Malignant Hyperthermia
M. Joanne Douglas MD, FRCPC
Chapter Outline
MANAGEMENT OF THE MALIGNANT HYPERTHERMIA–SUSCEPTIBLE PARTURIENT
Obstetric Drugs in Malignant Hyperthermia–Susceptible Parturients
Malignant hyperthermia (MH) is an inherited disorder of skeletal muscle. On exposure to triggering agents (e.g., succinylcholine, volatile halogenated anesthetic agents), affected individuals demonstrate a hypermetabolic syndrome characterized by hypercapnia, acidosis, muscle rigidity, arrhythmias, and hyperthermia. MH was first described in 1960 by Denborough and Lovell,1 but may have been responsible for some of the earlier deaths attributed to ether and chloroform anesthesia.2
Epidemiology
Ørding,3 reviewing the incidence of MH in Denmark, noted that the incidence of the fulminant syndrome (e.g., muscle rigidity, acidosis, hyperkalemia, arrhythmias, hyperthermia, increased creatine kinase [CK] levels, myoglobinuria) was 1 in 220,000 patients who received general anesthesia and 1 in 62,000 patients in whom succinylcholine was combined with a volatile halogenated agent. MH (either mild or fulminant) was suspected in 1 in 16,000 patients who received anesthesia of any type. The male-to-female ratio was 1.4 : 1.3 There is some geographic variation in the incidence of MH.4
There are few reports of development of MH during pregnancy and parturition.5–12 The infrequent occurrence during pregnancy probably reflects both the low frequency of this disorder in the general population and the widespread use of local and neuraxial anesthetic techniques in obstetric patients.
Pathophysiology
MH is the result of a disorder in the regulation of intracellular calcium in skeletal muscle. The precise mechanism by which volatile anesthetics and depolarizing muscle relaxants cause an MH crisis is still unknown.13 In muscle the sarcoplasmic reticulum is responsible for controlling calcium release and reuptake during muscle contraction.14 During skeletal muscle excitation-contraction coupling, calcium is released from the terminal sarcoplasmic reticulum via the ryanodine receptor (RYR1). Dihydropyridine receptors in the T-tubule membrane also participate in the excitation-contraction coupling. In humans, mutations in both the dihydropyridine receptor and the ryanodine receptor can result in clinical MH. Dantrolene inhibits excitation-contraction coupling, and succinylcholine, caffeine, and volatile halogenated agents increase it.
Genetics
MH is a heterogeneous disorder, meaning that more than one gene defect is responsible for expression of the clinical syndrome.15 It is inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion with variable penetrance, although this pattern has been questioned in some families.16 Porcine MH is transmitted as a recessive gene. The defective gene in MH-susceptible pigs has been localized to a single point mutation in the ryanodine receptor gene (RYR1) responsible for the calcium release channel.17
Investigators have found the corresponding point mutation on the human ryanodine receptor gene (RYR1) in some families with MH (chromosome 19q12.1-13.2; locus MHS-1), and other mutations in RYR1 have been linked to MH susceptibility.18 Other point mutations in RYR1 are found in patients with central core disease, a myopathy associated with MH.19 As of 2011, more than 200 RYR1 mutations associated with MH had been identified.15 Mutations responsible for MH in some families are located on chromosomes 5p, 17, 7q, 3q, and 1q.20 Other myopathies may be characterized by a hyperthermic state with muscle damage and metabolic derangements similar to those seen in MH, but their chromosomal abnormality has not been mapped to the same area.15
Triggers
Known triggers of MH include the depolarizing muscle relaxants (e.g., succinylcholine) and all the volatile halogenated anesthetic agents (i.e., sevoflurane, desflurane, isoflurane, halothane, enflurane) (Box 47-1). The dose and duration of exposure to the triggering agent may influence the onset and severity of a reaction. Previous uneventful administration of general anesthesia with triggering anesthetic agents does not rule out the diagnosis of MH.21
In contrast to the porcine model, reports of stress-induced MH in humans are rare.22–28 In one report two cases of fatal, stress-induced MH occurred in unrelated families26; both children had a known RYR1 mutation and one had a second mutation, possibly suggesting an additive effect.29 The sympathetic nervous system is active during an episode of acute MH, but there is insufficient evidence to implicate increased sympathetic activity as a cause in humans. Although muscle biopsy testing may help distinguish MH from exercise-induced myolysis, exertional heat stroke, and other myopathies, there is some evidence of a link between some cases of heat stroke and exercise-induced rhabdomyolysis and MH susceptibility.30
Investigators have explored other possible triggers of MH both in the porcine model and in humans. No evidence suggests that exogenous calcium, digoxin, hypercarbia, potassium,31 or norepinephrine32 triggers MH. Exercise33 and environmental temperature34–36 may intensify an existing reaction or modify a developing reaction. Sodium thiopental and pancuronium delay the onset in pigs and may modify the reaction in humans.37 Duke et al.38 postulated that hypomagnesemia may increase the probability and severity of an MH event in MH-susceptible humans.
There are case reports of the occurrence of MH during regional anesthesia and during general anesthesia with nontriggering agents.39–43 The cases that occurred during regional anesthesia appeared mild and responded readily to treatment. In some cases, however, the diagnosis was not confirmed with muscle biopsy or appropriate laboratory investigation at the time of the event.
Clinical Presentation
Individuals who are MH-susceptible may demonstrate the fulminant syndrome when anesthetized with a triggering agent. During an acute episode, the diagnosis is based on the finding of an elevated end-tidal CO2 concentration, muscle rigidity (generalized and/or masseter), respiratory and metabolic acidosis, rhabdomyolysis, hyperkalemia, elevated CK concentration, and myoglobinuria (Box 47-2). Hypoxemia, unstable blood pressure, and evidence of sympathetic hyperactivity (e.g., tachycardia, hypertension, arrhythmias) are other signs. Hyperthermia may occur early, but often it is a late sign. Perioperative rhabdomyolysis, without any of the previously mentioned clinical signs, also may indicate MH susceptibility.44,45
With the advent of routine end-tidal CO2 monitoring, MH may be detected early, often before the development of rhabdomyolysis and hyperthermia.46 This situation may lead to uncertainty about the clinical diagnosis of MH, given that many of the confirmatory signs and laboratory abnormalities may be absent during the early phase of MH. Thus, early treatment of possible MH could present a dilemma as to whether the patient should undergo diagnostic muscle biopsy or should be assumed to be MH susceptible.
