Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
John C. Byrd and Joseph M. Flynn
• Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is the most prevalent type of adult leukemia and is defined by a distinctive immunophenotype of CD19+, CD20+, CD5+, CD23+, and surface immunoglobulin (sIg)-positive cells.
• The environmental or genetic cause of CLL in most patients is not known, although 8% to 10% of patients have a first-degree relative with this diagnosis.
• CLL lacks a single driving mutation that defines the disease, although autonomous B-cell receptor signaling appears to be important; the role of stem cells remains controversial.
• Classic staging for CLL at diagnosis is not helpful in most patients for risk stratification, but new prognostic factors such as immunoglobulin variable heavy chain (IGHV1) mutational status, interphase cytogenetics, β2-microglobulin, and thymidine kinase activity have improved staging of this disease.
• Common disease-related complications associated with CLL include immune deficiency with associated infections, autoimmune complications, secondary cancers, and Richter transformation.
• CLL is treated only when it becomes symptomatic, based on earlier studies showing no survival advantage to early intervention. This same approach is followed for all patients irrespective of genetic risk.
• The current standard treatment for young and older patients with CLL is chemotherapy combined with an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody. Although this prolongs survival in CLL, it does not cure the disease.
• Reduced-intensity allogeneic stem cell transplant is curative in a subset of CLL patients but still carries with it treatment-related morbidity and mortality.
• B-cell receptor antagonists offer great promise as a new targeted therapy for CLL.
Introduction
B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is one of the most commonly occurring leukemias in the Western Hemisphere, accounting for approximately one third of all leukemias. CLL was initially described by Dameshek as an accumulative disorder of abnormal immunologically incompetent lymphocytes.1 Our understanding of the biology of CLL has changed dramatically as new basic science investigation has brought forth many new discoveries showing that the disease not only involves disrupted apoptosis but also has a strong dependence on microenvironment and proliferation. Similarly, the clinical evolution of CLL is now recognized to involve a precursor syndrome called monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis of uncertain significance that has the potential to progress to full-blown CLL at a frequency of 1% to 2% per year. The cause of CLL in most cases is not recognized, although there is a strong genetic predisposition to this disease in select families. Despite this high genetic predisposition, no common single-gene mutation has been associated with CLL as compared with other solid tumors such as breast and neuroendocrine tumors. CLL is no longer defined by morphology alone but rather immunophenotypically based on co-expression of traditional mature B-cell markers (CD19, CD20, dim surface immunoglobulin) with the pan–T-cell marker CD5. Despite much improved understanding in the biology of CLL, treatment of this disease is still not undertaken until symptoms arise, based on no evidence of improvement in survival with early treatment of asymptomatic individuals. Although for many decades treatment of symptomatic CLL was also not associated with improvement in survival, the introduction of chemoimmunotherapy has finally demonstrated improvement in this important end point. CLL is still not cured with this type of treatment, and immune suppression promoted both by progression of the disease and therapies used leads to many of the complications patients with this disease experience. The long natural history of CLL, complications arising from both the disease and treatment, and psychosocial issues occurring at different phases provide challenges to both the hematologist and primary care physician involved in the care of patients with this diagnosis.
Epidemiology
CLL is one of the most common types of leukemia in the Western Hemisphere. The Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program (SEER) estimated that 16,060 patients (9,490 men and 6,570 women) would be diagnosed with CLL and 4,580 would die as a consequence of this disease in 2012 (http://seer.cancer.gov/). The median age at diagnosis for CLL was 72 years during 2005 through 2009 according to the SEER database. Unlike other types of leukemia, CLL is extremely rare in individuals younger than the age of 20, making it exclusively a cancer of adults. The proportion of patients diagnosed with CLL increases with age. The frequency of diagnosis among CLL patients is 1.8% in persons 44 and younger; 9.0% between ages 45 and 54; 20.9% between ages 55 and 64; 26.5% between ages 65 and 74; 27.8% between ages 75 and 84; and 14.0% in those older than age 85. The age-adjusted incidence rate was 4.2 per 100,000 per year; this translates into a risk of approximately 1 in 202 patients being diagnosed with CLL during their lifetime. In general, CLL is more common in men, with a 2 : 1 frequency. Race and ethnicity contribute to the frequency of CLL, with the disease being most common in white (6.1/100,000) followed by black (4.3/100,000), American Indian (2.5/100,000), Hispanic (2.4/100,000), and Asian (1.3/100,000) men. The survival rate following diagnosis in CLL is 78.8% at 5 years, which explains the estimated prevalence of 95,123 patients currently living with CLL in the United States. Five-year relative estimated survival rates by race and sex are 77.6% for white men, 80.9% for white women, 64.0% for black men, and 69.1% for black women. The worse outcome for black patients was confirmed in another recently published paper.2
Similar to that for other types of leukemia, the risk of dying of disease-specific CLL causes increases proportionately with increasing age. Another analysis of the SEER database comparing outcome of elderly patients with CLL to age- and sex-matched healthy controls demonstrated that CLL has the greatest impact on survival in the most elderly group of patients. However, even for patients diagnosed with CLL before the age of 50, Montserrat and colleagues demonstrated that the median expected life span is only 12.3 years, compared with 31.2 years in age-matched controls.3 Thus, CLL is a significant health problem that can affect all ages of patients.
The varied frequency of CLL among different ethnic and racial backgrounds provides the opportunity to study the influence of environment on development of the disease. CLL is rare among Asians and Pacific Islanders, and this persists even in immigrants from these areas who have migrated to the Western Hemisphere.4,5 This implicates a possible genetic predisposition to the development of CLL. The relationship of environmental factors such as exposure to benzene and other chemicals to the development of CLL is not clearly defined. Select epidemiology studies have identified a higher risk of CLL among farmers and others with exposure to pesticides,6 but these findings have not been consistent.7 However, CLL is recognized as a service-connected illness among Vietnam War veterans who were exposed to Agent Orange (http://www.publichealth.va.gov/exposures/agentorange/). For patients in the theatre of the Vietnam conflict, it is important to identify this factor because additional compensation from the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs is possible. Occupational or environmental exposure to radiation does not appear to predispose patients to a higher risk of developing CLL as compared with other types of leukemia.8 This lack of increased risk for developing CLL after excessive radiation exposure was observed in both survivors of the atomic bomb at Hiroshima9,10 and also inhabitants of the Chernobyl nuclear reactor accident.11 In contrast, the frequency of acute myeloid leukemia, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and chronic myeloid leukemia was higher after exposure to radiation in these settings.
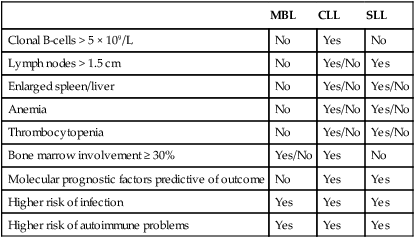
Recently, a precursor to CLL termed monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis (MBL) has been identified12 that has many similarities to monoclonal gammopathy of uncertain significance (MGUS) in multiple myeloma. The frequency of MBL in the general population is 3%, with increasing frequency of diagnosis based on age and also familial history of disease.13 Of patients with MBL, 1% to 2% will progress each year to meet the criteria of CLL (i.e., 5 × 109/L of malignant B cells in the blood), and risk for progression is best predicted by the absolute lymphocyte count.14,15 Although this condition until recently has been viewed as having little impact on outcome, several studies have identified an increased risk of infectious morbidity as compared with the age-matched control population without MBL.16 At this point, MBL should be viewed as not a malignant diagnosis because only a small subset of patients progress to a pathological disease. However, as with MGUS patients, these individuals do warrant serial follow-up with blood tests and physical examination to ensure signs and symptoms of CLL are not developing. The blurred definition between MBL and early-stage CLL has been exacerbated recently by changes in the definition of CLL from requiring 5 × 109/L lymphocytes to 5 × 109/L B lymphocytes.17 This change downstages a subset of early-stage CLL patients to MBL, and long term could influence survival estimates of CLL by removing patients with the most favorable prognosis.18 Differences between MBL, CLL, and small lymphocytic leukemia (SLL) are summarized in Table 102-1.
Table 102-1
Characteristics of Monoclonal B-Cell Lymphocytosis (MBL), Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL), and Small Lymphocytic Leukemia (SLL)
| MBL | CLL | SLL | |
| Clonal B-cells > 5 × 109/L | No | Yes | No |
| Lymph nodes > 1.5 cm | No | Yes/No | Yes |
| Enlarged spleen/liver | No | Yes/No | Yes/No |
| Anemia | No | Yes/No | Yes/No |
| Thrombocytopenia | No | Yes/No | Yes/No |
| Bone marrow involvement ≥ 30% | Yes/No | Yes | No |
| Molecular prognostic factors predictive of outcome | No | Yes | Yes |
| Higher risk of infection | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Higher risk of autoimmune problems | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Biology and Genetics
The knowledge of CLL biology and genetics has expanded tremendously during the past decade. This in part has occurred fortuitously from CLL patients with a large volume of readily available primary tumor cells this situation has facilitated easy application of new technologies to study gene expression profiling, miR profiling, and RNA/DNA whole-genome sequencing. These new technologies have allowed researchers to sort out important questions debated for many years in editorials, review papers, and book chapters related to the cell of origin of CLL. Based on the classic CD5, CD19, CD20, and dim surface immunoglobulin phenotype of CLL, for many years the cell of origin was assumed to be that of a B1 peritoneal B lymphocyte. This finding was challenged by application of gene expression profiling of normal B cells at different points in development and also distinct B-cell malignancies.19,20 Although the normal counterpart cell of origin of transformed CLL still remains controversial, it appears to be most closely related to a memory B cell.19 Within a distinct gene expression pattern for all CLL is the ability to differentiate genes that segregate the natural history of CLL from indolent to aggressive (see later discussion of IGHV1 mutational status). In addition, expansion of other technologies has expanded further the knowledge and risk stratification of CLL, including whole-exon and whole-genome sequencing projects in CLL that have identified genes such as NOTCH1 and SF3B121 that have a relatively high (10% to 20%) frequency of mutation in CLL and clearly have clinical relevance with respect to risk stratification and also treatment. The biology and genetics covered within this chapter focus predominantly on areas relevant to the clinician who cares for patients with CLL.
Is CLL a Stem Cell Disease?
For many years, the treatment of cancer has been characterized by attempts at eliminating macroscopic tumor cells that are the visible phenotype of the disease. Detailed study of normal hematopoiesis has demonstrated a very small number of normal stem cells that when isolated from the bone marrow could repopulate and establish normal human marrow function in irradiated, immune-deficient mice.22 These observations eventually led to successful application of both allogeneic and also autologous bone marrow transplantation as a curative treatment option for many patients with hematologic malignancies. Derived from this work was the hypothesis that leukemia (and potentially other cancers) was also derived from a small proportion of “leukemia” stem cells that proliferate and differentiate to produce more mature blast cells that ultimately represent the visible phenotype of the disease. The implications of such a finding are great, because the properties of stem cells are quite different from the more mature blast cells to which therapies were adapted. Research over the past 2 decades in acute leukemia, multiple myeloma, and many different solid tumors has provided significant support for this hypothesis. In contrast to other types of leukemia, for many years it was believed that CLL was not derived from a clonal stem cell, based on the inability of the leukemia cells to engraft and recapitulate the disease when tumor cells are inoculated or transplanted into immunocompromised mice. However, a recent sentinel paper demonstrated that bone marrow CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells from CLL patients have a higher number of cells with B-lymphoid progenitor phenotype and develop clonal B cells characteristic of CLL when engrafted into irradiated, immunocompromised mice.23 More notably, these cells demonstrated the ability to also be re-engrafted into irradiated, immunocompromised mice and again develop findings consistent with CLL, demonstrating true stem cell properties of these cells. In contrast to the CD34+ cells from the CLL bone marrow, this group also showed that lymphocytes lacking CD34 never demonstrated long-term engraftment in the mice. As compared with both normal CD34+ stem cells and more differentiated B-cell progenitor cells, these CLL stem cells had different gene expression, including absent NOTCH1 and increased GATA2 expression. Notably, the CLL cells developing in these mice after the first and successive engraftments did not have the genetic features of the patient’s CLL, suggesting that an additional transforming event or events in the clonal CLL cells may occur. Specifically, neither the common genetic translocations seen in the patient, that is, del(13q14), nor IGHV1 mutational status was the same for the CLL found in engrafted mice. These findings suggest overall that CLL patients have lymphoid primed stem cells and via acquisition of different genetic abnormalities, CLL ultimately develops. Although this paper describing CLL stem cells is quite provocative,23 it lacks validation by other groups working in the field. The findings, if true, will likely focus significant research attention on differentiating properties of these CLL stem cells from normal CD34+ stem cells to allow novel treatment approaches. Additionally, studies pursuing why Ighv1 status of tumors in the mouse uniformly is highly mutated will be pursued because this suggests some intrinsic feature of either a second genetic hit or an environmental influence is driving development of this high-risk phenotype CLL.
Is IGHV1 Mutational Status the Differentiating Feature of Low- Versus High-Risk CLL?
