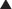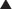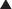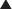Chapter 16 Hematology
Heparins
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
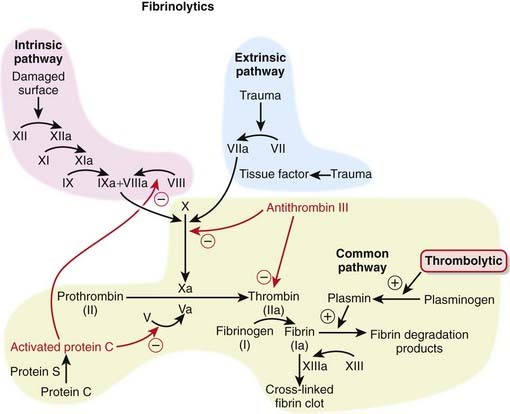
 The coagulation (clotting) system is composed of many proteins. Most of these proteins are procoagulants, which means they contribute to clotting. Some proteins are anticoagulants that serve to keep the coagulation system in balance.
The coagulation (clotting) system is composed of many proteins. Most of these proteins are procoagulants, which means they contribute to clotting. Some proteins are anticoagulants that serve to keep the coagulation system in balance. When a protein is activated, its name is followed by a small letter a. Each activated protein serves as an enzyme for the next protein downstream in the cascade (Figure 16-1).
When a protein is activated, its name is followed by a small letter a. Each activated protein serves as an enzyme for the next protein downstream in the cascade (Figure 16-1). Heparins interfere with the coagulation cascade by amplifying the anticoagulant effect of antithrombin III.
Heparins interfere with the coagulation cascade by amplifying the anticoagulant effect of antithrombin III. Antithrombin III, a natural plasma protease inhibitor, is an anticoagulant, and it inhibits thrombin (IIa) and factor Xa.
Antithrombin III, a natural plasma protease inhibitor, is an anticoagulant, and it inhibits thrombin (IIa) and factor Xa. To inhibit factor IIa, heparins must bind to both antithrombin III and factor IIa (dual binding not shown Figure 16-1).
To inhibit factor IIa, heparins must bind to both antithrombin III and factor IIa (dual binding not shown Figure 16-1).Pharmacokinetics
Unfractionated Heparin
 Very complex pharmacokinetics exist because there is a large range in molecular weight of the molecules
Very complex pharmacokinetics exist because there is a large range in molecular weight of the molecules The dose-response curve is difficult to predict, so the dose must be individualized in every patient, with frequent measurements (i.e., activated partial thromboplastin time [aPTT]) made to guide titration.
The dose-response curve is difficult to predict, so the dose must be individualized in every patient, with frequent measurements (i.e., activated partial thromboplastin time [aPTT]) made to guide titration.Indications
 Treatment and prevention of inappropriate thrombosis
Treatment and prevention of inappropriate thrombosis
Side Effects
 Hyperkalemia: Although not a common occurrence, heparin can cause increased serum potassium; it is more likely to occur in patients with diabetes or renal disease. In this regard the action of heparin is similar to that of spironolactone, which is an aldosterone blocker classified as a K-sparing diuretic.
Hyperkalemia: Although not a common occurrence, heparin can cause increased serum potassium; it is more likely to occur in patients with diabetes or renal disease. In this regard the action of heparin is similar to that of spironolactone, which is an aldosterone blocker classified as a K-sparing diuretic.Important Notes
 To measure the effect of UFH, the aPTT test is used (compare this with prothrombin time [PT] or International Normalized Ratio [INR], which is used with warfarin). It is a measure of time to coagulation (in the laboratory) and is measured in seconds. The higher the number, the more strongly a patient is anticoagulated.
To measure the effect of UFH, the aPTT test is used (compare this with prothrombin time [PT] or International Normalized Ratio [INR], which is used with warfarin). It is a measure of time to coagulation (in the laboratory) and is measured in seconds. The higher the number, the more strongly a patient is anticoagulated. Unlike UFH, LMWHs do not prolong the aPTT, and they also have a more predictable pharmacokinetic profile. These important differences make LMWH far more convenient for patients to use, with more stable administration and less rigorous monitoring.
Unlike UFH, LMWHs do not prolong the aPTT, and they also have a more predictable pharmacokinetic profile. These important differences make LMWH far more convenient for patients to use, with more stable administration and less rigorous monitoring. For cases of heparin overdose, protamine sulfate is a strongly basic protein that forms a complex with heparin, acting as a chemical antagonist. LMWH does not have an antidote.
For cases of heparin overdose, protamine sulfate is a strongly basic protein that forms a complex with heparin, acting as a chemical antagonist. LMWH does not have an antidote. Danaparoid works by the same mechanism as the heparins, but it is not structurally related to the heparins; it is therefore considered a heparinoid. Therefore it can be used in the management of patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) too.
Danaparoid works by the same mechanism as the heparins, but it is not structurally related to the heparins; it is therefore considered a heparinoid. Therefore it can be used in the management of patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) too. Fondaparinux is synthetic and is based on the structure of the antithrombin binding region of heparin. The binding region of heparin is only 5 saccharide units and is the basis for the pentasaccharide structure of fondaparinux. Fondaparinux could be thought of as really low molecular weight heparin.
Fondaparinux is synthetic and is based on the structure of the antithrombin binding region of heparin. The binding region of heparin is only 5 saccharide units and is the basis for the pentasaccharide structure of fondaparinux. Fondaparinux could be thought of as really low molecular weight heparin.Evidence
LMWH versus Warfarin for Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism
 A 2001 Cochrane review (seven studies, N = 1137 participants), updated in 2003, compared warfarin with LMWH for long-term treatment of VTE. There was no difference in the risk of recurrent VTE between warfarin and LMWH. There was a lower risk of bleeding with LMWH (odds ratio [OR] 0.38), and no difference in mortality rates between these two interventions was found.
A 2001 Cochrane review (seven studies, N = 1137 participants), updated in 2003, compared warfarin with LMWH for long-term treatment of VTE. There was no difference in the risk of recurrent VTE between warfarin and LMWH. There was a lower risk of bleeding with LMWH (odds ratio [OR] 0.38), and no difference in mortality rates between these two interventions was found.LMWH and Heparinoids versus UFH for Ischemic Stroke
 A 2008 Cochrane review (nine studies, N = 3137 patients) compared LMWH and heparinoids (danaparoid) with UFH in patients with acute, presumed or confirmed ischemic stroke. The odds of developing a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) were reduced with LMWH compared with UFH (OR 0.55); however, the incidence of key clinical outcomes such as PE, death, and hemorrhage (intracranial or extracranial) was too small to provide a reliable comparison.
A 2008 Cochrane review (nine studies, N = 3137 patients) compared LMWH and heparinoids (danaparoid) with UFH in patients with acute, presumed or confirmed ischemic stroke. The odds of developing a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) were reduced with LMWH compared with UFH (OR 0.55); however, the incidence of key clinical outcomes such as PE, death, and hemorrhage (intracranial or extracranial) was too small to provide a reliable comparison.Direct Factor Xa Inhibitors
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
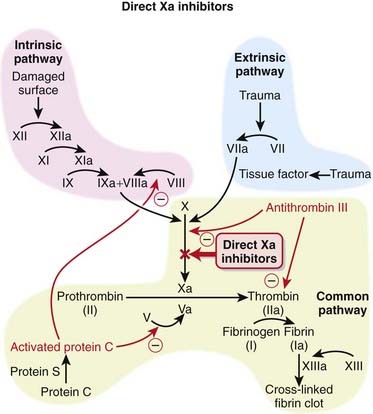
 The coagulation system is composed of many proteins: most of these proteins are procoagulants, which means they contribute to clotting. Some proteins are anticoagulants, which serve to keep the coagulation system in balance.
The coagulation system is composed of many proteins: most of these proteins are procoagulants, which means they contribute to clotting. Some proteins are anticoagulants, which serve to keep the coagulation system in balance. When a protein is activated, its name is given a small letter a at the end. Each activated protein serves as an enzyme for the next protein downstream in the cascade (Figure 16-2).
When a protein is activated, its name is given a small letter a at the end. Each activated protein serves as an enzyme for the next protein downstream in the cascade (Figure 16-2). Factor Xa converts prothrombin to thrombin (factor IIa). Thrombin is an enzyme that catalyzes the final step in the coagulation cascade, the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin.
Factor Xa converts prothrombin to thrombin (factor IIa). Thrombin is an enzyme that catalyzes the final step in the coagulation cascade, the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. Fibrin is a fibrous protein that forms a mesh, providing structural rigidity to a clot. The mesh is created by the cross-linking of fibrin, and this cross-linking step is facilitated by factor XIII.
Fibrin is a fibrous protein that forms a mesh, providing structural rigidity to a clot. The mesh is created by the cross-linking of fibrin, and this cross-linking step is facilitated by factor XIII. In addition to converting fibrinogen to fibrin, thrombin also activates factor XIII; thus thrombin not only catalyzes the creation of the key component of the clot, it also facilitates the provision of structural rigidity to the clot.
In addition to converting fibrinogen to fibrin, thrombin also activates factor XIII; thus thrombin not only catalyzes the creation of the key component of the clot, it also facilitates the provision of structural rigidity to the clot. Thrombin also activates factors V, VIII, and XI, therefore amplifying the coagulation cascade. In addition, thrombin activates platelets, leading to their aggregation.
Thrombin also activates factors V, VIII, and XI, therefore amplifying the coagulation cascade. In addition, thrombin activates platelets, leading to their aggregation.Pharmacokinetics
Important Notes
 There are no monitoring requirements for rivaroxaban. This and the fact that it is an orally administered agent suggest that drugs in its class, and perhaps the direct thrombin inhibitors, will supplant warfarin as the drugs of choice among oral anticoagulants.
There are no monitoring requirements for rivaroxaban. This and the fact that it is an orally administered agent suggest that drugs in its class, and perhaps the direct thrombin inhibitors, will supplant warfarin as the drugs of choice among oral anticoagulants.Advanced
Drug Interactions
 CYP450 3A4 enzymes are involved in the metabolism of rivaroxaban; thus the potential exists for pharmacokinetic drug interactions with inhibitors or inducers of this isozyme. Rivaroxaban is also a P-glycoprotein (Pgp) substrate, and therefore its levels could also be affected by inhibitors or inducers of Pgp.