Masseter Muscle Rigidity
Masseter muscle rigidity is one of the early signs of MH.46 The masseter muscles are sensitive to the action of succinylcholine and respond with increased tension in normal individuals.47,48 Often this tension is imperceptible, but in some patients it is impossible to open the mouth for laryngoscopy and intubation. The duration of rigidity parallels the duration of action of succinylcholine. Typically there is no difficulty with mask ventilation. Masseter muscle rigidity rarely occurs after the use of nondepolarizing muscle relaxants such as rocuronium and vecuronium.49 Patients with myopathies and other neuromuscular disorders also may have masseter muscle rigidity after the administration of succinylcholine.50
If masseter muscle rigidity is accompanied by generalized rigidity, anesthesia should be discontinued, dantrolene should be administered, and the patient should be monitored closely.51 However, there is controversy regarding the management of isolated masseter muscle rigidity.52 Options include (1) discontinuation of the anesthetic agents and administration of dantrolene; (2) continuation of anesthesia with nontriggering, “safe” agents and close attention to the end-tidal CO2 concentration; and (3) continuation of anesthesia with triggering agents and careful monitoring. In my judgment, the anesthesia provider should either discontinue anesthesia altogether or continue anesthesia with nontriggering agents. If the anesthesia is continued, the minute ventilation, end-tidal CO2 concentration, electrocardiogram (ECG), temperature, and arterial blood gas measurements should be monitored. The anesthesia provider also should look for evidence of rhabdomyolysis by monitoring CK levels and looking for myoglobinuria, and should recommend that the patient undergo muscle biopsy and caffeine-halothane contracture test (see later discussion).53
Diagnosis
Investigators have correlated clinical presentation (i.e., evidence of metabolic and muscle derangements) with abnormal contracture on the caffeine-halothane contracture test.54–56 The greater the number of clinical signs or abnormal laboratory findings, the greater the risk for MH (Table 47-1).54 An early assessment of the risk for MH allows the anesthesia provider to initiate appropriate treatment. The mortality rate for MH is as high as 80% without dantrolene therapy.56 Early administration of dantrolene lowers the mortality rate to 4%.57
TABLE 47-1
Risk for Malignant Hyperthermia (MH) with Associated Signs and Symptoms
| Type | Symptoms/Signs | Risk |
| Fulminant/classic | Metabolic acidosis | 0.96 |
| Muscle rigidity | ||
| Hyperthermia (> 38.5° C) | ||
| Arrhythmias | ||
| Hyperkalemia | ||
| Myoglobinuria | ||
| Increased creatine kinase level | ||
| Moderate | Inconclusive signs of MH involving metabolic and muscle abnormalities, with MH the probable diagnosis | 0.88 |
| Mild | Signs of metabolic derangement (pH > 7.3, body core temperature < 38.5° C) | 0.14 |
| Masseter spasm with rhabdomyolysis | Creatine kinase level > 1500 U/L, myoglobinuria | 0.76 |
| Masseter spasm with signs of metabolic disturbance | Arrhythmias, rising core temperature | 0.57 |
| Masseter spasm only | 0.28 | |
| Unexplained perioperative death or cardiac arrest | 0.66 | |
| Other | Postoperative pyrexia or rhabdomyolysis | 0.07 |
Data from Ellis FR, Halsall PJ, Christian AS. Clinical presentation of suspected malignant hyperthermia during anaesthesia in 402 probands. Anaesthesia 1990; 45:838-41.
An international group of experts has developed a clinical grading scale to predict MH susceptibility.58 This scale consists of six processes (rigidity, muscle breakdown, respiratory acidosis, temperature increase, cardiac involvement, family history) and their clinical indicators. Points are assigned for each indicator present in a patient, and the total represents a raw score. A rank is subsequently assigned to this score, which indicates the likelihood of development of MH in the patient.
Testing
Susceptibility to MH is determined by a positive caffeine-halothane contracture test result. During this test, fresh muscle is exposed to halothane and caffeine, and the extent of contraction is measured. The caffeine-halothane contracture test has been standardized in MH testing centers throughout North America (the North American protocol)59 and Europe (the European protocol is called the in vitro contracture test).60 This test is the “gold standard” for the diagnosis of MH. The sensitivity and specificity of the North American protocol are 97% and 78%, respectively.61 Some false-positive results may occur.62 Patients with a negative caffeine-halothane contracture test result subsequently have received anesthesia with triggering agents without incident.63–66
Testing for the known genetic mutations associated with MH is now available. However, because all the genetic mutations responsible for MH have yet to be identified, genetic testing is still not sensitive enough to use for routine screening.67 In the future, MH may be detected in most MH-susceptible patients without the need for an invasive muscle biopsy.67 In the absence of muscle biopsy results, a parturient with a positive family history should be treated as if she were MH susceptible.
Pregnancy and Malignant Hyperthermia
In 1972, Crawford68 wondered “whether or not there was a record of a pregnant or newly born patient or animal having developed hyperpyrexia and … whether hyperpyrexia has been encountered in a patient undergoing an operation under regional block anesthesia.” Subsequently there have been few reports of MH during parturition and fewer reports of maternal mortality attributable to MH. Wadhwa5 reported the death of a woman with a known family history of MH in whom muscle rigidity developed during twilight sleep for parturition. Douglas et al.6 reported one fatal case of MH in a parturient undergoing general anesthesia for cesarean delivery.
There are three published reports7–9 of nonfatal MH during cesarean delivery and one report of MH after cesarean hysterectomy performed because of postpartum hemorrhage.12 The triggering agents were succinylcholine and halothane,7 succinylcholine and isoflurane,12 cyclopropane,8 and succinylcholine alone (without a volatile halogenated agent).9 There are several reports of the successful administration of epidural and spinal anesthesia during labor and cesarean delivery in MH-susceptible parturients.5,12,69–76
Although it is unclear whether pregnancy alters susceptibility to MH, the rarity of MH events during pregnancy suggests that pregnancy protects against the occurrence of MH. However, it also may reflect the widespread use of neuraxial anesthesia for labor, vaginal delivery, and cesarean delivery.
Maternal Physiology
Basal metabolic rate, oxygen consumption, and minute ventilation increase during pregnancy (see Chapter 2). Serum bicarbonate, buffer base, and base excess decrease to maintain normal pH. Thus, the pregnant patient typically has a compensated respiratory alkalosis. The reduced buffering capacity could adversely affect the pregnant woman during an episode of MH.
