Oncogenes
Signal Transduction by Protein Tyrosine Kinase Receptors
RTKs and Cancer
Signaling Pathways of Tyrosine Kinase Receptors
RAS
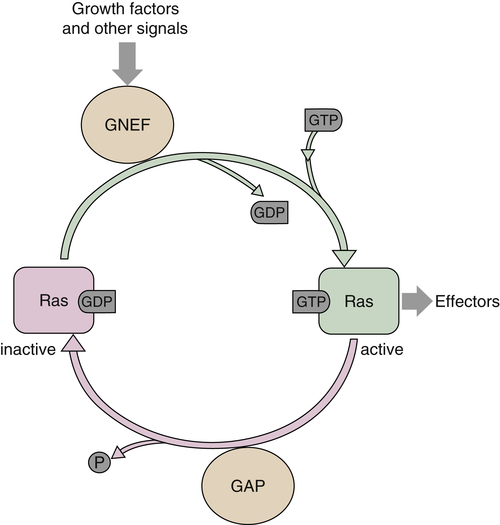
Ras Functions
Ras and Cancer
Signaling Downstream of RAS
Ras>Raf>Map Kinase Cascade
Functions of the MAP Kinase Pathway
Raf/Mek/MapK and Cancer
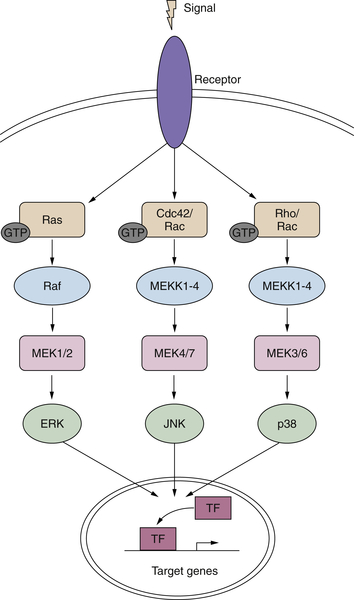
Other MAP Kinases
C-Myc
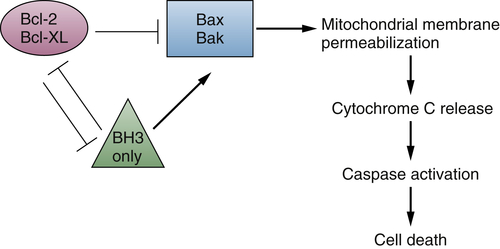
Oncogenes and Survival Signaling
The Bcl-2 Family
PI3K-Dependent Pathways
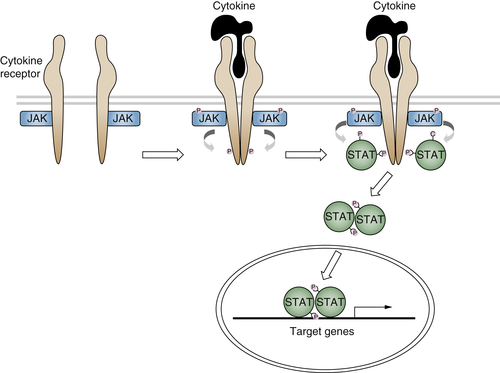
Cytokine Receptor Signaling
Neurotransmitters
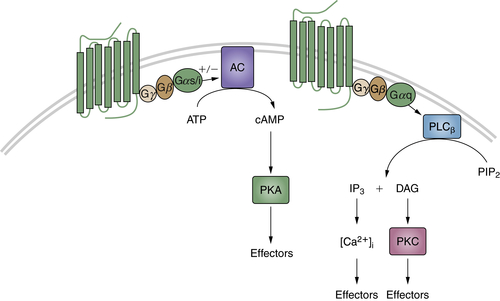
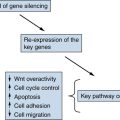
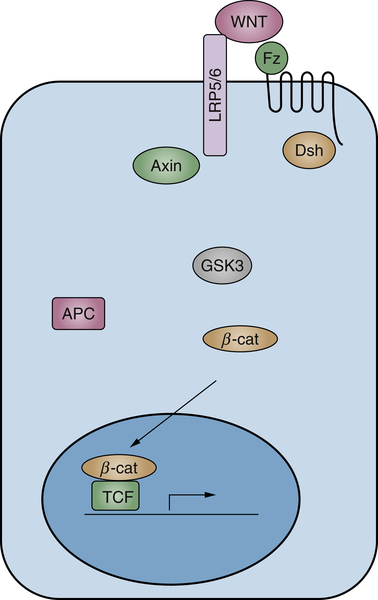
Wnt Signaling
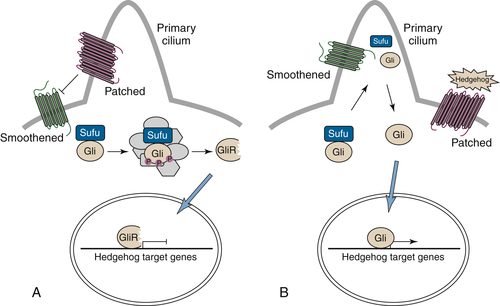
Hedgehog/Patched Signaling
Implications for Cancer Therapy
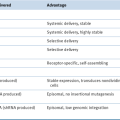
Table 2-1
Targeted Therapeutics Directed against Oncogene Products
