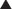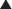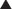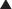Chapter 14 Endocrinology
α-Glucosidase Inhibitors (AGIs)
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
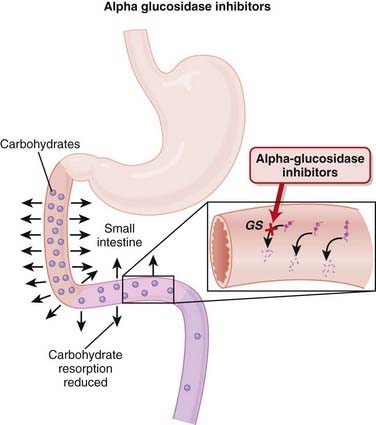
 Glucosidases (GSs) such as maltase, dextranase, sucrase, and glucoamylase aid in carbohydrate absorption by cleaving complex carbohydrates to yield glucose. Only monosaccharides such as glucose or fructose can be absorbed into the bloodstream (Figure 14-1).
Glucosidases (GSs) such as maltase, dextranase, sucrase, and glucoamylase aid in carbohydrate absorption by cleaving complex carbohydrates to yield glucose. Only monosaccharides such as glucose or fructose can be absorbed into the bloodstream (Figure 14-1). The AGIs are carbohydrate analogues that bind reversibly and with much greater affinity than carbohydrates to these GS enzymes.
The AGIs are carbohydrate analogues that bind reversibly and with much greater affinity than carbohydrates to these GS enzymes. The competitive inhibition of these GSs delays the absorption of carbohydrates along the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. These agents are therefore useful in reducing the spike in blood sugar that occurs after a meal.
The competitive inhibition of these GSs delays the absorption of carbohydrates along the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. These agents are therefore useful in reducing the spike in blood sugar that occurs after a meal.Pharmacokinetics
Side Effects
 GI (flatulence, bloating, abdominal discomfort, diarrhea): GI side effects are all caused by the actions of bacteria on undigested carbohydrates that reach the large intestine. The carbohydrate load that reaches the large intestine is a substrate for bacteria, which generate gas when they consume the carbohydrate. This side effect seems to be reduced with time, possibly because of an up-regulation of α-glucosidase enzymes in the distal small intestine.
GI (flatulence, bloating, abdominal discomfort, diarrhea): GI side effects are all caused by the actions of bacteria on undigested carbohydrates that reach the large intestine. The carbohydrate load that reaches the large intestine is a substrate for bacteria, which generate gas when they consume the carbohydrate. This side effect seems to be reduced with time, possibly because of an up-regulation of α-glucosidase enzymes in the distal small intestine.Important Notes
 Acarbose has been shown in some studies to have potential beneficial cardiovascular effects beyond that of simply lowering blood glucose.
Acarbose has been shown in some studies to have potential beneficial cardiovascular effects beyond that of simply lowering blood glucose. Because of their mechanism of action, namely reducing postprandial glucose levels, there has been considerable interest in the potential for AGIs to prevent onset of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Postprandial hyperglycemia is considered to be an early warning sign for development of type 2 diabetes. The STOP-NIDDM trial was a large (N = 1429 participants) double-blind randomized controlled trial that found that the number needed to treat (NNT) for preventing one new case of diabetes over 3 years was 11 for acarbose. Given that these results are from only one study, they should be interpreted with caution; however these findings do suggest further investigation is warranted.
Because of their mechanism of action, namely reducing postprandial glucose levels, there has been considerable interest in the potential for AGIs to prevent onset of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Postprandial hyperglycemia is considered to be an early warning sign for development of type 2 diabetes. The STOP-NIDDM trial was a large (N = 1429 participants) double-blind randomized controlled trial that found that the number needed to treat (NNT) for preventing one new case of diabetes over 3 years was 11 for acarbose. Given that these results are from only one study, they should be interpreted with caution; however these findings do suggest further investigation is warranted.Evidence
α-Glucosidase Inhibitors versus Placebo or Other Antidiabetics in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 A 2005 Cochrane review (41 trials, N = 8130 patients) included studies largely 24 to 52 weeks in duration, with all the various AGIs. Few data on mortality, morbidity, or quality of life were available. The AGIs improved surrogate markers such as HbA1c (−0.8%), fasting blood glucose (−1.1 mmol/L), and postload blood glucose (−2.3 mmol/L) versus placebo.
A 2005 Cochrane review (41 trials, N = 8130 patients) included studies largely 24 to 52 weeks in duration, with all the various AGIs. Few data on mortality, morbidity, or quality of life were available. The AGIs improved surrogate markers such as HbA1c (−0.8%), fasting blood glucose (−1.1 mmol/L), and postload blood glucose (−2.3 mmol/L) versus placebo.Biguanides
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
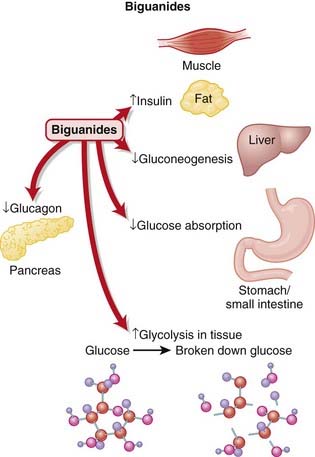
 There are several proposed mechanisms behind the glucose-reducing effects of biguanides (Figure 14-2):
There are several proposed mechanisms behind the glucose-reducing effects of biguanides (Figure 14-2):
 Reduced gluconeogenesis
Reduced gluconeogenesis
Side Effects
Important Notes
 Because metformin does not stimulate the release of insulin, it is less likely to cause hypoglycemia than the oral hypoglycemics.
Because metformin does not stimulate the release of insulin, it is less likely to cause hypoglycemia than the oral hypoglycemics. Metformin is also used in the management of polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS). Hyperinsulinemia is believed to contribute to PCOS by stimulating excess testosterone production by the ovaries and decreasing synthesis of sex hormone binding globulin in the liver. Metformin reduces insulin levels, therefore inhibiting this process.
Metformin is also used in the management of polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS). Hyperinsulinemia is believed to contribute to PCOS by stimulating excess testosterone production by the ovaries and decreasing synthesis of sex hormone binding globulin in the liver. Metformin reduces insulin levels, therefore inhibiting this process. Lactic acidosis was a major concern with this drug class, as an original member of this class (phenformin) was withdrawn from the market in the 1970s because of this potentially fatal side effect. The incidence of lactic acidosis with metformin is actually very low (less than one case per 1000 patient years). This risk can increase substantially if metformin is given with other agents that cause acidosis or in patients with renal impairment.
Lactic acidosis was a major concern with this drug class, as an original member of this class (phenformin) was withdrawn from the market in the 1970s because of this potentially fatal side effect. The incidence of lactic acidosis with metformin is actually very low (less than one case per 1000 patient years). This risk can increase substantially if metformin is given with other agents that cause acidosis or in patients with renal impairment.Advanced
 There is increasing evidence from animal and now human studies that metformin may have beneficial effects that extend beyond its known effects in reducing blood glucose. In particular, metformin may have beneficial cardiovascular effects, including a reduction in microvascular complications and improved endothelial function.
There is increasing evidence from animal and now human studies that metformin may have beneficial effects that extend beyond its known effects in reducing blood glucose. In particular, metformin may have beneficial cardiovascular effects, including a reduction in microvascular complications and improved endothelial function.Evidence
Metformin Monotherapy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 A 2005 Cochrane review compared metformin with sulfonylureas (13 trials, N = 1167 participants), placebo (12 trials, N = 702), diet (three trials, N = 493), thiazolidinediones (TZDs) (three trials, N = 132), insulin (two trials, N = 439), meglitinides (two trials, N = 208), and glucosidase inhibitors (two trials, N = 111). Obese participants with type 2 diabetes who were treated with intensive metformin therapy had a reduced risk for any clinical endpoint related to type 2 diabetes, including all-cause mortality and stroke compared with intensive therapy with chlorpropamide, glibenclamide, or insulin. The authors described metformin as eliciting a strong benefit for HbA1c compared with placebo or diet.
A 2005 Cochrane review compared metformin with sulfonylureas (13 trials, N = 1167 participants), placebo (12 trials, N = 702), diet (three trials, N = 493), thiazolidinediones (TZDs) (three trials, N = 132), insulin (two trials, N = 439), meglitinides (two trials, N = 208), and glucosidase inhibitors (two trials, N = 111). Obese participants with type 2 diabetes who were treated with intensive metformin therapy had a reduced risk for any clinical endpoint related to type 2 diabetes, including all-cause mortality and stroke compared with intensive therapy with chlorpropamide, glibenclamide, or insulin. The authors described metformin as eliciting a strong benefit for HbA1c compared with placebo or diet.Incretins
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus appear to have an impaired insulin response (insulin resistance) and an inappropriate increase in glucagon release compared with normal individuals. Glucagon is a hormone that does the opposite of insulin—it increases blood glucose.
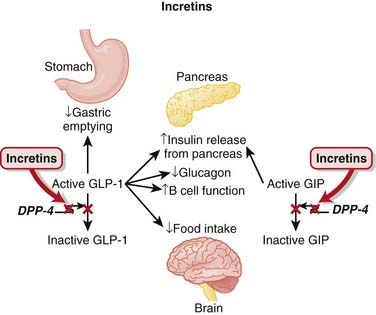
Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus appear to have an impaired insulin response (insulin resistance) and an inappropriate increase in glucagon release compared with normal individuals. Glucagon is a hormone that does the opposite of insulin—it increases blood glucose. Incretin hormones such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) lower blood glucose. They accomplish this by a number of mechanisms:
Incretin hormones such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) lower blood glucose. They accomplish this by a number of mechanisms:
 The DPP-4 enzyme inactivates incretin hormones, and therefore agents that overcome the actions of this enzyme enhance the effects of incretins (see Figure 14-3).
The DPP-4 enzyme inactivates incretin hormones, and therefore agents that overcome the actions of this enzyme enhance the effects of incretins (see Figure 14-3).Pharmacokinetics
Side Effects
Important Notes
 The first indication that incretins exist came from the observation that an oral glucose load is more effective at stimulating insulin secretion than glucose given intravenously. It was subsequently discovered that two hormones (GIP and GLP-1) that are released from the upper and lower bowel enhance glucose-dependent insulin release. This increased effect of oral glucose on insulin secretion is identified as the incretin effect.
The first indication that incretins exist came from the observation that an oral glucose load is more effective at stimulating insulin secretion than glucose given intravenously. It was subsequently discovered that two hormones (GIP and GLP-1) that are released from the upper and lower bowel enhance glucose-dependent insulin release. This increased effect of oral glucose on insulin secretion is identified as the incretin effect.Evidence
DPP-4 Inhibitors versus Other Antidiabetics and Placebo in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 A 2008 Cochrane review included studies of sitagliptin (11 trials, N = 6743 patients) and vildagliptin (14 trials, N = 6121 patients) from 12 to 52 weeks’ duration. No data were published for mortality, diabetic complications, or quality of life. Compared with placebo, absolute reductions in HbA1c were sitagliptin 0.7% and vildagliptin 0.6%. Compared with the effects of other agents, no improvements in metabolic control were detected.
A 2008 Cochrane review included studies of sitagliptin (11 trials, N = 6743 patients) and vildagliptin (14 trials, N = 6121 patients) from 12 to 52 weeks’ duration. No data were published for mortality, diabetic complications, or quality of life. Compared with placebo, absolute reductions in HbA1c were sitagliptin 0.7% and vildagliptin 0.6%. Compared with the effects of other agents, no improvements in metabolic control were detected.FYI
 Exenatide is a synthetic analogue of exendin-4, a peptide found in the venom of the Gila monster, a large lizard.
Exenatide is a synthetic analogue of exendin-4, a peptide found in the venom of the Gila monster, a large lizard. Original attempts to use GLP-1 therapeutically were thwarted by its rapid inactivation by DPP-4. The actions on GLP-1 lasted for only a few minutes; therefore it had to be administered by continuous infusion. Exenatide acts as an agonist at GLP-1 receptors but is not broken down to an appreciable extent by DPP-4; thus it represents the first clinically feasible incretin analogue.
Original attempts to use GLP-1 therapeutically were thwarted by its rapid inactivation by DPP-4. The actions on GLP-1 lasted for only a few minutes; therefore it had to be administered by continuous infusion. Exenatide acts as an agonist at GLP-1 receptors but is not broken down to an appreciable extent by DPP-4; thus it represents the first clinically feasible incretin analogue.Insulins
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
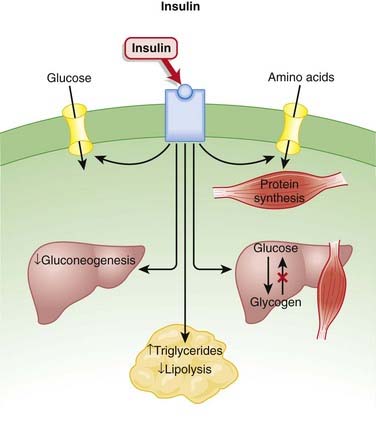
 Insulin is a hormone secreted by beta cells of the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas. It has several functions, many of which serve to lower blood glucose (Figure 14-4):
Insulin is a hormone secreted by beta cells of the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas. It has several functions, many of which serve to lower blood glucose (Figure 14-4):
 Controls the uptake, use, and storage of cellular nutrients:
Controls the uptake, use, and storage of cellular nutrients:
• The most widely known function of insulin is to promote the uptake of glucose by cells. Insulin does this by mobilizing glucose transporters (GLUT-4) on the surface of muscle and adipose tissue.
