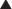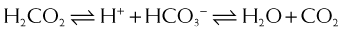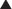Chapter 25 Renal and Genitourinary Systems
Prototype and Common Drugs
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
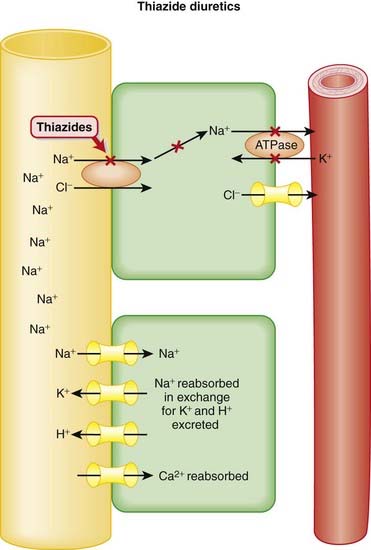
 Specifically, thiazide diuretics inhibit the Na+/Cl− co-transporter channel in the distal tubule of the nephron (Figure 25-1).
Specifically, thiazide diuretics inhibit the Na+/Cl− co-transporter channel in the distal tubule of the nephron (Figure 25-1). Therefore Na+, Cl− (and water) remain in the lumen of the tubule: natriuresis and diuresis. In addition, the actions of the thiazides impact other ions.
Therefore Na+, Cl− (and water) remain in the lumen of the tubule: natriuresis and diuresis. In addition, the actions of the thiazides impact other ions. A passive Na+/H+ exchange occurs at a distal site in the tubule. Na+ gradients drive this exchange. When the Na+/Cl− cotransporter is blocked, the Na+ concentration in the lumen of the tubule is high, which facilitates Na+ reabsorption in exchange for excretion of H+ ions at this distal site. Therefore thiazides create alkalosis by H+ ion loss through a secondary, passive exchange.
A passive Na+/H+ exchange occurs at a distal site in the tubule. Na+ gradients drive this exchange. When the Na+/Cl− cotransporter is blocked, the Na+ concentration in the lumen of the tubule is high, which facilitates Na+ reabsorption in exchange for excretion of H+ ions at this distal site. Therefore thiazides create alkalosis by H+ ion loss through a secondary, passive exchange. Similarly, Na+ is exchanged for K+ at a distal site in the tubule. By enhancing delivery of Na+ to distal sites of the nephron, Na+ is exchanged for K+, leading to enhanced K+ excretion, in a similar manner to the K+ depletion that occurs with loop diuretics.
Similarly, Na+ is exchanged for K+ at a distal site in the tubule. By enhancing delivery of Na+ to distal sites of the nephron, Na+ is exchanged for K+, leading to enhanced K+ excretion, in a similar manner to the K+ depletion that occurs with loop diuretics. Owing to the fact they act so distally in the nephron, after much of the Na+ reabsorption has already occurred, thiazides are relatively weak diuretics when compared with loop diuretics.
Owing to the fact they act so distally in the nephron, after much of the Na+ reabsorption has already occurred, thiazides are relatively weak diuretics when compared with loop diuretics.Pharmacokinetics
 Thiazide diuretics exert their pharmacologic actions from the luminal side; therefore they must be in the lumen of the tubule to achieve their effect.
Thiazide diuretics exert their pharmacologic actions from the luminal side; therefore they must be in the lumen of the tubule to achieve their effect. Thiazides primarily enter the renal tubule through secretion in the proximal tubule (PT) via the organic acid co-transporter. In patients with renal impairment, higher doses of thiazides may be required to overcome impaired tubular secretion and maintain sufficient tubular concentrations to achieve a pharmacologic effect.
Thiazides primarily enter the renal tubule through secretion in the proximal tubule (PT) via the organic acid co-transporter. In patients with renal impairment, higher doses of thiazides may be required to overcome impaired tubular secretion and maintain sufficient tubular concentrations to achieve a pharmacologic effect.Side Effects
 Hypokalemia or hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis: Thiazide diuretics enhance excretion of both K+ and H+ because of increased distal tubule delivery of Na+, and hence Na+ reabsorption, in the distal nephron.
