 3 weeks | |
| Fluphenazine decanoate | 3-4 weeks | |
| Pipotiazine palmitate | 3-6 weeks | |
| Intramuscular (IM) | ||
| Haloperidol IM | 30-45 minutes | |
| Chlorpromazine IM | 15-30 minutes | |
| Fluphenazine IM | <1 hour | |
Side Effects
Common
 Anticholinergic effects include dry mouth, constipation, difficulty urinating, and loss of accommodation.
Anticholinergic effects include dry mouth, constipation, difficulty urinating, and loss of accommodation. Extrapyramidal syndrome (EPS): Blockade of dopamine receptors in the basal ganglia leads to Parkinson-like symptoms such as slow movement (bradykinesia), stiffness, and tremor.
Extrapyramidal syndrome (EPS): Blockade of dopamine receptors in the basal ganglia leads to Parkinson-like symptoms such as slow movement (bradykinesia), stiffness, and tremor. Tardive dyskinesia: Slow-developing, often permanent dyskinesia typically appears well after initiation of therapy (months to years). This effect is characterized by repetitive, involuntary movements of the face, arms, and trunk. One theory is that D2 receptors become hypersensitive after prolonged blockade. It can be very resistant to treatment.
Tardive dyskinesia: Slow-developing, often permanent dyskinesia typically appears well after initiation of therapy (months to years). This effect is characterized by repetitive, involuntary movements of the face, arms, and trunk. One theory is that D2 receptors become hypersensitive after prolonged blockade. It can be very resistant to treatment.Rare but Serious
 Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) is a rare but life-threatening side effect. The mechanism is not fully understood, but it is thought to be a result of inhibition of dopamine in the hypothalamus, an area responsible for temperature regulation.
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) is a rare but life-threatening side effect. The mechanism is not fully understood, but it is thought to be a result of inhibition of dopamine in the hypothalamus, an area responsible for temperature regulation.
 Agranulocytosis: A decreased white blood cell count can occur as a result of antipsychotics. This will result in undesired immunosuppression and requires discontinuation of the drug. This effect is observed with chlorpromazine and other phenothiazines (<0.1% of patients).
Agranulocytosis: A decreased white blood cell count can occur as a result of antipsychotics. This will result in undesired immunosuppression and requires discontinuation of the drug. This effect is observed with chlorpromazine and other phenothiazines (<0.1% of patients). Cardiac conduction abnormalities such as long QT (thioridazine, droperidol) are a rare but serious side effect that has led to the market withdrawal of these agents in some jurisdictions. Antipsychotics appear to affect cardiac potassium channels, and these two agents are likely to have a greater impact on these channels than other agents.
Cardiac conduction abnormalities such as long QT (thioridazine, droperidol) are a rare but serious side effect that has led to the market withdrawal of these agents in some jurisdictions. Antipsychotics appear to affect cardiac potassium channels, and these two agents are likely to have a greater impact on these channels than other agents.Important Notes
 There is increasing concern about the metabolic side effects associated with long-term use of antipsychotics. The risk of some of these side effects may be lower with first-generation antipsychotics compared with second generation antipsychotics (see Evidence section).
There is increasing concern about the metabolic side effects associated with long-term use of antipsychotics. The risk of some of these side effects may be lower with first-generation antipsychotics compared with second generation antipsychotics (see Evidence section). After many years of research, the exact causes of schizophrenia remain a mystery. There are several theories as to the neurochemical origins; most involve serotonin and dopamine playing a key role. Glutamate, an excitatory neurotransmitter, has also become a major focus of research, based on the observation that N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) antagonists exacerbate cognitive impairment and psychosis in patients with schizophrenia. Glutamate receptor agonists are currently in development for schizophrenia.
After many years of research, the exact causes of schizophrenia remain a mystery. There are several theories as to the neurochemical origins; most involve serotonin and dopamine playing a key role. Glutamate, an excitatory neurotransmitter, has also become a major focus of research, based on the observation that N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) antagonists exacerbate cognitive impairment and psychosis in patients with schizophrenia. Glutamate receptor agonists are currently in development for schizophrenia.Evidence
Risk of Diabetes in First- versus Second-Generation Antipsychotics
 A 2008 systematic review (11 studies) compared diabetes risk among various antipsychotics. The majority of studies in this review were cross-sectional or retrospective cohort studies, which somewhat limits confidence in the analysis. The authors found an increased risk of diabetes in patients taking second-generation versus first-generation antipsychotics (RR 1.32). Data were insufficient to include aripiprazole, ziprasidone, and amisulpride in this analysis. Relative risks ranged from a low of 1.16 with risperidone to a high of 1.39 with clozapine. Differences in risk were statistically significant for all second-generation agents except risperidone.