CYP450 3A4 enzymes are involved in the metabolism of rivaroxaban; thus the potential exists for pharmacokinetic drug interactions with inhibitors or inducers of this isozyme. Rivaroxaban is also a P-glycoprotein (Pgp) substrate, and therefore its levels could also be affected by inhibitors or inducers of Pgp.Evidence
Postsurgical Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis
 The RECORD trials were a series of double-blind randomized controlled trials that compared rivaroxaban with enoxaparin for the prophylactic treatment of VTE after total hip replacement (RECORD-1 and RECORD-2) or total knee replacement (RECORD-3 and RECORD-4). The trials were all relatively large, randomizing 2509 to 4541 patients between the two treatment groups. Rivaroxaban-treated patients had fewer events of VTE and all-cause deaths compared with enoxaparin in each of the four studies. The risk of bleeding was slightly higher with rivaroxaban than with enoxaparin.
The RECORD trials were a series of double-blind randomized controlled trials that compared rivaroxaban with enoxaparin for the prophylactic treatment of VTE after total hip replacement (RECORD-1 and RECORD-2) or total knee replacement (RECORD-3 and RECORD-4). The trials were all relatively large, randomizing 2509 to 4541 patients between the two treatment groups. Rivaroxaban-treated patients had fewer events of VTE and all-cause deaths compared with enoxaparin in each of the four studies. The risk of bleeding was slightly higher with rivaroxaban than with enoxaparin.FYI
 For a quick summary of the difference between two of the newer oral anticoagulants—direct factor Xa and direct thrombin inhibitors. Direct factor Xa inhibitors inhibit the formation of thrombin, whereas direct thrombin inhibitors allow thrombin to be formed but interfere with the actions of thrombin.
For a quick summary of the difference between two of the newer oral anticoagulants—direct factor Xa and direct thrombin inhibitors. Direct factor Xa inhibitors inhibit the formation of thrombin, whereas direct thrombin inhibitors allow thrombin to be formed but interfere with the actions of thrombin.Direct Thrombin Inhibitors
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
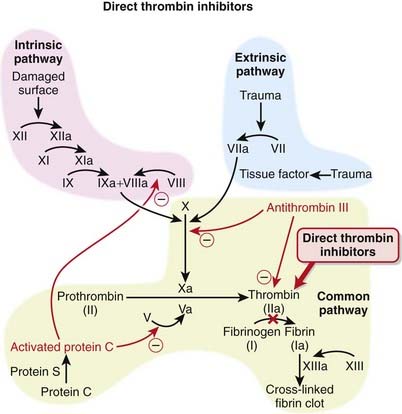
 The coagulation (clotting) system is a multistep cascade that eventually leads to the formation of fibrin and development of a clot.
The coagulation (clotting) system is a multistep cascade that eventually leads to the formation of fibrin and development of a clot. Thrombin (factor IIa) is an enzyme that catalyzes the final step in the coagulation cascade, the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin (Figure 16-3).
Thrombin (factor IIa) is an enzyme that catalyzes the final step in the coagulation cascade, the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin (Figure 16-3). Fibrin is a fibrous protein that forms a mesh, providing structural rigidity to a clot. The mesh is created by the cross-linking of fibrin, and this cross-linking step is facilitated by factor XIII.
Fibrin is a fibrous protein that forms a mesh, providing structural rigidity to a clot. The mesh is created by the cross-linking of fibrin, and this cross-linking step is facilitated by factor XIII. In addition to converting fibrinogen to fibrin, thrombin also activates factor XIII; thus thrombin not only catalyzes the creation of the key component of the clot, it also facilitates the provision of structural rigidity to the clot.
In addition to converting fibrinogen to fibrin, thrombin also activates factor XIII; thus thrombin not only catalyzes the creation of the key component of the clot, it also facilitates the provision of structural rigidity to the clot. Thrombin also activates factors V, VIII, and XI, therefore amplifying the coagulation cascade. Thrombin also has antiplatelet effects.
Thrombin also activates factors V, VIII, and XI, therefore amplifying the coagulation cascade. Thrombin also has antiplatelet effects. Thrombin has an active site as well as two other sites, referred to as exosite 1, which binds fibrin, and exosite 2, which binds heparin.
Thrombin has an active site as well as two other sites, referred to as exosite 1, which binds fibrin, and exosite 2, which binds heparin. Direct thrombin inhibitors all bind to thrombin directly at its active site. The bivalent inhibitors (-irudins) also bind at exosite 1 (hence the term “bivalent”, indicating two binding sites), while the univalent inhibitors only bind at the active site.
Direct thrombin inhibitors all bind to thrombin directly at its active site. The bivalent inhibitors (-irudins) also bind at exosite 1 (hence the term “bivalent”, indicating two binding sites), while the univalent inhibitors only bind at the active site. The univalent thrombin inhibitors (e.g., argatroban and dabigatran) and bivalirudin all bind reversibly, whereas the other bivalent inhibitors bind thrombin irreversibly.
The univalent thrombin inhibitors (e.g., argatroban and dabigatran) and bivalirudin all bind reversibly, whereas the other bivalent inhibitors bind thrombin irreversibly.Pharmacokinetics
Important Notes
 All of the agents in this class are approved for prophylaxis of DVT and VTE after orthopedic surgery. Patients undergoing knee or hip replacement surgeries, in particular, are at high risk for developing a DVT or VTE. The risk is so high that these patients receive prophylactic anticoagulants for several days postsurgery.
All of the agents in this class are approved for prophylaxis of DVT and VTE after orthopedic surgery. Patients undergoing knee or hip replacement surgeries, in particular, are at high risk for developing a DVT or VTE. The risk is so high that these patients receive prophylactic anticoagulants for several days postsurgery. The theoretical advantage of direct over indirect thrombin inhibitors such as LMWHs is that the direct inhibitors inactivate fibrin-bound thrombin, in addition to the thrombin in the fluid phase. This may lead to a greater inhibition of the thrombus. Direct thrombin inhibitors may also provide more predictable anticoagulation, as they are not bound to plasma proteins (unlike heparin) and are not neutralized by platelet factor 4 (a protein secreted by platelets) and other factors generated at the site of vascular injury.
The theoretical advantage of direct over indirect thrombin inhibitors such as LMWHs is that the direct inhibitors inactivate fibrin-bound thrombin, in addition to the thrombin in the fluid phase. This may lead to a greater inhibition of the thrombus. Direct thrombin inhibitors may also provide more predictable anticoagulation, as they are not bound to plasma proteins (unlike heparin) and are not neutralized by platelet factor 4 (a protein secreted by platelets) and other factors generated at the site of vascular injury. Warfarin has been the prototypical oral anticoagulant for decades, but with its narrow margin of safety, significant potential for drug-drug and drug-food interactions, and significant variability in response among patients, there is much anticipation that new oral anticoagulants will soon be able to replace it. The direct thrombin inhibitors, which lack any of these limitations associated with warfarin, are one of the classes that might replace warfarin.
Warfarin has been the prototypical oral anticoagulant for decades, but with its narrow margin of safety, significant potential for drug-drug and drug-food interactions, and significant variability in response among patients, there is much anticipation that new oral anticoagulants will soon be able to replace it. The direct thrombin inhibitors, which lack any of these limitations associated with warfarin, are one of the classes that might replace warfarin.Vitamin K Antagonists
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
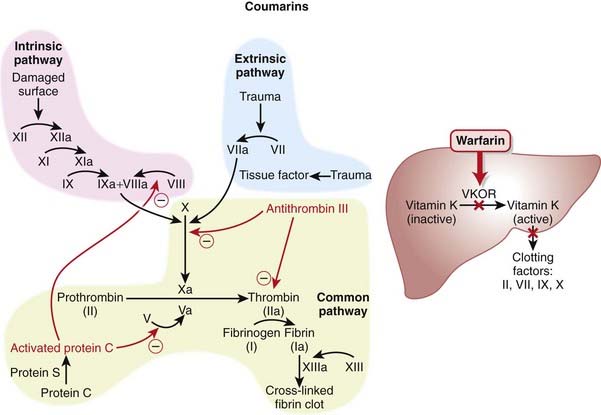
 Vitamin K is key cofactor in the hepatic activation of four coagulation factors. The four vitamin K-dependent clotting factors are II, VII, IX, and X (Figure 16-4).
Vitamin K is key cofactor in the hepatic activation of four coagulation factors. The four vitamin K-dependent clotting factors are II, VII, IX, and X (Figure 16-4). To act as a cofactor, vitamin K must be in its reduced form, vitamin K hydroxyquinone. The enzyme vitamin K epoxide reductase (VKOR) converts vitamin K to its reduced form.
To act as a cofactor, vitamin K must be in its reduced form, vitamin K hydroxyquinone. The enzyme vitamin K epoxide reductase (VKOR) converts vitamin K to its reduced form. Warfarin inhibits the enzyme VKOR. Blocking formation of the reduced form of vitamin K inhibits the activation of these four clotting factors.
Warfarin inhibits the enzyme VKOR. Blocking formation of the reduced form of vitamin K inhibits the activation of these four clotting factors. These clotting factors vary in their half-lives (6 to 50 hours), with factor II having the longest half-life and factor VII having the shortest. This delays the onset of action of warfarin, as one must wait until these clotting factors have been mostly depleted before the full anticoagulant effects have been achieved.
These clotting factors vary in their half-lives (6 to 50 hours), with factor II having the longest half-life and factor VII having the shortest. This delays the onset of action of warfarin, as one must wait until these clotting factors have been mostly depleted before the full anticoagulant effects have been achieved.Pharmacokinetics
Indications
Important Notes
 Warfarin therapy is monitored using the International Normalized Ratio (INR), which is a standardized form of the PT test. Because different laboratories use different reagents to test the PT, every laboratory generates a slightly different result, so the INR corrects for this discrepancy among laboratories.
Warfarin therapy is monitored using the International Normalized Ratio (INR), which is a standardized form of the PT test. Because different laboratories use different reagents to test the PT, every laboratory generates a slightly different result, so the INR corrects for this discrepancy among laboratories. Patients must undergo regular blood tests to ensure that their INR levels remain “therapeutic,” which means being in the appropriate range for their problem. For example, DVT treatment requires that the INR be 2.0 to 2.5 but for mechanical valves, the INR should be 2.5 to 3.5.