Based on the CD5+ status of CLL cells and the presence of surface igD (sigD) on CLL cells, this disease for many years was considered to be derived from a naïve B cell without somatic hypermutation that typically occurs in the germinal center. The process of somatic mutation is generally assessed by examining amino acid changes occurring in the first and second complementarity determining regions (CDR1 and CDR2). Early studies in the 1990s of small numbers of CLL patients demonstrated the sequence of immunoglobulin variable heavy (VH) chain genes was unmutated (germline), thereby providing further support that the cell of origin of CLL was a naïve B-cell. These studies were later challenged by several small reports and then by a more comprehensive study in 1994 by Schroeder and Dighiero, who identified approximately one half of the reported cases of CLL had VH genes with less than 98% sequence similarity to germline.24 Given the extent of extensive polymorphisms in this region, the 98% number for similarity to germline was established, although subsequent studies have challenged this as too high. The hypothesis from this thought-provoking paper by Schroeder and Dighiero was that CLL might be a heterogeneous disorder that could be differentiated on the basis of IGHV1 mutational status.24 It was 5 years before two separate research groups demonstrated that the IGHV1 gene had undergone somatic mutation, indicating that the patient’s CLL arose after this point in B-cell maturation, in 60% of CLL patients at diagnosis.25,26 In contrast, approximately 40% of patients had germline sequence appearance of the IGHV1 region mimicking a pre-germinal B-cell phenotype. From each of these papers came the very interesting observation that IGHV1 mutational status was highly segregated with disease outcome. Patients with IGHV1-mutated disease who had early-stage disease had a very long natural history with only a subset progressing to the point of requiring therapy, whereas those with IGHV1-nonmutated disease tended to have a much more aggressive natural history with virtually all requiring therapy and also having a shortened survival. Furthermore, many of the other high-risk genetic features (see later discussion) including del(17p13.1), del(11q22.3), 53 mutations, complex karyotype, shortened telomeres, and clonal evolution were identified to be associated with IGHV1-nonmutated status.27–34 At the time IGHV1 mutational status was identified, the technology available to widely export this finding to clinical practice was lacking. One of these papers suggested CD38 could serve as a surrogate of IGHV1 mutational status.26 Subsequent studies showed that like IGHV1 mutational status, CD38 was an unfavorable prognostic factor but changed during the course of the disease and only had approximately a 70% concordance with IGHV1 mutational status.27,28,35–39 This led to the active investigation of both surrogate markers of IGHV1 mutational status and also the biology behind it.
Is ZAP70 Expression a Surrogate for IGHV1 Mutational Status or Driver Gene in the Pathogenesis of CLL?
The scientific impact of identification of different clinical history among IGHV1-mutated and nonmutated CLL prompted great interest in CLL after the sentinel discovery in 1999. Several other investigators used new techniques of gene expression profiling to pursue identification of surrogate markers that could predict the presence or absence of IGHV1 mutational status and also elucidate new genes that might contribute to the biology. Rosenwald and Staudt were the first to identify a gene expression profile of CLL that identified it as one disease with a common signature.20 However, select gene expression distinguished IGHV1-nonmutated from IGHV1-mutated disease. Most notably was expression of the 70-kDa zeta-chain–associated protein (ZAP70). Other genes such as lipoprotein lipase were also noted to be differentially expressed and have been actively pursued by others.20,40,41 However, great focus in the field has focused on ZAP70 contribution to the biology of CLL. ZAP70 is a tyrosine kinase of the Syk family that acts centrally in T-cell receptor signaling. At the time of this study there was no known expression of ZAP70 protein in normal or transformed B cells. This work and others that followed confirmed that the majority of IGHV1-nonmutated CLL cells have ZAP70 expression and demonstrate evidence of SYK activation and other essential B-cell receptor (BCR) downstream activation signals after ligation of surface IgM (sIgM) that is related to overexpression of this protein.42,43 Of interest, several studies suggested that the kinase portion of ZAP70 is not required for enhanced BCR signaling because transfection of a kinase dead ZAP70 construct into CLL cells lacking this protein showed enhanced BCR signaling with IgM ligation.44,45 In contrast, cells from virtually all IGHV1-mutated patients lack significant ZAP70 expression and do not signal after ligation by sIgM, but can often weakly signal through other alternative BCRs. Subsequent studies examining ZAP70 for activating mutations have been unrevealing.46 Additionally, attempts to introduce ZAP70 into mouse models with B-cell CLL predisposition have not accelerated the phenotype of the disease. These studies have left questions as to the impact of ZAP70 as a driver in the pathogenesis of aggressive CLL.
B-Cell Receptor Signaling in the Pathogenesis of CLL
CLL has distinct BCR signaling as compared with normal B cells that is characterized by low-level IgM expression, variable response to antigen stimulation, and tonic activation of anti-apoptotic signaling pathways. CLL cells by mRNA expression share many features with antigen-activated mature B cells, suggesting a role for activation of BCR signaling in the disease pathogenesis. A recent publication validated the importance of BCR signaling but showed that it is antigen-independent cell-autonomous signaling.47 The importance of BCR signaling was further substantiated in a tissue-based comparison demonstrating enhanced upregulation of the BCR pathway–related genes by microarray in bone marrow and lymph nodes of all CLL patients as compared with blood irrespective of ZAP70 expression or IGHV1 mutational status.48 Thus, enhanced BCR gene expression is present in all CLL patients in nodal and lymph node sites. Additionally, patients with ZAP70-positive disease have higher BCR responsiveness to IgM stimulation in vitro compared with ZAP70-negative disease.
Dysregulation of the BCR signaling pathway in CLL is characterized by constitutively active phosphorylation of certain kinases and variable response to IgM stimulation. The best evidence of this lies in the tyrosine kinases Lyn and Syk, both having been shown to be upregulated in CLL. Activity of these kinases has also been shown to be amplified in primary CLL cells. Specifically, in vitro kinase assays indicate that Lyn is constitutively active in CLL.49 Baseline tyrosine phosphorylation of Syk as well is higher in CLL cells than normal B cells,50 whereas response to antigen stimulation via the BCR signaling pathway is variable.51 Although protein expression of the catalytic 110δ subunit, the predominant phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) subunit in hematopoietic cells,52 is comparable between normal B cells and CLL cells, PI3K has been shown to be constitutively active in CLL by in vitro kinase assay.53,54 Additionally, inhibition of PI3K by the pan-PI3K inhibitor LY29400253 and the PI3Kδ inhibitor GS110154 both promote CLL cell apoptosis in a caspase-dependent manner. Inhibition of PI3K by CAL-101 or LY294002 inhibits Akt activation, decreases myeloid cell leukemia sequence 1 (BCL2-related) (MCL1) expression,53,54 and inhibits protein expression of the B-cell CLL/lymphoma 2 (BCL2) family member BCL2-associated X protein (BAX) and the anti-apoptotic X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP).53 The Btk enzyme essential to BCR signaling has also been shown to have increased expression in CLL and evidence of autophosphorylation in a subset of patients, providing additional evidence for activation of this pathway.55 Btk activation leads to pro-survival signals through its effects on PI3K, PLCγ2, and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB). Inhibition of Btk by the kinase inhibitor ibrutinib induces apoptosis in a caspase-dependent manner and inhibits both phosphorylation of Btk after IgM ligation as well as downstream targets of Btk activation, including Erk, NF-κB, and Akt.55 Additionally, ibrutinib inhibits proliferation by CpG or microenvironment stimulation.55,56 Collectively, these studies provide evidence of the importance of BCR signaling CLL, which has led to introduction of new therapeutics for this disease.
Is CLL a Disease of Defective Apoptosis?
Since its initial description and early characterization, CLL has long been considered a disease of slow accumulation of tumor cells, resulting from disrupted or defective apoptosis. Multiple studies have demonstrated that CLL cells overexpress several anti-apoptotic proteins, including BCL2, MCL1, BCL2-antagonist/killer 1 (BAK), and XIAP and have diminished expression of compensatory pro-apoptotic proteins such as BAX.57 The balance of expression of these anti-apoptotic proteins in CLL cells in vivo has been shown to be quite volatile once the tumor cells are removed from their microenvironment, where apoptosis is often rapidly noted.58,59 Studies by multiple groups have demonstrated that CLL cells have in vivo constitutive activation of several anti-apoptotic transcription factors, including NF-κB, nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT), and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) that can influence one or more of the anti-apoptotic proteins that promote survival in vivo.60–63 The source of activation of these different transcription factors is not completely defined but may in part be due to autocrine and paracrine networks involving tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 13b (TNFSF13B); acidic (leucine-rich) nuclear phosphoprotein 32 family, member B (APRIL); vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF); interleukin (IL)-4; and TNF receptor superfamily member 5 (CD40) and provide an explanation of why many of the downstream survival anti-apoptotic genes decrease when out of the body.59,64 CLL cells are also maintained through contact with stromal cells (bone marrow and dendritic) and nurse similar cells through a complex interface of adhesion molecules and stromal survival factors such as stromal cell–derived factor (SDF-1).65–68
Genetic Abnormalities
Much of the advances in the understanding of the biology of acute leukemia have come from studying repetitively occurring cytogenetic abnormalities. Such detailed study of the genetics of CLL has been hindered by the inability to effectively induce proliferation of tumor cells for standard metaphase cytogenetic analysis and the poor response of CLL cells to B-cell mitogens. Nonetheless, several historic cytogenetic studies identified a variety of deletions, including del(11q22.3), del(17p13.1), del(13q14), and del(6q21-q23), as well as trisomy 12, as common abnormalities in CLL.69,70 The frequency of these abnormalities has been further refined through the use of interphase cytogenetic analysis, which does not require isolation of dividing cells. These studies have demonstrated that del(13q14) is by far the most common cytogenetic abnormality in CLL, followed by trisomy 12, del(11q22.3), del(17p13.1), and del(6q22.3).71 Stimulation studies with CpG oligonucleotides plus IL-4 or CD40 confirmed the prevalence of these abnormalities and also identified unbalanced translocations not generally observed with traditional metaphase cytogenetics.72,73 The prognostic significance of these unbalanced translocations appears to be important, and a study by the CLL Research Consortium demonstrated that these could be produced reproducibly from the same patient within different cytogenetic laboratories, which lowers the concern that this is an artificial finding of in vitro tumor stimulation.74 Similarly, complexity of karyotype, as already appreciated in acute leukemia, appears to be a poor prognostic factor in CLL. These genetic findings have been further refined with single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) or comparative genomic hybridization arrays from which a negative impact of complexity75 has been established. Additionally, new, yet undescribed deletions have been noted for chromosome 15 at the MGA locus76 that will require further study to determine their impact on biology and relevance to prognosis of CLL patients. A perplexing finding that needs to be reconciled is why CLL stem cells lack these common cytogenetic abnormalities. Current research would suggest that many of these are secondary events as part of the leukemia progression. Application of new technologies moving forward will likely facilitate better characterization of recurring genetic abnormalities in CLL.
The presence of recurrent deletions in CLL suggests the possibility of unique tumor suppressor genes in these different regions that has led to extensive study for more than 2 decades. In particular, attention to coding genes within the 13q14 region failed to identify a viable tumor suppressor gene candidate for many years. However, in 2002, Croce and colleagues identified miR15 and miR16, two noncoding microRNAs, in the deleted region of 13q14.77 Noncoding RNAs range in size from 21 to 25 nucleotides and represent a newly recognized class of gene products whose function is to silence genes through binding to the 3′-untranslated region of specific genes to inhibit translation. When near-compatible hybridization of the noncoding RNA exists, RNA transcription can also be antagonized. This same group later showed that miR16 regulates expression of BCL2, which is overexpressed in CLL and other B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders.78 Multiple different studies have associated specific miR expression with rapid disease progression, fludarabine resistance, and poor prognosis. In addition, miR34a has been directly related to the adverse outcome associated with TP53 dysfunction.79,80 At the time of this writing, several reports are coming forth about the role of miRs in cell-to-cell communication. Further study of miRs in CLL is underway to elucidate their full role in the pathogenesis and progression of this disease. In addition, other conserved larger noncoding RNAs with different small interfering RNA (siRNA) and epigenetic silencing roles have been identified to have a significant role in CLL.
Recurring Mutations in CLL
Until the advent of whole-exon and whole-genomic sequencing, CLL was not typically associated with recurring mutations early in the pathogenesis of the disease. Probably most characterized are p53 mutations, which occur in 3% to 5% of patients at diagnosis, often in conjunction with deletion of the alternative allele (at 17p13.1 loci) that is associated with rapid disease progression and poor survival.83–83 With treatment and subsequent relapse, the frequency of p53 mutations continues to increase proportionately and is most common in patients with Richter transformation.86–86 Another factor upstream of p53 that has also been shown to be recurrently mutated in 10% to 20% of patients is ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM).89–89 The ATM gene lies in the region of minimal deletion of del(11q22.3) that is commonly seen in CLL. ATM mutations are not exclusively observed in patients who have del(11q22.3), although loss of function of both alleles has been associated with diminished DNA damage response.90 Impact of ATM mutation on outcome in CLL has been reported in some,91,92 but not all93 studies.
The major impact in CLL biology related to recurring mutations has come with the advent of availability of whole-exon and whole-genomic DNA sequencing. During the past year, two papers have been published in which the authors identified unique properties of CLL cells compared with studies done in solid tumors relative to mutation frequency and also have identified several novel candidate genes with recurrent mutations that warrant further study. Puente and Campo were the first to report four individual patients (two IGHV1-mutated vs. two IGHV1-nonmutated) who had whole-genome sequencing.94 This study identified approximately 1000 somatic mutations per tumor in nonrepetitive regions similar to that observed in acute leukemia but much lower than that observed in lung cancer or malignant melanoma. The authors also detected a marked differences in the mutation pattern between CLL samples with IGHV1-mutated patients having a higher proportion of A>C/T>G mutations than cases with IGHV1-nonmutated disease. The authors hypothesized that differences between CLL subtypes might reflect the molecular mechanisms implicated in the IGHV1 mutational subtype. Specifically, for the IGHV1-mutated patients, an error-prone polymerase η during somatic hypermutation could contribute to the high frequency of A > T to C > G transversions. Extending this, the authors identified 46 somatic mutations that caused changes in the protein-coding sequences of 45 genes in the four patients studied. None of these nucleotide substitutions had been previously linked to CLL pathogenesis, and only one had been reported in a CLL patient (NOTCH1). This group validated 26 of these 46 genes that were expressed at an mRNA level in 169 CLL patients and identified four genes (NOTCH1, MYD88, XPO1, and KLHL6) that were present in at least one additional patient.94 Surprisingly, NOTCH1 mutations were present in approximately 12% of CLL samples at a site that deletes a proteolytic site in the carboxy (C) terminus, thus resulting in increased protein stability; furthermore, gene induction as determined by microarray analysis was consistent with elevated NOTCH pathway activity. Patients with NOTCH1 mutations were shown to have more aggressive disease, as measured by stage and also overall survival (OS). The findings by this group relative to incidence of NOTCH1 have been confirmed by several other groups, including high association of NOTCH1 mutations with treatment-refractory CLL.95–99 The authors also identified MYD88 as a recurrent mutation in IGHV1-mutated CLL that had functional significance based on enhanced Toll-like receptor signaling. The functions of less common XPO1 and KLH6 mutations were not explored.