Hypokalemia or hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis: Thiazide diuretics enhance excretion of both K+ and H+ because of increased distal tubule delivery of Na+, and hence Na+ reabsorption, in the distal nephron. Hyperlipidemia: Thiazide diuretics increase cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein (LDL); the mechanism has not been established.
Hyperlipidemia: Thiazide diuretics increase cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein (LDL); the mechanism has not been established.Important Notes
 Diuretics that act on the renal tubules require functioning kidneys to exert their effects. Patients with advanced renal dysfunction will not respond to these diuretics.
Diuretics that act on the renal tubules require functioning kidneys to exert their effects. Patients with advanced renal dysfunction will not respond to these diuretics. As noted, thiazides are weaker diuretics than loop diuretics (such as furosemide). This is because they act at a site distal to where loop diuretics act. The loop of Henle is positioned before the distal convoluted tubule, and 90% of Na+ will have already been reabsorbed before the ultrafiltrate reaches the distal tubule.
As noted, thiazides are weaker diuretics than loop diuretics (such as furosemide). This is because they act at a site distal to where loop diuretics act. The loop of Henle is positioned before the distal convoluted tubule, and 90% of Na+ will have already been reabsorbed before the ultrafiltrate reaches the distal tubule. Thiazides have what would appear to be a paradoxical role in the treatment of nephrogenic DI. Although the mechanism has not been confirmed, their efficacy likely stems from their ability to reduce intravascular volume, in turn stimulating Na+ reabsorption and reducing the amount of fluid presented to the distal segments of the nephron.
Thiazides have what would appear to be a paradoxical role in the treatment of nephrogenic DI. Although the mechanism has not been confirmed, their efficacy likely stems from their ability to reduce intravascular volume, in turn stimulating Na+ reabsorption and reducing the amount of fluid presented to the distal segments of the nephron. By enhancing reabsorption of calcium and subsequent reduction in urinary calcium concentration, thiazides can be used to reduce formation of calcium-containing renal stones.
By enhancing reabsorption of calcium and subsequent reduction in urinary calcium concentration, thiazides can be used to reduce formation of calcium-containing renal stones.Evidence
As First-Line Agents in Hypertension
 A 2009 Cochrane review (24 trials, N = 58,040 participants) compared benefits and harms of first-line antihypertensives with those of placebo or no treatment over a minimum of 1 year. Thiazides (19 trials) reduced mortality (relative risk [RR] 0.89), stroke (RR 0.63), and coronary heart disease (RR 0.84) versus placebo.
A 2009 Cochrane review (24 trials, N = 58,040 participants) compared benefits and harms of first-line antihypertensives with those of placebo or no treatment over a minimum of 1 year. Thiazides (19 trials) reduced mortality (relative risk [RR] 0.89), stroke (RR 0.63), and coronary heart disease (RR 0.84) versus placebo.Diuretics result in increased urine production and also lower blood pressure.
 Generally speaking, diuretics manipulate a solute (usually Na+), and water passively follows:
Generally speaking, diuretics manipulate a solute (usually Na+), and water passively follows:
 Loop diuretics inhibit the Na+/K+/2Cl− co-transporter channel in the thick ascending limb (Henle’s loop) of the renal tubule. This results in less Na+ being reabsorbed back into the body. Cl− and K+ also move in the same direction through this ion channel, as does Na+ (Figure 25-2).
Loop diuretics inhibit the Na+/K+/2Cl− co-transporter channel in the thick ascending limb (Henle’s loop) of the renal tubule. This results in less Na+ being reabsorbed back into the body. Cl− and K+ also move in the same direction through this ion channel, as does Na+ (Figure 25-2). Therefore Na+, Cl−, and K+ are lost in the urine: Natriuresis and diuresis. Blockade of the Na+/K+/2Cl− cotransporter has effects on other ions as well.
Therefore Na+, Cl−, and K+ are lost in the urine: Natriuresis and diuresis. Blockade of the Na+/K+/2Cl− cotransporter has effects on other ions as well. Normally, the K+ channel on the luminal membrane (cell membrane adjacent to the tubular lumen) and the Cl− channel on the basolateral membrane (cell membrane opposite the tubular lumen) creates a potential difference between the tubular lumen (positive) and the interstitium (negative). Blockade of the Na+/K+/2Cl− cotransporter interferes with the ability of these channels to create this positive to negative gradient.