Patients must undergo regular blood tests to ensure that their INR levels remain “therapeutic,” which means being in the appropriate range for their problem. For example, DVT treatment requires that the INR be 2.0 to 2.5 but for mechanical valves, the INR should be 2.5 to 3.5. The anticoagulant effects of warfarin can be reversed by administration of vitamin K. The time required for vitamin K to work is dependent on the time the liver requires to generate more proteins (many hours).
The anticoagulant effects of warfarin can be reversed by administration of vitamin K. The time required for vitamin K to work is dependent on the time the liver requires to generate more proteins (many hours). Fresh frozen plasma (plasma from another human) can be transfused to immediately replace clotting factors and is the fastest way to correct an overdose of warfarin.
Fresh frozen plasma (plasma from another human) can be transfused to immediately replace clotting factors and is the fastest way to correct an overdose of warfarin. When warfarin is being administered, all vitamin K–dependent protein synthesis is inhibited. This includes the prothrombotic factors II, VII, IX, and X but also includes the antithrombotic factors protein C and protein S. Protein C and S are inhibited very early with warfarin, and thus there can be a short duration of time when only the natural anticoagulants are inhibited and a paradoxical, temporary hypercoagulable state can be induced with warfarin. Therefore it is important to coadminister heparin with warfarin until the patient’s anticoagulation levels (measured by INR) are in the desired range.
When warfarin is being administered, all vitamin K–dependent protein synthesis is inhibited. This includes the prothrombotic factors II, VII, IX, and X but also includes the antithrombotic factors protein C and protein S. Protein C and S are inhibited very early with warfarin, and thus there can be a short duration of time when only the natural anticoagulants are inhibited and a paradoxical, temporary hypercoagulable state can be induced with warfarin. Therefore it is important to coadminister heparin with warfarin until the patient’s anticoagulation levels (measured by INR) are in the desired range.Evidence
Warfarin versus LMWH for Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism
 A 2001 Cochrane review (seven studies, N = 1137 participants), updated in 2003, compared warfarin with LMWHs for long-term treatment of VTE. There was no difference in the risk of recurrent VTE between warfarin and LMWH. There was a lower risk of bleeding with LMWH (OR 0.38), and no difference in mortality rates between these two interventions.
A 2001 Cochrane review (seven studies, N = 1137 participants), updated in 2003, compared warfarin with LMWHs for long-term treatment of VTE. There was no difference in the risk of recurrent VTE between warfarin and LMWH. There was a lower risk of bleeding with LMWH (OR 0.38), and no difference in mortality rates between these two interventions.Warfarin versus Acetylsalicylic Acid for Atrial Fibrillation
 A 2007 Cochrane review (eight studies, N = 9598 participants) compared warfarin with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) in atrial fibrillation patients who had not had a prior stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA). Treatment with warfarin led to a lower risk of stroke (OR 0.68), ischemic stroke (OR 0.53), and systemic emboli (OR 0.48). The risk of intracranial hemorrhage was increased with warfarin (OR 1.98). All-cause mortality and vascular deaths were similar between groups, and disabling or fatal strokes and MI were almost reduced with oral anticoagulants, but this did not reach statistical significance.
A 2007 Cochrane review (eight studies, N = 9598 participants) compared warfarin with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) in atrial fibrillation patients who had not had a prior stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA). Treatment with warfarin led to a lower risk of stroke (OR 0.68), ischemic stroke (OR 0.53), and systemic emboli (OR 0.48). The risk of intracranial hemorrhage was increased with warfarin (OR 1.98). All-cause mortality and vascular deaths were similar between groups, and disabling or fatal strokes and MI were almost reduced with oral anticoagulants, but this did not reach statistical significance.Salicylates
Prototype and Common Drugs
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
Salicylates
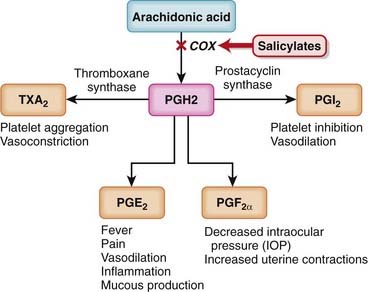
 Like nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), the salicylates work by inhibiting the actions of the cyclooxygenase (COX) enzyme (Figure 16-5).
Like nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), the salicylates work by inhibiting the actions of the cyclooxygenase (COX) enzyme (Figure 16-5).Aminosalicylates
 Although the aminosalicylates are related to salicylates in chemical structure, inhibition of prostaglandin (PG) synthesis is believed to play only a minor role, if any, in their efficacy in inflammatory bowel disease.
Although the aminosalicylates are related to salicylates in chemical structure, inhibition of prostaglandin (PG) synthesis is believed to play only a minor role, if any, in their efficacy in inflammatory bowel disease. Aminosalicylates appear to inhibit inflammatory cytokines. They appear to do this by inhibiting nuclear factor (NF)–κB, a transcription factor for inflammatory cytokines. Aminosalicylates are also peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor–gamma (PPAR-γ) agonists, and PPAR-γ is believed to play an important role in inflammation in ulcerative colitis.
Aminosalicylates appear to inhibit inflammatory cytokines. They appear to do this by inhibiting nuclear factor (NF)–κB, a transcription factor for inflammatory cytokines. Aminosalicylates are also peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor–gamma (PPAR-γ) agonists, and PPAR-γ is believed to play an important role in inflammation in ulcerative colitis.Pharmacokinetics
Salicylates
 Salicylates are also readily absorbed from the skin. They are absorbed to such an extent that systemic poisoning can occur if the agent is applied topically to a large surface area.
Salicylates are also readily absorbed from the skin. They are absorbed to such an extent that systemic poisoning can occur if the agent is applied topically to a large surface area.Aminosalicylates
 Aminosalicylates appear to exert their actions directly at the colon and therefore must be delivered directly to the colon.
Aminosalicylates appear to exert their actions directly at the colon and therefore must be delivered directly to the colon.Side Effects
Important Notes
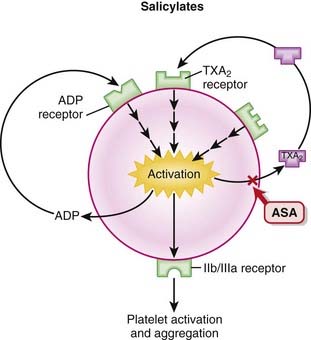
 Because the binding of ASA to the platelets is irreversible, the antiplatelet effect of ASA lasts for the lifespan of the platelet, which is about 5 to 7 days. Patients preparing for surgery must stop taking ASA 7 days before surgery.
Because the binding of ASA to the platelets is irreversible, the antiplatelet effect of ASA lasts for the lifespan of the platelet, which is about 5 to 7 days. Patients preparing for surgery must stop taking ASA 7 days before surgery. As with other NSAIDs, data from long-term epidemiologic studies suggest that ASA might prevent the development of colorectal cancer. The mechanism behind this protective effect has not been clearly established; however, COX is believed to mediate cell growth.
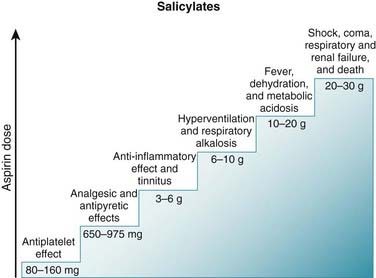
As with other NSAIDs, data from long-term epidemiologic studies suggest that ASA might prevent the development of colorectal cancer. The mechanism behind this protective effect has not been clearly established; however, COX is believed to mediate cell growth. Salicylates can stimulate respiration. They do this in two ways. Indirectly, they do this by increasing CO2 production, which in turn leads to an increase in the depth of respiration as the body tries to exhale the excess CO2. They also directly stimulate the respiratory center in the brain.
Salicylates can stimulate respiration. They do this in two ways. Indirectly, they do this by increasing CO2 production, which in turn leads to an increase in the depth of respiration as the body tries to exhale the excess CO2. They also directly stimulate the respiratory center in the brain. Salicylate poisoning can therefore lead to severe acid-base disturbances. Stimulation of respiration leads to a respiratory alkalosis, which is compensated for by the kidneys (Figure 16-7).
Salicylate poisoning can therefore lead to severe acid-base disturbances. Stimulation of respiration leads to a respiratory alkalosis, which is compensated for by the kidneys (Figure 16-7). Diflunisal is a salicylate derivative that is a competitive COX inhibitor and appears to lack antipyretic effects. It appears to be a more potent analgesic and antiinflammatory than ASA.
Diflunisal is a salicylate derivative that is a competitive COX inhibitor and appears to lack antipyretic effects. It appears to be a more potent analgesic and antiinflammatory than ASA. Many of the side effects of sulfasalazine have been attributed to the sulfapyridine component. Therefore later compounds were developed without the sulfapyridine group.
Many of the side effects of sulfasalazine have been attributed to the sulfapyridine component. Therefore later compounds were developed without the sulfapyridine group. Sulfasalazine may inhibit intestinal absorption of folate, and thus folate supplementation is typically indicated in patients taking sulfasalazine.
Sulfasalazine may inhibit intestinal absorption of folate, and thus folate supplementation is typically indicated in patients taking sulfasalazine.Advanced
 Salicylates are rapidly absorbed after oral administration. Despite the fact that salicylates are acids, and are therefore ionized in an alkaline environment, raising the pH of the stomach will enhance dissolution, and the net effect will be to enhance absorption. Therefore buffered preparations confer minimal advantage when it comes to rapid absorption.
Salicylates are rapidly absorbed after oral administration. Despite the fact that salicylates are acids, and are therefore ionized in an alkaline environment, raising the pH of the stomach will enhance dissolution, and the net effect will be to enhance absorption. Therefore buffered preparations confer minimal advantage when it comes to rapid absorption.Evidence
Aspirin Alone or in Combination with Clopidogrel for Prevention of Cardiovascular Events
 A 2007 Cochrane review (two studies, N = 28,165 patients) compared the combination of clopidogrel and aspirin with aspirin alone for preventing cardiovascular events in patients at high risk for cardiovascular disease and those with established cardiovascular disease. The authors included two large trials. CHARISMA patients were at high risk for cardiovascular events, with or without established cardiovascular disease, whereas patients in CURE had had a recent non–ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome. In CHARISMA the benefit of combination therapy was minimal: five cardiovascular events avoided and three major bleeds for every 1000 patients over 28 months. In CURE the benefits were more obvious, with 23 events avoided and 10 major bleeds over 9 months.