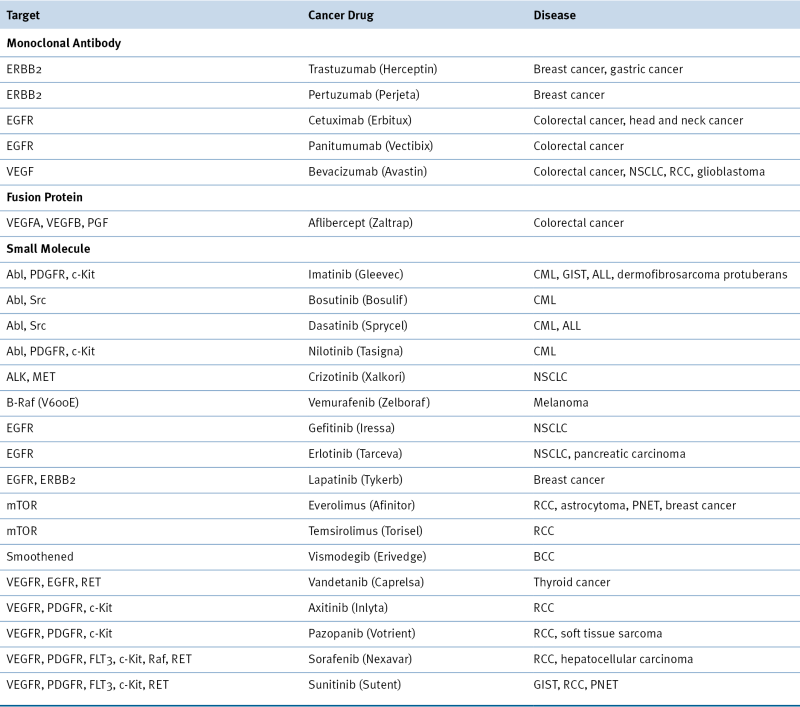
Drugs included in this table have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
ALL, acute lymphoblastic leukemia; BCC, basal cell carcinoma; CML, chronic myeloid leukemia; GIST, gastrointestinal stromal tumor; NSCLC, non-small-cell lung carcinoma; PGF, placental growth factor; PNET, pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor; RCC, renal cell carcinoma.
1. Dynamic control of signaling by modular adaptor proteins . Curr Opin Cell Biol . 2007 ; 19 : 112 – 116 .
2. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 1980 ; 77 : 1311 – 1315 .
3. Localization of the normal allele of T24 human bladder carcinoma oncogene to chromosome 11 . Nature . 1982 ; 300 : 773 – 774 .
4. Simian sarcoma virus onc gene, v-sis, is derived from the gene (or genes) encoding a platelet-derived growth factor . Science . 1983 ; 221 : 275 – 277 .