A 2008 systematic review (11 studies) compared diabetes risk among various antipsychotics. The majority of studies in this review were cross-sectional or retrospective cohort studies, which somewhat limits confidence in the analysis. The authors found an increased risk of diabetes in patients taking second-generation versus first-generation antipsychotics (RR 1.32). Data were insufficient to include aripiprazole, ziprasidone, and amisulpride in this analysis. Relative risks ranged from a low of 1.16 with risperidone to a high of 1.39 with clozapine. Differences in risk were statistically significant for all second-generation agents except risperidone.FYI
 Phenothiazines are among the earliest synthetic drugs, first synthesized in the late nineteenth century as a result of the development of aniline dyes. The first phenothiazines were antihistamines, and it was their sedative effects that led to their use in agitated psychiatric patients.
Phenothiazines are among the earliest synthetic drugs, first synthesized in the late nineteenth century as a result of the development of aniline dyes. The first phenothiazines were antihistamines, and it was their sedative effects that led to their use in agitated psychiatric patients. Chlorpromazine was developed in 1950 for use in anesthesia. Shortly after, it was used in psychiatry for agitation and anxiety. Initially its efficacy in these patients was attributed to its sedative properties, but it was later determined that chlorpromazine was effective in the treatment of a variety of psychoses.
Chlorpromazine was developed in 1950 for use in anesthesia. Shortly after, it was used in psychiatry for agitation and anxiety. Initially its efficacy in these patients was attributed to its sedative properties, but it was later determined that chlorpromazine was effective in the treatment of a variety of psychoses.Second-Generation Antipsychotics
MOA (Mechanism of Action) (Figure 23-9)
 Dopamine is believed to play a key role in schizophrenia and thought disorders. Patients with schizophrenia experience hallucinations (visual, auditory, and tactile experiences in the absence of stimulation—for example, seeing something that is not there) and delusions (beliefs that are not true).
Dopamine is believed to play a key role in schizophrenia and thought disorders. Patients with schizophrenia experience hallucinations (visual, auditory, and tactile experiences in the absence of stimulation—for example, seeing something that is not there) and delusions (beliefs that are not true). The second-generation antipsychotics are believed to antagonize several different receptors, primarily dopamine and serotonin (5-HT).
The second-generation antipsychotics are believed to antagonize several different receptors, primarily dopamine and serotonin (5-HT). There are several dopamine pathways in the CNS, but the following are key in both the efficacy and side effects of antipsychotic therapy:
There are several dopamine pathways in the CNS, but the following are key in both the efficacy and side effects of antipsychotic therapy:
 All antipsychotic drugs are D2-receptor antagonists, and it is believed that blockade of D2 receptors in the mesolimbic pathway leads to an antipsychotic effect, addressing the positive symptoms of schizophrenia.
All antipsychotic drugs are D2-receptor antagonists, and it is believed that blockade of D2 receptors in the mesolimbic pathway leads to an antipsychotic effect, addressing the positive symptoms of schizophrenia. Recently, subtypes of the D2 receptor have been identified: D3, and D4. Collectively, D2, D3, and D4 receptors are often referred to as the “D2-like receptors.” These receptors all have different distributions in the brain and subtle differences in pharmacology that are still not fully understood.
Recently, subtypes of the D2 receptor have been identified: D3, and D4. Collectively, D2, D3, and D4 receptors are often referred to as the “D2-like receptors.” These receptors all have different distributions in the brain and subtle differences in pharmacology that are still not fully understood. The role of serotonin (specifically 5-HT2A) antagonism in the efficacy of antipsychotics is less well understood. Unlike many of the first-generation agents, the second-generation agents are potent antagonists of 5-HT2A receptors. Because second-generation agents are better at treating the negative symptoms of schizophrenia, it is believed that blockade of 5-HT2A receptors may contribute to the improvement in negative symptoms.