A 2007 Cochrane review (two studies, N = 28,165 patients) compared the combination of clopidogrel and aspirin with aspirin alone for preventing cardiovascular events in patients at high risk for cardiovascular disease and those with established cardiovascular disease. The authors included two large trials. CHARISMA patients were at high risk for cardiovascular events, with or without established cardiovascular disease, whereas patients in CURE had had a recent non–ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome. In CHARISMA the benefit of combination therapy was minimal: five cardiovascular events avoided and three major bleeds for every 1000 patients over 28 months. In CURE the benefits were more obvious, with 23 events avoided and 10 major bleeds over 9 months.Single-Dose Aspirin versus Placebo for Acute Pain
 A 1999 Cochrane review (72 trials, N = 3253 participants) compared a single dose of aspirin with placebo for acute pain of moderate to severe intensity. The number needed to treat (NNT) for at least 50% pain relief was 4.4 for 600- to 650-mg doses, 4.0 for a 1000-mg dose, and 2.4 for a 1200-mg dose. A single dose of aspirin produced more drowsiness (number needed to harm [NNH] 28) and gastric irritation (NNH 38) than placebo.
A 1999 Cochrane review (72 trials, N = 3253 participants) compared a single dose of aspirin with placebo for acute pain of moderate to severe intensity. The number needed to treat (NNT) for at least 50% pain relief was 4.4 for 600- to 650-mg doses, 4.0 for a 1000-mg dose, and 2.4 for a 1200-mg dose. A single dose of aspirin produced more drowsiness (number needed to harm [NNH] 28) and gastric irritation (NNH 38) than placebo.Aspirin for Prevention or Regression of Sporadic Colorectal Adenomas
 A 2004 Cochrane review (nine trials, N = 24,143 participants) examined the use of NSAIDs and aspirin for the prevention or regression of sporadic colorectal adenomas and colorectal cancer. Fewer patients treated with low-dose ASA developed recurrent sporadic colorectal adenomas after 1 to 3 years (NNT 12.5) compared with controls, and these results were driven by one large placebo-controlled study. There was no significant difference in the outcomes for colorectal cancer or for adverse events in any trials.
A 2004 Cochrane review (nine trials, N = 24,143 participants) examined the use of NSAIDs and aspirin for the prevention or regression of sporadic colorectal adenomas and colorectal cancer. Fewer patients treated with low-dose ASA developed recurrent sporadic colorectal adenomas after 1 to 3 years (NNT 12.5) compared with controls, and these results were driven by one large placebo-controlled study. There was no significant difference in the outcomes for colorectal cancer or for adverse events in any trials.Aspirin versus Other Antiplatelets for Preventing Serious Vascular Events in High-Risk Patients
 A 2000 Cochrane review (four trials, N = 22,656 patients) compared the thienopyridines ticlopidine and clopidogrel with aspirin for the prevention of serious vascular events in high-risk patients, particularly those who had had previous TIA or ischemic stroke. Thienopyridines reduced the risk of a serious vascular event compared with aspirin, avoiding 11 events per 1000 patients over 2 years (OR 0.91). Thienopyridines also reduced the risk of stroke by seven events per 1000 patients over 2 years. This reduction in risk increased to 16 events per 1000 patients in individuals with a history of TIA or ischemic stroke. The thienopyridines reduced the risk of GI hemorrhage but increased the risk of skin rash and diarrhea versus aspirin. Ticlopidine also significantly increased the risk of neutropenia.
A 2000 Cochrane review (four trials, N = 22,656 patients) compared the thienopyridines ticlopidine and clopidogrel with aspirin for the prevention of serious vascular events in high-risk patients, particularly those who had had previous TIA or ischemic stroke. Thienopyridines reduced the risk of a serious vascular event compared with aspirin, avoiding 11 events per 1000 patients over 2 years (OR 0.91). Thienopyridines also reduced the risk of stroke by seven events per 1000 patients over 2 years. This reduction in risk increased to 16 events per 1000 patients in individuals with a history of TIA or ischemic stroke. The thienopyridines reduced the risk of GI hemorrhage but increased the risk of skin rash and diarrhea versus aspirin. Ticlopidine also significantly increased the risk of neutropenia.Maintenance of Remission in Ulcerative Colitis
 A 2006 Cochrane review (16 studies, N = 2479) assessed the newer release formulations of 5-ASA versus placebo or sulfasalazine in the maintenance of remission in ulcerative colitis. Compared with placebo, the NNT for failure to maintain clinical or endoscopic remission was six. However, newer formulations of 5-ASA were less effective than sulfasalazine (OR 1.29). Although the incidence of side effects was similar with 5-ASA and with sulfasalazine, the authors noted that sulfasalazine trials enrolled patients who were already tolerating sulfasalazine, perhaps biasing the comparison of side effects in favor of sulfasalazine.
A 2006 Cochrane review (16 studies, N = 2479) assessed the newer release formulations of 5-ASA versus placebo or sulfasalazine in the maintenance of remission in ulcerative colitis. Compared with placebo, the NNT for failure to maintain clinical or endoscopic remission was six. However, newer formulations of 5-ASA were less effective than sulfasalazine (OR 1.29). Although the incidence of side effects was similar with 5-ASA and with sulfasalazine, the authors noted that sulfasalazine trials enrolled patients who were already tolerating sulfasalazine, perhaps biasing the comparison of side effects in favor of sulfasalazine.FYI
 ASA originated from salicylic acid, derived from the bark of the willow tree. The use of salicylic acid dates back to ancient times, both in North America and in Europe, and its first official medical use was ascribed to Hippocrates. Chemists began synthesizing salicylic acid in the later nineteenth century. Salicylic acid had some significant GI side effects, and it was these side effects that led Hoffman, a chemist at Bayer, to acetylate the molecule and create what is still perhaps the most successful nonantibiotic in the history of pharmaceutical development.
ASA originated from salicylic acid, derived from the bark of the willow tree. The use of salicylic acid dates back to ancient times, both in North America and in Europe, and its first official medical use was ascribed to Hippocrates. Chemists began synthesizing salicylic acid in the later nineteenth century. Salicylic acid had some significant GI side effects, and it was these side effects that led Hoffman, a chemist at Bayer, to acetylate the molecule and create what is still perhaps the most successful nonantibiotic in the history of pharmaceutical development. ASA therapy is very inexpensive when compared with the other antiplatelets. Given that and its long history of use, it is a first-line agent in MI prevention.
ASA therapy is very inexpensive when compared with the other antiplatelets. Given that and its long history of use, it is a first-line agent in MI prevention.Adenosine Diphosphate (ADP) Blockers
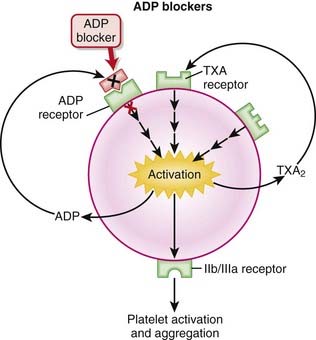
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 Platelets are activated by adhering to damaged endothelium by linking of glycoprotein Ia (GPIa) receptors with collagen and GPIb receptors with von Willebrand factor (vWF). The activation of platelets leads to aggregation and clot formation.
Platelets are activated by adhering to damaged endothelium by linking of glycoprotein Ia (GPIa) receptors with collagen and GPIb receptors with von Willebrand factor (vWF). The activation of platelets leads to aggregation and clot formation. Mediators such as ADP promote platelet aggregation by increasing GP receptor expression and promoting binding of fibrinogen to GPIIIa/IIb receptors. These actions are mediated by binding of ADP to the P2Y1 and P2Y12 receptors on platelets. Both P2Y1 and P2Y12 are receptors for ADP, and stimulation of both of these receptors is required for platelet activation.
Mediators such as ADP promote platelet aggregation by increasing GP receptor expression and promoting binding of fibrinogen to GPIIIa/IIb receptors. These actions are mediated by binding of ADP to the P2Y1 and P2Y12 receptors on platelets. Both P2Y1 and P2Y12 are receptors for ADP, and stimulation of both of these receptors is required for platelet activation.Pharmacokinetics
 Clopidogrel has a relatively slow onset of action, as it requires approximately 5 days to achieve a plateau in platelet inhibition.
Clopidogrel has a relatively slow onset of action, as it requires approximately 5 days to achieve a plateau in platelet inhibition. Because clopidogrel, prasugrel, and ticlopidine are irreversible inhibitors of the ADP receptor, the biologic half-lives of these drugs are longer than their elimination half-lives. The effects of each drug will be notable until the body replenishes its supply of platelets, requiring approximately 5 to 7 days (the life span of a platelet).
Because clopidogrel, prasugrel, and ticlopidine are irreversible inhibitors of the ADP receptor, the biologic half-lives of these drugs are longer than their elimination half-lives. The effects of each drug will be notable until the body replenishes its supply of platelets, requiring approximately 5 to 7 days (the life span of a platelet).Contraindications
Important Notes
 There is a significant range of responses to clopidogrel among patients. The extent of platelet inhibition can range from 5% to 90%, with patients at the lower end of the range (<10%) deemed to be “clopidogrel unresponsive.” Genetic polymorphisms are thought to play a role in these variable responses, including alterations in the PGY12 receptor as well as CYP450 mutations.
There is a significant range of responses to clopidogrel among patients. The extent of platelet inhibition can range from 5% to 90%, with patients at the lower end of the range (<10%) deemed to be “clopidogrel unresponsive.” Genetic polymorphisms are thought to play a role in these variable responses, including alterations in the PGY12 receptor as well as CYP450 mutations. Several other ADP-targeting antiplatelet agents are in various stages of clinical development, in an effort to improve on the toxicity issues associated with ticlopidine and the slow onset and prolonged effect of clopidogrel.