5. Platelet-derived growth factor is structurally related to the putative transforming protein p28sis of simian sarcoma virus . Nature . 1983 ; 304 : 35 – 39 .
6. Close similarity of epidermal growth factor receptor and v-erb-B oncogene protein sequences . Nature . 1984 ; 307 : 521 – 527 .
7. Epidermal growth factor . J Biol Chem . 1990 ; 265 : 7709 – 7712 .
8. Oncogenic kinase signalling . Nature . 2001 ; 411 : 355 – 365 .
9. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases . Cell . 2010 ; 141 : 1117 – 1134 .
10. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity . Cell . 1990 ; 61 : 203 – 212 .
11. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases . Cell . 2000 ; 103 : 211 – 225 .
12. PDGF receptors as cancer drug targets . Cancer Cell . 2003 ; 3 : 439 – 443 .
13. Expression of messenger RNAs for platelet-derived growth factor and transforming growth factor-alpha and their receptors in human malignant glioma cell lines . Cancer Res . 1988 ; 48 : 3910 – 3918 .
14. Coexpression of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and PDGF-receptor genes by primary human astrocytomas may contribute to their development and maintenance . J Clin Invest . 1990 ; 86 : 131 – 140 .
15. Chemokines in liver inflammation and fibrosis . Front Biosci . 2002 ; 7 : d1899 – d1914 .
16. VEGF and angiopoietin signaling in tumor angiogenesis and metastasis . Trends Mol Med . 2011 ; 17 : 347 – 362 .
17. The c-fms proto-oncogene product is related to the receptor for the mononuclear phagocyte growth factor, CSF-1 . Cell . 1985 ; 41 : 665 – 676 .
18. Targeting MET in cancer: rationale and progress . Nat Rev Cancer . 2012 ; 12 : 89 – 103 .
19. The ERBB network: at last, cancer therapy meets systems biology . Nat Rev Cancer . 2012 ; 12 : 553 – 563 .
20. Neurotrophic factor receptor RET: structure, cell biology, and inherited diseases . Ann Med . 2007 ; 39 : 572 – 580 .
21. Met, metastasis, motility and more . Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol . 2003 ; 4 : 915 – 925 .
22. The TEL/platelet-derived growth factor beta receptor (PDGF beta R) fusion in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia is a transforming protein that self-associates and activates PDGF beta R kinase-dependent signaling pathways . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 1996 ; 93 : 14845 – 14850 .
23. The DNA rearrangement that generates the TRK-T3 oncogene involves a novel gene on chromosome 3 whose product has a potential coiled-coil domain . Mol Cell Biol . 1995 ; 15 : 6118 – 6127 .
24. TRK-T1 is a novel oncogene formed by the fusion of TPR and TRK genes in human papillary thyroid carcinomas . Oncogene . 1992 ; 7 : 237 – 242 .
25. Tyrosine kinase oncogenes in normal hematopoiesis and hematological disease . Oncogene . 2002 ; 21 : 3314 – 3333 .
26. Phospholipase C-gamma is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein-tyrosine kinases in vivo and in vitro . Cell . 1989 ; 57 : 1109 – 1122 .
27. cDNA cloning of a novel 85 kd protein that has SH2 domains and regulates binding of PI3-kinase to the PDGF beta-receptor . Cell . 1991 ; 65 : 75 – 82 .
28. Two signaling molecules share a phosphotyrosine-containing binding site in the platelet-derived growth factor receptor . Mol Cell Biol . 1993 ; 13 : 6889 – 6896 .
29. The 64-kDa protein that associates with the platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta subunit via Tyr-1009 is the SH2-containing phosphotyrosine phosphatase Syp . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 1993 ; 90 : 6939 – 6943 .
30. Tyr-716 in the platelet-derived growth factor beta-receptor kinase insert is involved in GRB2 binding and Ras activation . Mol Cell Biol . 1994 ; 14 : 6715 – 6726 .
31. Binding of SH2 domains of phospholipase C gamma 1, GAP, and Src to activated growth factor receptors . Science . 1990 ; 250 : 979 – 982 .