Normally, the K+ channel on the luminal membrane (cell membrane adjacent to the tubular lumen) and the Cl− channel on the basolateral membrane (cell membrane opposite the tubular lumen) creates a potential difference between the tubular lumen (positive) and the interstitium (negative). Blockade of the Na+/K+/2Cl− cotransporter interferes with the ability of these channels to create this positive to negative gradient. Disruption of this electrochemical gradient facilitates excretion of Ca+2 and Mg+2. Normally these divalent cations undergo paracellular reabsorption, repelled by the positively charged tubular lumen and attracted to the negatively charged interstitium. Attenuation of the positive to negative gradient reduces paracellular reabsorption of Ca+2 and Mg+2, and they are excreted.
Disruption of this electrochemical gradient facilitates excretion of Ca+2 and Mg+2. Normally these divalent cations undergo paracellular reabsorption, repelled by the positively charged tubular lumen and attracted to the negatively charged interstitium. Attenuation of the positive to negative gradient reduces paracellular reabsorption of Ca+2 and Mg+2, and they are excreted. A passive Na+/H+ exchanger is present at a distal site in the tubule. Na+ gradients drive this exchange. When the Na+/K+/2Cl− channel is blocked, the Na+ concentration in the lumen of the tubule is high, which facilitates the reabsorption of Na+ and excretion of H+ at this distal site. Therefore furosemide creates alkalosis by H+ ion loss through a secondary, passive exchange.
A passive Na+/H+ exchanger is present at a distal site in the tubule. Na+ gradients drive this exchange. When the Na+/K+/2Cl− channel is blocked, the Na+ concentration in the lumen of the tubule is high, which facilitates the reabsorption of Na+ and excretion of H+ at this distal site. Therefore furosemide creates alkalosis by H+ ion loss through a secondary, passive exchange. Similarly, by enhancing delivery of Na+ to distal sites of the nephron, Na+ is exchanged for K+, leading to enhanced K+ excretion, and this further depletes K+.
Similarly, by enhancing delivery of Na+ to distal sites of the nephron, Na+ is exchanged for K+, leading to enhanced K+ excretion, and this further depletes K+. Loop diuretics act on the apical (lumen) side of the tubule and therefore must be in the tubule in order to exert their effects.
Loop diuretics act on the apical (lumen) side of the tubule and therefore must be in the tubule in order to exert their effects. Other electrolytes disturbances: Given the large number of ions (Na+, Cl−, and so on) that are affected by these agents, electrolytes should be monitored.
Other electrolytes disturbances: Given the large number of ions (Na+, Cl−, and so on) that are affected by these agents, electrolytes should be monitored. Ototoxicity: Reversible hearing loss occurs most often in those with reduced renal function or who are receiving other ototoxic agents such as aminoglycoside antibiotics. The mechanism has not been established, although the Na+/K+/2Cl− transporter is also found in the inner ear. High-dose furosemide can cause permanent deafness.
Ototoxicity: Reversible hearing loss occurs most often in those with reduced renal function or who are receiving other ototoxic agents such as aminoglycoside antibiotics. The mechanism has not been established, although the Na+/K+/2Cl− transporter is also found in the inner ear. High-dose furosemide can cause permanent deafness.Diuretics versus Placebo or Other Interventions for Treatment of Heart Failure
 A 2006 Cochrane review (14 trials, N = 525 participants) compared diuretics with placebo (seven trials) and other interventions (seven trials) for treatment of heart failure. The diuretics included were a mixture of loop diuretics, potassium-sparing diuretics, and thiazides. Based on three trials (N = 202 participants), diuretic treatment reduced the odds of death versus placebo (OR 0.24), and in two trials (N = 169 participants) it reduced the odds of admission because of worsening heart failure (OR 0.07). Diuretics improved exercise capacity in four trials (N = 91 participants) versus active controls.