Pharmacokinetics
 As is the case with most peptides, insulin cannot be administered orally. It is most frequently delivered parenterally, typically subcutaneously.
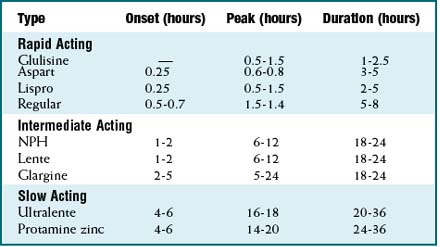
As is the case with most peptides, insulin cannot be administered orally. It is most frequently delivered parenterally, typically subcutaneously. A wide variety of insulins is available, characterized by onset and duration of action, summarized in Table 14-1.
A wide variety of insulins is available, characterized by onset and duration of action, summarized in Table 14-1.Side Effects
 Most of these signs and symptoms are secondary to the release of counterregulatory hormones such as epinephrine, glucagon, growth hormone (GH), cortisol, and norepinephrine, with epinephrine and glucagon playing the most important roles.
Most of these signs and symptoms are secondary to the release of counterregulatory hormones such as epinephrine, glucagon, growth hormone (GH), cortisol, and norepinephrine, with epinephrine and glucagon playing the most important roles. Mild hypoglycemia is typically managed by patients with intake of sugar, preferably glucose. More severe cases can be managed with intravenous glucose, or with glucagon, a hormone with actions opposite to those of insulin.
Mild hypoglycemia is typically managed by patients with intake of sugar, preferably glucose. More severe cases can be managed with intravenous glucose, or with glucagon, a hormone with actions opposite to those of insulin.Important Notes
 Recombinant human insulin was a very early example of the use of biotechnology in drug development. Insulins were originally derived from beef (bovine) or pork (porcine) sources, and these forms of insulin are still used in some areas of the world. As they were not of human origin, bovine and porcine insulins elicited immune responses that either made their administration unpredictable or in some cases led to hypersensitivity reactions. Porcine insulin differs from human by one amino acid, and bovine by three amino acids; therefore bovine insulin is more prone to cause immunogenic reactions.
Recombinant human insulin was a very early example of the use of biotechnology in drug development. Insulins were originally derived from beef (bovine) or pork (porcine) sources, and these forms of insulin are still used in some areas of the world. As they were not of human origin, bovine and porcine insulins elicited immune responses that either made their administration unpredictable or in some cases led to hypersensitivity reactions. Porcine insulin differs from human by one amino acid, and bovine by three amino acids; therefore bovine insulin is more prone to cause immunogenic reactions. The beta cells of the pancreas actually secrete a 110–amino acid polypeptide called preproinsulin, which is cleaved to proinsulin in the endoplasmic reticulum and then to insulin in the Golgi and secretory granules. Insulin is composed of two polypeptide chains: an A chain of 21 amino acids and a B chain of 30 amino acids. Modification of these chains has yielded several different analogues of insulin with different onset times and duration.
The beta cells of the pancreas actually secrete a 110–amino acid polypeptide called preproinsulin, which is cleaved to proinsulin in the endoplasmic reticulum and then to insulin in the Golgi and secretory granules. Insulin is composed of two polypeptide chains: an A chain of 21 amino acids and a B chain of 30 amino acids. Modification of these chains has yielded several different analogues of insulin with different onset times and duration.Evidence
Short-Acting Analogues versus Regular Insulin
 A 2006 Cochrane review (49 trials, N = 8274 participants) assessed the effects of short-acting insulin analogues versus regular human insulin. There were minimal differences in efficacy. In patients with type 1 diabetes, the weighted mean difference (WMD) of HbA1c was −0.1% in favor of short-acting insulin analogues versus insulin, and in patients with type 2 diabetes there was no difference. In type 1 diabetes the incidence of severe hypoglycemia was lower for insulin analogues versus insulin (median 22 versus 46 episodes per 100 person-years). In type 2 diabetes there were also fewer severe hypoglycemia events with analogues versus insulin (median 0.3 versus 1.4 per 100 person-years).
A 2006 Cochrane review (49 trials, N = 8274 participants) assessed the effects of short-acting insulin analogues versus regular human insulin. There were minimal differences in efficacy. In patients with type 1 diabetes, the weighted mean difference (WMD) of HbA1c was −0.1% in favor of short-acting insulin analogues versus insulin, and in patients with type 2 diabetes there was no difference. In type 1 diabetes the incidence of severe hypoglycemia was lower for insulin analogues versus insulin (median 22 versus 46 episodes per 100 person-years). In type 2 diabetes there were also fewer severe hypoglycemia events with analogues versus insulin (median 0.3 versus 1.4 per 100 person-years).Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
 A 2009 Cochrane review (eight trials, N = 1418 women) compared the effects of various treatment policies with one another or with routine antenatal care for gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) on both maternal and infant outcomes. Intensive management (including dietary advice and insulin) reduced the risk of preeclampsia compared with results of routine antenatal care (relative risk [RR] 0.65), based on one trial of 1000 participants. The risk of the composite outcome of perinatal morbidity (death, shoulder dystocia, bone fracture, and nerve palsy) was also reduced for those on intensive therapy for mild GDM versus routine antenatal care (RR 0.32), based on one trial of 1030 infants. Note that gestational diabetes leads to large babies, which can then experience complications in the birthing process because of their size.
A 2009 Cochrane review (eight trials, N = 1418 women) compared the effects of various treatment policies with one another or with routine antenatal care for gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) on both maternal and infant outcomes. Intensive management (including dietary advice and insulin) reduced the risk of preeclampsia compared with results of routine antenatal care (relative risk [RR] 0.65), based on one trial of 1000 participants. The risk of the composite outcome of perinatal morbidity (death, shoulder dystocia, bone fracture, and nerve palsy) was also reduced for those on intensive therapy for mild GDM versus routine antenatal care (RR 0.32), based on one trial of 1030 infants. Note that gestational diabetes leads to large babies, which can then experience complications in the birthing process because of their size.FYI
 Banting and Best are credited with the discovery of insulin in the 1920s. In essence, they were the first to isolate and identify insulin and to use this “pancreatic extract” in patients. This built on work that had begun in the late 1880s, when the pancreas had been identified as playing a role in diabetes, and work at the turn of the century that had first used pancreatic extracts to treat diabetic animals and (unsuccessfully) patients.
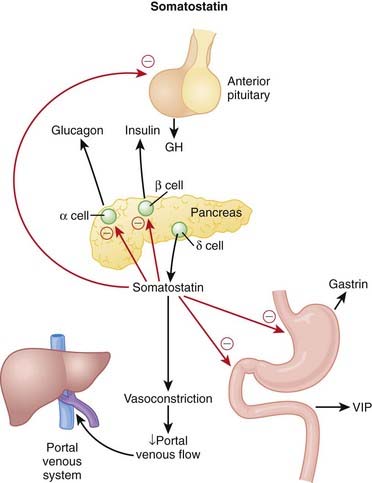
Banting and Best are credited with the discovery of insulin in the 1920s. In essence, they were the first to isolate and identify insulin and to use this “pancreatic extract” in patients. This built on work that had begun in the late 1880s, when the pancreas had been identified as playing a role in diabetes, and work at the turn of the century that had first used pancreatic extracts to treat diabetic animals and (unsuccessfully) patients. The islets of Langerhans have other specialized cells that are responsible for the secretion of glucagon (alpha cells) and somatostatin (delta cells).
The islets of Langerhans have other specialized cells that are responsible for the secretion of glucagon (alpha cells) and somatostatin (delta cells). NPH insulin is created by treating regular insulin with protamine and zinc at a neutral pH (7.2). This results in a fine precipitate of protamine zinc insulin that provides for slow and even absorption when administered subcutaneously. Hagedorn (the H in NPH) was the name of the scientist who created the formulation.
NPH insulin is created by treating regular insulin with protamine and zinc at a neutral pH (7.2). This results in a fine precipitate of protamine zinc insulin that provides for slow and even absorption when administered subcutaneously. Hagedorn (the H in NPH) was the name of the scientist who created the formulation.Meglitinides
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
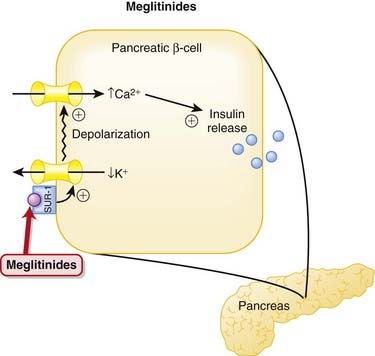
 The meglitinides are insulin secretagogues, stimulating the release of insulin from pancreatic beta cells in a manner similar to that of the sulfonylureas (Figure 14-5).
The meglitinides are insulin secretagogues, stimulating the release of insulin from pancreatic beta cells in a manner similar to that of the sulfonylureas (Figure 14-5). They bind to a beta cell sulfonylurea receptor (SUR-1) that is associated with an inward rectifier adenosine triphosphate (ATP)–sensitive potassium channel. Binding leads to depolarization, which then opens a voltage-gated calcium channel, leading to calcium influx and insulin release.
They bind to a beta cell sulfonylurea receptor (SUR-1) that is associated with an inward rectifier adenosine triphosphate (ATP)–sensitive potassium channel. Binding leads to depolarization, which then opens a voltage-gated calcium channel, leading to calcium influx and insulin release.Pharmacokinetics
 The meglitinides are rapidly and completely absorbed, achieving peak plasma concentrations in less than 1 hour after oral administration.
The meglitinides are rapidly and completely absorbed, achieving peak plasma concentrations in less than 1 hour after oral administration. They are metabolized in the liver, and have a short elimination half-life of 1 to 2 hours. Dose adjustments should be considered in patients with impaired liver function.
They are metabolized in the liver, and have a short elimination half-life of 1 to 2 hours. Dose adjustments should be considered in patients with impaired liver function.Contraindication
 Concomitant gemfibrozil and repaglinide: Gemfibrozil (a fibrate) significantly reduces the metabolism of repaglinide, leading to as much as an eightfold increase in repaglinide levels. In some cases this has lead to severe episodes of hypoglycemia. Gemfibrozil is used to lower cholesterol; multiple risk-reduction strategies are frequently used in patients with multiple risk factors for atherosclerosis and thus there is a risk that these two drugs can be co-administered.
Concomitant gemfibrozil and repaglinide: Gemfibrozil (a fibrate) significantly reduces the metabolism of repaglinide, leading to as much as an eightfold increase in repaglinide levels. In some cases this has lead to severe episodes of hypoglycemia. Gemfibrozil is used to lower cholesterol; multiple risk-reduction strategies are frequently used in patients with multiple risk factors for atherosclerosis and thus there is a risk that these two drugs can be co-administered.Important Notes
 The rapid onset of action of the meglitinides, particularly nateglinide, makes them useful agents in the management of postprandial hyperglycemia. Patients can take these agents just before eating, allowing them flexibility in choosing the timing of their meals. The sulfonylureas do not allow for this much flexibility.
The rapid onset of action of the meglitinides, particularly nateglinide, makes them useful agents in the management of postprandial hyperglycemia. Patients can take these agents just before eating, allowing them flexibility in choosing the timing of their meals. The sulfonylureas do not allow for this much flexibility.Evidence
Meglitinides versus One Another, Metformin, and Placebo
 A 2007 Cochrane review (15 trials, N = 3781 patients) did not find any studies that reported on morbidity or mortality. Compared with the effects of placebo, HbA1c was reduced by both repaglinide (0.1% to 2.1%) and nateglinide (0.2% to 0.6%). In trials comparing the two agents, repaglinide performed better than nateglinide with respect to reducing HbA1c. Repaglinide had similar reductions in HbA1c to metformin (three studies, N = 248 patients), whereas nateglinide had similar or slightly less of an effect on HbA1c compared to metformin (one study, N = 355 patients).
A 2007 Cochrane review (15 trials, N = 3781 patients) did not find any studies that reported on morbidity or mortality. Compared with the effects of placebo, HbA1c was reduced by both repaglinide (0.1% to 2.1%) and nateglinide (0.2% to 0.6%). In trials comparing the two agents, repaglinide performed better than nateglinide with respect to reducing HbA1c. Repaglinide had similar reductions in HbA1c to metformin (three studies, N = 248 patients), whereas nateglinide had similar or slightly less of an effect on HbA1c compared to metformin (one study, N = 355 patients).Sulfonylureas
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus appear to have an impaired insulin response (insulin resistance) and an inappropriate increase in glucagon release compared with normal individuals. Glucagon is a hormone that does the opposite of insulin—it increases blood glucose.