The role of serotonin (specifically 5-HT2A) antagonism in the efficacy of antipsychotics is less well understood. Unlike many of the first-generation agents, the second-generation agents are potent antagonists of 5-HT2A receptors. Because second-generation agents are better at treating the negative symptoms of schizophrenia, it is believed that blockade of 5-HT2A receptors may contribute to the improvement in negative symptoms. It is also thought that 5-HT2A blockade might affect nigrostriatal dopamine release, leading to reduced extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS). Other theories accounting for the different propensities among antipsychotics to cause EPS include different D2 binding affinities and anticholinergic activity.
It is also thought that 5-HT2A blockade might affect nigrostriatal dopamine release, leading to reduced extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS). Other theories accounting for the different propensities among antipsychotics to cause EPS include different D2 binding affinities and anticholinergic activity. Second-generation antipsychotics, as first-generation antipsychotics, antagonize numerous other receptors, including adrenergic and cholinergic (particularly olanzapine and clozapine) as well as histamine H1 receptors. Although it is still unclear to what extent, if any, antagonism of these receptors contributes to the efficacy of atypical antipsychotics, they have a clear role in mediating many of the side effects associated with these agents.
Second-generation antipsychotics, as first-generation antipsychotics, antagonize numerous other receptors, including adrenergic and cholinergic (particularly olanzapine and clozapine) as well as histamine H1 receptors. Although it is still unclear to what extent, if any, antagonism of these receptors contributes to the efficacy of atypical antipsychotics, they have a clear role in mediating many of the side effects associated with these agents.Pharmacokinetics
 The second-generation antipsychotics vary in bioavailability, elimination half-life, and metabolism.
The second-generation antipsychotics vary in bioavailability, elimination half-life, and metabolism.Contraindications
Side Effects
 The side effect profile of atypical antipsychotics varies widely owing to their heterogeneous receptor binding profiles.
The side effect profile of atypical antipsychotics varies widely owing to their heterogeneous receptor binding profiles.Serious
All Agents
 Increased mortality in elderly patients: These agents are associated with increased risk of death in elderly patients with dementia, from a variety of causes, largely cardiovascular or infectious. The mechanism is still unclear at this time.
Increased mortality in elderly patients: These agents are associated with increased risk of death in elderly patients with dementia, from a variety of causes, largely cardiovascular or infectious. The mechanism is still unclear at this time. Endocrine:
Endocrine:
 Weight gain occurs because of suppression of satiety and other factors. The receptor responsible has not been established, although the focus is currently on H1.
Weight gain occurs because of suppression of satiety and other factors. The receptor responsible has not been established, although the focus is currently on H1. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) is a rare but critically life-threatening effect seen with both first- and second-generation antipsychotics. The mechanism is not fully understood, but it is thought to be caused by inhibition of dopamine in the hypothalamus, an area responsible for temperature regulation. It is characterized by:
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) is a rare but critically life-threatening effect seen with both first- and second-generation antipsychotics. The mechanism is not fully understood, but it is thought to be caused by inhibition of dopamine in the hypothalamus, an area responsible for temperature regulation. It is characterized by:
Clozapine
 Agranulocytosis can be fatal and necessitates weekly or biweekly blood monitoring of all patients taking clozapine. The risk is about 1% in the first 3 months and then decreases to about 0.01% after 1 year. Although agranulocytosis is a risk with all antipsychotics, it is much more common with clozapine compared to other agents.
Agranulocytosis can be fatal and necessitates weekly or biweekly blood monitoring of all patients taking clozapine. The risk is about 1% in the first 3 months and then decreases to about 0.01% after 1 year. Although agranulocytosis is a risk with all antipsychotics, it is much more common with clozapine compared to other agents.Nonserious Adverse Effects, Common to All Agents (to Varying Extents)
 Orthostatic hypotension is most commonly observed with clozapine. This side effect is probably caused by α1 blockade
Orthostatic hypotension is most commonly observed with clozapine. This side effect is probably caused by α1 blockade EPS secondary to D2 receptor blockade in the nigrostriatal region. The incidence of EPS is lower with second-generation compared with first-generation agents, and among the second-generation agents, is lowest with clozapine.