A 2006 Cochrane review (14 trials, N = 525 participants) compared diuretics with placebo (seven trials) and other interventions (seven trials) for treatment of heart failure. The diuretics included were a mixture of loop diuretics, potassium-sparing diuretics, and thiazides. Based on three trials (N = 202 participants), diuretic treatment reduced the odds of death versus placebo (OR 0.24), and in two trials (N = 169 participants) it reduced the odds of admission because of worsening heart failure (OR 0.07). Diuretics improved exercise capacity in four trials (N = 91 participants) versus active controls.Blood-Pressure–Lowering Effect versus Placebo or No Treatment
 A 2009 Cochrane review (nine trials, N = 460 participants) compared the blood-pressure–lowering efficacy, tolerability, and biochemical effects of a variety of loop diuretics versus placebo or no treatment. The authors found a mean reduction (systolic/diastolic blood pressure) of −7.9/−4.4 mmHg and no differences between drugs in this class with respect to blood-pressure–lowering efficacy. This is considered to be a modest antihypertensive effect. Withdrawals because of adverse effects and biochemical changes were not significantly different from control.
A 2009 Cochrane review (nine trials, N = 460 participants) compared the blood-pressure–lowering efficacy, tolerability, and biochemical effects of a variety of loop diuretics versus placebo or no treatment. The authors found a mean reduction (systolic/diastolic blood pressure) of −7.9/−4.4 mmHg and no differences between drugs in this class with respect to blood-pressure–lowering efficacy. This is considered to be a modest antihypertensive effect. Withdrawals because of adverse effects and biochemical changes were not significantly different from control. Diuretics that exert their effects by acting on the renal tubules require functioning kidneys to induce diuresis. Patients with advanced renal dysfunction will not respond to these diuretics.
Diuretics that exert their effects by acting on the renal tubules require functioning kidneys to induce diuresis. Patients with advanced renal dysfunction will not respond to these diuretics. Loop diuretics are much stronger diuretics than thiazides. This is because they work in the loop of Henle, which is positioned before (proximal to) the distal convoluted tubule where the thiazides work.
Loop diuretics are much stronger diuretics than thiazides. This is because they work in the loop of Henle, which is positioned before (proximal to) the distal convoluted tubule where the thiazides work. Thus most diuretics lead to enhanced Na+ in the lumen of the tubule (i.e., the urine). High Na+ concentrations in the tubule lead to a compensatory reabsorption of Na+ in exchange for K+ excretion in the distal nephron, leading to the hypokalemia associated with many diuretics.
Thus most diuretics lead to enhanced Na+ in the lumen of the tubule (i.e., the urine). High Na+ concentrations in the tubule lead to a compensatory reabsorption of Na+ in exchange for K+ excretion in the distal nephron, leading to the hypokalemia associated with many diuretics. The goal of potassium-sparing diuretics is to prevent this reabsorption of Na+ and subsequent loss of K+ in the late distal tubule or collecting duct of the nephron.
The goal of potassium-sparing diuretics is to prevent this reabsorption of Na+ and subsequent loss of K+ in the late distal tubule or collecting duct of the nephron. The exchange of Na+ for K+ in the distal nephron is mediated by the actions of the epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC) on the luminal side of the membrane and the Na+/K+-ATPase pump on the basolateral membrane (side opposite the lumen of the tubule).
The exchange of Na+ for K+ in the distal nephron is mediated by the actions of the epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC) on the luminal side of the membrane and the Na+/K+-ATPase pump on the basolateral membrane (side opposite the lumen of the tubule). The basolateral Na+/K+-ATPase pump creates a gradient for the entry of Na+ into the cell from the ENaC on the luminal side of the membrane.
The basolateral Na+/K+-ATPase pump creates a gradient for the entry of Na+ into the cell from the ENaC on the luminal side of the membrane. The Na+/K+-ATPase pump actively pumps Na+ out of the cell into the interstitium, in exchange for a K+ ion.
The Na+/K+-ATPase pump actively pumps Na+ out of the cell into the interstitium, in exchange for a K+ ion. The potassium-sparing diuretics inhibit this exchange of Na+ for K+ by inhibiting ENaC alone or both ENaC and the Na+/K+-ATPase pump.
The potassium-sparing diuretics inhibit this exchange of Na+ for K+ by inhibiting ENaC alone or both ENaC and the Na+/K+-ATPase pump.Spironolactone and Eplerenone (Figure 25-3)
 Spironolactone and eplerenone directly antagonize aldosterone:
Spironolactone and eplerenone directly antagonize aldosterone:
 The MR-aldosterone complex translocates to the nucleus, where it binds to specific DNA sequences to increase the number of ENaC channels and Na+/K+-ATPase pump.