Several other ADP-targeting antiplatelet agents are in various stages of clinical development, in an effort to improve on the toxicity issues associated with ticlopidine and the slow onset and prolonged effect of clopidogrel.Advanced
 TTP is a life-threatening disease caused by abnormal activation and aggregation of platelets because of vWF macromolecules. The platelets aggregate in vessels and form pathologic thrombi, resulting in hemolysis (and anemia), a decreased platelet count (from consumption), central nervous system (CNS) dysfunction or stroke, and renal compromise because of vascular occlusion and fever. These five findings comprise the pentad of TTP.
TTP is a life-threatening disease caused by abnormal activation and aggregation of platelets because of vWF macromolecules. The platelets aggregate in vessels and form pathologic thrombi, resulting in hemolysis (and anemia), a decreased platelet count (from consumption), central nervous system (CNS) dysfunction or stroke, and renal compromise because of vascular occlusion and fever. These five findings comprise the pentad of TTP.Evidence
Adenosine Diphosphate Blockers versus Aspirin for Stroke Prevention in High-Risk Patients
 A 2000 Cochrane review (four trials, N = 22,656 patients) compared ADP inhibitors with aspirin for preventing serious vascular events in high-risk patients, including those who had had a prior TIA or ischemic stroke. One large trial (N = 19,185 patients) included clopidogrel, whereas the other three (N = 3471) included ticlopidine. Results suggested that ADP blockers would result in 11 fewer serious vascular events per 1000 patients treated over approximately 2 years. Strokes were also reduced, by seven events per 1000 patients.
A 2000 Cochrane review (four trials, N = 22,656 patients) compared ADP inhibitors with aspirin for preventing serious vascular events in high-risk patients, including those who had had a prior TIA or ischemic stroke. One large trial (N = 19,185 patients) included clopidogrel, whereas the other three (N = 3471) included ticlopidine. Results suggested that ADP blockers would result in 11 fewer serious vascular events per 1000 patients treated over approximately 2 years. Strokes were also reduced, by seven events per 1000 patients. Risk of GI hemorrhage and other GI events was reduced with ADP blockers versus aspirin, but risk of skin rash and diarrhea was increased. The risk of skin rash and diarrhea was greater with ticlopidine than clopidogrel, and ticlopidine was also associated with a higher risk of neutropenia than clopidogrel.
Risk of GI hemorrhage and other GI events was reduced with ADP blockers versus aspirin, but risk of skin rash and diarrhea was increased. The risk of skin rash and diarrhea was greater with ticlopidine than clopidogrel, and ticlopidine was also associated with a higher risk of neutropenia than clopidogrel.Clopidogrel with or without Aspirin for Preventing Cardiovascular Disease
 A 2007 Cochrane review included two large studies (CHARISMA and CURE, N = 28,165 patients). CHARISMA patients were at high risk for cardiovascular disease but did not necessarily have established cardiovascular disease, whereas patients in CURE had had a recent non–ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome. The combination of clopidogrel and aspirin reduced the risk of cardiovascular events by 13 events for every 1000 patients treated; however, six major bleeds would be caused over the same number of patients.
A 2007 Cochrane review included two large studies (CHARISMA and CURE, N = 28,165 patients). CHARISMA patients were at high risk for cardiovascular disease but did not necessarily have established cardiovascular disease, whereas patients in CURE had had a recent non–ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome. The combination of clopidogrel and aspirin reduced the risk of cardiovascular events by 13 events for every 1000 patients treated; however, six major bleeds would be caused over the same number of patients.Antiplatelet IIb/IIIa Inhibitors
Description
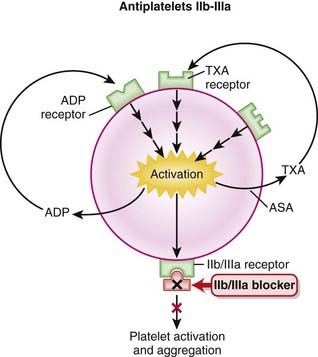
Antiplatelet IIb/IIIa inhibitors are antiplatelet drugs; they inhibit platelet function.
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 IIb/IIIa receptors are located on the outside of platelets, in very high numbers (50,000 to 80,000 per cell); in the resting platelet they are inactive.
IIb/IIIa receptors are located on the outside of platelets, in very high numbers (50,000 to 80,000 per cell); in the resting platelet they are inactive. Fibrinogen and vWF bind to IIb/IIIa receptors; once bound, they bind to foreign surfaces and also bridge other platelets to induce platelet aggregation.
Fibrinogen and vWF bind to IIb/IIIa receptors; once bound, they bind to foreign surfaces and also bridge other platelets to induce platelet aggregation.Pharmacokinetics
 Abciximab has a half-life of 10 minutes, but the effect lasts 24 hours because although the drug is cleared from the blood, it is still bound to platelets.
Abciximab has a half-life of 10 minutes, but the effect lasts 24 hours because although the drug is cleared from the blood, it is still bound to platelets.Evidence
Coronary Angioplasty
 A meta-analysis in 2007 (38 trials, N = 58,495 patients) demonstrated that with angioplasty compared with placebo, IIb/IIIa blockers decreased mortality at 30 days (OR 0.74) but not at 6 months. Death or MI was decreased both at 30 days (OR 0.67) and at 6 months (OR 0.71), although severe bleeding was increased (OR 1.38; absolute risk increase 8.6 per 1000).
A meta-analysis in 2007 (38 trials, N = 58,495 patients) demonstrated that with angioplasty compared with placebo, IIb/IIIa blockers decreased mortality at 30 days (OR 0.74) but not at 6 months. Death or MI was decreased both at 30 days (OR 0.67) and at 6 months (OR 0.71), although severe bleeding was increased (OR 1.38; absolute risk increase 8.6 per 1000).Fibrinolytics
Description
Fibrinolytics lyse (break up) blood clots. They are also called clot busters and thrombolytics.
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 Plasmin is a protease that digests fibrin (a fibrinolytic). Fibrin is a fibrous protein that forms a mesh, providing structural rigidity to a clot. The mesh is created by the cross-linking of fibrin.
Plasmin is a protease that digests fibrin (a fibrinolytic). Fibrin is a fibrous protein that forms a mesh, providing structural rigidity to a clot. The mesh is created by the cross-linking of fibrin. Tissue plasminogen activator is found in the body. It is a serine protease that is released from endothelial cells in response to injury. Its physiologic purpose is to gradually dissolve clots that have formed because of injury. Urokinase is also secreted endogenously and serves the same purpose, although it has some important differences, especially selectivity of action.
Tissue plasminogen activator is found in the body. It is a serine protease that is released from endothelial cells in response to injury. Its physiologic purpose is to gradually dissolve clots that have formed because of injury. Urokinase is also secreted endogenously and serves the same purpose, although it has some important differences, especially selectivity of action. The plasminogen activators can work either in the presence (alteplase, reteplase) or absence (streptokinase, urokinase) of fibrin.
The plasminogen activators can work either in the presence (alteplase, reteplase) or absence (streptokinase, urokinase) of fibrin. The physiologic advantage of requiring fibrin for activity is that the fibrinolytic effects will be (mainly) localized to the clot.
The physiologic advantage of requiring fibrin for activity is that the fibrinolytic effects will be (mainly) localized to the clot. The thrombolytics that do not need fibrin to enhance their activity will activate both bound and circulating plasmin. In addition to fibrin, plasmin also degrades fibrinogen and some clotting factors; thus circulating coagulation factors will be depleted. Therefore these agents are not considered to be “clot specific,” and this in theory may make them less safe to use than agents that need fibrin to work optimally.
The thrombolytics that do not need fibrin to enhance their activity will activate both bound and circulating plasmin. In addition to fibrin, plasmin also degrades fibrinogen and some clotting factors; thus circulating coagulation factors will be depleted. Therefore these agents are not considered to be “clot specific,” and this in theory may make them less safe to use than agents that need fibrin to work optimally.Pharmacokinetics
 They all have short elimination half-lives, most around 15 to 20 minutes, although the half-life of alteplase is only 5 minutes. Because of its short half-life, alteplase is typically delivered by infusion after an initial IV bolus, whereas the longer-acting agents can be given with repeat bolus injections.
They all have short elimination half-lives, most around 15 to 20 minutes, although the half-life of alteplase is only 5 minutes. Because of its short half-life, alteplase is typically delivered by infusion after an initial IV bolus, whereas the longer-acting agents can be given with repeat bolus injections.Side Effects
Important Notes
 There are advantages and disadvantages to using streptokinase versus rt-PA. rt-PA is more clot selective than urokinase or streptokinase, as it does a poor job of activating plasminogen in the absence of fibrin. However streptokinase is much cheaper than rt-PA. Streptokinase also elicits an immune response that can harm the patient.
There are advantages and disadvantages to using streptokinase versus rt-PA. rt-PA is more clot selective than urokinase or streptokinase, as it does a poor job of activating plasminogen in the absence of fibrin. However streptokinase is much cheaper than rt-PA. Streptokinase also elicits an immune response that can harm the patient. The use of streptokinase results in the patient developing antibodies to the drug. If a patient receives streptokinase and subsequently requires repeat fibrinolytic therapy (days to months later), then reteplase should be used.
The use of streptokinase results in the patient developing antibodies to the drug. If a patient receives streptokinase and subsequently requires repeat fibrinolytic therapy (days to months later), then reteplase should be used. Tenecteplase is more fibrin specific than alteplase. It is therefore believed to be less likely to elicit serious bleeding than alteplase, which is the major side effect of concern for drugs in this class.
Tenecteplase is more fibrin specific than alteplase. It is therefore believed to be less likely to elicit serious bleeding than alteplase, which is the major side effect of concern for drugs in this class. Reteplase is believed to work faster than alteplase. Reteplase appears to diffuse more quickly throughout the clot, allowing it to more efficiently lyse the clot.
Reteplase is believed to work faster than alteplase. Reteplase appears to diffuse more quickly throughout the clot, allowing it to more efficiently lyse the clot. Thrombolysis with any of the agents in this class is most successful on newly formed clots. The older the clot is, the more established the fibrin mesh is, and the harder the clot is to dissolve. Therefore time is of the essence when using fibrinolytics. Patients with MI appear to benefit most if they receive therapy within 6 hours of symptoms.