A second paper by this same group examining whole-exon sequencing21 together with another group led by Wu100 identified SF3B1, encoding a subunit of the spliceosomal U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP) as another recurring gene in CLL. Similar to the first paper characterizing NOTCH1, a phenotype of disordered splicing in CLL cells bearing SF3B1 mutations was identified. SF3B1 mutations were noted to be more frequently associated with del(11q22.3) and IGHV1-nonmutated status and had negative impact on OS.100 SF3B1 mutations similar to the mutation seen in CLL have been found in other types of leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. The biology behind how these mutations might contribute to the development or progression of CLL at this time is unknown. Similar to the gene expression profiling studies that identified ZAP70 expression as an important potential contributor to the biology of CLL more than a decade ago, whole-genome and whole-exon sequencing are now bringing forth new candidate genes that before these studies had little predicted relationship to CLL. These studies to date however provide evidence that there is likely not to be a common driving mutation such as seen with BRAF V600 mutations in hairy cell leukemia101 and MYD88 mutations in Waldenström macroglobulinemia.102
Immune Suppression in Development and Progression of CLL
Effective immune surveillance with protection from infection and malignancy requires a coordinated effort between the innate and adaptive components of the immune system. A central driving feature of the pathogenesis of CLL is early immune deficiency that facilitates tumor growth and expansion while evading classic immune surveillance by both the innate and adaptive immune system. The best evidence of the potential immune suppressive features of CLL cells comes from studies in which allogeneic T cells combined with CLL cells were unable to generate mixed lymphocyte reaction and cytotoxicity toward these tumor cells.103 Studies examining the function of the innate and adaptive immune system have documented early defects at diagnosis that tend to progress with expansion of the disease. For instance, studies have shown that the absolute number of T cells and natural killer (NK) cells and the presence of hypogammaglobulinemia in CLL patients at diagnosis have been shown to predict OS.104,105 With progression of disease from diagnosis to time of treatment, several studies have noted both expansion of suppressive T-regulatory cells106,107 and also change in CD4 helper cells from a T-helper (Th) type 1 (Th1) anti-tumor cytokine, anti-tumor type profile (tumor necrosis factor-α [TNF-α] and interferon-γ [IFN-γ]) to predominantly a Th2 anti-inflammatory cytokine profile (IL-4, IL-10) that facilitates CLL survival in the microenvironment.108 The immunosuppressive effects observed in CLL lie predominantly with the CLL clone, as recently demonstrated in very elegant work by the Gribben laboratory in humans and also representative mouse models of CLL.109 The Gribben group showed CLL cells express antigens such as CD200, CD270, CD274, and CD276 that functionally diminish the ability of both allogeneic and also autologous T cells to activate.110 In addition to the loss of direct anti-tumor cytotoxicity by CLL T cells, this defect also leads to much of the infectious morbidity associated with this disease. The importance of reversing the immune deficiency in CLL represents goals of therapy and of diminishing long-term morbidity caused by infections and secondary malignancy in this disease.
Contribution of Microenvironment in CLL Pathogenesis
It has been appreciated that for decades that CLL cells have a great tendency to undergo spontaneous apoptosis when removed from the body, similar to many other lymphoid tumors. Concomitant with this observation, several groups identified that CLL cells when grown on stromal cells65,66 or together with chemokines59,111 or integrin components112,113 relevant to CLL increased greatly their survival in culture.65,66 Furthermore, elegant studies by several groups showed that co-culture on bone marrow, mesenchymal, or nurselike cells enhanced CLL cell proliferation and also upregulated select anti-apoptotic genes such as MCL1, BCL2, and A1. Upregulation of these anti-apoptotic genes (and loss in culture) is one reason CLL cells in protected sites such as bone marrow and nodes have enhanced resistance to cytotoxic agents. In addition to enhancing anti-apoptotic genes, these same microenvironments can also promote CLL cells to secrete chemokines that can attract T cells that ultimately contribute further to CLL survival and growth in CLL proliferation centers.114,115 This direct and indirect cross-talk between CLL cells and the microenvironment is an area of significant investigation in CLL and, in part, forms the basis for many of the new targeted kinase inhibitors and also therapeutics such as stromal-derived factor 1 (SDF1)/chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 (CXCR4) antagonists that are currently under evaluation.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of CLL for many years has been made based on morphologic criteria of mature lymphocytes on the blood smear with an abundance of smudge cells. Smudge cells are an artificial remnant of the blood smear preparation, but in several series their number has been associated with adverse outcome. Specifically, patients with fewer smudge cells tend to have a more aggressive clinical course.118–118 Preparation of the smear from ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) versus EDTA and bovine serum albumin preparation can greatly influence the number of these cells as well based on their membrane features.119 Despite morphologic similarity, many diseases can mimic CLL in both appearance and clinical presentation. With the advent of distinct genetic markers that distinguish outcome and also new, more effective targeted therapies for CLL and other diseases, determining the correct diagnosis is of great importance. Immunophenotyping (flow cytometry) is the key test utilized to make the diagnosis of CLL and is an essential test at diagnosis. CLL cells have a relatively consistent immunophenotype, which differentiates CLL from mantle cell lymphoma, hairy cell leukemia, follicular center cell lymphoma, splenic lymphoma with villous lymphocytes, and other indolent B-cell malignancies.120,121 Specifically, CLL cells express a variety of B-cell markers, including dim surface immunoglobulin (sIg), CD19, dim CD20, and CD23, as well as the pan–T-cell marker CD5. Kappa or lambda light-chain restriction is always present, establishing the presence of a clonal B-cell population, although sIg expression may be so dim that light-chain restriction may be difficult to determine. In contrast, presence of CD10, FMC7, or CD79b (all typically absent on CLL cells) or bright expression of CD11c, CD20, or CD25 (all typically dim on CLL cells) suggests an alternative low-grade B-cell lymphoproliferative malignancy or a variant that often is typical of trisomy 12. Expression of CD5 without CD23 suggests mantle cell lymphoma, and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) for t(11;14) or immunohistochemical staining for CCND1 overexpression should be performed to exclude mantle cell lymphoma. Repeat immunophenotyping is generally done only to confirm tumor antigen expression if antibody (i.e., rituximab or ofatumumab)-based therapy is to be undertaken or the clinical history suggests that either CLL transformation to a more aggressive phenotype (i.e., prolymphocytic leukemia or large cell lymphoma [Richter transformation]) has occurred. In this setting the immunophenotype may remain the same or have changed, often with loss of CD5 or increased intensity of CD20, FMC7, or CD79b antibodies. If morphologic appearance of prolymphocytes or large lymphoid cells in blood, bone marrow, or lymph nodes is present, flow cytometry changes are not required to make this diagnosis. A bone marrow biopsy and aspirate are typically not required to make a diagnosis of CLL. It is important to understand that to make the diagnosis of CLL there must be at least 5 × 109/µL immunophenotypically confirmed clonal B lymphocytes. A bone marrow at diagnosis is not required to establish the diagnosis by the new International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (IWCLL) 2008 recommendations. Our practice is only to do a bone marrow study at diagnosis if there is cytopenia or some other finding at the time of presentation that raises suspicion for Richter transformation. Similarly, a confirmatory lymph node biopsy is not required at the diagnosis of CLL unless an alternative diagnosis is suspected based on the history and findings of physical examination.
Staging and Prognostic Factors
Staging for any type of cancer is performed at diagnosis to predict how the disease will impact outcome. In general, staging is not applied longitudinally through the course of the disease. The two most common staging criteria for CLL are the Rai122 and the Binet123 staging systems. Both were developed utilizing clinical parameters of disease and were the cornerstone of prognostic decision making until more recent molecular markers became available. The Rai classification was published in 1975122 and was the first disease-specific staging methodology for CLL (Table 102-2). This incorporated several clinical and laboratory manifestations of disease and correlated with median survival of patients. The Rai staging system includes five stages, 0 to 4, that are assigned based on the following: stage 0, presence of lymphocytosis; stage I, lymphocytosis with enlarged lymph nodes; stage II, lymphocytosis with organomegaly and or lymph node enlargement; stage III, lymphocytosis with anemia (hemoglobin < 11 g/dL); and stage IV, lymphocytosis with thrombocytopenia (platelets < 100 × 109/L). Poorer median survival was directly associated with increasing stage and ranged from 150 months for stage 0 to 19 months for stage IV. In studying a 129 French cohort of patients with CLL, Binet and colleagues reported a slightly modified staging schema in 1977 that has since been consolidated to three stages (Table 102-3). As with the Rai staging, Binet staging is based on clinical manifestations of disease and was associated with survivability and prognosis in their population. The modified Binet staging123 contains three groups: stage A is lymphocytosis with less than three nodal areas involved, stage B is lymphocytosis with three or more nodal areas involved without anemia or thrombocytopenia, and stage C is lymphocytosis with or without lymph node or splenomegaly but anemia (hemoglobin < 10 g/dL) or thrombocytopenia (platelets < 100 × 1012/L). Outcomes between these two staging systems are relatively similar, particularly for patients with more advanced stage disease who are cytopenic and in whom survival with traditional therapies is quite short. In North America, the Rai staging system is widely used, whereas in Europe the Binet staging system is used. Both of these staging systems are not very effective at risk-stratifying patients with early-stage disease. As a consequence of this, recent advances in staging systems have begun incorporating cytogenetic and molecular features of the CLL tumor cells as well as to better refine outcome, particularly among patients with early-stage disease.124,125
Table 102-2
| Stage | Lymphocytosis | Enlarged Nodes | Enlarged Spleen | Hgb < 11 g/dL | Platelets < 100 × 1012/L | Median Survival* |
| 0 | Yes | No | No | No | No | >150 months |
| 1 | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | 101 months |
| 2 | Yes | Yes/No | Yes | No | No | 71 months |
| 3 | Yes | Yes/No | Yes/No | Yes | No | 19 months |
| 4 | Yes | Yes/No | Yes/No | Yes/No | Yes | 19 months |
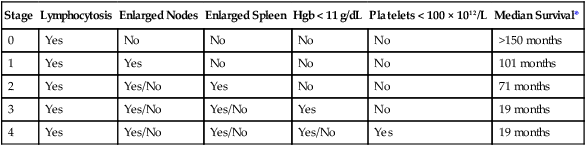
*Data from Rai KR, Sawitsky A, Cronkite EP, et al: Clinical staging of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1975;46:219–234.
Table 102-3
| Stage | Lymphocytosis | Three or More Nodal Areas Involved | Hgb < 10 g/dL or Platelets < 100 × 1012/L | Median Survival* |
| A | Yes | No | No | Similar to normal age-matched control |
| B | Yes | Yes | No | 7 years |
| C | Yes | Yes/No | Yes | 2 years |

*Data from Binet J, Auquier A, Dighiero G, et al: A new prognostic classification of chronic lymphocytic leukemia derived from a multivariate survival analysis. Cancer 1981;148:198–206.
Imaging Studies and Predicting CLL Outcome
Although lymphadenopathy is a common clinical feature of CLL and is incorporated into both major clinical staging systems, computed tomography (CT) was not available at the time these systems were devised. A common question arises as to the value of CT as part of the initial staging of newly diagnosed CLL. Several retrospective studies have recently examined whether the incorporation of CT in initial staging affects the ability to predict disease progression at diagnosis. One study examined abdominal CT scans in 140 serially seen patients with stage 0 CLL at a single institution and identified enlarged lymph nodes in 38 of them (27%).126 Patients with enlarged nodes had other high-risk features, including increased bone marrow infiltration, short lymphocyte doubling time, higher lymphocyte count, and increased ZAP70 expression. Patients with abdominal lymph nodes had a shorter treatment-free survival (3.5 years vs. not reached). This study lacked inclusion of all standard biomarkers used for predicting outcome and was too small for a multivariate analysis to definitively show the benefit of CT in this population. Other studies have confirmed127 or not shown the definitive benefit of CT over routine physical examination for decisions relative to treatment and response.128,129 At the present time, the current IWCLL 2008 treatment guidelines and also the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines do not recommend the need for CT evaluation of lymph nodes in the absence of symptoms referable to the abdomen.17,130 Similarly, although CT has been studied the most, positron emission tomography (PET) should also be briefly mentioned. Given the low proliferative index and metabolic activity in CLL cells, PET is generally not helpful for staging this disease.131 However, PET may be useful in detecting Richter transformation. In a single-institution study of 37 patients, PET identified 10 of 11 patients who had documented Richter transformation by tissue biopsy.132 However, 9 patients had false-positive scans. Thus, PET appears to be sensitive for Richter transformation, with a high negative predictive value, but specificity is poor. We generally use these studies to identify patients who warrant biopsy for Richter transformation and to localize where to perform it.
Thymidine Kinase Activity and β2-Microglobulin
Thymidine kinase is an enzyme involved in the salvage pathway of DNA synthesis and correlates with proliferative activity of tumor cells. Elevated thymidine kinase activity (TKA) has been observed to be predictive of early progression in a subgroup of untreated patients with smoldering CLL.135–135 The β2-microglobulin (β2M) is an extracellular protein component of the human leukocyte antigen class I complex. β2M has been shown to have significant prognostic relevance in lymphoma and multiple myeloma and correlates with disease burden in CLL. Hallek and colleagues examined 113 CLL and immunocytoma patients for β2M levels and TKA and demonstrated that elevated TKA and β2M both were independent predictors of shortened progression-free survival (PFS).133 Keating and colleagues confirmed the prognostic value of β2M in 622 CLL patients, reporting that an elevated level was associated with a significantly shorter survival for both untreated and previously treated patients.136 In this study, elevated β2M was observed in patients with high tumor burden and extensive bone marrow infiltration. In addition to disease progression, both β2M and TKA have been associated with short duration of remission and inferior survival after treatment. Given the time frame of these studies, prospective validation with other biomarkers will be essential.