Oxygen consumption and minute ventilation increase further during labor. Maternal lactate and pyruvate concentrations increase steadily during labor, indicating an increase in both aerobic and anaerobic metabolism. Hyperventilation during contractions may result in periods of hypoventilation between contractions, which may adversely affect the PaO2 of both the mother and the fetus. These metabolic and physiologic responses to pain are similar to the metabolic and physiologic changes that are observed during acute MH. Effective epidural analgesia decreases oxygen consumption and minute ventilation. If tachycardia and hyperventilation occur despite effective analgesia, they are more likely to signal an episode of MH.
Aortocaval compression from the pregnant uterus results in decreased cardiac output, hypotension, and reduced uteroplacental perfusion. Thus, aortocaval compression may accelerate the occurrence of acidosis during an episode of MH. Aortocaval compression hinders resuscitative efforts during cardiac arrest, and evacuation of the uterus (i.e., delivery of the fetus) facilitates maternal resuscitation.77 The obstetrician may need to deliver the fetus to facilitate maternal resuscitation during a fulminant case of MH.
CK concentrations are not diagnostic of MH. During pregnancy, there is a slight decrease in CK levels during the first trimester. CK levels remain stable until term, when they increase by approximately 50%. At delivery, there is an abrupt rise in the CK concentration, followed by a return to normal by 6 weeks postpartum (Figure 47-1).78 The increased CK concentration results from increases in both the CK-M fraction (skeletal muscle) and the CK-B fraction (myometrium, placenta, and fetal blood). Postpartum CK levels are higher in nulliparous women regardless of differences in duration of labor.79 Mean plasma CK activity is approximately 50% higher in African-Americans than in Caucasians or Asians.78
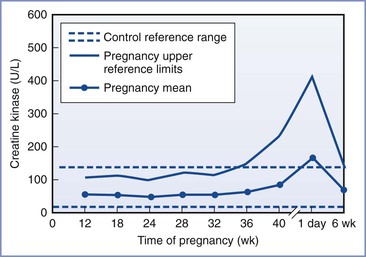
FIGURE 47-1 Changes in creatine kinase activity during and after pregnancy. (Modified from Lockitch G, editor. Handbook of Diagnostic Biochemistry and Hematology in Normal Pregnancy. Boca Raton, FL, CRC Press, 1993:59.)
Acute cocaine toxicity may mimic MH. Although cocaine does not induce contractures in MH-susceptible muscle,80 elevated CK concentrations and myoglobinemia can occur secondary to rhabdomyolysis and renal failure from cocaine intoxication.81 Umbilical cord blood CK and myoglobin levels are elevated when cocaine metabolites are present in maternal urine.82
Effects on the Fetus and Newborn
MH often is inherited as an autosomal dominant gene. In these cases there is a 50% chance that the infant of an MH-susceptible parent will also be MH susceptible. All anesthetic agents cross the placenta. Small quantities of succinylcholine also cross the placenta. This knowledge should prompt the anesthesia provider to question the choice of anesthetic agents for an MH-negative mother whose fetus has an MH-susceptible father. In this situation, the anesthesia provider should avoid the use of triggering agents until after delivery.83
There is only one published report of suspected MH in a newborn.84 The condition is rare in infancy, and some reports of infant MH may represent undiagnosed myopathy.50,85,86
Management of the Malignant Hyperthermia–Susceptible Parturient
Ideally, an anesthesiologist will evaluate every MH-susceptible pregnant patient before she is hospitalized for labor and delivery. Clearly, the obstetrician should consult an anesthesia provider immediately after the admission of each MH-susceptible patient. All hospitals and birthing facilities should be prepared to provide care for MH-susceptible patients. Adequate supplies of dantrolene (at least 36 vials), sterile water, and sodium bicarbonate should be immediately available.
Analgesia for Labor
Soon after admission, a large-gauge intravenous catheter should be placed in each MH-susceptible patient. Maternal temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure should be monitored throughout labor. During early labor, it may be acceptable to monitor temperature and heart rate intermittently to facilitate maternal ambulation, if desired. Once active labor is established, frequent monitoring of the maternal heart rate and temperature should be initiated. Continuous ECG and axillary temperature monitoring are ideal once the parturient is confined to bed. (Measurement of axillary temperature allows placement of a temperature probe in close proximity to large muscle groups.) Of course, aortocaval compression should be avoided throughout labor and delivery.
Most agents used for intrapartum analgesia are considered safe in the MH-susceptible parturient (Table 47-2). Both the obstetrician and the anesthesia provider should encourage the early administration of neuraxial analgesia. Relief of pain reduces maternal stress (as reflected by decreased catecholamine,87 cortisol,88 and adrenocorticotropic hormone [ACTH] concentrations), and decreases maternal metabolism and oxygen consumption.89 Although experts continue to debate the role of stress in human MH,90,91 it is best to diminish stress when possible. Further, the anesthesia provider may extend epidural analgesia for vaginal or cesarean delivery if necessary, thus avoiding administration of general anesthesia.
TABLE 47-2
Common Anesthetic Drugs and Their Safety in Malignant Hyperthermia–Susceptible (MHS) Women
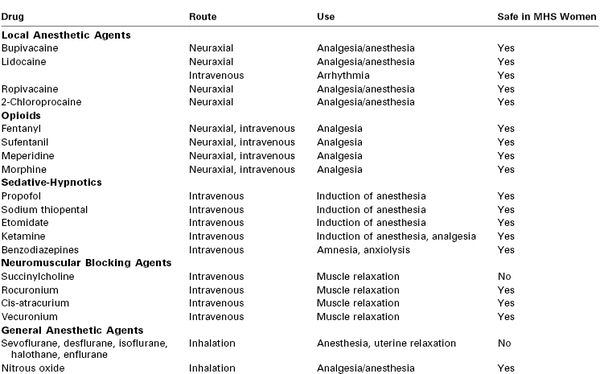
All local anesthetic agents appear safe for MH-susceptible patients. Epinephrine can be safely added to the local anesthetic agent to improve the quality and duration of analgesia, if clinically appropriate.