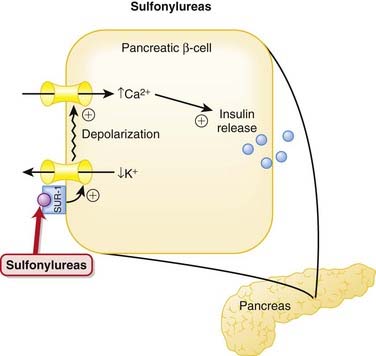
Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus appear to have an impaired insulin response (insulin resistance) and an inappropriate increase in glucagon release compared with normal individuals. Glucagon is a hormone that does the opposite of insulin—it increases blood glucose. The sulfonylureas are insulin secretagogues, meaning that they stimulate insulin release from the beta cells of the pancreas.
The sulfonylureas are insulin secretagogues, meaning that they stimulate insulin release from the beta cells of the pancreas. They bind to a beta-cell sulfonylurea receptor (SUR-1) that is associated with an inward rectifier ATP-sensitive potassium channel. Binding leads to depolarization, which then opens a voltage-gated calcium channel, leading to calcium influx and insulin release (Figure 14-6).
They bind to a beta-cell sulfonylurea receptor (SUR-1) that is associated with an inward rectifier ATP-sensitive potassium channel. Binding leads to depolarization, which then opens a voltage-gated calcium channel, leading to calcium influx and insulin release (Figure 14-6). Sulfonylureas also reduce serum glucagon levels. Although the mechanism behind this has not been definitively established, sulfonylureas enhance the release of insulin and somatostatin, and it is believed that one or both of these effects may in turn lead to a reduction in glucagon release from pancreatic alpha cells.
Sulfonylureas also reduce serum glucagon levels. Although the mechanism behind this has not been definitively established, sulfonylureas enhance the release of insulin and somatostatin, and it is believed that one or both of these effects may in turn lead to a reduction in glucagon release from pancreatic alpha cells.Pharmacokinetics
 The elimination half-lives of first-generation agents vary considerably, whereas the half-lives of second-generation agents are typically short (3 to 5 hours). However, the biologic half-lives, the amount of time for which they are effective, is longer than their elimination half-lives would suggest, for reasons that are still unknown.
The elimination half-lives of first-generation agents vary considerably, whereas the half-lives of second-generation agents are typically short (3 to 5 hours). However, the biologic half-lives, the amount of time for which they are effective, is longer than their elimination half-lives would suggest, for reasons that are still unknown. All sulfonylureas are metabolized by the liver and excreted in urine. Because of the risk of hypoglycemia, dose adjustments must be considered in patients with hepatic impairment. A small proportion is also excreted unchanged in urine, therefore caution should also be exercised in patients with renal impairment.
All sulfonylureas are metabolized by the liver and excreted in urine. Because of the risk of hypoglycemia, dose adjustments must be considered in patients with hepatic impairment. A small proportion is also excreted unchanged in urine, therefore caution should also be exercised in patients with renal impairment.Side Effects
 Hypoglycemia: Hypoglycemia is caused by oversecretion of insulin and occurs more frequently with glyburide. Glyburide may impair the body’s ability to prevent endogenous insulin secretion during hypoglycemia.
Hypoglycemia: Hypoglycemia is caused by oversecretion of insulin and occurs more frequently with glyburide. Glyburide may impair the body’s ability to prevent endogenous insulin secretion during hypoglycemia. Flushing: Flushing occurs when these drugs are taken with alcohol and is more common with older agents like chlorpropamide.
Flushing: Flushing occurs when these drugs are taken with alcohol and is more common with older agents like chlorpropamide.Important Notes
 Because of concerns over hypoglycemia, the sulfonylureas, particularly glyburide, should be initiated at a low dose, and patients should be observed carefully for changes in blood glucose over the first few weeks of therapy. Patients with irregular diets or who drink ethanol to excess are at increased risk for hypoglycemia.
Because of concerns over hypoglycemia, the sulfonylureas, particularly glyburide, should be initiated at a low dose, and patients should be observed carefully for changes in blood glucose over the first few weeks of therapy. Patients with irregular diets or who drink ethanol to excess are at increased risk for hypoglycemia. The hypoglycemic effects of the sulfonylureas tend to diminish with time. The most likely explanation for this reduced response is progressive loss of beta cells from diabetes.
The hypoglycemic effects of the sulfonylureas tend to diminish with time. The most likely explanation for this reduced response is progressive loss of beta cells from diabetes.Evidence
Glyburide for Hypoglycemic Events and Cardiovascular Risk
 A 2007 systematic review (21 trials, N = 7047 patients) compared glyburide with other insulin secretagogues and insulin for hypoglycemic and cardiovascular events. The authors found that glyburide was associated with a greater risk of experiencing a hypoglycemic event compared with other secretagogues (RR 1.52) or other sulfonylureas (1.83). Glyburide was not associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular events, death, or end-of-trial weight gain compared with other secretagogues.
A 2007 systematic review (21 trials, N = 7047 patients) compared glyburide with other insulin secretagogues and insulin for hypoglycemic and cardiovascular events. The authors found that glyburide was associated with a greater risk of experiencing a hypoglycemic event compared with other secretagogues (RR 1.52) or other sulfonylureas (1.83). Glyburide was not associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular events, death, or end-of-trial weight gain compared with other secretagogues.FYI
 The sulfonylureas were the first oral agents for type 2 diabetes and have been in use for over 50 years.
The sulfonylureas were the first oral agents for type 2 diabetes and have been in use for over 50 years. After a large study conducted in the 1970s found increased cardiovascular mortality with sulfonylureas, for many years there was an association drawn between this class and elevated cardiovascular risk. Subsequent studies have not found this association, although this class is still believed in some circles to carry this risk.
After a large study conducted in the 1970s found increased cardiovascular mortality with sulfonylureas, for many years there was an association drawn between this class and elevated cardiovascular risk. Subsequent studies have not found this association, although this class is still believed in some circles to carry this risk.Thiazolidinediones
MOA (Mechanism Of Action)
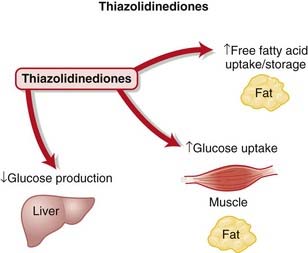
 The PPAR-γ receptors are a complex family of receptors found in the cell nucleus in muscle, fat, and liver. Among other roles, they regulate expression of genes responsible for lipid and protein metabolism, insulin signal transduction, and adipocyte and other tissue differentiation. It is through a combination of these effects that they are thought to decrease insulin resistance, although the relative importance of each has not been established (Figure 14-7).
The PPAR-γ receptors are a complex family of receptors found in the cell nucleus in muscle, fat, and liver. Among other roles, they regulate expression of genes responsible for lipid and protein metabolism, insulin signal transduction, and adipocyte and other tissue differentiation. It is through a combination of these effects that they are thought to decrease insulin resistance, although the relative importance of each has not been established (Figure 14-7). The TZDs are thought to exert their effects at PPAR-γ receptors in adipose tissue by promoting uptake and storage of free fatty acids (FFAs) in adipose tissue. They accomplish this by increasing the number of small adipocytes that store FFAs while decreasing the number of large adipocytes that release FFAs. Through a variety of poorly understood mechanisms, high concentrations of FFAs are thought to promote insulin resistance.
The TZDs are thought to exert their effects at PPAR-γ receptors in adipose tissue by promoting uptake and storage of free fatty acids (FFAs) in adipose tissue. They accomplish this by increasing the number of small adipocytes that store FFAs while decreasing the number of large adipocytes that release FFAs. Through a variety of poorly understood mechanisms, high concentrations of FFAs are thought to promote insulin resistance. The TZDs also promote the expression and translocation of glucose transporters in muscle and adipose tissue. This increases glucose uptake into muscle and adipose tissue. The TZDs also may reduce hepatic production of glucose, although the mechanism by which this is accomplished is unclear.
The TZDs also promote the expression and translocation of glucose transporters in muscle and adipose tissue. This increases glucose uptake into muscle and adipose tissue. The TZDs also may reduce hepatic production of glucose, although the mechanism by which this is accomplished is unclear. Activation of the PPAR-γ receptor also has several other effects, including inhibition of proinflammatory genes and cytokine production, as well as increased adiponectin production. Adiponectin is thought to play several protective roles in the body, stimulating glucose uptake in muscle, protecting against atherosclerosis and endothelial cell apoptosis, and stabilizing plaques.
Activation of the PPAR-γ receptor also has several other effects, including inhibition of proinflammatory genes and cytokine production, as well as increased adiponectin production. Adiponectin is thought to play several protective roles in the body, stimulating glucose uptake in muscle, protecting against atherosclerosis and endothelial cell apoptosis, and stabilizing plaques.Pharmacokinetics
Side Effects
 Weight gain: Weight gain is caused by redistribution of adipocytes from visceral to subcutaneous regions.
Weight gain: Weight gain is caused by redistribution of adipocytes from visceral to subcutaneous regions. Edema: TZDs promote retention of sodium and water by up-regulating tubular transporters for sodium and reducing glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
Edema: TZDs promote retention of sodium and water by up-regulating tubular transporters for sodium and reducing glomerular filtration rate (GFR).Important Notes
 The PPAR-γ receptor has an extensive list of biologic actions, making it difficult to sort out the actions of agonists such as the TZDs. The most difficult effects to sort out are the cardiovascular effects. The TZDs initially appeared to have beneficial cardiovascular effects, but recently adverse cardiovascular effects, specifically heart failure, have emerged.
The PPAR-γ receptor has an extensive list of biologic actions, making it difficult to sort out the actions of agonists such as the TZDs. The most difficult effects to sort out are the cardiovascular effects. The TZDs initially appeared to have beneficial cardiovascular effects, but recently adverse cardiovascular effects, specifically heart failure, have emerged.Evidence
Rosiglitazone versus Oral Antidiabetics or Placebo in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 A 2007 Cochrane review (18 trials, N = 3888 patients) found no improvement in mortality, morbidity, adverse effects, and quality of life in trials with a follow-up of at least 24 weeks. HbA1c was not improved by rosiglitazone compared with other oral antidiabetic agents. Edema occurred significantly more frequently in rosiglitazone-treated patients, and the ADOPT study identified an increased risk of cardiovascular events with rosiglitazone. Data from ADOPT and another trial, PROactive, suggest increased risk of fractures in women treated with rosiglitazone.
A 2007 Cochrane review (18 trials, N = 3888 patients) found no improvement in mortality, morbidity, adverse effects, and quality of life in trials with a follow-up of at least 24 weeks. HbA1c was not improved by rosiglitazone compared with other oral antidiabetic agents. Edema occurred significantly more frequently in rosiglitazone-treated patients, and the ADOPT study identified an increased risk of cardiovascular events with rosiglitazone. Data from ADOPT and another trial, PROactive, suggest increased risk of fractures in women treated with rosiglitazone.Pioglitazone versus Oral Antidiabetics or Placebo in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 A 2006 Cochrane review (22 trials, N = 6200 patients) did not find convincing evidence of improvement in mortality, morbidity, adverse effects, and health-related quality of life. Improvements in HbA1c were similar with pioglitazone compared with other oral antidiabetics. Edema occurred significantly more frequently with pioglitazone.
A 2006 Cochrane review (22 trials, N = 6200 patients) did not find convincing evidence of improvement in mortality, morbidity, adverse effects, and health-related quality of life. Improvements in HbA1c were similar with pioglitazone compared with other oral antidiabetics. Edema occurred significantly more frequently with pioglitazone.FYI
 The PPAR-γ receptor is very large and has several different distinct ligands, including warfarin, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, some nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and the angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) telmisartan.
The PPAR-γ receptor is very large and has several different distinct ligands, including warfarin, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, some nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and the angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) telmisartan.Glucagon
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 Glucagon is a 29–amino acid protein secreted from the alpha cells in the pancreas and has significant homology with secretin, vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP), and GI inhibitory polypeptide.
Glucagon is a 29–amino acid protein secreted from the alpha cells in the pancreas and has significant homology with secretin, vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP), and GI inhibitory polypeptide. Glucagon secretion is under the control of the sympathetic system and is regulated by the following:
Glucagon secretion is under the control of the sympathetic system and is regulated by the following:
 The main effects of glucagon are on the liver, mediated by G protein–linked glucagon receptors and increased intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). The important specific actions include the following (Figure 14-8):
The main effects of glucagon are on the liver, mediated by G protein–linked glucagon receptors and increased intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). The important specific actions include the following (Figure 14-8):
 Because glucagon acts to increase blood sugar, it works against insulin, which acts to lower blood sugar.
Because glucagon acts to increase blood sugar, it works against insulin, which acts to lower blood sugar. In cardiac tissue glucagon binds a glucagon receptor and raises cAMP, resulting in a positive inotropic (contractility) and chronotropic (heart rate) effect on the heart. This is the mechanism by which it is therapeutic in β-blocker and calcium channel blocker overdoses; importantly, its action is independent of β receptors or calcium channels.