IGHV1 Mutational Status
Although the malignant cell of CLL morphologically resembles a mature lymphocyte, genetic, immunologic, and phenotypic studies suggest that this cell is better designated as either a pregerminal or post germinal B cell. Somatic mutations in the first and second complementarity-determining regions (CDR1 and CDR2) of the IGHV1 genes are thought to occur in the germinal centers. Examination of IGHV1 genes in patient cells suggest that there may be two subsets of CLL: leukemias whose cell of origin has successfully traversed the germinal center, resulting in the mutated IGHV1 phenotype and leukemias that are derived from naïve B cells with the nonmutated (germline) IGHV1 sequence. Approximately 60% of CLL patients have cells with mutated IGHV1 genes (<98% sequence identity to germline), whereas the remaining patients have cells exhibiting nonmutated IGHV1 (≥98% sequence identity with germline), typical of pre-germinal B cells. The prognostic significance of the absence of IGHV1 gene mutations is substantial, with all studies uniformly noting an inferior survival and high predisposition to requiring early treatment in this patient subset.25,26 This patient group has a higher frequency of clonal evolution, autoimmune complications, infections,137 and Richter transformation. A CLL Research Consortium study examined the impact of IGHV1 mutation in 307 untreated CLL patients enrolled on a prospective tissue collection study.138 Fifty-three percent of these patients exhibited nonmutated IGHV1 genes, and this population had a significantly shorter median time to initial therapy (3.5 years) than those with mutated IGHV1 genes (9.2 years, P < .001). Results from a second study of more than 1000 patients from the CLL Research Consortium validated this finding.139
Because of the difficulties in determining IGHV1 gene mutational status, researchers have sought surrogate markers for this parameter. Correlation between the absence of IGHV1 gene mutations and elevated expression of the cell surface molecule CD38 on CLL cells was noted in one such report.26 In another work, ZAP70 expression was shown to correlate with IGHV1 gene mutational status.138–142 Other surrogate markers for the mutational status of the IGHV1 gene have been reported, including elevated levels of lipoprotein lipase,40,41,143,144 and related genes have been noted in patients with IGHV1-nonmutated disease. Additionally, it has been reported that IGHV1-mutated CLL cells have long telomeres with low telomerase activity, whereas IGHV1-nonmutated cells have short telomeres with high telomerase activity.29–32,145 The extreme shortening of telomeres and elevated telomerase activity are associated with both genetic instability and disrupted apoptosis in other diseases, suggesting that a similar process occurs in IGHV1-nonmutated CLL cells.
CD38 Expression
Multiple retrospective studies have shown that CD38 is an independent prognostic marker in CLL with high CD38 expression (7% to 30% positive tumor cells, depending on the series) being associated with both a shorter time from diagnosis to treatment and inferior survival.28,146–149 Unlike IGHV1 mutational status or ZAP70 expression, which remains relatively stable over the course of the disease in a given patient, CD38 expression status can change based on the compartment of disease localization and also over time with disease progression. Although CD38 expression was initially thought to be a good surrogate for IGHV1 mutational status,26 subsequent studies have shown a lower concordance and also that expression of this antigen changes over time.36,150
ZAP70
ZAP70 expression was identified as another surrogate marker for IGHV1 gene mutational status by a cDNA microarray analysis of untreated CLL patients.20 Multiple studies have shown that ZAP70 expression predicts for short time to treatment and also inferior survival.138–142,151 In one series reported by the CLL Research Consortium, the median time from initial diagnosis to treatment was 2.8 years, whereas for those without expression of ZAP70 it was 11 years.138 In several studies, multivariate analysis showed ZAP70 to be better at prediction than either IGHV1 mutational status or CD38139 and confirmed the time of diagnosis to treatment of patients with ZAP70 as being approximately 3 years. In addition to a poorer outcome, patients with ZAP70 also have a higher frequency of autoimmune complications arising from CLL.152
Despite clear data showing that ZAP70 is a prognostic factor, the reproducibility of this assay across laboratories has been problematic. Inconsistent measurement of ZAP70 may be the cause, because ZAP70 is a labile protein and laboratories have employed different methods and reagents. Given the challenges of measuring ZAP70 protein accurately, others have attempted to identify alternative markers or more stable readouts of ZAP70 expression. For example, methylation of select regions in the proximal 5′ region of the ZAP70 gene has been shown to correlate closely with expression of ZAP70 and influence treatment outcome.153,154 Our group recently completed a high-resolution, quantitative DNA methylation analysis of the entire ZAP70 gene regulatory region in 247 CLL patient samples from four separate clinical studies.155 Through this comprehensive analysis, we identified a small area in the 5′ regulatory region of ZAP70 with large variability in methylation. This sequence was found to be universally methylated in normal B cells. High correlation with mRNA and protein expression as well as activity in promoter reporter assays revealed that within this differentially methylated region, a single CpG dinucleotide and neighboring nucleotides are particularly important in ZAP70 transcriptional regulation. Furthermore, using clustering approaches, we identified a prognostic role for this site in four independent CLL patient data sets using time to treatment, PFS, and OS as clinical end points. Given the stability of genomic DNA methylation, resolution of quantification with this assay and high reproducibility of prognostic prediction across multiple clinical data sets, this test may facilitate rapid clinical assessment of ZAP70 status. Outside of such new tests, ZAP70 protein assessment by flow cytometry or other methods should still be used only in the setting of research.
Chromosomal Aberrations
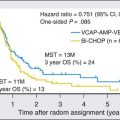
Conventional metaphase cytogenetics can identify chromosomal aberrations in only 20% to 50% of CLL cases because of the low in vitro mitotic activity of CLL cells.69 Abnormalities noted in descending frequency of occurrence include trisomy 12, deletions at 13q14, structural aberrations of 14q32, and deletions of 11q, 17p, and 6q. In addition, a complex karyotype (three or more abnormalities) occurs in approximately 15% of patients and predicts for rapid disease progression, Richter transformation, and inferior survival.156,157 A recent study showed that the use of CD40L or the combination of IL-2 and CpG stimulation revealed translocations in 33 of 96 patients (34%).73 These translocations were both balanced and unbalanced, occurring in 13q14, 11(q21q25), 14q32, or regions also seen in lymphomas such as 1(p32p36), 1(q21q25), 2(p11p13), 6(p11p12), 6(p21p25), and 18q21. These data define a new prognostic subgroup of patients with significantly shorter median time from diagnosis to requiring therapy (24 vs. 106 months) and OS (94 vs. 346 months) compared with those without translocations. The frequency of these translocations in untreated patients was less common, suggesting that these accumulate with disease progression.
Given the limitation of standard or stimulated karyotype analysis, interphase cytogenetics of known abnormalities by FISH has become the current state-of-the-art technique for accurately distinguishing genetic subtypes of CLL. The largest study of interphase cytogenetics resulted in improved sensitivity to detect partial trisomies (12q12, 3q27, 8q24), deletions (13q14, 11q22-23, 6q21, 6q27, 17p13), and translocations (band 14q32) in more than 80% of all cases. In a large study of 325 patients by Dohner and colleagues, a hierarchical model consisting of five genetic subgroups was constructed on the basis of regression analysis of CLL patients with chromosomal aberrations.71 Patients with a 17p deletion had the shortest median survival time of 32 months and the shortest treatment-free interval (TFI) of 9 months, whereas patients with an 11q deletion followed closely with 79 months and 13 months, respectively. The favorable 13q14 deletion group had a long TFI of 92 months and a median survival of 133 months, whereas the group without detectable chromosomal anomalies and those with trisomy 12 fell into the intermediate group with median survival of 111 and 114 months, respectively, and TFI of 33 and 49 months, respectively. According to this pivotal study, CLL patients are prioritized in a hierarchical order (deletion 17p13 > deletion 11q22-q23 > trisomy 12 > no aberration > deletion 13q14).156 The hierarchical model of cytogenetic abnormalities in predicting disease progression by FISH has been further confirmed by other studies. Other much less frequently documented abnormalities including MYC translocations have been reported in less than 1% of CLL patients, generally with unfavorable prognostic features, short time to treatment, and short survival.158 The impact of high-risk interphase cytogenetics relative to disease progression, outside of its association with IGHV1-nonmutated CLL, in at least one study had less impact on outcome.
Select Gene Mutations
Unlike other diseases, CLL has not yet had a common driving mutation that contributes significantly to the progression of the disease in a majority of patients. Until recently, the most common and well-characterized mutated gene in CLL was TP53, which often occurred in concert with del(17p13.1). The frequency of TP53 mutations and/or deletions at diagnosis of CLL is relatively infrequent (3% to 5%) but increases in patients with refractory disease when it may exceed 25%. Although approximately 75% of TP53 mutations occur together with del(17p13.1), a component of patients have isolated TP53 mutations without evidence of deletion in the other allele. Some studies have shown similar negative impact of these isolated point mutations in TP53 with respect to predicting time to treatment and also response to DNA-damaging agents such as alkylating agents and fludarabine.159–163 Many clinical studies are now including TP53 mutation screening as part of the standard risk stratification for early treatment intervention and also treatment stratification. Routine performance of TP53 mutations as part of all initial risk assessments at diagnosis and also at the time of treatment is not included outside of a clinical trial. Similarly, other recently identified recurring mutations such as NOTCH194,98,99 and also SF3B1 mutations have also shown frequency in high-risk genomic CLL of 10% or greater and may have prognostic significance.21,164 Further studies to prospectively validate these markers will be required before routine application of this assays can be recommended for clinical use in risk stratification.
Integration of Clinical and Molecular Markers
Until very recently there have been no published series that have integrated clinical, laboratory, and genomic features into a predictive model to identify patient risk for progressing onto early treatment as opposed to those who may have an extended period of observation. Wierda and colleagues from M.D. Anderson Cancer Center reported a prospective series of 930 patients who were newly diagnosed with the diagnosis of CLL who had examination, laboratory, and genomic assessment.125 With prospective follow-up, they identified each of the following criteria in a multivariate analysis to be significantly associated with progression: (1) three involved lymph node sites; (2) increased size of cervical lymph nodes; (3) the presence of del(17p13.1) or del(11q22.3); (4) increased serum lactate dehydrogenase level; and (5) nonmutated IGHV1 mutational status. A point algorithm to predict disease outcome using these features was established but requires validation from a second data set before widespread use can be recommended.
How to Use Staging and Biomarkers
Our understanding of the biology of CLL has improved dramatically, and many relevant biomarkers are now becoming useful for predicting when CLL will clinically progress. However, no study to date has demonstrated that earlier treatment will alter the natural history of the patient in even the higher-risk groups with high progression rates. Therefore, at the present time the use of staging and predictive biomarkers should be used only to provide patients with information relative to the expected course of their disease. Outside of a clinical trial, these results should never be used to initiate therapy in patients with asymptomatic disease and no indication for treatment. Before performing predictive tests, we generally discuss with the patient how we will use these tests and the potential consequences that can be derived from them. Specifically, for a subset of patients having low-risk disease at diagnosis with IGHV1-mutated disease and favorable karyotype, often significant relief occurs that allows resumption of regular life opportunities and more comfortable living with the diagnosis of CLL. However, in the patients who are identified to be at high risk for disease progression, significant anxiety can result after they are told they are at high risk for progression with ultimately expected short survival and yet no treatment or intervention will be pursued. With appropriate counseling, in our experience the majority of patients decide to have this testing whereas a small subset defers it. Currently such testing is recommended as optional and helpful by the NCCN130 and IWCLL 2008 guidelines.17 Box 102-1 provides an example of the initial evaluation provided by our group when seeing a newly diagnosed patient. It also includes a detailed discussion of complications that can arise as a consequence of CLL. Because the lymphocyte-doubling time is a prognostic feature in the progression of CLL,165,166 our approach is to follow patients every 3 months during the first year; if little change in clinical or laboratory parameters occurs at this point, we extend this time period to every 6 months in the absence of new complaints.
Complications
Autoimmune Complications
Over the course of the disease, approximately 20% of patients with CLL will experience autoimmune hematologic complications that include, in descending order of occurrence, autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA), idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura (ITP), and pure red cell aplasia. In general, the majority of patients with CLL will develop these autoimmune complications when their disease is active, although a small proportion (10% to 15%) of patients have AIHA at diagnosis.167 AIHA has variable symptoms most often referable to profound anemia, including fatigue, weakness, lethargy, dyspnea on exertion, and dizziness. Rare presentations can include new clinically visible jaundice, headaches, or chest pain that identifies anemia on further evaluation. Although the insidious onset of AIHA can occur over 2 to 3 months, acute symptoms may occur that require rapid intervention. The typical laboratory findings include indirect hyperbilirubinemia, elevated lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels, low haptoglobin, and hemoglobinuria. The direct antiglobulin Coombs test (DAT) is positive in up to 75% of patients with CLL with AIHA. However, patients can have a positive DAT and not ultimately experience clinically significant hemolysis. Most of the red cell-directed antibodies produced are warm reactive (IgG antibodies), but patients can occasionally present with cold agglutination syndrome (IgM antibodies). The antibodies are mostly polyclonal and derived from residual normal B cells as compared with the malignant B-cell clone. The exception to this is IgM-derived antibodies, which are often monoclonal and derived from the malignant B-cell clone.