Anesthesia for Cesarean Delivery
General anesthesia should be avoided for operative delivery if possible. Spinal or epidural anesthesia using either amide or ester local anesthetic agents can be given safely. Epidural anesthesia may be preferred because slow induction of anesthesia may decrease the risk for hypotension. Phenylephrine is probably the preferred agent for the treatment of hypotension. Ephedrine may exacerbate the catecholamine response during an acute episode of MH. In doses greater than those used clinically, ephedrine exacerbates halothane-induced muscle contractures in vitro.92
Rarely, the mother may refuse neuraxial anesthesia. In other cases, neuraxial anesthesia may be contraindicated (e.g., maternal hemorrhage, coagulopathy, prolonged fetal bradycardia). When the anesthesia provider encounters an MH-susceptible parturient, the anesthesia machine and delivery circuit should be flushed of volatile agents. Preparation consists of replacing the carbon dioxide absorbent and the delivery tubing, disabling the vaporizers, and purging the machine of residual anesthetic agent with a 10 L/min flow of oxygen through the circuit (including the ventilator).93 The time required to purge the anesthesia machine is dependent on the specific machine.93 Activated charcoal filters appear to be an effective alternative to the prolonged flushing required to reduce the volatile anesthetic concentration in new-model anesthesia machines.94
In cases of general anesthesia, the anesthesia provider should administer a nonparticulate antacid and perform adequate denitrogenation. Nontriggering agents should be administered for induction and maintenance of general anesthesia (Box 47-3, see also Table 47-2). Unless a difficult intubation is expected, rapid-sequence induction should be performed with a sedative-hypnotic drug and a nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent. All commonly used induction agents (e.g., propofol, thiopental, ketamine, etomidate) are safe in MH-susceptible patients. Succinylcholine and the volatile halogenated agents (sevoflurane, desflurane, isoflurane, halothane, enflurane) are contraindicated. For intubation, rapid onset (approximately 60 to 90 seconds) of muscle relaxation can be achieved with rocuronium (0.6 to 0.9 mg/kg, which is two to three times the effective dose in 95% of patients [ED95])95 or vecuronium96 (0.25 mg/kg). Nitrous oxide (delivered via a prepared anesthesia machine), opioids, and propofol are safe agents for the maintenance of anesthesia. Midazolam administered after delivery provides amnesia. It is safe to reverse neuromuscular blockade with glycopyrrolate and neostigmine or edrophonium. Atropine may cause an increase in temperature, which could cause a diagnostic dilemma.
At delivery, determination of maternal and umbilical cord blood gas and pH measurements may provide information about an impending reaction in either the mother or the neonate. As well, if the MH-susceptible mother has a known genetic mutation, umbilical cord blood may be used to assess MH susceptibility in the neonate.97 If uterine relaxation (tocolysis) is required to assist with delivery of the baby or to facilitate the removal of a retained placenta, I prefer to give 100-µg bolus doses of nitroglycerin intravenously98; the action of this agent is brief and easily reversed with oxytocin. Clearly, a volatile halogenated agent should never be given to effect uterine relaxation in an MH-susceptible patient.
Concern has been raised about administering triggering agents to a non–MH-susceptible mother who is carrying a fetus whose father is MH susceptible.99 In this situation the Malignant Hyperthermia Association of the United States recommends that the mother be treated as if she were MH susceptible to avoid a possible MH reaction in the neonate.83
Obstetric Drugs in Malignant Hyperthermia–Susceptible Parturients
Information on use of obstetric drugs in MH-susceptible patients is scant (Table 47-3). The beta-sympathomimetic tocolytic agents (e.g., terbutaline) produce anxiety and tachycardia in normal parturients. Such side effects may be confused with MH, although these agents most likely are safe in the MH-susceptible parturient.
TABLE 47-3
Drugs Commonly Used for Labor and Delivery and Their Safety in Malignant Hyperthermia–Susceptible (MHS) Women
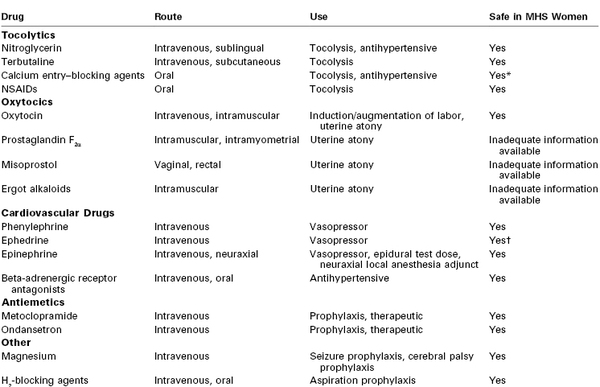
* Do not use during an MH crisis (see text).
† May exacerbate the catecholamine response during an MH crisis (see text).
NSAIDs, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Magnesium sulfate attenuates but does not prevent MH in MH-susceptible swine.100 There is one report of a fatal adverse interaction between dantrolene and the calcium entry–blocking agent diltiazem,101 and hyperkalemia has been described after the co-administration of dantrolene and verapamil.102 Administration of calcium entry–blocking agents should be avoided during an episode of MH. These agents do not prevent the development of MH.103
Oxytocin is safe. Some of the commercial preparations of oxytocin contain a preservative (chlorbutol) that has been shown to reverse the development of MH in susceptible pigs in vitro.104 The ergot alkaloids cause vasoconstriction, which may lead to decreased muscle perfusion and a greater tendency toward lactic acidosis. The prostaglandins may be associated with changes in blood pressure and maternal oxygen desaturation.105 Prostaglandin E2 and misoprostol may cause pyrexia, which may lead to confusion in the diagnosis of an MH episode.106 The routine postpartum administration of ergot alkaloids, prostaglandins, or misoprostol probably should not be performed in MH-susceptible patients. However, persistent uterine atony and postpartum hemorrhage may warrant the administration of these agents.
Assessment of Hyperthermia and Tachycardia
The hallmark signs of MH may be present during normal labor (Boxes 47-4 and 47-5). Other causes of fever and tachycardia in the MH-susceptible parturient should be excluded. Tachycardia and tachypnea are normal responses to pain, anxiety, and fever. Fever may be a sign of dehydration and infection. Pain and infection (e.g., chorioamnionitis, urinary tract infection) are much more common during parturition than MH. Some healthy parturients may have a gradual increase in temperature during epidural analgesia.107 The fever may be accompanied by corresponding increases in maternal and fetal heart rates.