EPS secondary to D2 receptor blockade in the nigrostriatal region. The incidence of EPS is lower with second-generation compared with first-generation agents, and among the second-generation agents, is lowest with clozapine.Important Notes
 Clozapine is itself considered to be atypical among atypical antipsychotics, with a unique side effect profile and a greater degree of success in treatment-resistant patients. Thus many consider clozapine to be in a class of its own.
Clozapine is itself considered to be atypical among atypical antipsychotics, with a unique side effect profile and a greater degree of success in treatment-resistant patients. Thus many consider clozapine to be in a class of its own. The second-generation antipsychotics are considered “atypical” because they do not cause EPS to the same extent as first-generation agents. It is important to note that EPS has still been observed with these agents, and the mechanistic rationale for why atypical agents are less likely to cause EPS has not been established.
The second-generation antipsychotics are considered “atypical” because they do not cause EPS to the same extent as first-generation agents. It is important to note that EPS has still been observed with these agents, and the mechanistic rationale for why atypical agents are less likely to cause EPS has not been established. The incidence of tardive dyskinesia tends to vary with age and drug class used. The incidence in children is low with second-generation antipsychotics, in adults it is lower with second-generation than first-generation agents, and first- and second-generation agents have the same annual incidence in the elderly.
The incidence of tardive dyskinesia tends to vary with age and drug class used. The incidence in children is low with second-generation antipsychotics, in adults it is lower with second-generation than first-generation agents, and first- and second-generation agents have the same annual incidence in the elderly. The weight gain associated with antipsychotics can be significant and lead to long-term health issues such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. It appears that olanzapine and clozapine may cause the greatest degree of weight gain among the second-generation agents.
The weight gain associated with antipsychotics can be significant and lead to long-term health issues such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. It appears that olanzapine and clozapine may cause the greatest degree of weight gain among the second-generation agents. Conversely, ziprasidone may be least associated with weight gain, and in fact has been associated with weight loss in some trials. The adverse lipid effects seen with other agents in this class are also not seen with ziprasidone. However, ziprasidone is associated with QT interval prolongation, a potentially fatal adverse effect. This creates an interesting dilemma—choosing between rare short-term side effects that are potentially fatal, and more common long-term side effects that have serious, but less readily identifiable consequences.
Conversely, ziprasidone may be least associated with weight gain, and in fact has been associated with weight loss in some trials. The adverse lipid effects seen with other agents in this class are also not seen with ziprasidone. However, ziprasidone is associated with QT interval prolongation, a potentially fatal adverse effect. This creates an interesting dilemma—choosing between rare short-term side effects that are potentially fatal, and more common long-term side effects that have serious, but less readily identifiable consequences.Advanced
Drug Interactions
 Clozapine is metabolized by CYP1A2 and CYP3A4, and its metabolism is affected by notable inducers or inhibitors of these isozymes, such as the following:
Clozapine is metabolized by CYP1A2 and CYP3A4, and its metabolism is affected by notable inducers or inhibitors of these isozymes, such as the following:
 Olanzapine is a weak inhibitor of CYP1A2, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4, but it has not been shown to have significant effects on other drugs. The metabolism of olanzapine has been affected by the following:
Olanzapine is a weak inhibitor of CYP1A2, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4, but it has not been shown to have significant effects on other drugs. The metabolism of olanzapine has been affected by the following:
Evidence
Schizophrenia
 A recent (2006) systematic review of atypical antipsychotics found differences in effectiveness among agents in this class:
A recent (2006) systematic review of atypical antipsychotics found differences in effectiveness among agents in this class:
 A 2010 Cochrane review (50 studies, N = 9476 participants) compared olanzapine with other second-generation agents. Fewer participants treated with olanzapine had to be rehospitalized compared with quetiapine (NNT 11, 2 RCTs) and ziprasidone (NNT 17, 2 RCTs) but not clozapine. Olanzapine improved symptoms more than aripiprazole (2 RCTs), quetiapine (10 RCTs), risperidone (15 RCTs) and ziprasidone (4 RCTs) but not amisulpride or clozapine. Olanzapine elicited more weight gain than all others except clozapine, and more EPS than quetiapine, but less EPS than risperidone and ziprasidone.