Treatment of AIHA is derived from small case series and small nonrandomized studies.168,169 Glucocorticoids are considered the first line of therapy of AIHA. Prednisone 1 mg/kg is given for 14 to 28 days, followed by a slow taper over 2 to 3 months. Prophylaxis for opportunistic infections (e.g., from Pneumocystis jiroveci and varicella zoster virus) should be given to patients on extended prednisone therapy. The overall response rates to prednisone are as high as 90%, but unfortunately approximately 60% of patients experience relapse when corticosteroid therapy is tapered or discontinued. A poor response or inability to taper prednisone therapy within a reasonable time period (2 to 3 months) is a reason to initiate second-line therapy. Rituximab 375 mg/m2 weekly for 4 weeks is often effective for corticosteroid-resistant AIHA and also if corticosteroid withdrawal is not possible.172–172 Because of the long-term morbidity of prolonged corticosteroid administration in CLL and data demonstrating benefit to concurrent corticosteroids and rituximab for rapid withdrawal of corticosteroids in ITP,173 some physicians administer these agents concurrently at the diagnosis of AIHA unless a relative contraindication (i.e., hepatitis B) exists. Rituximab is also effective if a poor response to corticosteroids is noted.174,175 Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), the next line of treatment, induces responses in 40% to 60% of patients with AIHA.176 Cyclosporine has been used for refractory AIHA of CLL at a dose of 5 mg/kg/day given in divided doses twice daily. Other treatment modalities include splenectomy177,178 or splenic irradiation,179 or chemoimmunotherapy180 if the disease is active. Treatment of the underlying CLL is generally required for long-term control of autoimmune cytopenias. However, our practice is to first control the autoimmune process with corticosteroids or other therapies before considering treatment of the underlying CLL. Supportive therapy with periodic red cell transfusions is also important in the management of AIHA. These cells should be irradiated and leukopore filtered to prevent development of transfusion-associated graft-versus-host disease.
One poorly characterized type of AIHA relates to that observed during fludarabine therapy. Generally this occurs in the setting of no evident hemolysis before starting therapy with a fludarabine-based regimen. Time of onset is usually during the first three cycles with classic laboratory findings. With this particular type of drug-related AIHA, cessation of fludarabine is warranted and transitioning to an alternative regimen is best advised. Fludarabine-associated hemolytic anemia does recur with rechallenge, and fatalities in this setting have been described.181 Rechallenge with pentostatin has been reported in one case to trigger recurrent AIHA.182
Similar to that of AIHA, treatment of ITP in CLL is generally driven by experience reported in small case series and nonrandomized studies. Most often the clinician is trying to discern activity of CLL versus ITP as the source of the thrombocytopenia. If the diagnosis of ITP is a certain cause of thrombocytopenia, applying the traditional cutoff for treatment of 30 × 1012/L is acceptable. Often it is not possible to clearly discern the contribution of disease and ITP contribution to thrombocytopenia, and our approach would be to initiate treatment earlier at a count of 50 × 1012/L or less. Therapy for ITP is similar to that for AIHA, with application of prednisone with the potential addition of rituximab to increase the ability to successfully taper prednisone.173 Rituximab has also been used in settings of corticosteroid-refractory disease quite successfully.174,183,184 There are no data supporting maintenance rituximab in this setting. IVIG 400 mg/kg/d for 5 days or 1 g/kg/d for 2 days is a frequent second-line therapy for ITP. If these two treatment approaches are unsuccessful, thrombopoietin agonists (eltrombopag and romiplostim) are effective for refractory ITP in CLL.185 As with AIHA, splenectomy can also be considered for severe cases,186 but unlike primary ITP, recurrence is more common with extended follow-up. Other refractory ITP therapies include cyclosporine and cytotoxic chemotherapy or chemoimmunotherapy combinations.187
Pure red cell aplasia (PRCA) is a relatively rare T-cell–dependent complication associated with CLL, but it can have an incidence as high as 6% that is characterized by a hypoproliferative anemia. This can be caused by both disease and also infections, such as parvovirus.188,189 The anemia can occur at all periods in the disease, including in early-stage CLL. PRCA is thought to be caused by cytotoxic effects of suppressor T cells or gamma T cells on erythroid progenitor cells preventing maturation of these cells.190,191 Therapy for PRCA begins with prednisone at a dose of 1 mg/kg/d. If a response is not obtained in 4 weeks, cyclosporine should be added and has been shown to be successful in small series.194–194 Most patients exhibit a response by having reticulocytosis within the first 10 to 14 days, but maximal response may occur an average of 10 weeks after the start of therapy. Mild reversible nephrotoxicity may warrant dose adjustment in some patients. Other agents that have shown promising activity in treating PRCA include rituximab,195 IVIG,196 alemtuzumab,197 and antithymocyte globulin.198,199 Packed red-cell transfusions are usually indicated in patients who are clinically symptomatic from severe anemia, and these should be irradiated and leukopore filtered.
Other rare autoimmune complications such as paraneoplastic pemphigus,202–202 angioedema caused by acquired C1-inhibitor deficiency,203 acquired von Willebrand factor,204 another factor deficiency,205 and nephrotic syndrome206 have been reported in CLL. Therapy for these complications generally follows the approach used for AIHA.
Infectious Complications
Infectious complications remain the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with CLL. The incidence of infectious complications has been estimated to be as high as 80%, with a mortality of approximately 60% over the course of the disease.207 The source of immune suppression that contributes to the high infectious rate is predominantly the disease. CLL affects host immunity through an impaired antibody response and hypogammaglobulinemia,105 weakened host cellular immune responses including impaired monocyte and granulocyte function,208 an increase in regulatory T cells,209 diminished T-cell response,109,210 and finally the acquired defects after immunosuppressive chemotherapy.
Recent studies have examined predictors of severe infections in patients with CLL. Francis and colleagues in a retrospective cohort identified advanced age, clinical stage B or C disease, nonmutated IGHV1, and positive CD38 status as independent predictors of both shorter time to first infection and infection-related mortality.137 Other risk factors that may also have an impact on development of infections include type of initial therapy and development of renal insufficiency.
Herpesvirus infections are especially common in patients treated with nucleoside analogs and alemtuzumab.211 Chronic, indolent oropharyngeal and circumoral herpes simplex virus outbreaks are more frequent than aggressive, disseminated visceral disease. Reactivation of Epstein–Barr virus can occur rarely and be the source of persistent fevers, cytopenias, and sometimes neurologic symptoms. Varicella-zoster virus can cause herpes zoster, herpetic neuralgia, and, rarely, meningoencephalitis. The JC polyoma virus has been implicated in the development of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Management of these infections depends on early recognition of disseminated viral disease and timely initiation of antiviral therapy in cases of herpes simplex virus, Epstein-Barr virus, and varicella-zoster virus. At diagnosis, all patients should be provided instruction to identify the signs and symptoms of herpesvirus infection.
Given the frequent finding of hypogammaglobulinemia in CLL and high occurrence of infection, several studies have examined if IVIG replacement therapy can reduce the incidence and severity of infectious complications.212,213 Patients receiving IVIG in a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial experienced significantly fewer bacterial infections than the placebo group.214 The therapy was well tolerated with few adverse reactions, but there was no observed benefit in terms of preventing viral or fungal infections. However, other studies have shown an almost 50% reduction in the number of serious infections per year with IVIG infusions.212,213 However, the cost of IVIG therapy is considerable and therefore it should be used only in patients with problematic recurrent infections. The usual dose used is 200 to 400 mg/kg every 4 to 6 weeks as needed, with the aim of keeping the trough serum IgG concentration greater than 500 mg/dL. Among the strategies for preventing infection in this patient population is immunization. CLL patients, however, typically respond poorly to pneumococcal and influenza vaccines.217–217 Recent studies have indicated that protein-conjugated vaccines may be more immunogenic.218,219 In light of the paucity of data on an appropriate immunization schedule, we suggest a modified immunization plan based on the recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. This includes use of pneumococcal 13-valent conjugate vaccine (Prevnar 13) for pneumococcal prophylaxis. Because of the risk of dissemination, CLL patients should avoid live vaccines including the varicella-zoster virus.
Secondary Malignancies
Likely as a consequence of disease-induced immune deficiency, CLL is associated with an increased risk of secondary malignancies. These include most commonly skin cancers but also Kaposi sarcoma, malignant melanoma, Merkel cell tumor, and kidney, laryngeal, and lung cancers.222–222 Patients with CLL should be advised to maintain vigilance in screening for secondary cancers and also discontinuing high-risk behaviors such as tobacco use. For CLL patients who experience either precancerous or cancerous skin lesions, serial 6- to 12-month monitoring examinations should be considered.
Hypersensitivity to Insect Bites
CLL patients commonly exhibit an exaggerated cutaneous response to insect bites.223,224 The reaction is characterized histologically by the presence of a dermal infiltrate comprising a mixed population of T and B cells, eosinophils, and eosinophilic granule protein. The extent of eosinophilic degranulation may also correlate with the severity of symptoms. Clinically, these patients have recurrent, painful, bullous eruptions that may be traced to an insect bite in some instances. In limited cases we have also observed CLL patients have hypersensitivity to bed bugs, and this should be considered in the differential diagnosis. Identification and avoidance of known triggers may be useful in some cases, but most patients are unable to identify the inciting exposure. Treatment with a short course of corticosteroids is usually effective.
Initial Treatment
The clinical spectrum of CLL at initial presentation is very heterogeneous, as outlined earlier, with many patients being asymptomatic. Historic trials summarized in a meta-analysis of 2048 patients from six trials demonstrated no difference in death rate between patients randomly assigned to early therapy (42.6%) and those whose treatment was deferred (41.6%). Thus, patients with asymptomatic or early-stage disease derive no therapeutic benefit from early alkylating agent therapy.225 However, in these studies chlorambucil was administered as initial therapy and it achieves complete response (CR) in few patients. When one considers current recommendations for treatment of CLL it has to be with a firm understanding of the history of this disease, grounded in two areas that arguably have experienced the most dichotomous shift over the past 15 years. First, the historic approach to prognosis has classically been based on stage (Rai or Binet) and the presence or absence of symptoms, whereas now it is focused on molecular characteristics. Second, the treatment options available today have shifted from those with limited responses and the potential for both long- and short-term toxicity to newer biological and molecular targeted therapies. However, to this day, our approach to patients with early disease is still based on data obtained with the use of agents such as chlorambucil. The past decade has seen the development of more effective treatments, including the targeted agents against BCR signaling kinases (GS1101 and ibrutinib) that offer great promise and are well tolerated with extended use. Given the ability to use molecular markers to better risk-stratify newly diagnosed CLL patients and the knowledge that select high-risk genomic feature CLL undergoes clonal evolution with propensity to develop increasing resistance to therapy, the issue of early treatment needs to be reconsidered. It is hoped that ongoing efforts within the German CLL Study Group (GCLLSG) will determine whether early intervention with chemoimmunotherapy regimens will improve long-term survival in patients with high-risk CLL. Pilot studies with targeted therapeutics such as lenalidomide and ibrutinib are also ongoing or being planned for this high-risk population.
To establish uniform clinical practice standards and ensure reproducible eligibility criteria for entrance into clinical studies, the National Cancer Institute226,227 and later the NCCN130 and IWCLL17 established guidelines for time when CLL therapy should be initiated. Indications to begin therapy include cytopenias; bulky, progressively enlarging, or symptomatic lymphadenopathy and/or hepatosplenomegaly; disease-related symptoms; and AIHA or thrombocytopenia that is poorly controlled (Box 102-2). In addition to the official IWCLL criteria for therapy, increasing frequency of infections and slowly progressive anemia are other indications that can aid the practicing physician in deciding when to initiate therapy in CLL. A useful paradigm for clinical practice is to institute treatment in CLL only for cytopenias or directly referable symptoms. The role of biomarkers in selecting the initial treatment for CLL is applied for older biomarkers and is currently under study by several groups with newly identified ones. In general, patients with del(17p13.1) do not respond well to traditional chemotherapy or chemoimmunotherapy and should be considered for more aggressive interventions such as allogeneic stem cell transplantation as part of initial therapy. Patients with del(11q22.3) appear to have improved outcomes with hyperfractionated cyclophosphamide as part of the FCR (fludarabine-cyclophosphamide-rituximab) regimen. Additionally, several studies have shown that CLL patients older than 70 or who have multiple co-morbid illnesses do not benefit from fludarabine-containing regimens, and this needs to be factored into treatment algorithms. Next, we summarize the findings of clinical studies of different treatments for CLL; where such data exist, we integrate genomic biomarkers as well as clinical factors, including age and co-morbid illnesses. Different therapies are outlined below with attention to details related to their initial use in previously untreated CLL. Because many of these regimens were also developed for relapsed CLL, these data are also reviewed in the later discussion on treatment of patients with relapsed CLL.
Cytotoxic Chemotherapy
Alkylating Agents
Chlorambucil has served as the first line of therapy for CLL for many years and is still used today. It is orally bioavailable and has a favorable toxicity profile of myelosuppression, nausea, vomiting, and rash. There have been a multitude of chlorambucil schedules and doses utilized in phase III trials, including administration as (1) a single pulse dose at 40 mg/m2 orally every 28 days228; (2) 0.4 mg/kg with an increase to 0.8 mg/kg every 15 days as tolerated229; and (3) 10 mg/m2 for 7 continuous days every 28 days.230 Older studies tended to administer chlorambucil together with corticosteroids, although the definitive benefit of this was never shown. If we choose to use chlorambucil, we do not use prednisone, because of the associated increased immune suppression and also poor tolerance in the elderly patient population. Although a high-dose continuous-dosing schedule of 15 mg orally daily has been evaluated in several large European studies and led to results superior to those of pulse therapy, high-dose therapy is associated with greater myelosuppression and frequently requires dose reduction,231 particularly in older or more fragile patients in whom chlorambucil is typically considered. Although high-dose therapy may be more effective if maximal cytoreduction is desired, the less intensive pulse-dosing schedule should generally be used outside the setting of a clinical study. Because most studies of alkylating agent therapy predated widespread use of cytogenetic and biological risk factors, data on the effect of biomarkers on response to chlorambucil are limited. However, the existing data indicate that patients with del(11q22.3), del(17p13.1), and IGHV1-nonmutated disease have a shorter remission duration to chlorambucil, as compared with patients without these abnormalities.230,232 Chlorambucil as monotherapy or in combination with rituximab (see later) is something that should be considered in older patients (≥age 65) in whom fludarabine has been shown to have adverse outcome and also in younger patients with renal insufficiency or other co-morbid problems that may predict poor tolerability of fludarabine therapy.229 Although chlorambucil can still be viewed as one standard therapy for elderly CLL patients, the promising results and favorable toxicity profile when combining this with rituximab in two large phase II studies prompted an ongoing phase III study with this combination by the GCLLSG.