In cardiac tissue glucagon binds a glucagon receptor and raises cAMP, resulting in a positive inotropic (contractility) and chronotropic (heart rate) effect on the heart. This is the mechanism by which it is therapeutic in β-blocker and calcium channel blocker overdoses; importantly, its action is independent of β receptors or calcium channels.Important Notes
 Intravenous or oral glucose is the first-line treatment for hypoglycemia. Glucagon is the second-line treatment. Insulin overdoses are usually not treated with glucagon unless hypoglycemia is refractory to glucose administration.
Intravenous or oral glucose is the first-line treatment for hypoglycemia. Glucagon is the second-line treatment. Insulin overdoses are usually not treated with glucagon unless hypoglycemia is refractory to glucose administration. Glucagon decreases hepatic glycogen but does not decrease skeletal muscle glycogen because there are no glucagon receptors on skeletal muscle.
Glucagon decreases hepatic glycogen but does not decrease skeletal muscle glycogen because there are no glucagon receptors on skeletal muscle. Although some drugs that treat acute heart failure result in an increase in cAMP (β agonists and phosphodiesterase inhibitors), glucagon is not used for treating heart failure despite its similar action on cAMP.
Although some drugs that treat acute heart failure result in an increase in cAMP (β agonists and phosphodiesterase inhibitors), glucagon is not used for treating heart failure despite its similar action on cAMP.Advanced
 Proglucagon is the precursor to glucagon and if cleaved at different locations also gives rise to glucagon-like peptides (GLP-1 and GLP-2), called incretins. Incretins are themselves a class of drugs used for diabetes management. GLP-1 and GLP-2 are secreted from intestinal cells and are involved with insulin and glucagon secretion, gastric emptying, intestinal blood flow, and permeability and appetite satiety.
Proglucagon is the precursor to glucagon and if cleaved at different locations also gives rise to glucagon-like peptides (GLP-1 and GLP-2), called incretins. Incretins are themselves a class of drugs used for diabetes management. GLP-1 and GLP-2 are secreted from intestinal cells and are involved with insulin and glucagon secretion, gastric emptying, intestinal blood flow, and permeability and appetite satiety.Evidence
 There are no human controlled studies of glucagon use in β-blocker or calcium channel blocker therapy. However, “the available animal data, human clinical experience, and minimal adverse effect profile support the use of glucagon early in the course of both β-blocker and calcium channel blocker toxicity.”
There are no human controlled studies of glucagon use in β-blocker or calcium channel blocker therapy. However, “the available animal data, human clinical experience, and minimal adverse effect profile support the use of glucagon early in the course of both β-blocker and calcium channel blocker toxicity.”FYI
 With the discovery that propranolol did not prevent the positive inotropic action of glucagon in cats and dogs, it was suggested that there was the possibility that glucagon may be useful in the treatment of heart failure induced by β-blockers; subsequently the logic was extended to the treatment of calcium channel blocker overdose.
With the discovery that propranolol did not prevent the positive inotropic action of glucagon in cats and dogs, it was suggested that there was the possibility that glucagon may be useful in the treatment of heart failure induced by β-blockers; subsequently the logic was extended to the treatment of calcium channel blocker overdose.Estrogens
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 Estrogens enter the cell passively (no receptor required) and bind to estrogen receptors in the nucleus, which then dimerize and bind DNA directly to regions called estrogen-responsive elements (EREs) and influence gene transcription.
Estrogens enter the cell passively (no receptor required) and bind to estrogen receptors in the nucleus, which then dimerize and bind DNA directly to regions called estrogen-responsive elements (EREs) and influence gene transcription.Contraindications
 Hypercoagulable states: Estrogen is a procoagulant, and estrogen administration is a risk factor for pathologic thromboses (deep vein thrombosis [DVT] and pulmonary embolus [PE]).
Hypercoagulable states: Estrogen is a procoagulant, and estrogen administration is a risk factor for pathologic thromboses (deep vein thrombosis [DVT] and pulmonary embolus [PE]).Side Effects
Important Notes
 Estrogens do not cause HTN at the doses in which they are currently prescribed but can cause HTN at very high doses.
Estrogens do not cause HTN at the doses in which they are currently prescribed but can cause HTN at very high doses. Estrogen is prothrombotic. It increases the probability of clot formation. Bleeding is a potential complication of natural childbirth, and the prothrombotic effects of estrogen are therefore beneficial during this time.
Estrogen is prothrombotic. It increases the probability of clot formation. Bleeding is a potential complication of natural childbirth, and the prothrombotic effects of estrogen are therefore beneficial during this time. The natural progression of sex hormone synthesis is as follows: progestins → androgens → estrogens (Figure 14-10). The similarity to aldosterone probably accounts for the water retention properties of sex hormones.
The natural progression of sex hormone synthesis is as follows: progestins → androgens → estrogens (Figure 14-10). The similarity to aldosterone probably accounts for the water retention properties of sex hormones.Evidence
(Note that many studies also include progesterone.)
 Many studies, often with different methodologies, have resulted in many results; summarizing is difficult because of the heterogeneity of studies that exists. Patient differences (age, gravida status, time since menopause) and drug differences (estrogen only versus estrogen with progesterone, dose, duration, estrogen formulation, estrogen delivery method) are some examples of the differences among studies. A very small subset of the evidence is presented here.
Many studies, often with different methodologies, have resulted in many results; summarizing is difficult because of the heterogeneity of studies that exists. Patient differences (age, gravida status, time since menopause) and drug differences (estrogen only versus estrogen with progesterone, dose, duration, estrogen formulation, estrogen delivery method) are some examples of the differences among studies. A very small subset of the evidence is presented here.
 Endometrial cancer risk: An analysis of 45 RCTs with 38,702 postmenopausal women demonstrated that unopposed estrogen (without any progesterone coadministered) of any dose for a duration of only 1 year increases risk of endometrial hyperplasia (and by extension, endometrial cancer) in patients being treated for menopausal symptoms. This effect increased with increasing dose of estrogen and increasing duration of administration.
Endometrial cancer risk: An analysis of 45 RCTs with 38,702 postmenopausal women demonstrated that unopposed estrogen (without any progesterone coadministered) of any dose for a duration of only 1 year increases risk of endometrial hyperplasia (and by extension, endometrial cancer) in patients being treated for menopausal symptoms. This effect increased with increasing dose of estrogen and increasing duration of administration. Cardiovascular risk: A single large double-blind RCT of 10,739 postmenopausal women comparing estrogen with placebo demonstrated no difference in myocardial infarction or cardiac death. However, the hazard ratio for stroke was 1.39, indicating an almost 40% increase in risk for stroke. Average follow-up time was 6.8 years.
Cardiovascular risk: A single large double-blind RCT of 10,739 postmenopausal women comparing estrogen with placebo demonstrated no difference in myocardial infarction or cardiac death. However, the hazard ratio for stroke was 1.39, indicating an almost 40% increase in risk for stroke. Average follow-up time was 6.8 years. Bone health (bone density, fractures):
Bone health (bone density, fractures):
• An analysis in 2008 of 13 RCTs (two were placebo controlled), provides evidence that combined hormone oral contraceptives does not affect bone health. Depot progesterone alone (depot medroxyprogesterone acetate or DMPA) was associated with decreased bone density. Note that oral contraceptives would be administered to women of childbearing age.
 DVT risk: In a 2006 RCT, 10,739 women followed for an average of 7.1 years demonstrated a rate of venous thrombosis of 3.0 per 1000 person-years in the estrogen group versus 2.2 in the placebo group. This represents a statistically significant hazard ratio of 1.47 (47% more likely to get a blood clot if on estrogen). Compared with estrogen plus progesterone, it appears that the risk is greater with combination therapy versus estrogen alone.
DVT risk: In a 2006 RCT, 10,739 women followed for an average of 7.1 years demonstrated a rate of venous thrombosis of 3.0 per 1000 person-years in the estrogen group versus 2.2 in the placebo group. This represents a statistically significant hazard ratio of 1.47 (47% more likely to get a blood clot if on estrogen). Compared with estrogen plus progesterone, it appears that the risk is greater with combination therapy versus estrogen alone. Cognitive function: A meta-analysis in 2007 of 16 studies with 10,114 women with normal brain function demonstrated no benefit in prevention of cognitive decline over a period of 3 to 5 years compared with placebo. In fact, there was a slight trend toward better function with placebo. It has been previously suggested that estrogen deficiency is associated with decreased cognitive function.
Cognitive function: A meta-analysis in 2007 of 16 studies with 10,114 women with normal brain function demonstrated no benefit in prevention of cognitive decline over a period of 3 to 5 years compared with placebo. In fact, there was a slight trend toward better function with placebo. It has been previously suggested that estrogen deficiency is associated with decreased cognitive function. Weight gain: An analysis of available literature in 2008 included five RCTs (957 women) comparing hormone with placebo and did not find strong evidence to support an association between weight gain and the use of oral contraceptives; however, most studies were not designed to study this particular outcome.
Weight gain: An analysis of available literature in 2008 included five RCTs (957 women) comparing hormone with placebo and did not find strong evidence to support an association between weight gain and the use of oral contraceptives; however, most studies were not designed to study this particular outcome. Acne: A meta-analysis in 2009 found 25 trials evaluating combined hormones and acne treatment. Of the 25, seven were placebo controlled, and these studies showed improvement in acne with hormone therapy. The remaining studies compared different hormone combinations and doses. Hormones containing cyproterone acetate might be superior in treating acne, but data are somewhat conflicting.
Acne: A meta-analysis in 2009 found 25 trials evaluating combined hormones and acne treatment. Of the 25, seven were placebo controlled, and these studies showed improvement in acne with hormone therapy. The remaining studies compared different hormone combinations and doses. Hormones containing cyproterone acetate might be superior in treating acne, but data are somewhat conflicting.FYI
 A state of estrus in mammals (excluding humans) is the time around ovulation when the female is receptive to sexual activity (being in heat); estrogen peaks right before this time in the cycle.
A state of estrus in mammals (excluding humans) is the time around ovulation when the female is receptive to sexual activity (being in heat); estrogen peaks right before this time in the cycle.Estrogen Receptor Antagonists
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 There are several forms of estrogen, but 17β-estradiol is the predominant form intracellularly. Estrogens have multiple effects in females, from maintaining bone to regulating the menstrual cycle and development. Important effects of estrogen include the following:
There are several forms of estrogen, but 17β-estradiol is the predominant form intracellularly. Estrogens have multiple effects in females, from maintaining bone to regulating the menstrual cycle and development. Important effects of estrogen include the following:
 Estrogens also mediate cell proliferation, in both normal and malignant cells. There are two estrogen receptors (ERα and ERβ), both of which either increase or decrease transcription of target genes.
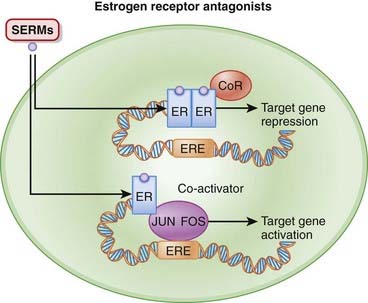
Estrogens also mediate cell proliferation, in both normal and malignant cells. There are two estrogen receptors (ERα and ERβ), both of which either increase or decrease transcription of target genes. On binding of estrogen, the receptors dimerize (join together) and then bind to EREs, typically found in the promoter region of target genes. A promoter is a region of a gene that facilitates transcription. Binding of agonist to the estrogen receptor also recruits coactivators, which help to stimulate transcription. The net effect of all of this is to initiate transcription (Figure 14-11).
On binding of estrogen, the receptors dimerize (join together) and then bind to EREs, typically found in the promoter region of target genes. A promoter is a region of a gene that facilitates transcription. Binding of agonist to the estrogen receptor also recruits coactivators, which help to stimulate transcription. The net effect of all of this is to initiate transcription (Figure 14-11). Estrogen receptor antagonists inhibit transcription by promoting the binding of co-repressors (CoRs) to the ERE. CoRs inhibit transcription.
Estrogen receptor antagonists inhibit transcription by promoting the binding of co-repressors (CoRs) to the ERE. CoRs inhibit transcription. The SERMs are partial agonists, antagonizing the effects of estrogen in some tissues (breast) and stimulating estrogen receptors in others (bone, brain, liver). This is in contrast to the estrogen antagonists (e.g., clomiphene), which block estrogen receptors in all tissues.
The SERMs are partial agonists, antagonizing the effects of estrogen in some tissues (breast) and stimulating estrogen receptors in others (bone, brain, liver). This is in contrast to the estrogen antagonists (e.g., clomiphene), which block estrogen receptors in all tissues. Some breast cancers express estrogen receptors, and estrogen antagonists are used to treat these tumors.
Some breast cancers express estrogen receptors, and estrogen antagonists are used to treat these tumors. Clomiphene has a unique mechanism in that it stimulates the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). It does this by antagonizing the negative feedback of estrogen on gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). Estrogen normally has an inhibitory effect on GnRH, so through blocking of this inhibitory effect, more FSH is released, promoting ovulation in patients with infertility.