A 2010 Cochrane review (50 studies, N = 9476 participants) compared olanzapine with other second-generation agents. Fewer participants treated with olanzapine had to be rehospitalized compared with quetiapine (NNT 11, 2 RCTs) and ziprasidone (NNT 17, 2 RCTs) but not clozapine. Olanzapine improved symptoms more than aripiprazole (2 RCTs), quetiapine (10 RCTs), risperidone (15 RCTs) and ziprasidone (4 RCTs) but not amisulpride or clozapine. Olanzapine elicited more weight gain than all others except clozapine, and more EPS than quetiapine, but less EPS than risperidone and ziprasidone.Psychosis and Aggression Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease
 A 2006 Cochrane review (10 trials) found that although risperidone and olanzapine were useful in reducing aggression and risperidone was useful for psychosis, these agents also had serious harmful effects such as a higher incidence of stroke as well as EPS and other adverse events. There were insufficient data to assess cognitive function.
A 2006 Cochrane review (10 trials) found that although risperidone and olanzapine were useful in reducing aggression and risperidone was useful for psychosis, these agents also had serious harmful effects such as a higher incidence of stroke as well as EPS and other adverse events. There were insufficient data to assess cognitive function.FYI
 Clozapine is widely recognized as being the atypical antipsychotic with the greatest efficacy; however, its 50-year history has been tumultuous. From its early trials in the 1960s, clozapine was noted as being “atypical” because of its lack of disabling neurologic side effects. However, the lack of EPS was interpreted as an indication that it lacked antipsychotic efficacy as well, as at that time the two effects were considered to be connected.
Clozapine is widely recognized as being the atypical antipsychotic with the greatest efficacy; however, its 50-year history has been tumultuous. From its early trials in the 1960s, clozapine was noted as being “atypical” because of its lack of disabling neurologic side effects. However, the lack of EPS was interpreted as an indication that it lacked antipsychotic efficacy as well, as at that time the two effects were considered to be connected. The first serious impediment to clozapine’s widespread use was the discovery of orthostatic hypotension. After this hurdle was overcome, reports of deaths from severe blood disorders began to emerge from Finland in the mid-1970s. The incidence of agranulocytosis was much higher in the Finnish population, shedding light on a rare toxicity that had previously been overlooked. The manufacturer of clozapine dropped its request for approval by the FDA, and the drug became available only through a “compassionate use” program.
The first serious impediment to clozapine’s widespread use was the discovery of orthostatic hypotension. After this hurdle was overcome, reports of deaths from severe blood disorders began to emerge from Finland in the mid-1970s. The incidence of agranulocytosis was much higher in the Finnish population, shedding light on a rare toxicity that had previously been overlooked. The manufacturer of clozapine dropped its request for approval by the FDA, and the drug became available only through a “compassionate use” program. Interest in clozapine reemerged in North America in the 1980s, because of both the rising health care costs of mental illness and the success the Europeans had had using a monitoring program to minimize harm. Clozapine was approved by the FDA in 1989 and continues to be a vital drug for those refractory to other therapies.
Interest in clozapine reemerged in North America in the 1980s, because of both the rising health care costs of mental illness and the success the Europeans had had using a monitoring program to minimize harm. Clozapine was approved by the FDA in 1989 and continues to be a vital drug for those refractory to other therapies.Benzodiazepines
Prototypes and Common Drugs
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the CNS. GABA binds to three different types of receptors: GABAA, GABAB, and GABAC.
γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the CNS. GABA binds to three different types of receptors: GABAA, GABAB, and GABAC.
 BZDs also have their own receptor directly on the Cl− channel. Binding of BZDs to this BZD receptor enhances the effects of GABA at the GABAA receptor.
BZDs also have their own receptor directly on the Cl− channel. Binding of BZDs to this BZD receptor enhances the effects of GABA at the GABAA receptor. BZDs are unable to activate the GABAA receptor on their own; therefore BZDs have no pharmacologic effects on the Cl− channel when GABA is absent.
BZDs are unable to activate the GABAA receptor on their own; therefore BZDs have no pharmacologic effects on the Cl− channel when GABA is absent. Atypical BZDs also act as GABA enhancers but bind to a different subunit of the BZD receptor than typical BZDs.
Atypical BZDs also act as GABA enhancers but bind to a different subunit of the BZD receptor than typical BZDs.Pharmacokinetics
 The elimination half-lives of BZDs play a key role in determining how they are used (see Important Notes for further discussion).
The elimination half-lives of BZDs play a key role in determining how they are used (see Important Notes for further discussion). Lorazepam, midazolam, and diazepam are all available for intravenous administration. Onset time is quite short (minutes) when these drugs are given intravenously.