A disappointing extension of research derived from the initial success of chlorambucil in treating CLL was the lack of benefit observed with the addition of other cytotoxic agents. A phase III Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) study comparing chlorambucil and prednisone with an alternative alkylating agent combination used in lymphoma (i.e., CVP: cyclophosphamide-vincristine-prednisone) demonstrated no benefit in PFS for subjects in the CVP arm of the study.233 The French CLL group showed that a modified CHOP regimen (with cyclophosphamide, hydroxy doxorubicin [Adriamycin], vincristine [Oncovin], and prednisone) was superior to CVP and achieved similar results as fludarabine monotherapy.234 A meta-analysis compared alkylating agent–based combination regimens with a single-agent regimen based on an alkylating agent and demonstrated no survival benefit.225 Given that alkylating agent–based combination regimens are associated with more toxicity, they have not been adequately studied in elderly patients and show no benefit over fludarabine-based therapy. Our approach is to use alkylating agents for elderly patients and fludarabine-based regimens for younger individuals with CLL. Only in rare cases of de novo CLL do we consider alkylating agent–based combination therapy (e.g., a young patient without co-morbid illnesses who has fludarabine toxicity that prohibits further use or a patient with renal failure who cannot receive fludarabine).
Purine Analogs
The introduction of purine analogs in the 1980s by Grever and colleagues revolutionized CLL therapy.237–237 Despite being approved for more than 20 years, the exact mechanism of fludarabine and cladribine in the treatment of CLL is uncertain. Pentostatin was the first nucleoside analog introduced and differs from fludarabine and cladribine in its ability to inhibit adenosine deaminase. Pentostatin demonstrated clinical activity in CLL and hairy cell leukemia; however, subsequent phase II studies showed modest activity as compared with other agents in this class of drugs. Two other purine analogs, fludarabine and then cladribine, were found to be clinically active in CLL. Phase II studies of fludarabine and cladribine yielded similar beneficial results in untreated CLL patients, with more cumulative thrombocytopenia appreciated with the latter. Based on demonstrated benefit of fludarabine in alkylating agent–resistant CLL, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved fludarabine for this indication, leading to its wide exploration in CLL as an initial treatment and then in combination with other agents. Similar parallel development of cladribine occurred in Poland and other select European countries, although cladribine either as monotherapy or in combination is not generally used in the United States.238,239 One exception is when central nervous system involvement is present because cladribine has much better central nervous system penetration.240,241 The summary that follows focuses predominantly on fludarabine use for initial CLL therapy.
Keating and colleagues were the first to report a high overall response rate (ORR) and, more importantly, a 33% CR rate in previously untreated CLL.242 These promising results prompted several large prospective randomized studies in previously untreated CLL patients comparing alkylating agent–based regimens with fludarabine.228,230,234,243 These studies collectively established fludarabine as an accepted standard first-line therapy for CLL based on improved response rates and PFS. Notably, none of these studies, including the North American Intergroup Study with 10 years of follow-up, demonstrated an advantage in OS.205 Although the benefit of fludarabine was clearly observed in younger patients, one retrospective examination of impact of age demonstrated no benefit in those patients older than 70 years. A second prospective study by the GCLLSG V demonstrated fludarabine improved the ORR (72% vs. 51%) and CR rate (7% vs. 0%), but there was no difference in PFS or OS between the two groups.229 In addition, the fludarabine group demonstrated a shorter median survival time and higher rate of toxicity, indicating that there is no major clinical benefit of fludarabine over chlorambucil in the elderly population. The impact of prognostic factors on response rates and duration of PFS to fludarabine was recently examined; patients with high-risk cytogenetic abnormalities including del(11q22.3), del(17p13.1), and IGHV1-nonmutated disease had significantly shorter PFS in response to fludarabine-based therapy than patients with other cytogenetic abnormalities or IGHV1-mutated disease.160,163,230
Combining Fludarabine with Alkylating Agents
The combination of fludarabine and alkylating agents is derived from preclinical studies showing that fludarabine inhibits DNA repair that is activated after exposure to DNA-damaging agents.244 Concurrent with these preclinical studies, several trials combining either chlorambucil or cyclophosphamide with fludarabine were initiated. Chlorambucil proved to be difficult to combine with fludarabine, perhaps in part owing to variable oral absorption.245 Cyclophosphamide administered intravenously together with fludarabine was combined successfully with favorable response and PFS in two separate phase I/II studies.246,247 These ultimately led to three randomized phase III studies in symptomatic, but previously untreated CLL patients. The GCLLSG randomly assigned 375 previously untreated patients (age < 65 years) to standard fludarabine or FC (fludarabine 30 mg/m2 IV and cyclophosphamide 250 mg/m2 IV daily for 3 days) every 28 days for six cycles.248 The ORR (94% vs. 83%), CR rate (24% vs. 7%) and median PFS (48 vs. 20 months) were superior with the FC regimen, although there were more patients with cytopenias in the combination arm. Furthermore, no difference in OS was observed. ECOG randomly assigned 278 patients to single fludarabine or fludarabine 25 mg/m2 days 1 to 5, cyclophosphamide 600 mg/m2 day 1, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) support every 28 days for six cycles. The FC regimen achieved superior ORR (74% vs. 59%) and CR rates (23% vs. 5%) and duration of PFS (32 vs. 19 months), although no OS advantage was observed.249 Most recently, the United Kingdom LRF CLL4 study randomly assigned 777 patients to oral chlorambucil, fludarabine, or the FC regimen. Patients randomized to the FC regimen enjoyed better ORR, CR rates, and 5-year PFS rates (94%, 39%, and 33%, respectively) than did patients who received chlorambucil (72%, 7%, and 9%, respectively) or fludarabine (80%, 15%, and 14%, respectively).230 All three of these studies demonstrated enhanced cytopenias with the combination as compared with monotherapy with fludarabine. Additionally, one study suggested long-term myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia were associated with the combination regimen.250 In conclusion, three large, prospective, randomized, multicenter studies in the United States and Europe have clearly demonstrated that therapy with the FC regimen is associated with better response rates and duration of PFS than single-agent fludarabine. Although toxicity has generally been manageable, greater hematologic toxicity and a higher frequency of therapy-related myeloid neoplasm (trMN) have been observed with the FC regimen. Additionally, patients older than 65 or 70, who make up the majority of CLL patients receiving initial therapy in clinical practice, have either been excluded or minimally represented in these trials. Examination of outcome by cytogenetic risk groups showed that patients with high-risk cytogenetic abnormalities including del(11q22.3) and del(17p13.1) had a significantly shorter remission than patients in the groups with good-risk or intermediate-risk cytogenetic findings when cyclophosphamide was given as a single dose.166 In contrast, patients with del(11q22.3) but not del(17p13.1) had similar outcomes when fractionated cyclophosphamide was administered over 3 days.
Rituximab
Rituximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody that targets the CD20 antigen on the surface of normal and malignant B lymphocytes. CD20 function is uncertain but appears to serve as a calcium channel that interacts with the BCR complex. CD20 is only minimally internalized or shed, making it an ideal target for antibody-directed therapeutics. Rituximab induces antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and complement-dependent cytotoxicity, activates caspase 3, and induces apoptosis in CLL and B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). Thus multiple mechanisms of action likely contribute to rituximab’s effectiveness in CLL.174,251 Although an ORR of 60% was achieved in indolent B-cell NHL, only 4 of 30 patients (13%) with SLL/CLL responded.252 Similarly, disappointing results were obtained in several other small studies in CLL.255–255 Responses in each of these studies were predominantly in the blood and nodal compartment, with little improvement in marrow disease. In contrast, two trials in which higher doses of rituximab weekly or thrice weekly at the NHL dose were given to patients with relapsed CLL showed an improved response rate with response duration.256 Further improvement was observed when weekly single-agent rituximab was given to patients with previously untreated SLL/CLL.257,258 Forty-four previously untreated patients with SLL/CLL received four weekly doses of rituximab 375 mg/m2; the ORR after the first course of rituximab was 51% (CR, 4%). Twenty-eight patients with stable or responsive disease received additional 4-week courses of rituximab every 6 months for up to four cycles. With continued rituximab, there was only a modest increase in ORR (58%) and CR rates (9%), with a median duration of PFS of 19 months that was shorter than observed in low-grade NHL. Nonetheless, this response duration compared favorably with the response duration achieved with fludarabine in the upfront setting, suggesting that rituximab is active and may have a role in the upfront therapy for SLL/CLL.
Rituximab is selective for the B-cell antigen CD20 and therefore has a relatively favorable toxicity profile. Common side effects include infusion toxicity (fever, rigors, transient hypoxemia, dyspnea, and hypotension), which are partly due to an inflammatory cytokine release syndrome. Although poorly understood, CLL patients with platelet counts less than 50 × 1012/L may experience transient, severe thrombocytopenia associated with this infusional toxicity and may require platelet transfusions with the first one or two doses of rituximab. Infusion toxicity is not predicted by the absolute lymphocyte count, and a high degree of monitoring should be provided to all patients during the first one to two infusion events of rituximab. Patients with preexisting thrombocytopenia should therefore have a post therapy platelet count after the first one or two doses of rituximab. Another uncommon, but potentially severe, toxicity is a tumor lysis syndrome, which is generally observed in patients with a high circulating peripheral lymphocyte count with CLL variants. Such patients should receive prophylactic allopurinol, hydration, and careful observation; and inpatient monitoring and administration of rituximab can be considered for the highest-risk patients. Other rare toxicities with rituximab therapy include delayed neutropenia, hepatitis B reactivation, skin toxicity, interstitial pneumonitis, and serum sickness. Patients with prior hepatitis B exposure should receive prophylaxis or close monitoring for viral reactivation.259,260 Patients who experience pulmonary or skin toxicity with rituximab should not be challenged with repeated dosing. In general, rituximab is a very well-tolerated therapy, making it ideal for use in combination with other agents in patients with CLL.
Rituximab Chemoimmunotherapy
Fludarabine and Rituximab
The Cancer and Leukemia Group (CALGB) 9712 study randomly assigned 104 previously untreated CLL patients to fludarabine combined with either sequential or concurrent rituximab (FR) therapy.261,262 Patients received standard fludarabine 25 mg/m2 on days 1 to 5 every 4 weeks for six cycles, with or without concurrent rituximab 375 mg/m2 on day 1 of each cycle, with an additional dose on day 4 of cycle 1. Patients in both study arms received rituximab 375 mg/m2 weekly for four doses beginning 2 months after completion of fludarabine; thus, patients in the concurrent study arm received 11 total doses of rituximab, compared with four in the sequential arm. Patients receiving concurrent FR therapy enjoyed a superior CR rate (47% vs. 28%) and ORR (90% vs. 77%) to patients in the sequential study arm. Other than neutropenia, no other toxicity was observed more frequently with the combination as compared with monotherapy with fludarabine. A retrospective comparison with a fludarabine-only containing treatment study performed previously by CALGB demonstrated improved PFS and OS as compared with fludarabine treatment.263 Analysis of prognostic cytogenetic abnormalities demonstrated that patients with del(11q22.3) and del(17p13.1) have a shorter duration of response to this regimen.264 A recent update of this study with a median follow-up of 117 months showed the median OS was 85 months and 71% of patients alive at 5 years.261 The median PFS was 42 months, with 27% progression free at 5 years. Importantly, an estimated 13% of patients remained free of progression at almost 10 years of follow-up. IGHV1-mutated disease status was favorably associated with extended PFS and OS, whereas not having high-risk cytogenetics was associated with OS. Notably, there were no cases of tr-MN occurring before relapse, which contrasted to prior studies with fludarabine and alkylating agent–containing regimens.
Fludarabine-Cyclophosphamide-Rituximab
This FCR chemoimmunotherapy regimen was piloted by the M.D. Anderson Cancer Center group in 300 previously untreated CLL patients in which the ORR was 95%, with 72% of patients attaining a CR. Six-year PFS was 51%, whereas OS was 77%.265 Features associated with poor response included high β2M, del(17p13.1), age older than 70, and elevated white blood cell count greater than 150 × 109/L. Late infections or other complications were uncommon except for tr-MN, which occurred in 3% of patients.266 Outcome of patients with tr-MN was poor irrespective of treatment. In a multivariate analysis of patients receiving fludarabine-based therapy, FCR therapy was significantly associated with improved survival, thereby validating the experience with the FR regimen and suggesting that rituximab therapy was improving OS. This regimen was less well tolerated in patients older than the age of 70 and is not being explored currently in this population.
Bendamustine-Rituximab
The GCLLSG CLL2M study enrolled 117 symptomatic, previously untreated CLL patients who were treated with bendamustine 90 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2 and with rituximab 375 mg/m2 on cycle 1 and 500 mg/m2 on cycles 2 through 6).267 Treatment was administered every 28 days for up to six cycles. Demographics of the patients included a median age of 64 years, with 26% being older than 70 years and 46% having Binet stage C disease. The overall response rate was 88%, and CR was 23%. The median event-free survival with this treatment was 33 months. The treatment was well tolerated, with cytopenias and infections being most problematic. Treatment-related mortality was 4%, mostly as a consequence of infections. Patients with all genomic groups except for del(17p13.1) responded favorably. Based on these encouraging phase II data, the GCLLSG initiated a phase III study comparing this to the FCR regimen (CLL10) that is ongoing.
Chlorambucil-Rituximab
Based on the success of chemoimmunotherapy and also potential absence of benefit of nucleoside analogs in elderly CLL patients, Hillmen and colleagues initiated a study in elderly, previously untreated CLL patients combining rituximab (day 1: 375 mg/m2 IV cycle 1; 500 mg/m2 cycles 2 through 6) and chlorambucil (days 1-7: 10 mg/m2/day orally) every 28 days for six cycles.268 Patients were permitted to continue six additional cycles of chlorambucil if they had evidence of response. A further six cycles of chlorambucil alone was permitted in patients with continuing clinical response at six cycles. A total of 100 patients included in this study had a median age of 70 years. ORR on an intent-to-treat analysis was 82% (95% confidence interval [CI], 73.1 to 89.0), with 9 patients achieving CR, 58 patients showing partial response (PR), 15 patients showing nodular PR, and 11 patients with stable disease (SD). Median PFS to date was 23.5 months. The response in this study was significantly higher in patients receiving chlorambucil alone in the CLL4 study, suggesting the benefit of rituximab. A second Italian phase II study using a similar combination regimen of chlorambucil and rituximab together demonstrated similar favorable response data.269 Based on these phase II data, a randomized phase III study comparing chlorambucil to chlorambucil with either rituximab or GA101 is currently ongoing by the GCLLSG.