The MR-aldosterone complex translocates to the nucleus, where it binds to specific DNA sequences to increase the number of ENaC channels and Na+/K+-ATPase pump.Other Effects
 Spironolactone also binds to androgen and progesterone receptors. This is not by design but reflects the similarities in chemical structure between androgens (e.g., testosterone) progesterone, and aldosterone. Because these receptors are also similar in structure, spironolactone, which was designed before these receptors were mapped, binds to all three.
Spironolactone also binds to androgen and progesterone receptors. This is not by design but reflects the similarities in chemical structure between androgens (e.g., testosterone) progesterone, and aldosterone. Because these receptors are also similar in structure, spironolactone, which was designed before these receptors were mapped, binds to all three. Spironolactone has an active metabolite, canrenone, which is also marketed in some jurisdictions. Canrenone has a much longer elimination half-life (16 hours) than spironolactone (2 hours).
Spironolactone has an active metabolite, canrenone, which is also marketed in some jurisdictions. Canrenone has a much longer elimination half-life (16 hours) than spironolactone (2 hours). As adjunct (add-on) therapy to a regular (potassium-depleting) diuretic such as a thiazide or loop diuretic, in the treatment of:
As adjunct (add-on) therapy to a regular (potassium-depleting) diuretic such as a thiazide or loop diuretic, in the treatment of:
 K+-sparing diuretics all produce a fairly modest diuresis and are typically given as adjunctive (add-on) therapy with more potent diuretics, with the intention of mitigating the hypokalemia associated with those agents.
K+-sparing diuretics all produce a fairly modest diuresis and are typically given as adjunctive (add-on) therapy with more potent diuretics, with the intention of mitigating the hypokalemia associated with those agents. Antagonism of the aldosterone receptor might have beneficial effects beyond diuresis. The Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study (RALES) found that treatment with spironolactone significantly reduced mortality in a moderate-sized (approximately 800 subjects in each group) population, reducing the risk of death by about 30%. Risk of hospitalization was reduced by about 35%.
Antagonism of the aldosterone receptor might have beneficial effects beyond diuresis. The Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study (RALES) found that treatment with spironolactone significantly reduced mortality in a moderate-sized (approximately 800 subjects in each group) population, reducing the risk of death by about 30%. Risk of hospitalization was reduced by about 35%. The results of RALES suggested that in heart failure patients, spironolactone was not simply acting as a diuretic. There are many theories as to what this additional beneficial effect might be, but most focus around the link between elevated aldosterone and heart failure. A large trial, EPHESUS (N = 6000 patients), had similar results for eplerenone in patients who had developed heart failure after a myocardial infarction. However, in EPHESUS the magnitude of benefit was not as great as in RALES; therefore it is not clear whether aldosterone antagonism alone is contributing to benefit or whether there is some other factor involved.
The results of RALES suggested that in heart failure patients, spironolactone was not simply acting as a diuretic. There are many theories as to what this additional beneficial effect might be, but most focus around the link between elevated aldosterone and heart failure. A large trial, EPHESUS (N = 6000 patients), had similar results for eplerenone in patients who had developed heart failure after a myocardial infarction. However, in EPHESUS the magnitude of benefit was not as great as in RALES; therefore it is not clear whether aldosterone antagonism alone is contributing to benefit or whether there is some other factor involved. Drospirenone is a new progestogen that also antagonizes aldosterone receptors. It is used as a component in oral contraceptive regimens with estrogen, in the hope that the aldosterone antagonism will counteract the Na+ and water retention from the estrogen.
Drospirenone is a new progestogen that also antagonizes aldosterone receptors. It is used as a component in oral contraceptive regimens with estrogen, in the hope that the aldosterone antagonism will counteract the Na+ and water retention from the estrogen. All three prototypical K+-sparing diuretics (spironolactone, triamterene, and amiloride) are available in fixed-dose combinations (i.e., in the same pill) with hydrochlorothiazide.