The butyrophenones, phenothiazines, thioxanthenes, and other miscellaneous antipsychotic agents may produce tachycardia, fever, and rigidity (i.e., neuroleptic malignant syndrome).108 There is one published report of neuroleptic malignant syndrome in a pregnant woman.109 Drugs capable of increasing serotonin in the central nervous system (i.e., serotonin reuptake inhibitors) also can produce a hypermetabolic reaction. Cocaine intoxication causes severe vasoconstriction, fever, and rhabdomyolysis.110
Treatment
Box 47-6 summarizes the treatment of MH; a more detailed protocol for the management of an MH episode is available online from the Malignant Hyperthermia Association of the United States (http://www.mhaus.org). The anesthesia provider should call for help, obtain dantrolene, and notify the surgeon. All triggering agents must be stopped immediately, and the patient should be hyperventilated with 100% oxygen at 10 L or more per minute. The level of volatile agent decreases rapidly with flushing of the machine with 100% oxygen. Therefore, substitution with a vapor-free machine is not an immediate priority. Insertion of an activated charcoal filter into the breathing circuit, if available, may also be helpful, but administration of dantrolene is the first priority.111
The anesthesia provider should give dantrolene intravenously in a dose of 2.5 mg/kg, until the signs and symptoms (e.g., tachycardia, hypercarbia, rigidity, fever) have subsided.112 Although the maximum dantrolene dose is often listed as 10 mg/kg, there are case reports in which higher doses of dantrolene were required to control an MH reaction. Oxygen saturation, end-tidal CO2, ECG, blood pressure, arterial and venous blood gas measurements, core temperature, potassium levels, lactate concentration, CK levels, coagulation profile, urine output, and urine myoglobin should be monitored.
The anesthesia provider must initiate treatment of acidosis, hyperkalemia, arrhythmias, and hyperthermia. Metabolic acidosis is treated by giving sodium bicarbonate in 1- to 2-mEq/kg increments as guided by blood gas and pH measurements. Hyperkalemia is treated by administration of bicarbonate, glucose, and insulin. Calcium administration may also be indicated.
Early administration of dantrolene often prevents or successfully treats arrhythmias. If arrhythmias persist, one should follow standard advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) protocols. Amiodarone, lidocaine, procainamide, and adenosine may be used safely. Calcium entry–blocking agents should be avoided because simultaneous administration of dantrolene and a calcium entry–blocking agent may precipitate cardiovascular collapse.102
The operating room care team should actively cool the patient. Options for doing so include (1) intravenous administration of cold saline; (2) surface cooling with ice and/or a hypothermia blanket; and (3) lavage of stomach, bladder, rectal, peritoneal, and thoracic cavities with iced saline.
Myoglobin is excreted in the urine. Thus, diuresis should be maintained by giving adequate volumes of crystalloid and furosemide 1 mg/kg and/or mannitol 0.25 g/kg. Mannitol is present in dantrolene, and separate administration of a diuretic agent may not be necessary. Sedation should be administered as necessary.
After an acute episode of MH, postoperative administration of dantrolene (1 mg/kg or more intravenously every 4 to 6 hours for 24 to 48 hours) is recommended. In addition, the patient should be monitored closely in an intensive care unit for at least 24 to 48 hours. In a retrospective analysis of data from the North American Malignant Hyperthermia Registry, 20% of patients had recrudescence of MH after the initial MH episode.113 Recrudescence was associated with increased muscle mass and a longer interval between anesthesia induction and intraoperative reaction. Counseling and diagnostic muscle biopsy should be performed after recovery from the acute episode. The Malignant Hyperthermia Association of the United States provides a registry and an informative newsletter for MH-susceptible patients. An MH hotline (800-MH-HYPER [800-644-9737] or, outside the United States, +1-209-417-3722) is available 24 hours a day to assist physicians with questions on treatment, diagnosis, and follow-up.
Dantrolene in Pregnancy
Dantrolene is the drug of choice for the treatment of an MH crisis. Dantrolene works by blocking the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of skeletal muscle cells.114 It crosses the placenta and can be detected in the fetus after maternal administration.115 Clinical doses do not adversely affect maternal or fetal cardiovascular and acid-base measurements in gravid ewes. Morison74 reported a fetal-to-maternal serum dantrolene concentration ratio of approximately 0.4 after prophylactic oral administration of dantrolene. Theoretically, dantrolene may cause neonatal hypotonia if it is administered before delivery.
There is one published report of postpartum uterine atony after the administration of dantrolene.10 Laboratory testing of the effects of dantrolene sodium on pregnant uterine muscle suggests that the relaxant effect is secondary to the mannitol.116
There is no benefit to dantrolene prophylaxis in the MH-susceptible patient when all triggering agents are avoided.114 However, the anesthesia provider should give dantrolene promptly when an MH crisis is suspected.
Fricker et al.117 reported serial measurements of dantrolene concentrations in breast milk after administration of dantrolene in a patient with suspected MH during cesarean delivery (Figure 47-2). They estimated that the half-life of dantrolene in breast milk is approximately 9 hours. They concluded that “breast-feeding can be expected to be safe for the newborn 2 days after discontinuation of intravenous dantrolene administration in the mother.”117
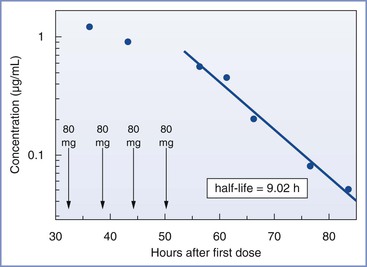
FIGURE 47-2 Estimation of the half-life of dantrolene in breast milk by log-linear fitting of the terminal elimination phase (dantrolene measured in breast milk by high-pressure liquid chromatography, reverse-phase high-pressure liquid chromatographic column, by in-line ultraviolet absorption spectrometer; detection limit, 0.02 µg/mL). (From Fricker RM, Hoerauf KH, Drewe J, Kress HG. Secretion of dantrolene into breast milk after acute therapy of a suspected malignant hyperthermia crisis during cesarean section. Anesthesiology 1998; 89:1023-5.)
References
1. Denborough M, Lovell R. Anaesthetic deaths in a family [letter]. Lancet. 1960;2:45.
2. Harrison GG, Isaacs H. Malignant hyperthermia: an historical vignette. Anaesthesia. 1992;47:54–56.
3. Ørding H. Incidence of malignant hyperthermia in Denmark. Anesth Analg. 1985;64:700–704.
4. Rosero EB, Adesanya AO, Timaran CH, Joshi GP. Trends and outcomes of malignant hyperthermia in the United States, 2000 to 2005. Anesthesiology. 2009;110:89–94.
5. Wadhwa RK. Obstetric anesthesia for a patient with malignant hyperthermia susceptibility. Anesthesiology. 1977;46:63–64.