Lorazepam, midazolam, and diazepam are all available for intravenous administration. Onset time is quite short (minutes) when these drugs are given intravenously. Patients who use alcohol regularly will have significant resistance to BZDs and require larger doses to achieve the same effect as would be achieved in an otherwise identical patient who does not use alcohol regularly.
Patients who use alcohol regularly will have significant resistance to BZDs and require larger doses to achieve the same effect as would be achieved in an otherwise identical patient who does not use alcohol regularly.TABLE 23-4 Elimination Half-Lives of Various Benzodiazepines
| Half-life Duration | Half-Life (Hours) |
|---|---|
| Short Half-Life Agents | |
| Triazolam | 2-3 |
| Intermediate Half-Life Agents | |
| Alprazolam | 12-15 |
| Lorazepam | 10-20 |
| Oxazepam | 10-20 |
| Temazepam | 10-40 |
| Chlordiazepoxide* | 15-40 |
| Long Half-Life Agents | |
| Diazepam* | 20-80 |
| Flurazepam* | 40-100 |
Side Effects
 Respiratory depression may be seen at higher doses and can lead to respiratory acidosis, particularly in those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Respiratory depression may be seen at higher doses and can lead to respiratory acidosis, particularly in those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Decreased blood pressure, increased heart rate: These cardiovascular effects are seen at higher doses and are likely mediated by a decrease in vascular resistance (midazolam) or cardiac output (diazepam).
Decreased blood pressure, increased heart rate: These cardiovascular effects are seen at higher doses and are likely mediated by a decrease in vascular resistance (midazolam) or cardiac output (diazepam).Important Notes
 The ability of BZDs to cause amnesia is advantageous in the performance of uncomfortable procedures, as the patient is still able to comply with instructions but does not retain memory of the procedure afterward.
The ability of BZDs to cause amnesia is advantageous in the performance of uncomfortable procedures, as the patient is still able to comply with instructions but does not retain memory of the procedure afterward. Although the clinical effects of the BZDs resemble and overlap with those of other sedative-hypnotics, BZDs are more effective as anxiolytics.
Although the clinical effects of the BZDs resemble and overlap with those of other sedative-hypnotics, BZDs are more effective as anxiolytics. Because BZDs are CNS depressants (inhibitors), and seizures are states of pathologically elevated electrical activity in the brain, BZDs are ideally suited for treating seizures.
Because BZDs are CNS depressants (inhibitors), and seizures are states of pathologically elevated electrical activity in the brain, BZDs are ideally suited for treating seizures. Tolerance, dependence, and withdrawal are all of major concern with BZDs. Discontinuation of BZDs can be particularly unpleasant for the patient and, typical of drug withdrawal, is characterized by side effects that are the opposite of those intended with therapy—that is, insomnia, anxiety, tremor, and (rarely) seizures.
Tolerance, dependence, and withdrawal are all of major concern with BZDs. Discontinuation of BZDs can be particularly unpleasant for the patient and, typical of drug withdrawal, is characterized by side effects that are the opposite of those intended with therapy—that is, insomnia, anxiety, tremor, and (rarely) seizures. Longer half-life agents are less prone to cause withdrawal than agents with a short half-life, as the longer half-life agents allow time for receptor density to return to predrug levels before the drug is completely eliminated. However, for certain indications, particularly when used as hypnotics, shorter-acting agents are preferable because of their reduced propensity for a hangover effect (i.e., grogginess).
Longer half-life agents are less prone to cause withdrawal than agents with a short half-life, as the longer half-life agents allow time for receptor density to return to predrug levels before the drug is completely eliminated. However, for certain indications, particularly when used as hypnotics, shorter-acting agents are preferable because of their reduced propensity for a hangover effect (i.e., grogginess).Evidence
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
 A 2007 systematic review examined three commonly used BZDs—diazepam (12 trials), lorazepam (7 trials), and alprazolam (4 trials)—versus placebo. All included studies were DBRCTs. The authors chose withdrawal from study as their primary outcome measure, and fewer patients treated with BZD withdrew for any reason (RR 0.78) or for lack of efficacy (RR 0.29). However, more BZD-treated patients withdrew because of an adverse event compared with placebo (RR 1.54).