All three prototypical K+-sparing diuretics (spironolactone, triamterene, and amiloride) are available in fixed-dose combinations (i.e., in the same pill) with hydrochlorothiazide.Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors (CAIs)
 Carbonic Anhydrase (CA) is classified as a diuretic, but its important clinical effects are related to its effect on acid-base balance and on intraocular fluid formation.
Carbonic Anhydrase (CA) is classified as a diuretic, but its important clinical effects are related to its effect on acid-base balance and on intraocular fluid formation. CA catalyzes the following reaction:
CA catalyzes the following reaction:
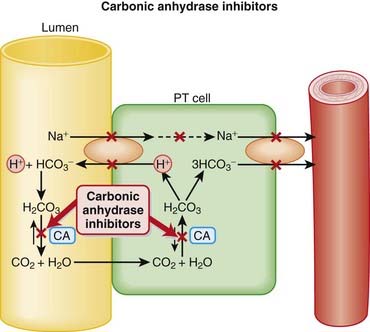
 CAIs inhibit this enzyme, which results in this reaction occurring at a much slower rate compared with the catalyzed rate, effectively stopping the reaction. The difference in reaction speed is over 1000-fold (Figure 25-4).
CAIs inhibit this enzyme, which results in this reaction occurring at a much slower rate compared with the catalyzed rate, effectively stopping the reaction. The difference in reaction speed is over 1000-fold (Figure 25-4). CA is present at various sites throughout the nephron, but is mainly found on the luminal membrane of proximal tubule cells.
CA is present at various sites throughout the nephron, but is mainly found on the luminal membrane of proximal tubule cells. As seen in the diagram, this allows for the recycling of H+ from the lumen into the cell and back to the lumen again.
As seen in the diagram, this allows for the recycling of H+ from the lumen into the cell and back to the lumen again. The Na+ is transported across the basolateral membrane (the side opposite the tubular lumen) into the blood along with the HCO3−. The net effect of these movements is Na+ and HCO3− reabsorption. Note that “H2O” is embedded in HCO3−.
The Na+ is transported across the basolateral membrane (the side opposite the tubular lumen) into the blood along with the HCO3−. The net effect of these movements is Na+ and HCO3− reabsorption. Note that “H2O” is embedded in HCO3−. The movement of these ions is largely driven by electrical and concentration gradients. Therefore inhibiting CA will effectively stop this entire cycle.
The movement of these ions is largely driven by electrical and concentration gradients. Therefore inhibiting CA will effectively stop this entire cycle. Acetazolamide is cleared by the kidneys, whereas methazolamide is cleared primarily by the kidneys but also partially by the liver.
Acetazolamide is cleared by the kidneys, whereas methazolamide is cleared primarily by the kidneys but also partially by the liver. Dorzolamide and brinzolamide are administered topically, as eye drops in the management of glaucoma.
Dorzolamide and brinzolamide are administered topically, as eye drops in the management of glaucoma. Renal stones: Renal output of phosphates and calcium increases with CAI use. Chronic use of CAIs may also reduce excretion of solubilizing factors and, coupled with the alkalinization of the urine (Ca+2 salts are relatively insoluble at alkaline pH), creates an ideal environment for stone development.
Renal stones: Renal output of phosphates and calcium increases with CAI use. Chronic use of CAIs may also reduce excretion of solubilizing factors and, coupled with the alkalinization of the urine (Ca+2 salts are relatively insoluble at alkaline pH), creates an ideal environment for stone development. Hypokalemia: Additional NaHCO3 in the collecting tubule stimulates the secretion of K+ because of maintenance of the ion gradient.
Hypokalemia: Additional NaHCO3 in the collecting tubule stimulates the secretion of K+ because of maintenance of the ion gradient. Acting early in the nephron, the diuretic actions of CAIs are countered by a number of sites for Na+ reabsorption that appear distally in the tubule. That, coupled with the complication of metabolic acidosis, has limited the therapeutic usefulness of CAIs in the management of edema, and certainly in hypertension. In fact, CAIs are not even used for the treatment of edema or hypertension currently.