6. Douglas M, O’Connor G, Allanson J. Malignant hyperthermia in British Columbia. Br Columbia Med J. 1983;25:299–300.
7. Liebenschutz F, Mai C, Pickerodt VWA. Increased carbon-dioxide production in two patients with malignant hyperpyrexia and its control by dantrolene. Br J Anaesth. 1979;51:899–903.
8. Lips FJ, Newland M, Dutton G. Malignant hyperthermia triggered by cyclopropane during cesarean section. Anesthesiology. 1982;56:144–146.
9. Cupryn JP, Kennedy A, Byrick RJ. Malignant hyperthermia in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1984;150:327–328.
10. Weingarten AE, Korsh JI, Neuman GG, Stern SB. Postpartum uterine atony after intravenous dantrolene. Anesth Analg. 1987;66:269–270.
11. Tettambel M. Malignant hyperthermia in an obstetric patient. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 1980;79:773–775.
12. Wu YC, Ho CM, Tsou MY, et al. Successful management of malignant hyperthermia susceptibility during cesarean hysterectomy for postpartum hemorrhage. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1999;78:738–739.
13. Wappler F. Malignant hyperthermia. Eur J Anaesth. 2001;18:632–652.
14. Ross AE, Dirksen RT. Sarcoplasmic reticulum: the dynamic calcium governor of muscle. Muscle Nerve. 2006;33:715–731.
15. Dirksen SJH, Larach MG, Rosenberg H, et al. Future directions in malignant hyperthermia research and patient care. Anesth Analg. 2011;113:1108–1119.
16. Fagerlund TH, Islander G, Twetman ER, Berg K. Malignant hyperthermia susceptibility, an autosomal dominant disorder? Clin Genet. 1997;51:365–369.
17. Fujii J, Otsu K, Zorzato F, et al. Identification of a mutation in porcine ryanodine receptor associated with malignant hyperthermia. Science. 1991;253:448–451.
18. Sambuughin N, Holley H, Muldoon S, et al. Screening of the entire ryanodine receptor type 1 coding region for sequence variants associated with malignant hyperthermia susceptibility in the North American population. Anesthesiology. 2005;102:515–521.
19. Wu SW, Ibarra CA, Malicdan MCV, et al. Central core disease is due to RYRI mutations in more than 90% of patients. Brain. 2006;129:1470–1480.
20. Hopkins PM. Malignant hyperthermia: advances in clinical management and diagnosis. Br J Anaesth. 2000;85:118–128.
21. Strazis KP, Fox AW. Malignant hyperthermia: a review of published cases. Anesth Analg. 1993;77:297–304.
22. Britt BA. Combined anesthetic-induced and stress-induced malignant hyperthermia in two offspring of malignant hyperthermic-susceptible parents. Anesth Analg. 1988;67:393–399.
23. Feuerman T, Gade GF, Reynolds R. Stress-induced malignant hyperthermia in a head-injured patient. J Neurosurg. 1988;68:297–299.
24. Hackl W, Winkler M, Mauritz W, et al. Muscle biopsy for diagnosis of malignant hyperthermia susceptibility in two patients with severe exercise-induced myolysis. Br J Anaesth. 1991;66:138–140.
25. Gronert GA, Thompson RL, Onofrio BM. Human malignant hyperthermia: awake episodes and correction by dantrolene. Anesth Analg. 1980;59:377–378.
26. Groom L, Muldoon SM, Tang ZZ, et al. Identical de novo mutation in the type 1 ryanodine receptor gene associated with fatal, stress-induced malignant hyperthermia in two unrelated families. Anesthesiology. 2011;115:938–945.
27. Capacchione JF, Sambuughin N, Bina S, et al. Exertional rhabdomyolysis and malignant hyperthermia in a patient with ryanodine receptor type 1 gene, L-type calcium channel alpha-1 subunit gene, and calsequestrin-1 gene polymorphisms. Anesthesiology. 2010;112:239–244.
28. Tobin JR, Jason DR, Challa VR, et al. Malignant hyperthermia and apparent heat stroke. JAMA. 2001;286:168–169.
29. Lehmann-Horn F, Klingler W, Jurkat-Rott K. Nonanesthetic malignant hyperthermia. Anesthesiology. 2011;115:915–917.
30. Capacchione JF, Muldoon SM. The relationship between exertional heat illness, exertional rhabdomyolysis, and malignant hyperthermia. Anesth Analg. 2009;109:1065–1069.
31. Gronert GA, Ahern CP, Milde JH, White RD. Effect of CO2, calcium, digoxin, and potassium on cardiac and skeletal-muscle metabolism in malignant hyperthermia–susceptible swine. Anesthesiology. 1986;64:24–28.
32. Maccani RM, Wedel DJ, Hofer RE. Norepinephrine does not potentiate porcine malignant hyperthermia. Anesth Analg. 1996;82:790–795.
33. Allsop P, Jorfeldt L, Rutberg H, et al. Delayed recovery of muscle pH after short duration, high-intensity exercise in malignant hyperthermia susceptible subjects. Br J Anaesth. 1991;66:541–545.
34. Nelson TE. Porcine malignant hyperthermia: critical temperatures for in vivo and in vitro responses. Anesthesiology. 1990;73:449–454.
35. Denborough M, Hopkinson KC, O’Brien RO, Foster PS. Overheating alone can trigger malignant hyperthermia in piglets. Anaesth Intens Care. 1996;24:348–354.
36. Iaizzo PA, Kehler CH, Carr RJ, et al. Prior hypothermia attenuates malignant hyperthermia in susceptible swine. Anesth Analg. 1996;82:803–809.
37. Gronert GA, Milde JH. Variations in onset of porcine malignant hyperthermia. Anesth Analg. 1981;60:499–503.
38. Duke AM, Hopkins PM, Halsall PJ, Steele DS. Mg2+ dependence of Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum induced by sevoflurane or halothane in skeletal muscle from humans susceptible to malignant hyperthermia. Br J Anaesth. 2006;97:320–328.
39. Katz JD, Krich LB. Acute febrile reaction complicating spinal anesthesia in a survivor of malignant hyperthermia. Can Anaesth Soc J. 1976;23:285–289.
40. Kemp DR, Choong LS. Malignant hyperthermia and the conscious patient. Aust NZ J Surg. 1988;58:423–427.
41. Motegi Y, Shirai M, Arai M, et al. Malignant hyperthermia during epidural anesthesia. J Clin Anesth. 1996;8:157–160.
42. Pollock N, Hodges M, Sendall J. Prolonged malignant hyperthermia in the absence of triggering agents. Anaesth Intens Care. 1992;20:520–523.