Thrombolysis with any of the agents in this class is most successful on newly formed clots. The older the clot is, the more established the fibrin mesh is, and the harder the clot is to dissolve. Therefore time is of the essence when using fibrinolytics. Patients with MI appear to benefit most if they receive therapy within 6 hours of symptoms.Evidence
Thrombolytics versus Heparin or Placebo for Treatment of Acute Pulmonary Embolism
 A 2009 Cochrane review (eight trials, N = 679 participants) compared thrombolytics with placebo or heparin in patients with acute PE. The rates of mortality, PE recurrence, major hemorrhagic events, and minor hemorrhagic events were similar between thrombolytics and heparin. In one study that examined combination therapy, the use of rt-PA combined with heparin versus heparin alone reduced the need for further treatment for in-hospital events (OR 0.35).
A 2009 Cochrane review (eight trials, N = 679 participants) compared thrombolytics with placebo or heparin in patients with acute PE. The rates of mortality, PE recurrence, major hemorrhagic events, and minor hemorrhagic events were similar between thrombolytics and heparin. In one study that examined combination therapy, the use of rt-PA combined with heparin versus heparin alone reduced the need for further treatment for in-hospital events (OR 0.35).Thrombolytics for Treatment of Ischemic Stroke
 A 2009 Cochrane review (26 trials, N = 7152 participants) compared thrombolytics with controls in patients with definite ischemic stroke. Although thrombolytics reduced the proportion of patients who were dead or dependent at 3 to 6 months after stroke (OR 0.81), they increased the risk of symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (OR 3.49) and death by 3 to 6 months after stroke (OR 1.31).
A 2009 Cochrane review (26 trials, N = 7152 participants) compared thrombolytics with controls in patients with definite ischemic stroke. Although thrombolytics reduced the proportion of patients who were dead or dependent at 3 to 6 months after stroke (OR 0.81), they increased the risk of symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (OR 3.49) and death by 3 to 6 months after stroke (OR 1.31).Thrombolytics versus Angioplasty in Myocardial Infarction
 A 2003 systematic review (23 trials, N = 7739 participants) compared percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) with thrombolytics for acute STEMI. There were fewer overall deaths in the short term with PTCA compared with thrombolytics (incidence of 7% versus 9%, respectively), and also a lower incidence of nonfatal reinfarction (3% versus 7%) and stroke (1% versus 2%) with PTCA versus thrombolytics. The results for PTCA continued to be better than thrombolytics during long-term follow-up.
A 2003 systematic review (23 trials, N = 7739 participants) compared percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) with thrombolytics for acute STEMI. There were fewer overall deaths in the short term with PTCA compared with thrombolytics (incidence of 7% versus 9%, respectively), and also a lower incidence of nonfatal reinfarction (3% versus 7%) and stroke (1% versus 2%) with PTCA versus thrombolytics. The results for PTCA continued to be better than thrombolytics during long-term follow-up.Erythropoietins
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
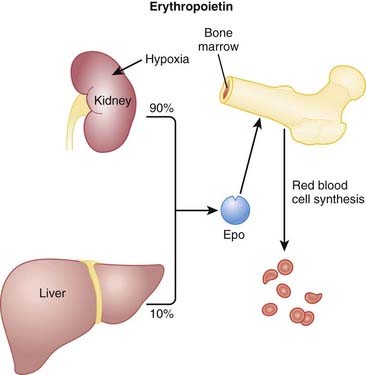
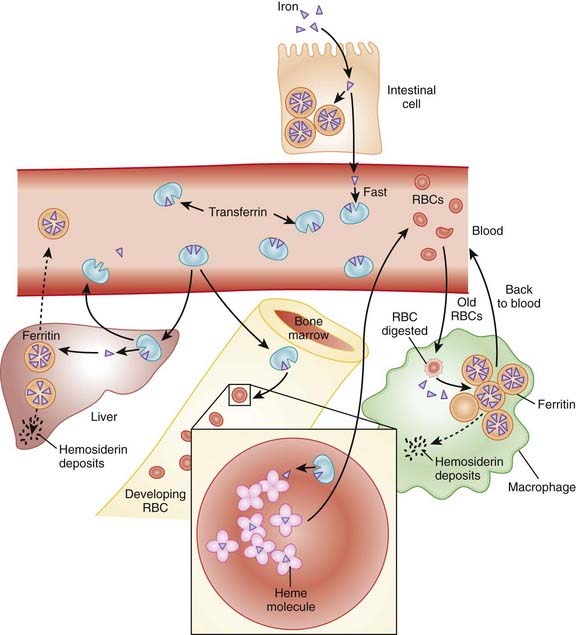
 Erythropoietin is an endogenous protein that stimulates the production of RBCs (erythrocytes). Erythropoietin is typically released in response to hypoxia and is largely synthesized in the kidneys, with a small amount coming from the liver (Figure 16-11).
Erythropoietin is an endogenous protein that stimulates the production of RBCs (erythrocytes). Erythropoietin is typically released in response to hypoxia and is largely synthesized in the kidneys, with a small amount coming from the liver (Figure 16-11). Patients with a deficiency of erythropoietin will be anemic. This occurs commonly in patients with renal failure.
Patients with a deficiency of erythropoietin will be anemic. This occurs commonly in patients with renal failure. Once released, erythropoietin binds to a receptor on the surface of committed erythroid progenitor cells in the bone marrow. Binding to this receptor mediates a variety of intracellular effects through tyrosine kinases, including the inhibition of apoptosis. Inhibiting apoptosis prevents RBCs from dying at an early stage of development. Erythropoietin also promotes proliferation through Janus protein kinase-2 (JAK2) pathways.
Once released, erythropoietin binds to a receptor on the surface of committed erythroid progenitor cells in the bone marrow. Binding to this receptor mediates a variety of intracellular effects through tyrosine kinases, including the inhibition of apoptosis. Inhibiting apoptosis prevents RBCs from dying at an early stage of development. Erythropoietin also promotes proliferation through Janus protein kinase-2 (JAK2) pathways.Pharmacokinetics
Side Effects
 Iron deficiency: If iron stores cannot keep up with erythropoiesis, patients may develop a functional iron deficiency. Patients on chronic erythropoietin therapy will likely need an iron supplement.
Iron deficiency: If iron stores cannot keep up with erythropoiesis, patients may develop a functional iron deficiency. Patients on chronic erythropoietin therapy will likely need an iron supplement. Thrombosis: Serious thromboembolic events have been reported, particularly in patients on dialysis. It is recommended that these patients receive anticoagulant therapy as a prophylactic measure.
Thrombosis: Serious thromboembolic events have been reported, particularly in patients on dialysis. It is recommended that these patients receive anticoagulant therapy as a prophylactic measure.Important Notes
 Some formulations of erythropoietin contain benzyl alcohol, which has been shown to be toxic to premature infants.
Some formulations of erythropoietin contain benzyl alcohol, which has been shown to be toxic to premature infants. A link between cancer and erythropoietin use has been proposed. Some studies in certain cancers have reported an increased risk of death and/or worsening of condition with erythropoietin use. Erythropoietin appears to act through receptors similar to those of growth factors associated with neoplasia, although these problems do not appear to be associated with all cancers.
A link between cancer and erythropoietin use has been proposed. Some studies in certain cancers have reported an increased risk of death and/or worsening of condition with erythropoietin use. Erythropoietin appears to act through receptors similar to those of growth factors associated with neoplasia, although these problems do not appear to be associated with all cancers.Evidence
Recombinant Human Erythropoietin in Predialysis Patients with Anemia
 A 2005 Cochrane review (15 trials, N = 461 participants) compared the use of rHuEPO with no treatment or placebo in predialysis patients with renal anemia. rHuEPO significantly improved hemoglobin and hematocrit and significantly reduced the number of patients requiring blood transfusions (relative risk [RR] 0.32). Quality of life and exercise capacity were also improved, where reported. rHuEPO did not appear to have an effect on the progression of renal disease, and there was no increase in the incidence of adverse events with rHuEPO therapy.
A 2005 Cochrane review (15 trials, N = 461 participants) compared the use of rHuEPO with no treatment or placebo in predialysis patients with renal anemia. rHuEPO significantly improved hemoglobin and hematocrit and significantly reduced the number of patients requiring blood transfusions (relative risk [RR] 0.32). Quality of life and exercise capacity were also improved, where reported. rHuEPO did not appear to have an effect on the progression of renal disease, and there was no increase in the incidence of adverse events with rHuEPO therapy.Recombinant Human Erythropoietin in Preventing Transfusion in Premature Infants
 A 2006 Cochrane review (19 studies, N = 912 infants) compared rHuEPO with placebo or no treatment in reducing the use of RBC transfusions in preterm and/or low–birth-weight infants. The authors found that rHuEPO reduced the risk of having one or more transfusions (typical RR 0.66 [0.59 to 0.74]). rHuEPO also reduced the average volume of blood transfused per infant by 7 mL and the average number of transfusions per infant; however, the clinical significance of these small differences was questioned by the authors. Several hard outcomes such as mortality, hypertension, and numerous other complications were not affected by therapy.
A 2006 Cochrane review (19 studies, N = 912 infants) compared rHuEPO with placebo or no treatment in reducing the use of RBC transfusions in preterm and/or low–birth-weight infants. The authors found that rHuEPO reduced the risk of having one or more transfusions (typical RR 0.66 [0.59 to 0.74]). rHuEPO also reduced the average volume of blood transfused per infant by 7 mL and the average number of transfusions per infant; however, the clinical significance of these small differences was questioned by the authors. Several hard outcomes such as mortality, hypertension, and numerous other complications were not affected by therapy.Darbepoetin or Epoetin in Anemia Associated with Cancer Treatment
 A 2006 Cochrane review (57 trials, N = 9353 participants) assessed darbepoetin and epoetin in the prevention or treatment of anemia in cancer patients. Both agents reduced the risk of transfusions (RR 0.64 [0.60 to 0.68]) and resulted in a requirement for an average of one less unit of blood. However, the risk of thromboembolic events was increased (RR 1.67 [1.35 to 2.06]). The authors were not able to conclude whether these agents have an impact on tumor response or overall survival.