32. beta-receptor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of GAP and association of GAP with a signaling complex . Cell . 1990 ; 61 : 125 – 133 .
33. PDGF induction of tyrosine phosphorylation of GTPase activating protein . Nature . 1989 ; 342 : 711 – 714 .
34. The product of the protooncogene c-src is modified during the cellular response to platelet-derived growth factor . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 1985 ; 82 : 7845 – 7849 .
35. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling . Nature . 1989 ; 341 : 197 – 205 .
36. Protein kinase C and other diacylglycerol effectors in cancer . Nat Rev Cancer . 2007 ; 7 : 281 – 294 .
37. The evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism . Nat Rev Genet . 2006 ; 7 : 606 – 619 .
38. PI3K signalling: the path to discovery and understanding . Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol . 2012 ; 13 : 195 – 203 .
39. Ras oncogenes: split personalities . Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol . 2008 ; 9 : 517 – 531 .
40. Epidermal growth factor regulates p21ras through the formation of a complex of receptor, Grb2 adapter protein, and Sos nucleotide exchange factor . Cell . 1993 ; 73 : 611 – 620 .
41. Activation of Ras by receptor tyrosine kinases . J Am Soc Nephrol . 1994 ; 5 : 1288 – 1299 .
42. Ras superfamily GEFs and GAPs: validated and tractable targets for cancer therapy? Nat Rev Cancer . 2010 ; 10 : 842 – 857 .
43. ras genes . Annu Rev Biochem . 1987 ; 56 : 779 – 827 .
44. Structural and functional properties of ras proteins . FASEB J . 1989 ; 3 : 2151 – 2163 .
45. Transformation by activated ras or fos prevents myogenesis by inhibiting expression of MyoD1 . Cell . 1989 ; 58 : 659 – 667 .
46. p21 ras and phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase are required for survival of wild-type and NF1 mutant sensory neurons . J Neurosci . 1998 ; 18 : 10420 – 10428 .
47. Ras is not required for the interleukin 3-induced proliferation of a mouse pro-B cell line, BaF3 . J Biol Chem . 1995 ; 270 : 27880 – 27886 .
48. K-ras is an essential gene in the mouse with partial functional overlap with N-ras [published erratum appears in Genes Dev 1997 Dec 1;11(23):3277] . Genes Dev . 1997 ; 11 : 2468 – 2481 .
49. The murine N-ras gene is not essential for growth and development . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 1995 ; 92 : 1709 – 1713 .
50. Hyperactive Ras in developmental disorders and cancer . Nat Rev Cancer . 2007 ; 7 : 295 – 308 .
51. Oncogenic ras provokes premature cell senescence associated with accumulation of p53 and p16INK4a . Cell . 1997 ; 88 : 593 – 602 .
52. NF1 tumor suppressor gene function: narrowing the GAP . Cell . 2001 ; 104 : 593 – 604 .
53. Raf-1 protein kinase is required for growth of induced NIH/3T3 cells . Nature . 1991 ; 349 : 426 – 428 .
54. The RAF proteins take centre stage . Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol . 2004 ; 5 : 875 – 885 .
55. Raf kinases in cancer roles and therapeutic opportunities . Oncogene . 2011 ; 30 : 3477 – 3488 .
56. MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer . Oncogene . 2007 ; 26 : 3279 – 3290 .
57. The RSK family of kinases: emerging roles in cellular signalling . Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol . 2008 ; 9 : 747 – 758 .
58. The dual-specificity MAP kinase phosphatases: critical roles in development and cancer . Am J Physiol Cell Physiol . 2010 ; 299 : C189 – C202 .
59. Cyclin D as a therapeutic target in cancer . Nat Rev Cancer . 2011 ; 11 : 558 – 572 .
60. The landscape of somatic copy-number alteration across human cancers . Nature . 2010 ; 463 : 899 – 905 .
61. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer . Nature . 2002 ; 417 : 949 – 954 .
62. Rearrangements of the RAF kinase pathway in prostate cancer, gastric cancer and melanoma . Nat Med . 2010 ; 16 : 793 – 798 .