A 2007 systematic review examined three commonly used BZDs—diazepam (12 trials), lorazepam (7 trials), and alprazolam (4 trials)—versus placebo. All included studies were DBRCTs. The authors chose withdrawal from study as their primary outcome measure, and fewer patients treated with BZD withdrew for any reason (RR 0.78) or for lack of efficacy (RR 0.29). However, more BZD-treated patients withdrew because of an adverse event compared with placebo (RR 1.54).Older Adults with Insomnia
 A 2005 systematic review examined the risks and benefits of sedative use for insomnia in adults 60 years of age or older. The review included 20 DBRCTs, covering sleep quality, sleep time, awakenings, or latency of sleep onset. BZDs (830 participants) and non-BZDs (1099 participants) were the main interventions used, versus placebo (468 participants). Based on four studies, the authors calculated a number needed to treat (NNT) of 13 for improvement in sleep quality with sedatives. However, the number needed to harm (NNH) was six versus placebo. No difference in sleep quality was detected across three studies that compared BZDs with atypical BZDs. Sedatives increased sleep time by 25 minutes overall. Cognitive adverse effects were significantly more common with sedatives than with placebo (OR 4.78).
A 2005 systematic review examined the risks and benefits of sedative use for insomnia in adults 60 years of age or older. The review included 20 DBRCTs, covering sleep quality, sleep time, awakenings, or latency of sleep onset. BZDs (830 participants) and non-BZDs (1099 participants) were the main interventions used, versus placebo (468 participants). Based on four studies, the authors calculated a number needed to treat (NNT) of 13 for improvement in sleep quality with sedatives. However, the number needed to harm (NNH) was six versus placebo. No difference in sleep quality was detected across three studies that compared BZDs with atypical BZDs. Sedatives increased sleep time by 25 minutes overall. Cognitive adverse effects were significantly more common with sedatives than with placebo (OR 4.78).Alcohol Withdrawal
 A 2005 Cochrane review found that BZDs were significantly better for alcohol withdrawal seizures compared with placebo and had similar efficacy to other drugs, or anticonvulsants specifically. BZDs elicited similar changes in alcohol withdrawal scores compared with other drugs. The findings of the review are complicated by the heterogeneity among trials.
A 2005 Cochrane review found that BZDs were significantly better for alcohol withdrawal seizures compared with placebo and had similar efficacy to other drugs, or anticonvulsants specifically. BZDs elicited similar changes in alcohol withdrawal scores compared with other drugs. The findings of the review are complicated by the heterogeneity among trials.Central Nervous System Stimulants
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 Methylphenidate and amphetamine work by increasing neurotransmitter levels in the synapse, specifically, levels of dopamine (DA) and noradrenaline (NA). They accomplish this through a variety of mechanisms.
Methylphenidate and amphetamine work by increasing neurotransmitter levels in the synapse, specifically, levels of dopamine (DA) and noradrenaline (NA). They accomplish this through a variety of mechanisms. Methylphenidate and amphetamine also inhibit the reuptake of the monamines as well as inhibiting the activity of a key enzyme that breaks them down, MAO (Figure 23-11).
Methylphenidate and amphetamine also inhibit the reuptake of the monamines as well as inhibiting the activity of a key enzyme that breaks them down, MAO (Figure 23-11). Methylphenidate and amphetamine increase dopamine levels in the prefrontal cortex, an area thought to play an important role in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The connection between the increased dopamine and noradrenaline in the synapse and the behavioral improvements seen in ADHD is still unclear. Dopamine is thought to be the key neurotransmitter mediating the beneficial effects of these agents in ADHD.
Methylphenidate and amphetamine increase dopamine levels in the prefrontal cortex, an area thought to play an important role in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The connection between the increased dopamine and noradrenaline in the synapse and the behavioral improvements seen in ADHD is still unclear. Dopamine is thought to be the key neurotransmitter mediating the beneficial effects of these agents in ADHD.Pharmacokinetics
 The elimination half-life of methylphenidate is relatively short (approximately 2 hours); therefore it is also available in extended release (ER) forms. The main metabolite is ritalinic acid, and the methylphenidate metabolites are mostly excreted in urine.