A 2006 Cochrane review (57 trials, N = 9353 participants) assessed darbepoetin and epoetin in the prevention or treatment of anemia in cancer patients. Both agents reduced the risk of transfusions (RR 0.64 [0.60 to 0.68]) and resulted in a requirement for an average of one less unit of blood. However, the risk of thromboembolic events was increased (RR 1.67 [1.35 to 2.06]). The authors were not able to conclude whether these agents have an impact on tumor response or overall survival.FYI
 The chemical structure of epoetin alfa differs slightly from that of human endogenous erythropoietin. Although this difference does not have any clinical relevance, it has proven useful in trying to detect athletes who have been using epoetin alfa for blood doping. This is a practice by which athletes will try to stimulate an artificial increase in hematocrit before a competition to increase the oxygen-carrying capacity of their blood, presumably enhancing performance.
The chemical structure of epoetin alfa differs slightly from that of human endogenous erythropoietin. Although this difference does not have any clinical relevance, it has proven useful in trying to detect athletes who have been using epoetin alfa for blood doping. This is a practice by which athletes will try to stimulate an artificial increase in hematocrit before a competition to increase the oxygen-carrying capacity of their blood, presumably enhancing performance.Colony-Stimulating Factors
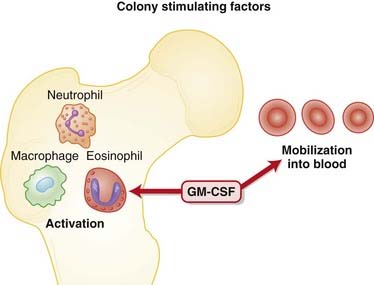
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 Neutropenia is a common and serious side effect of cytotoxic cancer chemotherapy. Cytotoxic agents preferentially target rapidly dividing cells, including those of the bone marrow. The major complication of neutropenia is a reduced immune response, greatly increasing the probability of developing infections of both “normal” and opportunistic microbes.
Neutropenia is a common and serious side effect of cytotoxic cancer chemotherapy. Cytotoxic agents preferentially target rapidly dividing cells, including those of the bone marrow. The major complication of neutropenia is a reduced immune response, greatly increasing the probability of developing infections of both “normal” and opportunistic microbes. The CSFs work by binding to receptors on myeloid progenitor cells. These are cells in the bone marrow that make RBCs, platelets, granulocytes, and monocytes. The actions of these receptors are mediated through the Janus protein kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription (JAK/STAT) pathway.
The CSFs work by binding to receptors on myeloid progenitor cells. These are cells in the bone marrow that make RBCs, platelets, granulocytes, and monocytes. The actions of these receptors are mediated through the Janus protein kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription (JAK/STAT) pathway. G-CSFs stimulate proliferation and differentiation only of progenitors commited to becoming neutrophils.
G-CSFs stimulate proliferation and differentiation only of progenitors commited to becoming neutrophils.Pharmacokinetics
Side Effects
 Renal dysfunction: G-CSF causes a transient and reversible renal impairment, believed to be caused by leukostasis (clumping of leukocytes) in the kidneys.
Renal dysfunction: G-CSF causes a transient and reversible renal impairment, believed to be caused by leukostasis (clumping of leukocytes) in the kidneys.Evidence
Colony-Stimulating Factor in Children with Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia
 A 2005 Cochrane review (six studies, N = 332 patients) looked at safety and effectiveness of adjunctive G-CSF or GM-CSF in children with acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL). There was not enough data to assess survival. CSF significantly reduced the number of episodes of febrile neutropenia, length of hospitalization, and number of infectious disease episodes. CSF did not affect the length of neutropenia episodes or delays in chemotherapy episodes.
A 2005 Cochrane review (six studies, N = 332 patients) looked at safety and effectiveness of adjunctive G-CSF or GM-CSF in children with acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL). There was not enough data to assess survival. CSF significantly reduced the number of episodes of febrile neutropenia, length of hospitalization, and number of infectious disease episodes. CSF did not affect the length of neutropenia episodes or delays in chemotherapy episodes.B Vitamins
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
Vitamin B1
 Vitamin B1 is converted to thiamine in the body and is a coenzyme in carbohydrate metabolism, including the decarboxylation of pyruvic acid. Increased pyruvic acid levels are therefore indicative of vitamin B1 deficiency. Deficiency can lead to damage in regions of the brain, including the thalamus, midbrain, and brainstem, and this appears to be mediated, at least in part, by oxidative stress. This brain damage manifests as Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, a condition associated with alcoholism (Figure 16-13).
Vitamin B1 is converted to thiamine in the body and is a coenzyme in carbohydrate metabolism, including the decarboxylation of pyruvic acid. Increased pyruvic acid levels are therefore indicative of vitamin B1 deficiency. Deficiency can lead to damage in regions of the brain, including the thalamus, midbrain, and brainstem, and this appears to be mediated, at least in part, by oxidative stress. This brain damage manifests as Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, a condition associated with alcoholism (Figure 16-13).Vitamin B2
 The two coenzyme forms of vitamin B2 (riboflavin-5-phosphate and flavin adenine dinucleotide) play a role in adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production, through the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Deficiency typically manifests as fissures in lips or cracks in the mouth, swelling of the tongue, or seborrheic dermatitis. Normochromic-normocytic anemias can also occur, as well as peripheral neuropathy.
The two coenzyme forms of vitamin B2 (riboflavin-5-phosphate and flavin adenine dinucleotide) play a role in adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production, through the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Deficiency typically manifests as fissures in lips or cracks in the mouth, swelling of the tongue, or seborrheic dermatitis. Normochromic-normocytic anemias can also occur, as well as peripheral neuropathy.Niacin (Vitamin B3)
 Niacin is converted in vivo to nicotinic adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP). These metabolites serve as coenzymes for a number of reactions involving lipid and protein metabolism, as well as anaerobic reactions in the Krebs cycle.
Niacin is converted in vivo to nicotinic adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP). These metabolites serve as coenzymes for a number of reactions involving lipid and protein metabolism, as well as anaerobic reactions in the Krebs cycle. Niacin binds to a G protein–coupled receptor in adipocytes and inhibits lipolysis in adipose tissue. This reduces the supply of free fatty acids, and because the liver uses free fatty acids to produce triglycerides, which are then used in very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) synthesis, VLDL is reduced. Accordingly, niacin decreases low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and also increases high-density lipoprotein (HDL) by reducing its catabolism.
Niacin binds to a G protein–coupled receptor in adipocytes and inhibits lipolysis in adipose tissue. This reduces the supply of free fatty acids, and because the liver uses free fatty acids to produce triglycerides, which are then used in very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) synthesis, VLDL is reduced. Accordingly, niacin decreases low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and also increases high-density lipoprotein (HDL) by reducing its catabolism.Vitamin B12 and Folic Acid
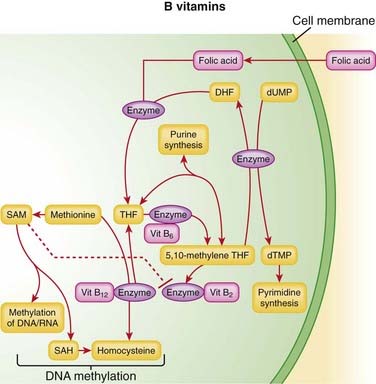
 Vitamin B12 and folic acid play key roles in DNA synthesis. Active forms of folic acid serve as enzyme cofactors that play key roles in the synthesis of purines and pyrimidines, as well as amino acids, in the body.
Vitamin B12 and folic acid play key roles in DNA synthesis. Active forms of folic acid serve as enzyme cofactors that play key roles in the synthesis of purines and pyrimidines, as well as amino acids, in the body. A deficiency of folic acid or B12 therefore has the greatest impact on cells that are actively dividing, such as the cells of the bone marrow, which are involved in erythropoiesis. Therefore the primary complication of deficiencies of these vitamins is anemia.
A deficiency of folic acid or B12 therefore has the greatest impact on cells that are actively dividing, such as the cells of the bone marrow, which are involved in erythropoiesis. Therefore the primary complication of deficiencies of these vitamins is anemia.Pharmacokinetics
 Vitamin B1 combines with ATP to form thiamine in vivo. The maximum amount of B1 that can be absorbed in a single dose is 4 to 8 mg. The absorption of thiamine is markedly reduced in alcoholics and in those with folate deficiency.
Vitamin B1 combines with ATP to form thiamine in vivo. The maximum amount of B1 that can be absorbed in a single dose is 4 to 8 mg. The absorption of thiamine is markedly reduced in alcoholics and in those with folate deficiency. Vitamin B1 is stored in the body, in heart, liver, skeletal muscle, kidneys, and brain. It undergoes hepatic metabolism and is excreted by the kidneys. Large doses of vitamin B1 may simply be renally excreted.
Vitamin B1 is stored in the body, in heart, liver, skeletal muscle, kidneys, and brain. It undergoes hepatic metabolism and is excreted by the kidneys. Large doses of vitamin B1 may simply be renally excreted. Vitamin B2 absorption occurs by active transport in the upper ileum, and this transport mechanism is saturable (maximum of 20 to 25 mg vitamin B2 can be absorbed in a single dose). It is widely distributed to tissues, but very little is stored. Riboflavin is excreted in urine unchanged.
Vitamin B2 absorption occurs by active transport in the upper ileum, and this transport mechanism is saturable (maximum of 20 to 25 mg vitamin B2 can be absorbed in a single dose). It is widely distributed to tissues, but very little is stored. Riboflavin is excreted in urine unchanged. Niacin (B3) is converted to niacinamide in the liver. This conversion is saturable, so when patients take higher doses for an antihyperlipidemic effect, much of the niacin is not converted to niacinamide and instead is excreted unchanged in urine. Niacinamide is widely distributed and undergoes further hepatic metabolism before being excreted in urine.
Niacin (B3) is converted to niacinamide in the liver. This conversion is saturable, so when patients take higher doses for an antihyperlipidemic effect, much of the niacin is not converted to niacinamide and instead is excreted unchanged in urine. Niacinamide is widely distributed and undergoes further hepatic metabolism before being excreted in urine. Vitamin B6 absorption is not via active transport, and therefore is not saturable. It is stored, and its metabolite is excreted in urine.