43. Sheu CC, Tsai JR, Hung JY. Possible malignant hyperthermia during spinal anaesthesia with tetracaine. Anaesthesia. 2007;62:200–201.
44. Fierobe L, Nivoche Y, Mantz J, et al. Perioperative severe rhabdomyolysis revealing susceptibility to malignant hyperthermia. Anesthesiology. 1998;88:263–265.
45. Harwood TN, Nelson TE. Massive postoperative rhabdomyolysis after uneventful surgery: a case report of subclinical malignant hyperthermia. Anesthesiology. 1998;88:265–268.
46. Larach MG, Gronert GA, Allen GC, et al. Clinical presentation, treatment, and complications of malignant hyperthermia in North America from 1987 to 2006. Anesth Analg. 2010;110:498–507.
47. Vanderspek AFL, Fang WB, Ashtonmiller JA, et al. Increased masticatory muscle stiffness during limb muscle flaccidity associated with succinylcholine administration. Anesthesiology. 1988;69:11–16.
48. Smith CE, Donati F, Bevan DR. Effects of succinylcholine at the masseter and adductor pollicis muscles in adults. Anesth Analg. 1989;69:158–162.
49. Albrecht A, Wedel DJ, Gronert GA. Masseter muscle rigidity and nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking agents. Mayo Clin Proc. 1997;72:329–332.
50. Hinkle AJ, Dorsch JA. Maternal masseter muscle rigidity and neonatal fasciculations after induction for emergency cesarean section. Anesthesiology. 1993;79:175–177.
51. O’Flynn RP, Shutack JG, Rosenberg H, Fletcher JE. Masseter muscle rigidity and malignant hyperthermia susceptibility in pediatric patients: an update on management and diagnosis. Anesthesiology. 1994;80:1228–1233.
52. Kaplan RF. Clinical controversies in malignant hyperthermia susceptibility. Anesth Clin North Am. 1994;1994:537–551.
53. Allen GC, Rosenberg H. Malignant hyperthermia susceptibility in adult patients with masseter muscle rigidity. Can J Anaesth. 1990;37:31–35.
54. Ellis FR, Halsall PJ, Christian AS. Clinical presentation of suspected malignant hyperthermia during anesthesia in 402-probands. Anaesthesia. 1990;45:838–841.
55. Hackl W, Mauritz W, Schemper M, et al. Prediction of malignant hyperthermia susceptibility: statistical evaluation of clinical signs. Br J Anaesth. 1990;64:425–429.
56. Larach MG, Rosenberg H, Larach DR, Broennle AM. Prediction of malignant hyperthermia susceptibility by clinical signs. Anesthesiology. 1987;66:547–550.
57. Allen GC. Malignant hyperthermia susceptibility. Anesth Clin North Am. 1994;513–535.
58. Larach MG, Localio AR, Allen GC, et al. A clinical grading scale to predict malignant hyperthermia susceptibility. Anesthesiology. 1994;80:771–779.
59. Larach MG. Standardization of the caffeine halothane muscle contracture test. Anesth Analg. 1989;69:511–515.
60. The European Malignant Hyperpyrexia Group. A protocol for the investigation of malignant hyperpyrexia (MH) susceptibility. Br J Anaesth. 1984;56:1267–1269.
61. Allen GC, Larach MG, Kunselman AR. The sensitivity and specificity of the caffeine-halothane contracture test: a report from the North American Malignant Hyperthermia Registry. Anesthesiology. 1998;88:579–588.
62. Serfas KD, Bose D, Patel L, et al. Comparison of the segregation of the RYR1 C1840T mutation with segregation of the caffeine/halothane contracture test results for malignant hyperthermia susceptibility in a large Manitoba Mennonite family. Anesthesiology. 1996;84:322–329.
64. Ørding H, Hedengran AM, Skovgaard LT. Evaluation of 119 anaesthetics received after investigation for susceptibility to malignant hyperthermia. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1991;35:711–716.
65. Islander G, Ranklev-Twetman E. Evaluation of anaesthesias in malignant hyperthermia negative patients. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1995;39:819–821.
66. Scala D, Di Martino A, Cozzolino S, et al. Follow-up of patients tested for malignant hyperthermia susceptibility. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2006;23:801–805.
67. Litman RS, Rosenberg H. Malignant hyperthermia: update on susceptibility testing. JAMA. 2005;293:2918–2924.
68. Crawford S. Hyperpyrexia during pregnancy. Lancet. 1972;1:1244.
69. Willatts SM. Malignant hyperthermia susceptibility: management during pregnancy and labour. Anaesthesia. 1979;34:41–46.
70. Isherwood DM, Ridley J, Wilson J. Creatine phosphokinase (CPK) levels in pregnancy: a case report and a discussion of the value of CPK levels in the prediction of possible malignant hyperpyrexia. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1975;82:346–349.
71. Douglas MJ, McMorland GH. The anaesthetic management of the malignant hyperthermia susceptible parturient. Can Anaesth Soc J. 1986;33:371–378.
72. Khalil SN, Williams JP, Bourke DL. Management of a malignant hyperthermia susceptible patient in labor with 2-chloroprocaine epidural anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 1983;62:119–121.
73. Sorosky JI, Ingardia CJ, Botti JJ. Diagnosis and management of susceptibility to malignant hyperthermia in pregnancy. Am J Perinatol. 1989;6:46–48.
74. Morison DH. Placental transfer of dantrolene. Anesthesiology. 1983;59:265.
75. Lucy SJ. Anaesthesia for caesarean delivery of a malignant hyperthermia susceptible parturient. Can J Anaesth. 1994;41:1220–1226.
76. Pollock NA, Langton EE. Management of malignant hyperthermia susceptible parturients. Anaesth Intensive Care. 1997;25:398–407.
77. Vanden Hoek TL, Morrison LJ, Shuster M, et al. Part 12: cardiac arrest in special situations: 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. Circulation. 2010;122:S829–S861.
78. Lockitch G. Handbook of Diagnostic Biochemistry and Hematology in Normal Pregnancy. CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL; 1993:48–59.
79. Abramov Y, Abramov D, Abrahamov A, et al. Elevation of serum creatine phosphokinase and its MB isoenzyme during normal labor and early puerperium. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1996;75:255–260.
80. Sato N, Brum JM, Mitsumoto H, DeBoer GE. Effect of cocaine on the contracture response to 1% halothane in patients undergoing diagnostic muscle biopsy for malignant hyperthermia. Can J Anaesth. 1995;42:158–162.