Acting early in the nephron, the diuretic actions of CAIs are countered by a number of sites for Na+ reabsorption that appear distally in the tubule. That, coupled with the complication of metabolic acidosis, has limited the therapeutic usefulness of CAIs in the management of edema, and certainly in hypertension. In fact, CAIs are not even used for the treatment of edema or hypertension currently. The main use for CAIs at present is in the treatment of glaucoma (increased intraocular pressure [IOP]). The most popular agents are topical (dorzolamide, brinzolamide) drops administered to the eye. Locally administered agents are very low dose and therefore avoid the diuretic and systemic metabolic effects.
The main use for CAIs at present is in the treatment of glaucoma (increased intraocular pressure [IOP]). The most popular agents are topical (dorzolamide, brinzolamide) drops administered to the eye. Locally administered agents are very low dose and therefore avoid the diuretic and systemic metabolic effects. The tendency toward metabolic acidosis helps to stimulate breathing, which, through a mechanism not entirely understood, helps a climber acclimatize more quickly to high altitude.
The tendency toward metabolic acidosis helps to stimulate breathing, which, through a mechanism not entirely understood, helps a climber acclimatize more quickly to high altitude. One systematic review found that acetazolamide was more efficacious than placebo in preventing acute mountain sickness (number needed to treat [NNT], two to three). A lower dose was not found to be more effective than placebo.
One systematic review found that acetazolamide was more efficacious than placebo in preventing acute mountain sickness (number needed to treat [NNT], two to three). A lower dose was not found to be more effective than placebo. How do CAIs work in the treatment of glaucoma? Glaucoma is a condition of the eye characterized by increased intraocular pressure (IOP). CA located in the ciliary processes of the eye results in the formation of HCO3− in aqueous humor. By decreasing the rate of formation of aqueous humor, CAIs reduce IOP.
How do CAIs work in the treatment of glaucoma? Glaucoma is a condition of the eye characterized by increased intraocular pressure (IOP). CA located in the ciliary processes of the eye results in the formation of HCO3− in aqueous humor. By decreasing the rate of formation of aqueous humor, CAIs reduce IOP.Osmotic diuretics increase the oncotic pressure of fluids and carry water with them.
 Osmotic agents increase the oncotic pressure of the blood; this pulls water from tissues and increases the volume of the blood acutely. The increased blood volume will inhibit renin release, thus increasing renal blood flow.
Osmotic agents increase the oncotic pressure of the blood; this pulls water from tissues and increases the volume of the blood acutely. The increased blood volume will inhibit renin release, thus increasing renal blood flow. Osmotic agents freely enter the glomerulus and Bowman’s space and enter the nephron in the ultrafiltrate.
Osmotic agents freely enter the glomerulus and Bowman’s space and enter the nephron in the ultrafiltrate. Osmotic diuretics are not reabsorbed from the lumen of the nephron and create an osmotic force, pulling more fluid into the lumen. This is then carried out as urine.
Osmotic diuretics are not reabsorbed from the lumen of the nephron and create an osmotic force, pulling more fluid into the lumen. This is then carried out as urine. As a second primary mechanism for a diuretic, the increased renal blood flow effectively washes away solutes from the renal medulla, reducing tonicity in this region of the kidney. The hypertonicity of the medulla is a major driving force for reabsorption of fluid from the renal tubule. Reducing this tonicity mitigates the forces that concentrate the urine in the ascending limb of Henle.
As a second primary mechanism for a diuretic, the increased renal blood flow effectively washes away solutes from the renal medulla, reducing tonicity in this region of the kidney. The hypertonicity of the medulla is a major driving force for reabsorption of fluid from the renal tubule. Reducing this tonicity mitigates the forces that concentrate the urine in the ascending limb of Henle. Lowering the concentration of Na+ in the ascending limb of Henle reduces the driving force for Na+ reabsorption in this region, leading to diuresis.
Lowering the concentration of Na+ in the ascending limb of Henle reduces the driving force for Na+ reabsorption in this region, leading to diuresis. Raised intracranial pressure (ICP) and cerebral edema. The concept behind using osmotic manipulation for treating raised ICP is that water will get sucked out of the brain and into the blood (which has high osmotic pressure from the mannitol); this will reduce brain swelling and ICP.