Clomiphene has a unique mechanism in that it stimulates the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). It does this by antagonizing the negative feedback of estrogen on gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). Estrogen normally has an inhibitory effect on GnRH, so through blocking of this inhibitory effect, more FSH is released, promoting ovulation in patients with infertility.Pharmacokinetics
 Tamoxifen’s elimination is biphasic, as the parent drug has a much shorter half-life (6 hours) than the active metabolite (5 to 10 days). The major route of elimination for tamoxifen is through metabolism by CYP3A4 and CYP2D6.
Tamoxifen’s elimination is biphasic, as the parent drug has a much shorter half-life (6 hours) than the active metabolite (5 to 10 days). The major route of elimination for tamoxifen is through metabolism by CYP3A4 and CYP2D6.Side Effects
 Endometrial: Some of the partial agonists have estrogen agonist effects on the endometrium, leading to abnormal cell growth. This can manifest as increased endometrial thickness, endometrial polyps, leiomyomas, and even endometrial cancer.
Endometrial: Some of the partial agonists have estrogen agonist effects on the endometrium, leading to abnormal cell growth. This can manifest as increased endometrial thickness, endometrial polyps, leiomyomas, and even endometrial cancer. Thromboembolism: Increased risk of thromboembolic events, including pulmonary embolism, have been observed in large studies.
Thromboembolism: Increased risk of thromboembolic events, including pulmonary embolism, have been observed in large studies.Important Notes
 Although they are all partial agonists, the SERMs are a heterogeneous drug class because they have different effects (agonist or antagonist) depending on the tissue they target.
Although they are all partial agonists, the SERMs are a heterogeneous drug class because they have different effects (agonist or antagonist) depending on the tissue they target. Raloxifene began as an investigational drug for treatment of breast cancer but was first approved for its beneficial effects in osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Since then it has been “rediscovered” as a preventive therapy for postmenopausal women at high risk of invasive breast cancer.
Raloxifene began as an investigational drug for treatment of breast cancer but was first approved for its beneficial effects in osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Since then it has been “rediscovered” as a preventive therapy for postmenopausal women at high risk of invasive breast cancer. Several large trials have reported a benefit of tamoxifen in the prevention of breast cancer, particularly in high-risk groups. The National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) P-1 trial randomized 13,388 high-risk women to either tamoxifen or placebo. The risk of estrogen receptor–positive breast cancer was reduced by 69% at 5 years. The International Breast Cancer Intervention Study (IBIS) randomized 7154 women to tamoxifen or placebo and also found a 32% reduction in the overall risk of breast cancer.
Several large trials have reported a benefit of tamoxifen in the prevention of breast cancer, particularly in high-risk groups. The National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) P-1 trial randomized 13,388 high-risk women to either tamoxifen or placebo. The risk of estrogen receptor–positive breast cancer was reduced by 69% at 5 years. The International Breast Cancer Intervention Study (IBIS) randomized 7154 women to tamoxifen or placebo and also found a 32% reduction in the overall risk of breast cancer.Evidence
Tamoxifen and Breast Cancer Treatment
 A 1998 meta-analysis (55 trials, N = 37,000) clearly established the role of tamoxifen in the treatment of estrogen receptor–positive breast cancer. The analysis included women with early breast cancer, finding that adjuvant tamoxifen for approximately 5 years reduced breast cancer recurrence by 42% and mortality by 22%.
A 1998 meta-analysis (55 trials, N = 37,000) clearly established the role of tamoxifen in the treatment of estrogen receptor–positive breast cancer. The analysis included women with early breast cancer, finding that adjuvant tamoxifen for approximately 5 years reduced breast cancer recurrence by 42% and mortality by 22%.Aromatase Inhibitors (AIs)
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
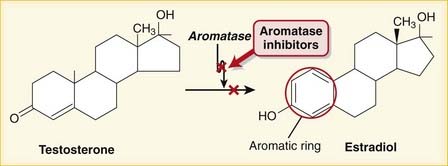
 Aromatization is the process of converting a nonaromatic ring into an aromatic ring and is catalyzed by aromatase, a P450 enzyme. Aromatization converts androgens into estrogens. Estrogens contain an aromatic six-carbon ring. Androgens do not (Figure 14-12).
Aromatization is the process of converting a nonaromatic ring into an aromatic ring and is catalyzed by aromatase, a P450 enzyme. Aromatization converts androgens into estrogens. Estrogens contain an aromatic six-carbon ring. Androgens do not (Figure 14-12). Steroid-type AIs have an androgen structure and bind the substrate binding site in a noncompetitive, irreversible fashion.
Steroid-type AIs have an androgen structure and bind the substrate binding site in a noncompetitive, irreversible fashion. Nonsteroid-type AIs bind the cytochrome P450 moiety of the enzyme and are competitive and reversible.
Nonsteroid-type AIs bind the cytochrome P450 moiety of the enzyme and are competitive and reversible. Aromatase inhibition results in the following:
Aromatase inhibition results in the following:
 Lower levels of estradiol, estrone, and estrone sulfate. This is beneficial for conditions that require lower estrogen levels, including breast cancer and precocious puberty.
Lower levels of estradiol, estrone, and estrone sulfate. This is beneficial for conditions that require lower estrogen levels, including breast cancer and precocious puberty.Important Notes
 Comparisons between AIs and SERMs:
Comparisons between AIs and SERMs:
 Aromatase is present in many tissues, including the ovaries, brain, placenta, adipose tissue, muscle, liver, breast, and estrogen-dependent breast cancer. Adipose is the primary source of estrogen production in both men and postmenopausal women.
Aromatase is present in many tissues, including the ovaries, brain, placenta, adipose tissue, muscle, liver, breast, and estrogen-dependent breast cancer. Adipose is the primary source of estrogen production in both men and postmenopausal women.Evidence
Anovulation
 A 2008 review (9 studies, N = 2573 women) examined the impact of adding letrozole to conventional infertility treatments. There were no statistically significant improvements in ovulatory cycles nor pregnancies per ovulatory cycle. Large RCTs are required to clarify the roles of AIs for anovulation therapy.
A 2008 review (9 studies, N = 2573 women) examined the impact of adding letrozole to conventional infertility treatments. There were no statistically significant improvements in ovulatory cycles nor pregnancies per ovulatory cycle. Large RCTs are required to clarify the roles of AIs for anovulation therapy.FYI
 The prototype first-generation (aminoglutethimide) and second-generation (fadrozole and formestane) AIs are no longer used because of low potency, lack of specificity, and side effects.
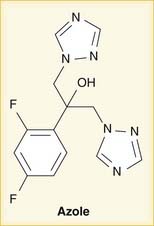
The prototype first-generation (aminoglutethimide) and second-generation (fadrozole and formestane) AIs are no longer used because of low potency, lack of specificity, and side effects. The nonsteroidal AIs contain a triazole structure. An azole is a five-membered ring that includes at least one noncarbon atom. Triazoles have three nitrogens. There is also a class of antifungals called “azoles” whose mechanism of action is also inhibition of a P450 enzyme (Figure 14-13).
The nonsteroidal AIs contain a triazole structure. An azole is a five-membered ring that includes at least one noncarbon atom. Triazoles have three nitrogens. There is also a class of antifungals called “azoles” whose mechanism of action is also inhibition of a P450 enzyme (Figure 14-13). Total body aromatization of plasma androstenedione increased from 0.5% to 10% with a rise in body weight from 100 to 400 pounds in women.
Total body aromatization of plasma androstenedione increased from 0.5% to 10% with a rise in body weight from 100 to 400 pounds in women.Progestins
Common Drugs
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 Progestins enter the cell passively (no receptor required) and bind to progesterone receptors in the nucleus, which then dimerize and bind DNA directly and influence gene transcription.
Progestins enter the cell passively (no receptor required) and bind to progesterone receptors in the nucleus, which then dimerize and bind DNA directly and influence gene transcription.Contraindications
 Severe migraine headache: There are relationships among estrogen, progesterone, and serotonin levels. Serotonin is implicated in migraine pathophysiology; administration of estrogen or progesterone can potentially exacerbate (or alleviate) migraines.
Severe migraine headache: There are relationships among estrogen, progesterone, and serotonin levels. Serotonin is implicated in migraine pathophysiology; administration of estrogen or progesterone can potentially exacerbate (or alleviate) migraines. Unexplained vaginal bleeding: Prolonged progesterone administration can cause vaginal bleeding; it is important to diagnose any pathologic causes of bleeding before starting treatment that could confound other bleeding.
Unexplained vaginal bleeding: Prolonged progesterone administration can cause vaginal bleeding; it is important to diagnose any pathologic causes of bleeding before starting treatment that could confound other bleeding.Side Effects
 Androgenic activity: Because of the similarity of progestins to androgens and the conversion of progestins to androgens, androgenic side effects are not uncommon. Levonorgestrel is the most androgenic. Third-generation progestins are less androgenic than second-generation progestins.
Androgenic activity: Because of the similarity of progestins to androgens and the conversion of progestins to androgens, androgenic side effects are not uncommon. Levonorgestrel is the most androgenic. Third-generation progestins are less androgenic than second-generation progestins.
Important Notes
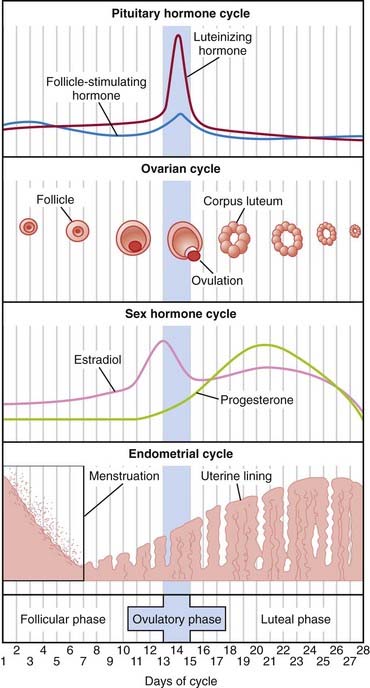
 Progesterone is secreted by the ovary, mainly by the corpus luteum during the luteal phase (second half) of the menstrual cycle. See Figure 14-9.
Progesterone is secreted by the ovary, mainly by the corpus luteum during the luteal phase (second half) of the menstrual cycle. See Figure 14-9. Bioidentical hormones are hormones that are chemically identical to what is naturally produced in the human body. Because minor chemical changes can result in a change in function, some women experience fewer side effects with bioidentical hormones.
Bioidentical hormones are hormones that are chemically identical to what is naturally produced in the human body. Because minor chemical changes can result in a change in function, some women experience fewer side effects with bioidentical hormones. Drospirenone is derived from spironolactone (an aldosterone antagonist) and also has antialdosterone effects.
Drospirenone is derived from spironolactone (an aldosterone antagonist) and also has antialdosterone effects.
 Progestins can be administered alone or in combination with estrogens for birth control. Long-term contraception (e.g., depot injections, implants, IUDs) are progestin only. Their use is associated with menstrual irregularities, including abnormal bleeding.
Progestins can be administered alone or in combination with estrogens for birth control. Long-term contraception (e.g., depot injections, implants, IUDs) are progestin only. Their use is associated with menstrual irregularities, including abnormal bleeding. HRT is administered as estrogen only or a combination of estrogen and progesterone, but not progesterone alone.
HRT is administered as estrogen only or a combination of estrogen and progesterone, but not progesterone alone.Evidence
Hormone Replacement Therapy and Cardiovascular Outcomes
 A Cochrane review in 2005 (10 studies, N = 24,000 women) compared HRT (estrogen only and estrogen combined with progesterone) with placebo or no treatment and found that there were no protective effects of HRT on all-cause mortality, cardiovascular death, or myocardial infarction. However, there was an increased risk of DVT and PE (RR 2.15) and stroke (RR 1.44) in patients treated with HRT.
A Cochrane review in 2005 (10 studies, N = 24,000 women) compared HRT (estrogen only and estrogen combined with progesterone) with placebo or no treatment and found that there were no protective effects of HRT on all-cause mortality, cardiovascular death, or myocardial infarction. However, there was an increased risk of DVT and PE (RR 2.15) and stroke (RR 1.44) in patients treated with HRT.FYI
 Gestation refers to pregnancy. The man who co-discovered progesterone in the 1930s, American medical student Willard H. Allen (later to become an obstetrician), described a pregestational proliferation of the uterus and coined the names progestin and progesterone.
Gestation refers to pregnancy. The man who co-discovered progesterone in the 1930s, American medical student Willard H. Allen (later to become an obstetrician), described a pregestational proliferation of the uterus and coined the names progestin and progesterone. The word root -sterone refers to steroid ketones, which testosterone is, but estrogen is not. This similarity of progesterone to testosterone is the reason for the androgenic side effect profile of progesterones.
The word root -sterone refers to steroid ketones, which testosterone is, but estrogen is not. This similarity of progesterone to testosterone is the reason for the androgenic side effect profile of progesterones.