Phase III Chemoimmunotherapy Trials in Previously Untreated CLL Patients
One phase III study has been published related to the use of rituximab as part of chemoimmunotherapy. This trial, performed by the GCLLSG (CLL8), enrolled 761 previously untreated CLL patients with a randomization between FC and FCR as administered and reported previously by the M.D. Anderson group.270 This study was reported at a median observation time of 37.7 months when ORR (95.1% vs. 88.4%) and CR (44.1% vs. 21.8%) were both significantly superior for the FCR regimen as compared with FC therapy. For these patients, the median PFS was significantly improved (P < .001) with FCR (51.8 vs. 32.8 months) as compared with FC. Unlike other phase II studies performed with chemotherapy to date in CLL, OS was significantly improved (P = .01) for those patients who received FCR (84.1% vs. 79.0%) as compared with those in the FC study arm. Emerging from this study were numerous biological correlative studies showing the most predictive test of long-term PFS and OS was attainment of minimal residual disease (MRD)-negative disease by high-sensitivity flow cytometry. In addition, patients with IGHV1-nonmutated disease had a shorter PFS and OS with both FCR and FC, although rituximab appeared to benefit both treatment groups. All genetic groups benefited from addition of rituximab with exception of the del(17p13.1) and normal karyotype patients. Toxicity was manageable with a 2% regimen-related toxicity, with cytopenias and infection being the most common cause of morbidity. As with other chemoimmunotherapy trials in CLL, neutropenia was more common with FCR than FC. Further long-term follow-up of this study is ongoing for late complications and assessment of newer prognostic factors identified since initiation of this study. Based on the results of this study, a randomized phase III study comparing FCR (as given here) to bendamustine-rituximab is now underway by the GCLLSG (CLL10).
Treatment of Patients with Relapsed CLL
Fludarabine-Cyclophosphamide-Rituximab in Relapsed CLL
The most active phase II results with chemoimmunotherapy have been achieved by the M.D. Anderson group with the FCR regimen in both previously treated and untreated CLL. In the concluding report of this study, 284 previously treated patients with CLL were reported.271 The ORR was 74%, with 30% CR. The estimated median OS was 47 months and the median PFS for all patients was 21 months. Patients with best outcomes included those with three or fewer prior treatments, who were not refractory to fludarabine, and who had absence of del(17p13.1). A phase III study was performed for registration of rituximab based on these results in which the FCR regimen was compared with the FC regimen.272 This international, multicenter, randomized trial compared six cycles of rituximab plus fludarabine and cyclophosphamide (R-FC) with six cycles of FC in patients with previously treated CLL. A total of 552 patients were enrolled in this trial in which the addition of rituximab was shown to significantly improve CR (9% vs. 3%), ORR (49% vs. 61%), and PFS (median 30.6 months vs. 20.6 months) in patients with previously treated CLL. Although the rates of adverse events, grade 3 or 4 events, and serious adverse events were slightly higher in the FCR study arm, this regimen was generally well tolerated. FCR cytoreduction is clearly a reasonable option for CLL patients provided they have minimal prior treatment history, lack del(17p13.1), and are not fludarabine refractory. This regimen is also quite challenging for patients older than age 70 years. In general, our practice is to give prophylaxis for P. jiroveci and also varicella-zoster virus when patients are treated with this regimen.
Bendamustine-Rituximab in Relapsed CLL
Bendamustine-rituximab is a common second-line therapy utilized in the treatment of relapsed CLL. This in part is based on multiple single-agent studies demonstrating single-agent activity and the potential of rituximab to enhance the cytotoxic effect of bendamustine similar to that documented with FCR. Unlike FCR, there are not yet phase III studies that compare directly bendamustine alone with bendamustine-rituximab. In the phase II study reported fully, 78 patients were treated with bendamustine using a lower dose (70 mg/m2) on days 1 and 2 of a 28-day cycle together with rituximab given day 1 of cycle 1 at 375 mg/m2 and then 500 mg/m2 thereafter for a maximum of six cycles.267 Demographics in this trial were representative of the general population of treated CLL patients with a median age of 65 years and 37% being older than age 70 years. A total of 48% of the patients had Binet stage C disease. The median number of prior therapies was two, and 80% had previously received fludarabine. A total of 54% of patients were able to complete all six cycles of therapy. The ORR using the new IWCLL 2008 criteria was 59%, with 9% attaining CR. Response by genetic groups of CLL was similar except in the del(17p) patients in whom only 7% responded. Similarly, response among patients who were fludarabine sensitive was 61% whereas those with fludarabine-refractory disease had only a 46% response rate. The median event-free survival with bendamustine-rituximab for all patients was 14.7 months. Severe infections occurred in 12.8% of patients and grade 3 or 4 cytopenias in 50% of patients. The overall mortality of this treatment was 4%, with most patients being lost to infections. Based on these data, bendamustine-rituximab is generally considered an acceptable second-line therapy for CLL. Lower doses of bendamustine are used in relapsed CLL as compared with untreated CLL or typical regimens used in NHL. Additionally, the response to select genetic groups such as those patients with del(17p) are very low, making this a poor choice for such individuals. Similarly, patients with heavily pretreated CLL who are fludarabine refractory are less likely to respond and have increased toxicity from this regimen.
Ofatumumab in Relapsed CLL
Ofatumumab is a newly approved, human type I CD20 monoclonal antibody. In vitro, it has improved complement-dependent cytotoxicity, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, and direct killing (with cross-linking) as compared with rituximab. Ofatumumab has a different binding epitope of CD20 than rituximab and a slower off rate as well.251 Based on these promising data, a phase I/II study of ofatumumab in relapsed/refractory patients demonstrated that it is generally well tolerated, even at high doses, and is active, with an ORR of 50%.273 Infusion-related adverse events are similar to those reported with rituximab and decrease after the first infusion. Infections were fairly common, occurring in 51% of patients, including one fatal infection. These results prompted a pivotal, single-arm study of ofatumumab administered as eight weekly infusions of ofatumumab followed by four monthly infusions.274 Patients included in this study were required to be fludarabine refractory and to also be alemtuzumab refractory (FA-refractory group) or to have bulky lymphadenopathy (>5 cm) (BF-refractory group). The ORR was 58% for the FA-refractory group and 47% for the BR-refractory group, with one CR observed in the BF-refractory group. All other responses were partial. The median duration of response was 7.1 months in the FA-refractory group and 5.6 months in the BF-refractory group, with most patients experiencing progression of their disease during treatment. The presence of del(17p13.1) in the BF-refractory group was associated with lower response, which was most apparent among patients with bulky lymph nodes. The median PFS was 5.7 months in the FA-refractory group and 5.9 months in the BF-refractory group, with median OS of 13.7 months and 15.4 months, respectively. Toxicity included infusion-related reactions, infections, and cytopenias. This trial led to accelerated approval of ofatumumab in fludarabine- and alemtuzumab-refractory CLL. The clinical superiority of ofatumumab to rituximab will require randomized trials comparing equivalent doses. Currently, several phase III studies of ofatumumab in combination with chlorambucil (initial treatment), FC (salvage), or as single-agent maintenance therapy are ongoing.
Methylprednisolone and Rituximab in Relapsed CLL
The frequency of del(17p13.1) and TP53 mutations becomes more frequent at the time of relapse. Traditional options for these patients are limited, which has prompted investigation of p53-independent agents in this patient subgroup. Corticosteroid-mediated apoptosis is generally independent of TP53 in lymphocytes. Additionally, corticosteroids diminish activation of many of the stromal cells that promote survival of CLL in the microenvironment. Although very early studies of low-dose corticosteroids demonstrated modest activity against CLL cells, both preclinical and pilot clinical studies suggest that higher doses of methylprednisolone were active in CLL.275,276 A subsequent validation study of 14 patients included 11 CLL and 3 CLL/prolymphocytic leukemia patients who were treated with methoprednisolone (Solu-Medrol) 1 g/m2 IV daily for 5 days.277 Six of the 11 CLL patients attained a PR with this treatment, with the median response duration being 8 months. Treatment resulted in improvement in cytopenias and reduction in nodes. Toxicities of this therapy included hyperglycemia, fluid retention, and life-threatening infection in 2 patients. A second study by this same group included 25 patients, with 45% having TP53 abnormalities where high-dose methylprednisolone as given above was given alone or with select other alkylating agent–based cytotoxic therapies. An ORR of 77% was observed with a median response duration of 1 year. Response occurred in 5 of 10 patients with abnormal TP53 function. Toxicities were similar to the previous regimen, including life-threatening infections.278 Building on this combination, Castro and Kipps piloted this same 5-day methylprednisolone treatment with weekly rituximab (375 mg/m2) for 4 weeks.279 Cycles could be repeated up to three courses. All patients included had fludarabine-refractory disease. Responses were observed in 93% of patients with a CR of 36%. The median time to progression was 15 months, and the median time to next treatment was 22 months. A second retrospective assessment of this regimen was reported by the Mayo Clinic of 37 patients receiving this treatment.280 Nine of these patients had del(17p13.1). After one cycle of therapy, 78% patients had a response including 5 of 9 patients with del(17p13.1). Infectious morbidity was common, with 11 (29%) of patients experiencing this complication during the first month of therapy. Several other groups have confirmed these results281 or built on this regimen by substituting alemtuzumab for rituximab or dexamethasone for methylprednisolone with similar efficacy, including in del(17p) patients.282,283 Given the infectious morbidity associated with high-dose corticosteroid and rituximab-containing regimens, aggressive viral, bacterial, P. jiroveci, and fungal prophylaxis should be administered during and for a period after treatment. Additionally, close monitoring for metabolic complications including hyperglycemia and tumor lysis syndrome should occur.
Myeloablative Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation
Allogeneic SCT has been utilized in CLL for more than 2 decades and offers several theoretical advantages to autologous SCT, including lack of contamination of the stem cell source and an immunologic graft-versus-leukemia (GVL) effect that is quite active in this disease. The major limitation of this therapy has been the high treatment morbidity and mortality, even when applied to younger CLL patients who are not generally representative of the population with this disease. Limited data suggest that total-body irradiation (TBI)–containing conditioning regimens are superior to chemotherapy-only regimens in CLL transplant patients.284 Although myeloablative transplant in CLL can result in durable remissions, rates of transplant-related mortality are unacceptably high, ranging from 46% to 57%.284,285 Patients who survive, notably those who experienced chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD), have a good chance of experiencing long-term disease control, suggesting a strong GVL effect. The high mortality of myeloablative SCT in CLL even among young patients greatly reduced its application in this disease even in the most refractory and high-risk individuals.
Reduced-Intensity Conditioning Myeloablative Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation
Several groups have attempted varied degrees of RIC allogeneic SCT in CLL. Fludarabine was evaluated by researchers at M.D. Anderson Cancer Center as a conditioning agent for RIC hematopoietic SCT both because it is an effective treatment for CLL and because it is highly immunosuppressive, as shown by others in more high-risk diseases. This initial study yielded a complete response in 8 of 11 patients, and donor lymphocyte infusions were able to induce remissions after transplant, again providing evidence of a GVL effect.286 The Cooperative German Transplant Study Group evaluated RIC conditioning with fludarabine, busulfan, and antithymocyte globulin in 30 patients with advanced CLL, half of whom had unrelated donors. They reported 72% OS at 2 years, with 67% PFS and 15% transplant-related mortality. Fifty-six percent of patients experienced grades 2 to 4 acute GVHD, whereas 75% developed cGVHD. Of note, late CRs were observed as long as 2 years after transplant, again providing evidence of a GVL effect.287 The 2-year OS among 46 patients with advanced CLL who received nonmyeloablative fludarabine and busulfan conditioning at the Dana Farber Cancer Center was 54%, with a PFS of 34%. In this analysis, the primary cause of treatment failure was relapse, and chemotherapy-refractory disease at transplant was associated with a 3.2-fold risk of progression (P = .01) and a 4.6-fold risk of death (P = .02). Other factors that increased the risk of relapse were low levels of donor chimerism at day 30, increased number of previous therapies, and adverse cytogenetics.288 Five-year follow-up after nonmyeloablative transplant has been reported from a multi-institutional protocol led by the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center. The 5-year incidences of non-relapse mortality (NRM), OS, and PFS were 23%, 50%, and 39%, respectively. Of the patients who survived, 76% were entirely well, whereas 24% continued to receive immunosuppression for cGVHD.289 The CLL3X trial from the GCLLSG was a phase II study that prospectively evaluated the long-term outcome of RIC HSCT in patients with poor-risk CLL. Ninety patients received allogeneic transplant after fludarabine and cyclophosphamide-based conditioning. The 4-year NRM, event-free survival, and OS were 23%, 42%, and 65%, respectively. Of the patients with MRD monitoring available, 52% were alive and MRD negative at 12 months after transplant, and the 4-year EFS of this group of patients was 89%. Recent efforts have focused on diminishing the frequency of cGVHD and also disease relapse by introduction of antibodies or other novel therapies.