Vitamin B6 absorption is not via active transport, and therefore is not saturable. It is stored, and its metabolite is excreted in urine. Gastric intrinsic factor facilitates the absorption of vitamin B12, and absorption is also pH sensitive. Intrinsic factor is secreted by parietal cells, so patients who have had gastric surgery or some other disruption of their parietal cells may have a relative deficiency of intrinsic factor and thus a vitamin B12 deficiency. These patients can be treated with intramuscular injections of B12, which bypasses the need for intrinsic factor.
Gastric intrinsic factor facilitates the absorption of vitamin B12, and absorption is also pH sensitive. Intrinsic factor is secreted by parietal cells, so patients who have had gastric surgery or some other disruption of their parietal cells may have a relative deficiency of intrinsic factor and thus a vitamin B12 deficiency. These patients can be treated with intramuscular injections of B12, which bypasses the need for intrinsic factor.Side Effects
 Adverse effects can be seen at high doses (15 mg daily) of folic acid, although these are well above the recommended daily intake, which is typically 1 mg or less.
Adverse effects can be seen at high doses (15 mg daily) of folic acid, although these are well above the recommended daily intake, which is typically 1 mg or less.Niacin
 At the recommended daily intake, niacin is well tolerated; however, when used as an antihyperlipidemic, it is often used at high doses, which can result in the following:
At the recommended daily intake, niacin is well tolerated; however, when used as an antihyperlipidemic, it is often used at high doses, which can result in the following:
Important Notes
 B12 preparations are available that contain intrinsic factor from animal sources. Although these might be useful initially in patients with intrinsic factor deficiency, patients typically become less responsive to the intrinsic factor, perhaps because of an antibody response launched against the animal protein.
B12 preparations are available that contain intrinsic factor from animal sources. Although these might be useful initially in patients with intrinsic factor deficiency, patients typically become less responsive to the intrinsic factor, perhaps because of an antibody response launched against the animal protein. Folinic acid, also known as leucovorin, is a reduced form of folic acid. It is used as rescue therapy in patients who are being treated with methotrexate. Methotrexate is an antifolate drug, and patients who are on high doses or chronic therapy are likely to experience severe symptoms of folate deficiency unless they are treated adjunctively with leucovorin.
Folinic acid, also known as leucovorin, is a reduced form of folic acid. It is used as rescue therapy in patients who are being treated with methotrexate. Methotrexate is an antifolate drug, and patients who are on high doses or chronic therapy are likely to experience severe symptoms of folate deficiency unless they are treated adjunctively with leucovorin. Folic acid alone will not be effective in treating pernicious anemia, as it does not address the neurologic complications. If used in pernicious anemia, folic acid should be given as an adjunct to vitamin B12.
Folic acid alone will not be effective in treating pernicious anemia, as it does not address the neurologic complications. If used in pernicious anemia, folic acid should be given as an adjunct to vitamin B12.| Overdose Agent | Mechanism of Toxicity | Mechanism of Pyridoxine as Antidote |
|---|---|---|
| Isoniazid (INH) |
Evidence
Folic Acid with or without Vitamin B12 for Cognition
 A 2008 Cochrane review (eight studies, N = 1317 participants) examined the effects of folic acid supplementation, with or without vitamin B12, on healthy elderly or demented participants, in preventing cognitive impairment or slowing its progress. The authors found no evidence that folic acid, with or without B12, has a positive impact on mood and cognitive function in healthy elderly people.
A 2008 Cochrane review (eight studies, N = 1317 participants) examined the effects of folic acid supplementation, with or without vitamin B12, on healthy elderly or demented participants, in preventing cognitive impairment or slowing its progress. The authors found no evidence that folic acid, with or without B12, has a positive impact on mood and cognitive function in healthy elderly people.FYI
 The discovery of vitamin B12 as a treatment for pernicious anemia began with an experiment in the 1920s in which patients with this condition were fed large quantities of raw liver. A few years later, it was discovered that patients whose stomachs had been removed did not respond to the liver “cure.” It was hypothesized that an “intrinsic factor” must be secreted by the stomach to facilitate the absorption of the yet-unnamed curative “extrinsic factor.” This extrinsic factor was later isolated from the liver, and named vitamin B12.
The discovery of vitamin B12 as a treatment for pernicious anemia began with an experiment in the 1920s in which patients with this condition were fed large quantities of raw liver. A few years later, it was discovered that patients whose stomachs had been removed did not respond to the liver “cure.” It was hypothesized that an “intrinsic factor” must be secreted by the stomach to facilitate the absorption of the yet-unnamed curative “extrinsic factor.” This extrinsic factor was later isolated from the liver, and named vitamin B12. The preferred source of B vitamins for daily supplementation is from the diet. Food sources and recommended intakes are summarized in Table 16-2.
The preferred source of B vitamins for daily supplementation is from the diet. Food sources and recommended intakes are summarized in Table 16-2.TABLE 16-2 Sources and Recommended Dietary Intakes for Various B Vitamins
| Vitamin | Recommended Dietary Allowances | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| B1 (thiamine) |
Iron
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 Most iron is recycled through the body; RBCs contain the majority of iron in hemoglobin. Because the life span of an RBC is about 120 days, in 1 day about 0.8% of the RBCs are broken down, and their iron is recycled:
Most iron is recycled through the body; RBCs contain the majority of iron in hemoglobin. Because the life span of an RBC is about 120 days, in 1 day about 0.8% of the RBCs are broken down, and their iron is recycled:
 Senescent (old) RBCs are taken up by the reticular system (spleen and macrophages) and are relieved of their iron (Figure 16-14).
Senescent (old) RBCs are taken up by the reticular system (spleen and macrophages) and are relieved of their iron (Figure 16-14).Pharmacokinetics
 Ferrous iron (Fe2+) is better absorbed than ferric iron (Fe3+) and is absorbed in the duodenum. About 25% of ferrous iron is absorbed.
Ferrous iron (Fe2+) is better absorbed than ferric iron (Fe3+) and is absorbed in the duodenum. About 25% of ferrous iron is absorbed. Iron from animals (heme iron) is ferrous; iron from vegetarian foods (nonheme iron) is ferric, and so a smaller percentage is available for absorption.
Iron from animals (heme iron) is ferrous; iron from vegetarian foods (nonheme iron) is ferric, and so a smaller percentage is available for absorption. Iron should be taken on an empty stomach; many foods inhibit iron absorption. Other factors that markedly decrease absorption include antacids, H2 blockers, proton pump antagonists, and calcium supplements.
Iron should be taken on an empty stomach; many foods inhibit iron absorption. Other factors that markedly decrease absorption include antacids, H2 blockers, proton pump antagonists, and calcium supplements.Side Effects
Oral Administration
Important Notes
 Free inorganic iron is extremely toxic; therefore iron is quickly bound by transferrin and subsequently stored in the body in the form of hemoglobin, myoglobin, ferritin, and, to a small degree, transferrin. Hemoglobin and myoglobin constitute about 80% of all stored iron.
Free inorganic iron is extremely toxic; therefore iron is quickly bound by transferrin and subsequently stored in the body in the form of hemoglobin, myoglobin, ferritin, and, to a small degree, transferrin. Hemoglobin and myoglobin constitute about 80% of all stored iron. Iron deficiency results in small, pale RBCs: microcyctic, hypochromic anemia. RBC size is measured by the mean cell volume (MCV).
Iron deficiency results in small, pale RBCs: microcyctic, hypochromic anemia. RBC size is measured by the mean cell volume (MCV). A number of laboratory measurements can be used for the diagnosis of iron deficiency. See Table 16-3.
A number of laboratory measurements can be used for the diagnosis of iron deficiency. See Table 16-3. The goal of iron therapy is twofold: to correct the anemia, and to correct the deficient iron stores in the body. It can take 6 to 12 months of oral iron therapy to correct the iron stores.
The goal of iron therapy is twofold: to correct the anemia, and to correct the deficient iron stores in the body. It can take 6 to 12 months of oral iron therapy to correct the iron stores. The hemoglobin should increase by about 2 g/dL (20 g/L) after 3 weeks of therapy in a normally responding patient.
The hemoglobin should increase by about 2 g/dL (20 g/L) after 3 weeks of therapy in a normally responding patient. Iron toxicity occurs in iron storage diseases including hemochromatosis and hemosiderosis, as well as iron-loading anemias such as thalassemia.
Iron toxicity occurs in iron storage diseases including hemochromatosis and hemosiderosis, as well as iron-loading anemias such as thalassemia. Iron toxicity is treated with phlebotomy (removing blood) and iron chelators deferoxamine (parenteral), deferasirox (oral), and deferiprone (oral but not available in the United States). Phlebotomy is not indicated when the patient is anemic or being treating for anemia. Chelators are discussed further in Chapter 7.
Iron toxicity is treated with phlebotomy (removing blood) and iron chelators deferoxamine (parenteral), deferasirox (oral), and deferiprone (oral but not available in the United States). Phlebotomy is not indicated when the patient is anemic or being treating for anemia. Chelators are discussed further in Chapter 7.TABLE 16-3 Laboratory Measurements Used for Diagnosis of Iron Deficiency
| Hemoglobin | Low |
| Serum iron: measure of iron bound to serum ferritin | Low |
| Ferritin: ferritin level correlates with total body iron stores | Low |
| Total iron binding capacity (TIBC): refers to the number of unoccupied binding sites on transferrin and is determined by both the iron levels and the transferrin levels | High |
| Transferrin percent saturation: percent of iron bound to transferrin; a calculated value based on serum iron and TIBC | Low |
| Bone marrow iron | Low |
Advanced
 Myelodysplastic syndrome (a bone marrow disease resulting in abnormal blood counts) can produce a microcytic hypochromic anemia. However, iron storage measurements are not low, and this is not an iron deficiency state. It is an abnormality of iron utilization in the bone marrow.
Myelodysplastic syndrome (a bone marrow disease resulting in abnormal blood counts) can produce a microcytic hypochromic anemia. However, iron storage measurements are not low, and this is not an iron deficiency state. It is an abnormality of iron utilization in the bone marrow. Thalassemia is a hemoglobinopathy (hemoglobin disease) that also results in a microcytic hypochromic anemia with a normal iron profile.
Thalassemia is a hemoglobinopathy (hemoglobin disease) that also results in a microcytic hypochromic anemia with a normal iron profile.