 There is no aromatic ring in progesterone (as there is in estrogen). Instead, there is a ketone group (C=O) on the A ring (similar to testosterone).
There is no aromatic ring in progesterone (as there is in estrogen). Instead, there is a ketone group (C=O) on the A ring (similar to testosterone).Hormone Contraception
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
Progestins
Pharmacokinetics
 Estrogen is metabolized by CYP3A4 liver enzymes, and thus the birth control pill (BCP) can become less effective if coadministered with other drugs that are CYP3A4 inducers:
Estrogen is metabolized by CYP3A4 liver enzymes, and thus the birth control pill (BCP) can become less effective if coadministered with other drugs that are CYP3A4 inducers:
Contraindications
 Smoking is a relative contraindication because of the increased risk of thrombus and atherosclerotic disease.
Smoking is a relative contraindication because of the increased risk of thrombus and atherosclerotic disease.Side Effects
 Breakthrough bleeding is common when the BCP is started. Bleeding in cycle 1 (after starting the pill) is often reduced by cycle 4.
Breakthrough bleeding is common when the BCP is started. Bleeding in cycle 1 (after starting the pill) is often reduced by cycle 4. Although doses are not routinely reported in this textbook, doses of hormones in BCPs are important and require mention:
Although doses are not routinely reported in this textbook, doses of hormones in BCPs are important and require mention:
 Side effects are usually attributed to the estrogen; the higher the dose, the higher the probability of side effects.
Side effects are usually attributed to the estrogen; the higher the dose, the higher the probability of side effects. Progestin-related side effects are primarily androgenic: acne and hirsutism. Levonorgestrel is the most androgenic progestin.
Progestin-related side effects are primarily androgenic: acne and hirsutism. Levonorgestrel is the most androgenic progestin. Different formulations and routes of administration are associated with slightly different side effect profiles:
Different formulations and routes of administration are associated with slightly different side effect profiles:
 Progestin only: Side effects include increased breakthrough bleeding and a slightly lower efficacy for preventing pregnancy.
Progestin only: Side effects include increased breakthrough bleeding and a slightly lower efficacy for preventing pregnancy.Important Notes
 A few BCPs use iron pills instead of placebo pills during the 7 days of no hormone. This is to help maintain iron levels in women who have low iron stores because of regular menstrual blood loss.
A few BCPs use iron pills instead of placebo pills during the 7 days of no hormone. This is to help maintain iron levels in women who have low iron stores because of regular menstrual blood loss. Ultra-low–dose estrogen should be avoided in adolescents because of the requirement for slightly higher estrogen levels for proper bone development.
Ultra-low–dose estrogen should be avoided in adolescents because of the requirement for slightly higher estrogen levels for proper bone development. The estrogen-containing morning-after pill has about 3 to 5 times the dose of estrogen compared with the BCP. It is usually prescribed with an antinausea medication.
The estrogen-containing morning-after pill has about 3 to 5 times the dose of estrogen compared with the BCP. It is usually prescribed with an antinausea medication.Evidence
Breakthrough Bleeding
 A systematic review in 2007 did not find a clear association between type or dose of oral BCP and breakthrough bleeding; however, studies were heterogeneous with respect to methodology and reporting of bleeding. Bleeding in cycle 1 (first menstrual cycle after starting the BCP) was higher than in cycle 4.
A systematic review in 2007 did not find a clear association between type or dose of oral BCP and breakthrough bleeding; however, studies were heterogeneous with respect to methodology and reporting of bleeding. Bleeding in cycle 1 (first menstrual cycle after starting the BCP) was higher than in cycle 4.FYI
 Many brands of BCP are named according to the dose of hormone. For example, 1/30 would represent 1000 mcg of a progestin formulation plus 30 mcg of an estrogen formulation.
Many brands of BCP are named according to the dose of hormone. For example, 1/30 would represent 1000 mcg of a progestin formulation plus 30 mcg of an estrogen formulation. BCPs are also named according to phases. For example, if there are three different doses, each for 7 days, then 7/7/7 is used to denote this.
BCPs are also named according to phases. For example, if there are three different doses, each for 7 days, then 7/7/7 is used to denote this. Related to reproduction and the coagulation cascade, a hypercoagulable state can give rise to recurrent spontaneous abortions (also called miscarriages). The mechanism is utero-placental thrombi resulting in impaired circulation to the placenta. Affected women should be investigated for hypercoagulable states, such as the presence of factor V Leiden.
Related to reproduction and the coagulation cascade, a hypercoagulable state can give rise to recurrent spontaneous abortions (also called miscarriages). The mechanism is utero-placental thrombi resulting in impaired circulation to the placenta. Affected women should be investigated for hypercoagulable states, such as the presence of factor V Leiden.Oxytocin
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 Oxytocin is produced in the hypothalamus but is secreted by the posterior pituitary and acts primarily on smooth muscle of breast and uterine tissue (Figure 14-14):
Oxytocin is produced in the hypothalamus but is secreted by the posterior pituitary and acts primarily on smooth muscle of breast and uterine tissue (Figure 14-14):
 Increased uterine contraction helps to expel the fetus. After delivery, uterine contraction is critical to help stop bleeding; the uterus contracts down on intramyometrial vessels, which clamps them shut.
Increased uterine contraction helps to expel the fetus. After delivery, uterine contraction is critical to help stop bleeding; the uterus contracts down on intramyometrial vessels, which clamps them shut.Pharmacokinetics
 Oxytocin is a peptide, so it cannot be given orally; it is given by intravenous or subcutaneous injection. The half-life of oxytocin is 3 minutes.
Oxytocin is a peptide, so it cannot be given orally; it is given by intravenous or subcutaneous injection. The half-life of oxytocin is 3 minutes.Side Effects
 Abnormally high uterine tone: Increased contraction can lead to decreased blood flow to the uterus and thus decreased oxygen delivery to the fetus. Uterine tone and oxytocin administered must be considered as a cause of fetal distress. Reducing the dose or discontinuing the oxytocin is required if oxytocin is thought to be the cause.
Abnormally high uterine tone: Increased contraction can lead to decreased blood flow to the uterus and thus decreased oxygen delivery to the fetus. Uterine tone and oxytocin administered must be considered as a cause of fetal distress. Reducing the dose or discontinuing the oxytocin is required if oxytocin is thought to be the cause.Important Notes
 The first stage of labor is cervical dilation; the second stage is expulsion of the fetus once the cervix is fully dilated; the third stage is the period after the baby is delivered until the placenta is delivered.
The first stage of labor is cervical dilation; the second stage is expulsion of the fetus once the cervix is fully dilated; the third stage is the period after the baby is delivered until the placenta is delivered.Evidence
Postpartum Bleeding (Including the Third Stage of Labor)
 Oxytocin versus nothing: In a meta-analysis in 2004 (seven trials, N = 3000 women), prophylactic oxytocin was found to reduce blood loss with an RR of 0.50 for blood loss greater than 500 mL.
Oxytocin versus nothing: In a meta-analysis in 2004 (seven trials, N = 3000 women), prophylactic oxytocin was found to reduce blood loss with an RR of 0.50 for blood loss greater than 500 mL. Oxytocin versus ergot alkaloids: A meta-analysis in 2004 (six trials, N = 2800 women) demonstrated little difference. Manual placenta removals were less frequent with oxytocin (RR 0.57).
Oxytocin versus ergot alkaloids: A meta-analysis in 2004 (six trials, N = 2800 women) demonstrated little difference. Manual placenta removals were less frequent with oxytocin (RR 0.57). Oxytocin versus oxytocin plus ergot alkaloids: A meta-analysis in 2007 (six trials, N = 9332 women) demonstrated that if blood loss was defined as >1000 mL, there was no difference, but if blood loss was defined as >500 mL, then there was a small reduction in blood loss with the combination therapy. Combination therapy significantly increased the following side effects: HTN, vomiting, and nausea.
Oxytocin versus oxytocin plus ergot alkaloids: A meta-analysis in 2007 (six trials, N = 9332 women) demonstrated that if blood loss was defined as >1000 mL, there was no difference, but if blood loss was defined as >500 mL, then there was a small reduction in blood loss with the combination therapy. Combination therapy significantly increased the following side effects: HTN, vomiting, and nausea. Carbetocin versus oxytocin: A meta-analysis in 2007 (four studies, N = 1032 women) did not demonstrate a difference in blood loss or risk of PPH. However, with carbetocin there was a reduction (RR 0.44) in the use of uterotonics and a reduction (RR 0.38) in the need for uterine massage (used to stimulate contraction). There was no difference in side effects.
Carbetocin versus oxytocin: A meta-analysis in 2007 (four studies, N = 1032 women) did not demonstrate a difference in blood loss or risk of PPH. However, with carbetocin there was a reduction (RR 0.44) in the use of uterotonics and a reduction (RR 0.38) in the need for uterine massage (used to stimulate contraction). There was no difference in side effects.Induction or Augmentation of Labor
 Oxytocin versus no treatment: A meta-analysis in 2001 (26 studies, N = 6660 women) showed that oxytocin reduced the rate of unsuccessful vaginal delivery within 24 hours: 8.3% versus 54% (RR 0.16), but the caesarean section rate was increased: 10.4% versus 8.9% (RR 1.17).
Oxytocin versus no treatment: A meta-analysis in 2001 (26 studies, N = 6660 women) showed that oxytocin reduced the rate of unsuccessful vaginal delivery within 24 hours: 8.3% versus 54% (RR 0.16), but the caesarean section rate was increased: 10.4% versus 8.9% (RR 1.17). Oxytocin versus vaginal PGs: A meta-analysis in 2001 (27 studies, N = 4649 women) showed that oxytocin was associated with increased unsuccessful vaginal deliveries within 24 hours (52% versus 28%, RR 1.85), irrespective of membrane status (ruptured or not ruptured). There was no difference in caesarean section rates.
Oxytocin versus vaginal PGs: A meta-analysis in 2001 (27 studies, N = 4649 women) showed that oxytocin was associated with increased unsuccessful vaginal deliveries within 24 hours (52% versus 28%, RR 1.85), irrespective of membrane status (ruptured or not ruptured). There was no difference in caesarean section rates.Reproductive Prostaglandins (PGs)
Description
PGs are involved with many processes in the body; this section discusses reproductive uses of PGs.
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 PGs act on a family of receptors that are coupled to G proteins. Some G proteins are stimulatory and some are inhibitory, depending on the specific receptor type. Therefore the physiologic effect of a given PG depends on the receptor and the tissue type. The actions are ultimately mediated by changes in cAMP and intracellular calcium concentrations.
PGs act on a family of receptors that are coupled to G proteins. Some G proteins are stimulatory and some are inhibitory, depending on the specific receptor type. Therefore the physiologic effect of a given PG depends on the receptor and the tissue type. The actions are ultimately mediated by changes in cAMP and intracellular calcium concentrations. Second messengers associated with PG receptors include G proteins, which link to adenylyl cyclase and phospholipase 3.
Second messengers associated with PG receptors include G proteins, which link to adenylyl cyclase and phospholipase 3.Pharmacokinetics
Contraindications
Important Notes
 Missed abortions are also commonly treated expectantly (wait for spontaneous passage of products of conception) or procedurally with dilatation and curettage (D&C), a procedure that involves mechanical dilation of the cervix and then gentle removal of intrauterine contents with a suction catheter or curettage, an instrument that scrapes away the endometrium.
Missed abortions are also commonly treated expectantly (wait for spontaneous passage of products of conception) or procedurally with dilatation and curettage (D&C), a procedure that involves mechanical dilation of the cervix and then gentle removal of intrauterine contents with a suction catheter or curettage, an instrument that scrapes away the endometrium.Evidence
Induction of Labor
 Intravenous PGs versus oxytocin: A meta-analysis in 2004 (13 trials, N = 1165 women) showed that intravenous PG was associated with higher rates of uterine hyperstimulation, both with changes in the fetal heart rate (RR 6.76) and without (RR 4.25), compared with oxytocin. Use of PG was also associated with significantly more maternal side effects: GI effects, thrombophlebitis, and pyrexia. PG was no more likely to result in vaginal delivery than oxytocin.
Intravenous PGs versus oxytocin: A meta-analysis in 2004 (13 trials, N = 1165 women) showed that intravenous PG was associated with higher rates of uterine hyperstimulation, both with changes in the fetal heart rate (RR 6.76) and without (RR 4.25), compared with oxytocin. Use of PG was also associated with significantly more maternal side effects: GI effects, thrombophlebitis, and pyrexia. PG was no more likely to result in vaginal delivery than oxytocin. Vaginal PGs versus oxytocin: A meta-analysis in 2001 (27 studies, N = 4649 women) showed that vaginal PGs were associated with decreased unsuccessful vaginal deliveries within 24 hours (28% versus 52%, RR 0.54), irrespective of membrane status (ruptured or not ruptured). There was no difference in caesarean section rates.