63. Signal integration by JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in cancer development . Nat Rev Cancer . 2009 ; 9 : 537 – 549 .
64. Analysis of FBJ-MuSV provirus and c-fos (mouse) gene reveals that viral and cellular fos gene products have different carboxy termini . Cell . 1983 ; 32 : 1241 – 1255 .
65. Avian sarcoma virus 17 carries the jun oncogene . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 1987 ; 84 : 2848 – 2852 .
66. c-fos protein can induce cellular transformation: a novel mechanism of activation of a cellular oncogene . Cell . 1984 ; 36 : 51 – 60 .
67. AP-1 as a regulator of cell life and death . Nat Cell Biol . 2002 ; 4 : E131 – E136 .
68. Transcriptional regulation and transformation by Myc proteins . Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol . 2005 ; 6 : 635 – 645 .
69. MYC on the path to cancer . Cell . 2012 ; 149 : 22 – 35 .
70. The Myc oncoprotein as a therapeutic target for human cancer . Semin Cancer Biol . 2006 ; 16 : 318 – 330 .
71. The BCL-2 family reunion . Mol Cell . 2010 ; 37 : 299 – 310 .
72. Deciphering the rules of programmed cell death to improve therapy of cancer and other diseases . EMBO J . 2011 ; 30 : 3667 – 3683 .
73. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway . Science . 2002 ; 296 : 1655 – 1657 .
74. Targeting PI3K signalling in cancer: opportunities, challenges and limitations . Nat Rev Cancer . 2009 ; 9 : 550 – 562 .
75. Transformation of chicken cells by the gene encoding the catalytic subunit of PI 3-kinase . Science . 1997 ; 276 : 1848 – 1850 .
76. The functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor . Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol . 2012 ; 13 : 283 – 296 .
77. Cytokine signaling through nonreceptor protein tyrosine kinases . Science . 1995 ; 268 : 251 – 255 .
78. Structural biology of shared cytokine receptors . Annu Rev Immunol . 2009 ; 27 : 29 – 60 .
79. The JAK-STAT pathway at twenty . Immunity . 2012 ; 36 : 503 – 514 .
80. Signaling through the JAK/STAT pathway, recent advances and future challenges . Gene . 2002 ; 285 : 1 – 24 .
81. Janus kinase inhibitors for the treatment of myeloproliferative neoplasias and beyond . Nat Rev Drug Discov . 2011 ; 10 : 127 – 140 .
82. Ectopic expression of murine TPO receptor (c-mpl) in mice is pathogenic and induces erythroblastic proliferation . Blood . 1996 ; 88 : 1656 – 1665 .
83. MPLW515L is a novel somatic activating mutation in myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia . PLoS Med . 2006 ; 3 e270 .
84. JAK-STAT pathway regulates wing vein formation in Drosophila . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 1996 ; 93 : 5842 – 5847 .
85. A TEL-JAK2 fusion protein with constitutive kinase activity in human leukemia . Science . 1997 ; 278 : 1309 – 1312 .
86. Somatic mutations activating STAT3 in human inflammatory hepatocellular adenomas . J Exp Med . 2011 ; 208 : 1359 – 1366 .
87. STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: a leading role for STAT3 . Nat Rev Cancer . 2009 ; 9 : 798 – 809 .
88. G-protein-coupled receptors and cancer . Nat Rev Cancer . 2007 ; 7 : 79 – 94 .
89. GTPase inhibiting mutations activate the alpha chain of Gs and stimulate adenylyl cyclase in human pituitary tumours . Nature . 1989 ; 340 : 692 – 696 .
90. Two G protein oncogenes in human endocrine tumors . Science . 1990 ; 249 : 655 – 659 .
91. Gastrin-releasing peptide receptors in the human prostate: relation to neoplastic transformation . Cancer Res . 1999 ; 59 : 1152 – 1159 .
92. Renin-angiotensin system is an important factor in hormone refractory prostate cancer . Prostate . 2006 ; 66 : 822 – 830 .
93. Expression of CCK2 receptors in the murine pancreas: proliferation, transdifferentiation of acinar cells, and neoplasia . Gastroenterology . 2002 ; 122 : 428 – 437 .