81. Lampley EC, Williams S, Myers SA. Cocaine-associated rhabdomyolysis causing renal failure in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 1996;87:804–806.
82. Roby PV, Glenn CM, Watkins SL, et al. Association of elevated umbilical cord blood creatine kinase and myoglobin levels with the presence of cocaine metabolites in maternal urine. Am J Perinatol. 1996;13:453–455.
83. Malignant Hyperthermia Association of the United States. Parturient with MHS Partner. http://www.mhaus.org/recommendations/parturient-with-mhs-partner/ [Accessed December 2012] .
84. Sewall K, Flowerdew RM, Bromberger P. Severe muscular rigidity at birth: malignant hyperthermia syndrome? Can Anaesth Soc J. 1980;27:279–282.
85. Wilhoit RD, Brown RE Jr, Bauman LA. Possible malignant hyperthermia in a 7-week-old infant. Anesth Analg. 1989;68:688–691.
86. Allen G, Rosenberg H. Diagnosis of malignant hyperthermia in infants. Anesth Analg. 1990;70:115–116.
87. Lederman RP, McCann DS, Work B Jr, Huber MJ. Endogenous plasma epinephrine and norepinephrine in last-trimester pregnancy and labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1977;129:5–8.
88. Thornton CA, Carrie LE, Sayers L, et al. A comparison of the effect of extradural and parenteral analgesia on maternal plasma cortisol concentrations during labour and the puerperium. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1976;83:631–635.
89. Pearson JF, Davies P. The effect of continuous lumbar epidural analgesia on the acid-base status of maternal arterial blood during the first stage of labour. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw. 1973;80:218–224.
90. Sessler DI. Malignant hyperthermia. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand Suppl. 1996;109:25–30.
91. Gronert GA, Tobin JR, Muldoon S. Malignant hyperthermia: human stress triggering. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1813:2191–2192.
92. Urwyler A, Censier K, Seeberger MD, et al. In vitro effect of ephedrine, adrenaline, noradrenaline and isoprenaline on halothane-induced contractures in skeletal muscle from patients potentially susceptible to malignant hyperthermia. Br J Anaesth. 1993;70:76–79.
93. Kim TW, Nemergut ME. Preparation of modern anesthesia workstations for malignant hyperthermia-susceptible patients: a review of past and present practice. Anesthesiology. 2011;114:205–212.
94. Birgenheier N, Stoker R, Westenskow D, Orr J. Activated charcoal effectively removes inhaled anesthetics from modern anesthesia machines. Anesth Analg. 2011;112:1363–1370.
95. Abouleish E, Abboud T, Lechevalier T, et al. Rocuronium (Org 9426) for caesarean section. Br J Anaesth. 1994;73:336–341.
96. Lennon RL, Olson RA, Gronert GA. Atracurium or vecuronium for rapid sequence endotracheal intubation. Anesthesiology. 1986;64:510–513.
97. Girard T, Jöhr M, Schaefer C, Urwyler A. Perinatal diagnosis of malignant hyperthermia susceptibility. Anesthesiology. 2006;104:1353–1354.
98. Mayer DC, Weeks SK. Antepartum uterine relaxation with nitroglycerin at caesarean delivery. Can J Anaesth. 1992;39:166–169.
99. Nanson JK, Sheikh A. Anaesthesia for emergency caesarean section in a parturient with bleeding placenta praevia and a potentially malignant hyperthermia-susceptible fetus. Int J Obstet Anesth. 2000;9:276–278.
100. Lopez JR, Sanchez V, Lopez I, et al. The effects of extracellular magnesium on myoplasmic [Ca2+] in malignant hyperthermia susceptible swine. Anesthesiology. 1990;73:109–117.
101. Yoganathan T, Casthely PA, Lamprou M. Dantrolene-induced hyperkalemia in a patient treated with diltiazem and metoprolol. J Cardiothorac Anesth. 1988;2:363–364.
102. Rubin AS, Zablocki AD. Hyperkalemia, verapamil, and dantrolene. Anesthesiology. 1987;66:246–249.
103. Harrison GG, Wright IG, Morrell DF. The effects of calcium channel blocking drugs on halothane initiation of malignant hyperthermia in MHS swine and on the established syndrome. Anaesth Intensive Care. 1988;16:197–201.
104. Sim AT, White MD, Denborough MA. The effect of oxytocin on porcine malignant hyperpyrexia susceptible skeletal muscle. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1987;14:605–610.
105. Hankins GD, Berryman GK, Scott RT Jr, Hood D. Maternal arterial desaturation with 15-methyl prostaglandin F2-alpha for uterine atony. Obstet Gynecol. 1988;72:367–370.
106. Hofmeyr GJ, Walraven G, Gulmezoglu AM, et al. Misoprostol to treat postpartum haemorrhage: a systematic review. BJOG. 2005;112:547–553.
107. Segal S. Labor epidural analgesia and maternal fever. Anesth Analg. 2010;111:1467–1475.
108. Gillman PK. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome: mechanisms, interactions, and causality. Mov Disord. 2010;25:1780–1790.
109. Russell CS, Lang C, McCambridge M, Calhoun B. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 2001;98:906–908.
110. Chan TC, Evans SD, Clark RF. Drug-induced hyperthermia. Crit Care Clin. 1997;13:785–808.
111. Block FE Jr. Malignant hyperthermia and charcoal absorbent: too hot to handle. Anesth Analg. 2011;112:1270–1271.
113. Burkman JM, Posner KL, Domino KB. Analysis of the clinical variables associated with recrudescence after malignant hyperthermia reactions. Anesthesiology. 2007;106:901–906.
114. Krause T, Gerbershagen MU, Fiege M, et al. Dantrolene—a review of its pharmacology, therapeutic use and new developments. Anaesthesia. 2004;59:364–373.
115. Craft JB Jr, Goldberg NH, Lim M, et al. Cardiovascular effects and placental passage of dantrolene in the maternal-fetal sheep model. Anesthesiology. 1988;68:68–72.
116. Shin YK, Kim YD, Collea JV, Belcher MD. Effect of dantrolene sodium on contractility of isolated human uterine muscle. Int J Obstet Anesth. 1995;4:197–200.
117. Fricker RM, Hoerauf KH, Drewe J, Kress HG. Secretion of dantrolene into breast milk after acute therapy of a suspected malignant hyperthermia crisis during cesarean section. Anesthesiology. 1998;89:1023–1025.