Vaginal PGs versus oxytocin: A meta-analysis in 2001 (27 studies, N = 4649 women) showed that vaginal PGs were associated with decreased unsuccessful vaginal deliveries within 24 hours (28% versus 52%, RR 0.54), irrespective of membrane status (ruptured or not ruptured). There was no difference in caesarean section rates.Erectile Dysfunction
 PGE1 versus placebo or no treatment: A meta-analysis in 2009 (4 studies, N = 1873 men) demonstrated increased probability (odds ratio [OR] 7.22) of at least one successful intercourse. Adverse effects were most frequent in the treated groups and occurred more often and intensely as doses increased. Penile pain and minor urethral trauma were predominant.
PGE1 versus placebo or no treatment: A meta-analysis in 2009 (4 studies, N = 1873 men) demonstrated increased probability (odds ratio [OR] 7.22) of at least one successful intercourse. Adverse effects were most frequent in the treated groups and occurred more often and intensely as doses increased. Penile pain and minor urethral trauma were predominant.FYI
 In 1934, Dr. Ulf von Euler found that extracts of sheep vesicular gland dramatically lowered blood pressure when injected into animals. Human seminal fluid also seemed to possess similar qualities. Von Euler named it prostaglandin, believing that it originated in the prostate gland.
In 1934, Dr. Ulf von Euler found that extracts of sheep vesicular gland dramatically lowered blood pressure when injected into animals. Human seminal fluid also seemed to possess similar qualities. Von Euler named it prostaglandin, believing that it originated in the prostate gland. Nomenclature:
Nomenclature:
 Eicosa is Greek for 20. Eicosanoids have 20 carbon atoms. Eicosanoids include PGs, prostacyclins, leukotrienes, and thromboxane. Arachidonic acid is the most abundant precursor.
Eicosa is Greek for 20. Eicosanoids have 20 carbon atoms. Eicosanoids include PGs, prostacyclins, leukotrienes, and thromboxane. Arachidonic acid is the most abundant precursor. The letter after PG represents a historical designation.
The letter after PG represents a historical designation.
Nonsteroidal Androgen Antagonists (NSAAs)
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
Pharmacokinetics
Side Effects
Important Notes
 Bicalutamide has essentially replaced flutamide because of once-daily dosing (flutamide administration was 3 times a day) and a lower incidence of diarrhea.
Bicalutamide has essentially replaced flutamide because of once-daily dosing (flutamide administration was 3 times a day) and a lower incidence of diarrhea. NSAAs are usually used in combination therapy with either chemical or surgical castration in advanced metastatic prostate cancer.
NSAAs are usually used in combination therapy with either chemical or surgical castration in advanced metastatic prostate cancer.
Androgens
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 Testosterone can be converted in the body to DHT (another physiologically active androgen) and also to estradiol (an estrogen).
Testosterone can be converted in the body to DHT (another physiologically active androgen) and also to estradiol (an estrogen).Pharmacokinetics
 Androgens administered orally undergo extensive first-pass hepatic metabolism. Therefore modifications to the hormone and also alternative methods of delivery have been developed.
Androgens administered orally undergo extensive first-pass hepatic metabolism. Therefore modifications to the hormone and also alternative methods of delivery have been developed.Side Effects
 Salt and water retention from the mild mineralocorticoid effect (remember that aldosterone is a similar steroid hormone)
Salt and water retention from the mild mineralocorticoid effect (remember that aldosterone is a similar steroid hormone) Masculinization if used in women: hirsutism, deeper voice, baldness, amenorrhea, breast and uterine atrophy, and infertility
Masculinization if used in women: hirsutism, deeper voice, baldness, amenorrhea, breast and uterine atrophy, and infertility Consequences of anabolic steroid abuse include the following:
Consequences of anabolic steroid abuse include the following:
 Central nervous system (CNS): Aggression and depression are associated but may also have been present before steroid abuse; difficult to differentiate
Central nervous system (CNS): Aggression and depression are associated but may also have been present before steroid abuse; difficult to differentiate Cardiovascular system: HTN, accelerated atherosclerosis, sudden death, cardiac hypertrophy, cardiac fibrosis
Cardiovascular system: HTN, accelerated atherosclerosis, sudden death, cardiac hypertrophy, cardiac fibrosisSomatostatin Analogs
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 Somatostatin acts on somatostatin receptors; five subtypes have been identified, named SR1 through SR5. Octreotide acts primarily on SR2 and SR5.
Somatostatin acts on somatostatin receptors; five subtypes have been identified, named SR1 through SR5. Octreotide acts primarily on SR2 and SR5. Somatostatin is secreted by the delta cells of the pancreatic islet cells and inhibits the release of the following:
Somatostatin is secreted by the delta cells of the pancreatic islet cells and inhibits the release of the following:
 Somatostatin also lowers portal blood pressure, possibly through its inhibitory action of other vasodilating hormones, particularly glucagon. Inhibition of vasodilators results in vasoconstriction that reduces blood flow into the portal system and thus reduces the pressure in this system (Figure 14-16).
Somatostatin also lowers portal blood pressure, possibly through its inhibitory action of other vasodilating hormones, particularly glucagon. Inhibition of vasodilators results in vasoconstriction that reduces blood flow into the portal system and thus reduces the pressure in this system (Figure 14-16).Pharmacokinetics
Important Notes
 Variceal bleeding occurs when liver cirrhosis increases resistance to the passage of blood through the liver and hence causes portal HTN, resulting in dilated fragile veins in the esophagus, stomach, and rectum.
Variceal bleeding occurs when liver cirrhosis increases resistance to the passage of blood through the liver and hence causes portal HTN, resulting in dilated fragile veins in the esophagus, stomach, and rectum. Because of the actions on glucose-mediating hormones (primarily glucagon, insulin, and glucagon-like peptides), administration to patients with type 1 diabetes can result in reduced insulin requirements and thus a risk of hypoglycemia. Paradoxically, administration to patients with type 2 diabetes can result in hyperglycemia.
Because of the actions on glucose-mediating hormones (primarily glucagon, insulin, and glucagon-like peptides), administration to patients with type 1 diabetes can result in reduced insulin requirements and thus a risk of hypoglycemia. Paradoxically, administration to patients with type 2 diabetes can result in hyperglycemia.Growth Hormone Antagonists
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 GH is a protein. The substitution of one amino acid converts endogenous GH into an antagonist. Commercial GH antagonists have multiple substitutions to enhance binding affinity.
GH is a protein. The substitution of one amino acid converts endogenous GH into an antagonist. Commercial GH antagonists have multiple substitutions to enhance binding affinity. IGF-1 mediates the effects of GH; GH stimulates release of IGF-1 from the liver, and IGF-1 stimulates growth in bone and soft tissues (Figure 14-17).
IGF-1 mediates the effects of GH; GH stimulates release of IGF-1 from the liver, and IGF-1 stimulates growth in bone and soft tissues (Figure 14-17). Pathologically high levels of GH result in gigantism (very large stature) and acromegaly, a condition of bone and soft tissue overgrowth that occurs with high GH levels after growth plates have been fused and vertical growth is finished.
Pathologically high levels of GH result in gigantism (very large stature) and acromegaly, a condition of bone and soft tissue overgrowth that occurs with high GH levels after growth plates have been fused and vertical growth is finished.Pharmacokinetics
Important Notes
 Surgery, dopamine agonists, and somatostatin are standard first-line treatments for acromegaly. Dopamine agonists and somatostatin are inhibitors of GH secretion but are not direct antagonists of GH; therefore their mechanism of action is slightly different, and they act at a different location in the biochemical pathway.
Surgery, dopamine agonists, and somatostatin are standard first-line treatments for acromegaly. Dopamine agonists and somatostatin are inhibitors of GH secretion but are not direct antagonists of GH; therefore their mechanism of action is slightly different, and they act at a different location in the biochemical pathway. Some signs of acromegaly include coarse facial features (prominent brow, cheekbones, chin), large hands and fingers, large tongue (macroglossia), obstructive sleep apnea (because of the macroglossia), vocal changes, HTN, cardiomegaly, and insulin resistance.
Some signs of acromegaly include coarse facial features (prominent brow, cheekbones, chin), large hands and fingers, large tongue (macroglossia), obstructive sleep apnea (because of the macroglossia), vocal changes, HTN, cardiomegaly, and insulin resistance.
 IGF-1 levels are measured to help monitor effectiveness of acromegaly treatment. A drop in levels indicates that GH antagonism has occurred, and drug doses are titrated to IGF-1 levels. It is possible to lower IFG-1 levels to below normal, which is probably undesirable.
IGF-1 levels are measured to help monitor effectiveness of acromegaly treatment. A drop in levels indicates that GH antagonism has occurred, and drug doses are titrated to IGF-1 levels. It is possible to lower IFG-1 levels to below normal, which is probably undesirable.Advanced
 Nelson’s syndrome is a condition of rapid growth of the pituitary as a result of cortisol absence (lack of negative feedback). Concerns about the development of Nelson’s syndrome have been raised with regard to the use of GH antagonists and the resulting loss of negative feedback from IGF-1 on the pituitary. So far, Nelson’s syndrome has not been demonstrated.
Nelson’s syndrome is a condition of rapid growth of the pituitary as a result of cortisol absence (lack of negative feedback). Concerns about the development of Nelson’s syndrome have been raised with regard to the use of GH antagonists and the resulting loss of negative feedback from IGF-1 on the pituitary. So far, Nelson’s syndrome has not been demonstrated.Evidence
Biochemical Markers
 In an observational study in 2001 (N = 160), it was demonstrated that somatostatin normalizes IGF-1 levels in about 65% of patients. Pegvisomant normalized IGF-1 levels in 97% of patients and reduced insulin and resting glucose levels but not HbA1c. However, GH levels almost double. The mechanism of this increase is unknown, but it could be related to loss of negative feedback on the pituitary from IGF-1.
In an observational study in 2001 (N = 160), it was demonstrated that somatostatin normalizes IGF-1 levels in about 65% of patients. Pegvisomant normalized IGF-1 levels in 97% of patients and reduced insulin and resting glucose levels but not HbA1c. However, GH levels almost double. The mechanism of this increase is unknown, but it could be related to loss of negative feedback on the pituitary from IGF-1.FYI
 Andre the Giant, a professional wrestler in the 1970s who passed away in 1993 from heart failure, had acromegaly.
Andre the Giant, a professional wrestler in the 1970s who passed away in 1993 from heart failure, had acromegaly. Acro– means top, height, or summit. The name would suggest that acromegaly means large height; however, the term gigantism is used instead. Acromegaly describes the non–height-related effects of GH excess.
Acro– means top, height, or summit. The name would suggest that acromegaly means large height; however, the term gigantism is used instead. Acromegaly describes the non–height-related effects of GH excess.Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) is released from the hypothalamus and stimulates the anterior pituitary.
Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) is released from the hypothalamus and stimulates the anterior pituitary. ACTH is produced and secreted from the anterior pituitary. ACTH binds ACTH receptors on the adrenal cortex. As a result, cortisol production and secretion from the adrenal cortex are increased (Figure 14-18).
ACTH is produced and secreted from the anterior pituitary. ACTH binds ACTH receptors on the adrenal cortex. As a result, cortisol production and secretion from the adrenal cortex are increased (Figure 14-18). Activation of the ACTH receptor results in activation of the following signaling process: G proteins → increased cAMP → increased protein kinase A (PKA) → increased intracellular Ca2+, all of which result in:
Activation of the ACTH receptor results in activation of the following signaling process: G proteins → increased cAMP → increased protein kinase A (PKA) → increased intracellular Ca2+, all of which result in:
Important Notes
 Cortisol insufficiency is rarely, if ever, treated with ACTH. It is usually treated with systemic steroids to replace the cortisol.
Cortisol insufficiency is rarely, if ever, treated with ACTH. It is usually treated with systemic steroids to replace the cortisol. Cortisol insufficiency manifests as:
Cortisol insufficiency manifests as:
 Hyponatremia with hyperkalemia (aldosterone conserves Na+ and excretes K+ in the kidney, so deficiency causes Na+ wasting and K+ retention)
Hyponatremia with hyperkalemia (aldosterone conserves Na+ and excretes K+ in the kidney, so deficiency causes Na+ wasting and K+ retention) Measurements of serum cortisol are difficult to interpret in different disease states because 90% of circulating cortisol is protein bound to corticosteroid-binding globulin. During severe illness, the corticosteroid-binding globulin drops by as much as 50%. Most assays measure total cortisol and so will not be able to measure free (unbound) cortisol, which is the fraction that is biologically available. This severely limits the ability to interpret the results.
Measurements of serum cortisol are difficult to interpret in different disease states because 90% of circulating cortisol is protein bound to corticosteroid-binding globulin. During severe illness, the corticosteroid-binding globulin drops by as much as 50%. Most assays measure total cortisol and so will not be able to measure free (unbound) cortisol, which is the fraction that is biologically available. This severely limits the ability to interpret the results.Advanced
 ACTH is also (in smaller quantities) produced by the immune system, including T cells, B cells, and macrophages. Fighting off infection usually results in the body mounting an increased metabolic response, so the interplay between adrenal function and the immune system is logical.