A common question for practicing oncologists is how should RIC allogeneic SCT be applied in the management of CLL patients? There are several CLL patient groups such as those with genetic abnormalities including del(17p13.1), del(11q22.3), and IGHV1-nonmutated disease or patients with a poor response to chemoimmunotherapy for whom survival is poor. A case-control study comparing outcomes of patients who underwent RIC hematopoietic SCT with patients who received conventional therapy demonstrated that the median OS was 113 months for SCT patients and 85 months for controls when calculated from the time of diagnosis and 103 and 67 months, respectively, when calculated from time of first therapy. Both patient groups were well balanced with respect to cytogenetics, CD38 and ZAP70 expression, and IGHV1 mutational status.290 A small retrospective analysis of outcomes among patients receiving RIC SCT stratified by prognostic risk group suggested that RIC SCT could overcome the adverse prognosis associated with del(11q) or del(17p), as well as those with nonmutated IGHV1 disease.291 A study of 44 patients with del(17p) CLL from the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation database, 89% of whom received RIC, demonstrated 3-year OS and PFS rates of 44% and 37%, respectively. The cumulative incidence of progressive disease at 4 years was 34%, and no late relapses occurred in the 9 patients with follow-up longer than 4 years, suggesting a survival plateau in even this high-risk group of patients. Extensive cGVHD occurred in 53% of patients.292 Fit patients with del(17p), those who are refractory to fludarabine and alemtuzumab, and those who have a PFS of less than 24 months after intensive chemoimmunotherapy-containing regimens should all be considered for RIC SCT if remission is achieved.293 However, the development of targeted therapies that induce durable remission may diminish the number of CLL patients going forth for transplantation.294
Richter Transformation and Prolymphocytic Transformation
Richter transformation was described as the development of high-grade diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in patients with CLL.295 Over the years, the classification of Richter transformation has expanded to include lymphoid malignancies such as Hodgkin disease,296 acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and prolymphocytic leukemia.297,298 Incidence estimates range from 2.8% to 10.7%. Clearly identifiable risk factors for the development of RS are lacking, and its development has been shown to be independent of disease stage, duration of disease, type of therapy, or response to therapy. However, the presence of diffuse lymphomatous involvement, advanced Rai stage, IGHV1-nonmutated disease, ZAP70 expression, high LDH, del(17p13.1), high serum β2M levels, and recently NOTCH1 mutations may predict the development of Richter transformation.99,299 Richter transformation is characterized by sudden onset of B-symptoms (fever, night sweats, weight loss) and rapidly progressive lymphadenopathy at any anatomic site. Rarely, the lymphomatous clone may arise from the bone or an extranodal site. Laboratory abnormalities including anemia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia may be due to large cell transformation in the bone marrow. A rapid increase in the serum LDH is seen in the majority of patients. The diagnosis is generally made on examining the histology of a rapidly enlarging lymph node, which typically reveals large cell lymphoma. PET can be helpful in these patients to localize the most hypermetabolic node for biopsy.132 A stratification scheme has been put forth based on performance status, presence of TP53 mutation/deletion, and response to treatment of Richter transformation that accurately predicts survival.300 Historically, Richter transformation has been treated with regimens similar to those used for the treatment of large cell lymphomas involving multiple agents such as methotrexate, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, prednisone, bleomycin, dexamethasone, cytarabine, and cisplatin (e.g., MACOP-B: methotrexate-cytarabine [Ara-C]-vincristine [Oncovin]-prednisone-bleomycin; CHOP-B: cyclophosphamide-doxorubicin [hydroxydaunomycin]-vincristine [Oncovin]-prednisone-bleomycin; DHAP: dexamethasone-cytarabine [Ara-C]-cisplatin; and VAD: vincristine-doxorubicin [Adriamycin]-dexamethasone). Recently, regimens incorporating oxaliplatin (i.e., OFAR: oxaliplatin-fludarabine-cytarabine [Ara-C]-rituximab)301 have been reported, although their benefit in Richter transformation is uncertain over traditional lymphoma regimens. Our institution prefers dose-adjusted infusion therapy (i.e., R-EPOCH: rituximab-etoposide-prednisone-vincristine [Oncovin]-doxorubicin [hydroxydaunomycin]) for the initial treatment of these patients. The duration of response and the OS rates are dismal, with most patients likely to die within 6 months of their diagnosis despite aggressive therapy. Long-term remissions and survival have been reported in a few patients after allogeneic SCT, but this approach is associated with a higher treatment-related mortality.299 When Richter transformation occurs, consolidation with allogeneic SCT is the preferred treatment.
Investigational Agents Currently in Phase II/III Testing for Relapsed CLL
Lenalidomide
Lenalidomide (Revlimid) is an immunomodulatory drug that is a more potent analog of thalidomide and is approved in multiple myeloma and transfusion-dependent myelodysplasia. It has clinical activity in a variety of other malignancies, including CLL. Two initial studies examining either an intermittent 25-mg daily oral dose for 21 days302 or a 5-mg daily oral dose with dose escalation to a 10-mg daily oral dose as tolerated given as continuous therapy were pursued initially in patients with relapsed CLL.303 The higher-dose, intermittent schedule was active with an ORR of 47% and a 9% CR. Major side effects of this therapy were cytopenias, rash, and tumor flare, which in some cases can be life threatening.304 The continuous, low-dose regimen had a 32% intent-to-treat ORR with a 7% CR rate. Toxicity was less with this schedule but still included cytopenias that prevented dose escalation above 10 mg in virtually all patients.303 On the basis of these promising phase II clinical studies, a large, multicenter trial randomizing patients to low-dose (10 mg) or high-dose (25 mg) lenalidomide was undertaken that was halted early owing to life-threatening adverse events in patients receiving the higher dose of therapy.305 These toxicities at high doses were confirmed by other groups.306 Subsequent studies have shown that lower doses of lenalidomide administered as continuous treatment in patients with relapsed CLL are feasible.307 These findings have prompted several single-agent studies in symptomatic, previously untreated CLL where the clinical activity has ranged from an ORR of 56% to 65% with up to a 10% CR.308,309 Most provocative from these studies was the observation that lenalidomide reversed the hypogammaglobulinemia observed in CLL patients. The PFS with this treatment is approximately 2 years. Toxicity including tumor flare, cytopenias, rash, and infection has been noted but is manageable.
In other disease states, such as multiple myeloma, cereblon appears to be the target of lenalidomide with subsequent degradation of IRF4.310–315 This has not been pursued to date in CLL. In an attempt to understand both the pathogenesis of tumor flare and also immunoglobulin recovery, laboratory studies have demonstrated that lenalidomide activates CLL cells to promote expression of CD154, CD80, and CD86.306,316–318 These activated CLL cells also can serve as a second signal with T cells to promote normal B cells to produce antibody, thus possibly explaining why hypogammaglobulinemia is reversed in many of the de novo treated patients. Other studies have shown lenalidomide enhances T-cell and natural killer (NK)-cell response to CLL cells.109 The recent recognition of the profound immunologic effects of lenalidomide on CLL suggests that it might also serve as an effective agent earlier in the course of the disease or as an adjuvant to vaccine-based approaches. These hypotheses are currently being pursued at this time by several different groups.
Moving forward, efforts with lenalidomide have focused in part on combining it with other therapeutics used in CLL treatment. Preliminary reports have suggested diminished tumor flare when administered with therapeutic antibodies but increased cytopenias and adverse events when combined with chemoimmunotherapy regimens. When administered as monotherapy or with rituximab in the setting of relapse, lenalidomide has been shown to induce partial responses and durable remission in patients with relapsed CLL, including those with del(17p).319,320 Similarly, lenalidomide has been given as consolidation maintenance in several completed phase II chemoimmunotherapy trials and has been shown by polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based analysis to potentially extend PFS over that previously seen with PCR alone.321 Based on the clinical activity observed with lenalidomide, two phase III registration studies are underway examining lenalidomide versus chlorambucil for elderly CLL patients and also as a consolidation therapy after second treatment for this disease. Because of the relative modest activity in heavily pretreated patients, other alternatives in first-line therapy, and potential for life-threatening tumor flare and other toxicity with lenalidomide, this agent should not be used outside the setting of a well-planned clinical trial.
Agents Targeting BCR Signaling Pathways
GS-1101
GS-1101 (formerly CAL-101) is a reversible inhibitor of the PI3K δ isoform of the p110 catalytic subunit with strong preclinical data to support early phase I exploration of this molecule in CLL.54,322 In a broad phase I trial in indolent B-cell malignancies, a dose of 150 mg twice a day was identified to be ideal for the phase II dose in CLL based on tolerability and minimal increase in plasma Cmax at increasing doses above the 150 mg twice-a-day schedule. A total of 54 CLL patients were enrolled on this trial, with 84% achieving a 50% or more decrease in lymph node and spleen size. An increase in peripheral lymphocyte count of 50% or more was seen in 58% of patients that peaked at 2 months and resolved over time in a subset of patients. As a consequence of the asymptomatic lymphocytosis, response across all patients enrolled was 24% by IWCLL 2008 response criteria. This response was independent of high-risk genetic features, bulky adenopathy, prior therapy, or presence of cytopenias. Median PFS was 15 months, with 46% of patients continuing on therapy at the time of the report.323 Whereas response did not vary by genetic group, PFS to GS-1101 was considerably less in patients with del(17p13.1). Side effects of GS-1101 included rare cytopenias and pneumonia. Approximately 5% of patients developed grade 3 or 4 transient liver function abnormalities during the early phase of treatment, which were reversible by withholding therapy and generally did not recur with resumption at a lower dose level. Based on the significant clinical activity and favorable safety data, GS-110 has also been investigated in combination with either the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies rituximab (GR) or ofatumumab or the chemotherapy agents bendamustine (GB), GB-rituximab (GBR), or fludarabine in the phase I setting. GS-1101 was dosed at 100 mg twice a day or 150 mg twice a day, with other drugs administered as standard therapy. Therapy was well tolerated, with no toxicities other than those expected with the single agents. Response data have been reported for the GR, GB, and GBR regimens. For GR and GB, 13 of 14 patients and 9 of 10 patients, respectively, achieved a 50% or more reduction in lymph node size. For 3 patients treated with GBR, all patients achieved a lymph node response.324 Using traditional CLL response criteria, more than 80% of patients receiving each regimen met the criteria for response. GS-1101 is currently being investigated in the phase II setting as a single agent and in the up front setting for elderly patients in combination with rituximab. FDA registration phase III studies with GS-1101 are also ongoing in patients with relapsed CLL.
Ibrutinib
Ibrutinib (formerly PCI-32765) is an irreversible inhibitor of Btk with pharmacology that allows for daily dosing and effective continued target inhibition.325 Preclinical data supporting its exploration in CLL55,56 and promising data from the initial phase I study of this agent prompted early interest in ibrutinib as an exceptional drug for CLL therapy. Forty-seven patients were enrolled in the initial phase I study, including 15 patients with CLL. Objective responses were observed in 9 of these 15 patients, and safety was confirmed with extended continuous dosing of ibrutinib. A dose of 420 mg daily was established for further study based on more than 90% occupancy of Btk using a novel drug probe developed by Pharmacyclics.326 In a subsequent phase Ib/II study that was recently completed for patients with relapsed or refractory CLL, two doses of 420 mg and 840 mg were pursued and a 67% overall response was observed, with another 20% of patients having a nodal PR with persistent lymphocytosis. At a median follow-up of 22 months, the estimated PFS for this patient group was 76%. Response to ibrutinib occurs independently of high-risk genomic features including IGHV1 mutational status and del(17p13.1). This trial also included a cohort of elderly patients with previously untreated CLL, in which 31 evaluable patients (71%) responded, with an additional 10% having a nodal PR with persistent lymphocytosis. The estimated PFS at 22 months was 96% for this group. Toxicities have been mild, with a low rate of hematologic toxicity. The most common toxicities have been diarrhea, rash, bruising, and dyspepsia. Infections have been seen, although, like with GS-1101, the rate is not clearly different from that seen in this refractory patient population. Studies are currently ongoing with this agent in combination with ofatumumab, bendamustine, or rituximab in the relapsed CLL setting. Based on the success of ibrutinib as a single agent, FDA phase III registration studies in patients with relapsed CLL comparing this agent to ofatumumab and in the up-front setting comparing it with chlorambucil are being initiated.
Other Agents in Late Clinical Trials for CLL
Cyclin-Dependent Kinase (CDK) Inhibitors
Flavopiridol is a first-generation CDK inhibitor with an approximately 50% response rate in highly refractory CLL. Flavopiridol has a dose-limiting side effect of tumor lysis syndrome but produces durable remissions in a subset of CLL patients, including those with del(17p13.1).327,328 Off-target effects of flavopiridol of diarrhea and fatigue prompted transition of a second-generation CDK inhibitor dinaciclib, which has a more favorable therapeutic index and even more promising preclinical efficacy in CLL.329 This agent has completed phase I studies in CLL with similar efficacy to flavopiridol, including dose-limiting toxicity of hyperacute tumor lysis syndrome but without many of the off-target effects of flavopiridol.330 Dinaciclib has moved forward to a phase III registration study for therapy for relapsed CLL in comparison with ofatumumab.
BCL2 Inhibitors
BCL2 is an anti-apoptotic protein that is overexpressed in CLL. Preclinically, efforts that inhibit or decrease tumor expression of BCL2 promote apoptosis. Attempts to target BCL2 in CLL were initially pursued with the BCL2 antisense molecule genasense.331 Phase III trials with Genasense demonstrated clinical activity but did not meet the required PFS end point when combined with FC chemotherapy.332,333 This modest success with Genasense prompted investigation to target BCL2 with small molecule inhibitors. The most potent inhibitor of BCL2, navitoclax (formerly ABT263) has demonstrated single-agent activity in relapsed CLL with a target-specific (BCL-XL) dose-limiting toxicity of profound thrombocytopenia.334 A second-generation inhibitor (ABT199) that lacks off-target effect on BCL-XL is now entering phase I studies. It is hoped that dramatic clinical activity of navitoclax will be maintained with the loss of BCL-XL inhibition in the ABT199 molecule.
Type II CD20 Antibodies
GA-101 is a type II human CD20 directed antibody that has the ability to induce direct apoptosis of CLL and NHL tumor cells, has enhanced NK-cell–mediated killing, but lacks CDC activity.335 Studies have shown GA-101 is superior to rituximab preclinically in CLL cells.336 GA-101 has completed phase I studies in NHL and CLL in which clinical activity was shown in a dose-dependent fashion. GA-101 is now being tested in a phase III registration study in combination with chlorambucil versus chlorambucil alone. In addition, it is being tested as both a single agent in previously untreated CLL and in combination with the FC chemotherapeutic regimen.