The elimination half-life of methylphenidate is relatively short (approximately 2 hours); therefore it is also available in extended release (ER) forms. The main metabolite is ritalinic acid, and the methylphenidate metabolites are mostly excreted in urine. Once-daily formulations are considered ideal for convenience. However, after evidence suggesting that the period immediately after a dose of methylphenidate provides the most benefit, manufacturers have tried to develop formulations that release the drug in a biphasic manner. These formulations have both an immediate-release (IR) and an ER component, in a variety of proportions. The agents with a large proportion of the IR component have greater efficacy early (2 hours) after administration, whereas the agents with a larger ER proportion have greater efficacy later (12 hours).
Once-daily formulations are considered ideal for convenience. However, after evidence suggesting that the period immediately after a dose of methylphenidate provides the most benefit, manufacturers have tried to develop formulations that release the drug in a biphasic manner. These formulations have both an immediate-release (IR) and an ER component, in a variety of proportions. The agents with a large proportion of the IR component have greater efficacy early (2 hours) after administration, whereas the agents with a larger ER proportion have greater efficacy later (12 hours).Contraindications
Side Effects
Evidence
Safety of Methylphenidate in Adults
 A 2009 systematic review (26 trials, 811 participants) examined the safety of methylphenidate versus placebo for a variety of disorders, including ADHD, in adults. The trials were of relatively short duration (1 to 12 weeks) and therefore provide no information about chronic use. No serious (life-threatening or irreversible) adverse effects were reported in any studies. Dry mouth, anorexia, changes in mood, “jitteriness,” depression or sadness, weight loss, and vertigo were the most common adverse events that occurred more frequently with methylphenidate than placebo. The five studies reporting cardiovascular changes found slight increases in blood pressure and pulse rate.
A 2009 systematic review (26 trials, 811 participants) examined the safety of methylphenidate versus placebo for a variety of disorders, including ADHD, in adults. The trials were of relatively short duration (1 to 12 weeks) and therefore provide no information about chronic use. No serious (life-threatening or irreversible) adverse effects were reported in any studies. Dry mouth, anorexia, changes in mood, “jitteriness,” depression or sadness, weight loss, and vertigo were the most common adverse events that occurred more frequently with methylphenidate than placebo. The five studies reporting cardiovascular changes found slight increases in blood pressure and pulse rate.FYI
 Amphetamine was first introduced commercially in the 1930s as Benzedrine, for narcolepsy. The product was available without a prescription, and when word got out about its stimulant properties, sales soared until it reverted back to prescription-only status.
Amphetamine was first introduced commercially in the 1930s as Benzedrine, for narcolepsy. The product was available without a prescription, and when word got out about its stimulant properties, sales soared until it reverted back to prescription-only status. Methylphenidate is an old drug that has seen a variety of indications over the years. First synthesized in 1944, it has been used for chronic fatigue, lethargy, and depression, among other indications.
Methylphenidate is an old drug that has seen a variety of indications over the years. First synthesized in 1944, it has been used for chronic fatigue, lethargy, and depression, among other indications. The behavioral effects of amphetamines in children were first noted 70 years ago. After observing positive responses in a small study of benzedrine, an amphetamine derivative, larger clinical trials demonstrated that “behavior disorders” in children responded to this agent.
The behavioral effects of amphetamines in children were first noted 70 years ago. After observing positive responses in a small study of benzedrine, an amphetamine derivative, larger clinical trials demonstrated that “behavior disorders” in children responded to this agent. The CNS stimulants are a heterogeneous drug class, and that heterogeneity is seen in the wide variety of plant sources of agents in this class. Leaves of the shrub tree Catha edulis, native to Africa and the Middle East, contain norpseudoephedrine. Fresh leaves or stems are referred to as Khat and are an integral part of many social rituals in Middle Eastern countries such as Yemen. Ephedra sinica yields ephedra, an herb that dates back to first-century Chinese books of herbal medicine, used for asthma and upper respiratory tract infections.
The CNS stimulants are a heterogeneous drug class, and that heterogeneity is seen in the wide variety of plant sources of agents in this class. Leaves of the shrub tree Catha edulis, native to Africa and the Middle East, contain norpseudoephedrine. Fresh leaves or stems are referred to as Khat and are an integral part of many social rituals in Middle Eastern countries such as Yemen. Ephedra sinica yields ephedra, an herb that dates back to first-century Chinese books of herbal medicine, used for asthma and upper respiratory tract infections.