94. G protein-coupled receptors: novel targets for drug discovery in cancer . Nat Rev Drug Discov . 2011 ; 10 : 47 – 60 .
95. Peptide receptors as molecular targets for cancer diagnosis and therapy . Endocr Rev . 2003 ; 24 : 389 – 427 .
96. Peptide-receptor radionuclide therapy for endocrine tumors . Nat Rev Endocrinol . 2009 ; 5 : 382 – 393 .
97. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease . Cell . 2006 ; 127 : 469 – 480 .
98. Deciphering the function of canonical Wnt signals in development and disease: conditional loss- and gain-of-function mutations of beta-catenin in mice . Genes Dev . 2008 ; 22 : 2308 – 2341 .
99. Wnt signalling in stem cells and cancer . Nature . 2005 ; 434 : 843 – 850 .
100. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and disease . Cell . 2012 ; 149 : 1192 – 1205 .
101. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases . Dev Cell . 2009 ; 17 : 9 – 26 .
102. Wnt genes . Cell . 1992 ; 69 : 1073 – 1087 .
103. A retrovirus vector expressing the putative mammary oncogene int-1 causes partial transformation of a mammary epithelial cell line . Cell . 1986 ; 46 : 1001 – 1009 .
104. Characterization of Wnt-1 and Wnt-2 induced growth alterations and signaling pathways in NIH3T3 fibroblasts . Oncogene . 1998 ; 16 : 2819 – 2825 .
105. An autocrine mechanism for constitutive Wnt pathway activation in human cancer cells . Cancer Cell . 2004 ; 6 : 497 – 506 .
106. Wnt pathway aberrations including autocrine Wnt activation occur at high frequency in human non-small-cell lung carcinoma . Oncogene . 2009 ; 28 : 2163 – 2172 .
107. High-frequency canonical Wnt activation in multiple sarcoma subtypes drives proliferation through a TCF/beta-catenin target gene, CDC25A . Cancer Cell . 2011 ; 19 : 601 – 612 .
108. Drugging Wnt signalling in cancer . EMBO J . 2012 ; 31 : 2737 – 2746 .
109. Recurrent R-spondin fusions in colon cancer . Nature . 2012 ; 488 : 660 – 664 .
110. The Hedgehog response network: sensors, switches, and routers . Science . 2004 ; 304 : 1755175 – 1755179 .
111. Hedgehog signaling: from the Drosophila cuticle to anti-cancer drugs . Dev Cell . 2005 ; 8 : 143 – 151 .
112. Mechanisms and functions of Hedgehog signalling across the metazoa . Nat Rev Genet . 2011 ; 12 : 393 – 406 .
113. Hedgehog secretion and signal transduction in vertebrates . J Biol Chem . 2012 ; 287 : 17905 – 17913 .
114. Mutations of the human homolog of Drosophila patched in the nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome . Cell . 1996 ; 85 : 841 – 851 .
115. Activating Smoothened mutations in sporadic basal-cell carcinoma . Nature . 1998 ; 391 : 90 – 92 .
116. A paracrine requirement for hedgehog signalling in cancer . Nature . 2008 ; 455 : 406 – 410 .
117. The Hedgehog’s tale: developing strategies for targeting cancer . Nat Rev Cancer . 2011 ; 11 : 493 – 501 .
118. Cancer. Addiction to oncogenes—the Achilles heal of cancer . Science . 2002 ; 297 : 63 – 64 .
119. Clinical efficacy of a RAF inhibitor needs broad target blockade in BRAF-mutant melanoma . Nature . 2010 ; 467 : 596 – 599 .
120. Inhibition of mutated, activated BRAF in metastatic melanoma . N Engl J Med . 2010 ; 363 : 809 – 819 .
121. Mutant BRAF melanomas—dependence and resistance . Cancer Cell . 2011 ; 19 : 11 – 15 .
122. Unresponsiveness of colon cancer to BRAF(V600E) inhibition through feedback activation of EGFR . Nature . 2012 ; 483 : 100 – 103 .