ACTH is also (in smaller quantities) produced by the immune system, including T cells, B cells, and macrophages. Fighting off infection usually results in the body mounting an increased metabolic response, so the interplay between adrenal function and the immune system is logical. The ACTH test usually involves administration of 250 mcg of ACTH. This dose has been criticized for being far too large (supraphysiologic) to be sensitive. A more appropriate dose of 1 mcg has been suggested, but data to recommend the use of this dose are lacking.
The ACTH test usually involves administration of 250 mcg of ACTH. This dose has been criticized for being far too large (supraphysiologic) to be sensitive. A more appropriate dose of 1 mcg has been suggested, but data to recommend the use of this dose are lacking. In severe illness, such as septic shock or acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), ACTH stimulation tests are not recommended for identifying patients who require steroid therapy. Confounding the interpretation of this test is the fact that cortisol is protein bound and the active component is unbound. Most assays for serum cortisol measure both bound and unbound components, and in critical illness protein binding is abnormal, so it is difficult to know what the unbound (active) levels of cortisol are with these results.
In severe illness, such as septic shock or acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), ACTH stimulation tests are not recommended for identifying patients who require steroid therapy. Confounding the interpretation of this test is the fact that cortisol is protein bound and the active component is unbound. Most assays for serum cortisol measure both bound and unbound components, and in critical illness protein binding is abnormal, so it is difficult to know what the unbound (active) levels of cortisol are with these results.FYI
 The adrenal glands sit on top of the kidneys. Originally named the suprarenal glands, they were renamed to the adrenal glands. Each is composed of a cortex and a medulla. Thus, adrenocortico refers to action primarily on the adrenal cortex.
The adrenal glands sit on top of the kidneys. Originally named the suprarenal glands, they were renamed to the adrenal glands. Each is composed of a cortex and a medulla. Thus, adrenocortico refers to action primarily on the adrenal cortex. The zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, and zona reticularis are the three zones of the adrenal cortex.
The zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, and zona reticularis are the three zones of the adrenal cortex.
Thyroid Replacements
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 Exogenously administered thyroxine replaces deficient endogenous thyroid hormone, a condition called hypothyroidism.
Exogenously administered thyroxine replaces deficient endogenous thyroid hormone, a condition called hypothyroidism. Thyroid-releasing hormone (TRH) from the hypothalamus stimulates the pituitary to release thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which stimulates the thyroid gland to synthesize and release thyroid hormone. Thyroid hormone has negative feedback loop activity on both TRH and TSH.
Thyroid-releasing hormone (TRH) from the hypothalamus stimulates the pituitary to release thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which stimulates the thyroid gland to synthesize and release thyroid hormone. Thyroid hormone has negative feedback loop activity on both TRH and TSH. There are three major forms of thyroid hormone: T4, T3, and rT3 (reverse T3).
There are three major forms of thyroid hormone: T4, T3, and rT3 (reverse T3).
 Thyroid hormones bind intracellular nuclear thyroid hormone receptors (THRs) and influence RNA transcription directly. THRs have 10 times the affinity for T3 that they have for T4.
Thyroid hormones bind intracellular nuclear thyroid hormone receptors (THRs) and influence RNA transcription directly. THRs have 10 times the affinity for T3 that they have for T4.Pharmacokinetics
 It has a long half-life of 7 days, meaning that achievement of steady state (five half-lives) requires about 35 days; dose adjustments based on TSH levels should not be made before steady state is reached.
It has a long half-life of 7 days, meaning that achievement of steady state (five half-lives) requires about 35 days; dose adjustments based on TSH levels should not be made before steady state is reached. Thyroid hormone is deiodinized (iodine molecule removed) to inactive forms by the liver. Doses might require adjustment in liver disease.
Thyroid hormone is deiodinized (iodine molecule removed) to inactive forms by the liver. Doses might require adjustment in liver disease. T4 is almost always administered orally. An indication for intravenous administration of T4 is severe life-threatening hypothyroidism (myxedema coma).
T4 is almost always administered orally. An indication for intravenous administration of T4 is severe life-threatening hypothyroidism (myxedema coma). Thyroid hormone contains iodine. Therefore other iodinated agents such as amiodarone or iodinated contrast media can inhibit the 5’-deiodinase necessary for the conversion of T4 to T3. β-Blockers, corticosteroids, and severe illness or starvation can also produce the same effect. This results in more T4 being converted to the inactive form of rT3.
Thyroid hormone contains iodine. Therefore other iodinated agents such as amiodarone or iodinated contrast media can inhibit the 5’-deiodinase necessary for the conversion of T4 to T3. β-Blockers, corticosteroids, and severe illness or starvation can also produce the same effect. This results in more T4 being converted to the inactive form of rT3.Important Notes
 TSH is the most commonly used test to monitor hypothyroid states. In primary (thyroid gland dysfunction) hypothyroidism, TSH levels are elevated in an attempt to further stimulate the thyroid gland. Secondary hypothyroidism (pituitary gland dysfunction) would result in a low TSH.
TSH is the most commonly used test to monitor hypothyroid states. In primary (thyroid gland dysfunction) hypothyroidism, TSH levels are elevated in an attempt to further stimulate the thyroid gland. Secondary hypothyroidism (pituitary gland dysfunction) would result in a low TSH. Adrenal and thyroid hypofunctioning can coexist. Thyroid hormone replacement without additional corticosteroids may precipitate acute adrenal insufficiency in patients with impaired adrenal function. The outcome can be fatal; however, patients are usually very sick if both adrenal function and thyroid function are significantly abnormal. This can occur in myxedema coma.
Adrenal and thyroid hypofunctioning can coexist. Thyroid hormone replacement without additional corticosteroids may precipitate acute adrenal insufficiency in patients with impaired adrenal function. The outcome can be fatal; however, patients are usually very sick if both adrenal function and thyroid function are significantly abnormal. This can occur in myxedema coma. T4 is preferred over T3 administration because T4 has a longer half-life, enabling daily administration, and has a lower potential for cardiac toxicity.
T4 is preferred over T3 administration because T4 has a longer half-life, enabling daily administration, and has a lower potential for cardiac toxicity. Diseases associated with abnormal levels of thyroid hormones include the following:
Diseases associated with abnormal levels of thyroid hormones include the following:
 Grave’s disease: Grave’s disease consists of elevated T4 resulting from antibodies stimulating the TSH receptors on the thyroid.
Grave’s disease: Grave’s disease consists of elevated T4 resulting from antibodies stimulating the TSH receptors on the thyroid. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: Antibodies against the TSH receptor destroy the thyroid gland, eventually resulting in hypothyroidism. Through the destruction process, there can be episodes of increased release of thyroid hormone, causing episodic hyperthyroidism.
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: Antibodies against the TSH receptor destroy the thyroid gland, eventually resulting in hypothyroidism. Through the destruction process, there can be episodes of increased release of thyroid hormone, causing episodic hyperthyroidism.Advanced
 Subclinical hypothyroidism is a condition of elevated TSH but with normal T3 and T4 levels. Patients are usually healthy and without symptoms.
Subclinical hypothyroidism is a condition of elevated TSH but with normal T3 and T4 levels. Patients are usually healthy and without symptoms. Sick euthyroid syndrome is a condition of normal TSH but with decreased T3. It is a term used in patients who are critically ill, but whose disease is not a primary thyroid disorder.
Sick euthyroid syndrome is a condition of normal TSH but with decreased T3. It is a term used in patients who are critically ill, but whose disease is not a primary thyroid disorder. T3 therapy is rarely ever required but has a faster onset of action than T4 because T4 first needs to be converted to T3. Myxedema coma would be the only indication for T3 administration, and evidence is lacking to support that T3 is superior to T4 in myxedema coma. In fact, cardiovascular toxicity (tachycardia and arrhythmias) can result from too high a dose or too fast an onset of action—a reason to consider avoiding intravenous T3 in critically ill patients.
T3 therapy is rarely ever required but has a faster onset of action than T4 because T4 first needs to be converted to T3. Myxedema coma would be the only indication for T3 administration, and evidence is lacking to support that T3 is superior to T4 in myxedema coma. In fact, cardiovascular toxicity (tachycardia and arrhythmias) can result from too high a dose or too fast an onset of action—a reason to consider avoiding intravenous T3 in critically ill patients.Evidence
Subclinical Hypothyroidism
 A meta-analysis in 2007 (12 trials, 350 patients) compared levothyroxine replacement with placebo or no treatment for patients with subclinical hypothyroidism. No significant differences were found with respect to symptoms, survival or cardiac function. There was some evidence that thyroid replacement slightly improved lipid levels.
A meta-analysis in 2007 (12 trials, 350 patients) compared levothyroxine replacement with placebo or no treatment for patients with subclinical hypothyroidism. No significant differences were found with respect to symptoms, survival or cardiac function. There was some evidence that thyroid replacement slightly improved lipid levels.Antithyroids
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 Synthesis of thyroid hormone requires the following steps:
Synthesis of thyroid hormone requires the following steps:
 Through the action of thyroid peroxidase, the following occurs:
Through the action of thyroid peroxidase, the following occurs:
• Iodination (addition of iodine) of the tyrosine groups of thyroglobulin (Tg): addition of one iodine makes monoiodotyrosine (MIT); addition of two iodines makes diiodotyrosine (DIT). Coupling two DITs makes T4 (a total of four iodines). Coupling an MIT with a DIT makes T3 (a total of three iodines).
 A simplified way to think about synthesis is that thyroid hormone is really like two tyrosine amino acids combined together with either three or four iodine molecules. Thyroglobulin is the tyrosine amino acid supplier (Figure 14-19).
A simplified way to think about synthesis is that thyroid hormone is really like two tyrosine amino acids combined together with either three or four iodine molecules. Thyroglobulin is the tyrosine amino acid supplier (Figure 14-19). Thioamides act primarily by blocking the synthesis of thyroid hormone. They do the following:
Thioamides act primarily by blocking the synthesis of thyroid hormone. They do the following:
Contraindications
Side Effects
Thioamides
 The most common side effects (in 6% to 10% of patients) are skin rash, fever, and arthralgia (sore joints).
The most common side effects (in 6% to 10% of patients) are skin rash, fever, and arthralgia (sore joints).Serious, Rare Side Effects
 Agranulocytosis: Patients can develop a serious reduction in the granulocyte count (neutrophil count), which severely impairs the immune system and results in high risk for serious life-threatening infections. Discontinuing the drug results in restoration of the blood count. A blood count should be performed before the drugs are started, and if the patient develops a fever, cough, sore throat, or urinary tract infection or other symptom that might be suggestive of infection, then a blood count must be repeated. The thioamides must be stopped if the granulocyte count is low.
Agranulocytosis: Patients can develop a serious reduction in the granulocyte count (neutrophil count), which severely impairs the immune system and results in high risk for serious life-threatening infections. Discontinuing the drug results in restoration of the blood count. A blood count should be performed before the drugs are started, and if the patient develops a fever, cough, sore throat, or urinary tract infection or other symptom that might be suggestive of infection, then a blood count must be repeated. The thioamides must be stopped if the granulocyte count is low. Hepatotoxicity: A small percent (0.2%) of patients develop liver damage, which is an allergic-type response and can result in liver failure, necessity for transplant, or death.
Hepatotoxicity: A small percent (0.2%) of patients develop liver damage, which is an allergic-type response and can result in liver failure, necessity for transplant, or death.Important Notes
 β-Blocker therapy is an important part of hyperthyroidism treatment. However, it treats the downstream effects (signs and symptoms) of hyperthyroidism but does not reduce thyroid production or secretion. β-Blocker therapy works within hours of the start of treatment and so is an important component of therapy, because antithyroid medication requires at least 3 to 4 weeks before lowering thyroid hormone levels.
β-Blocker therapy is an important part of hyperthyroidism treatment. However, it treats the downstream effects (signs and symptoms) of hyperthyroidism but does not reduce thyroid production or secretion. β-Blocker therapy works within hours of the start of treatment and so is an important component of therapy, because antithyroid medication requires at least 3 to 4 weeks before lowering thyroid hormone levels. TSH levels should be tested on a monthly basis and then when symptoms are under control, every 1 to 3 months thereafter.
TSH levels should be tested on a monthly basis and then when symptoms are under control, every 1 to 3 months thereafter. Hyperthyroid remission can occur, so treatment with thioamides can be used without thyroid ablation or thyroidectomy. Choice of therapy is not always straightforward and must balance the risks and benefits of the three different options (surgery, 131I ablation, and suppressive therapy). If a patient could be predicted to go into remission, then suppressive therapy might be the best option; however, predicting remission is difficult.
Hyperthyroid remission can occur, so treatment with thioamides can be used without thyroid ablation or thyroidectomy. Choice of therapy is not always straightforward and must balance the risks and benefits of the three different options (surgery, 131I ablation, and suppressive therapy). If a patient could be predicted to go into remission, then suppressive therapy might be the best option; however, predicting remission is difficult. 131I has been suggested to be associated with increased cancer formation (nonthyroid cancers). The evidence is still under debate.
131I has been suggested to be associated with increased cancer formation (nonthyroid cancers). The evidence is still under debate.