Raised intracranial pressure (ICP) and cerebral edema. The concept behind using osmotic manipulation for treating raised ICP is that water will get sucked out of the brain and into the blood (which has high osmotic pressure from the mannitol); this will reduce brain swelling and ICP. Disequilibrium syndrome in dialysis (rare): Osmotic diuretics restore fluid to the extracellular compartment in patients who have been dialyzed and develop problems with the rapid shift in fluid and electrolytes that can sometimes accompany dialysis.
Disequilibrium syndrome in dialysis (rare): Osmotic diuretics restore fluid to the extracellular compartment in patients who have been dialyzed and develop problems with the rapid shift in fluid and electrolytes that can sometimes accompany dialysis. Active cranial bleeding: If bleeding is occurring into the brain, then the mannitol will be directly added to the brain and will raise the osmotic pressure in the brain and lead to water being added to the brain, which is the opposite of what the mannitol is being given for.
Active cranial bleeding: If bleeding is occurring into the brain, then the mannitol will be directly added to the brain and will raise the osmotic pressure in the brain and lead to water being added to the brain, which is the opposite of what the mannitol is being given for. Continuous administration of mannitol should not occur, because the drug will accumulate in the tissues and result in osmotic-induced tissue edema, including in the brain.
Continuous administration of mannitol should not occur, because the drug will accumulate in the tissues and result in osmotic-induced tissue edema, including in the brain. Extracellular volume expansion: Osmotic diuretics rapidly distribute to the extracellular compartment, extracting water from cells. Before onset of the diuresis, this can lead to expansion of the extracellular space. Frank pulmonary edema can arise in patients with heart failure or pulmonary congestion.
Extracellular volume expansion: Osmotic diuretics rapidly distribute to the extracellular compartment, extracting water from cells. Before onset of the diuresis, this can lead to expansion of the extracellular space. Frank pulmonary edema can arise in patients with heart failure or pulmonary congestion. Dehydration and hypernatremia: Excess use without fluid replacement can lead to dehydration. Composition of serum ions and fluid balance should be monitored.
Dehydration and hypernatremia: Excess use without fluid replacement can lead to dehydration. Composition of serum ions and fluid balance should be monitored. Osmotic diuretics increase the excretion of nearly all electrolytes (Na+, K+, Ca+2, Mg+2, Cl−, HCO3−, and phosphate).
Osmotic diuretics increase the excretion of nearly all electrolytes (Na+, K+, Ca+2, Mg+2, Cl−, HCO3−, and phosphate). Patients with uncontrolled diabetes mellitus will have an osmotic diuresis from elevated blood glucose. This is what causes polyuria (excessive urination), leading to thirst and excessive drinking of fluids (polydipsia).
Patients with uncontrolled diabetes mellitus will have an osmotic diuresis from elevated blood glucose. This is what causes polyuria (excessive urination), leading to thirst and excessive drinking of fluids (polydipsia). A 2007 Cochrane review (four trials, N = 197 participants) compared different mannitol regimens with other interventions, including placebo and no treatment, in patients with acute traumatic brain injury. There was no difference in the incidence of death between mannitol and “standard care,” pentobarbital, hypertonic saline, or placebo.
A 2007 Cochrane review (four trials, N = 197 participants) compared different mannitol regimens with other interventions, including placebo and no treatment, in patients with acute traumatic brain injury. There was no difference in the incidence of death between mannitol and “standard care,” pentobarbital, hypertonic saline, or placebo. Mannitol is a six-carbon sugar alcohol. It was first discovered in the sap of a plant and was thought to resemble biblical food; therefore the plant was called manna ash, after manna (biblical reference to food).
Mannitol is a six-carbon sugar alcohol. It was first discovered in the sap of a plant and was thought to resemble biblical food; therefore the plant was called manna ash, after manna (biblical reference to food).Antidiuretic Hormone (Vasopressin) Analogues
 Vasopressin is produced in the hypothalamus and stored in the posterior pituitary gland. Factors that stimulate its physiologic release include increased serum osmolarity and hypotension. Its primary actions are therefore to increase body water to control osmolality and to increase blood pressure. A third action that it exerts is to help stop bleeding through platelet stimulation.
Vasopressin is produced in the hypothalamus and stored in the posterior pituitary gland. Factors that stimulate its physiologic release include increased serum osmolarity and hypotension. Its primary actions are therefore to increase body water to control osmolality and to increase blood pressure. A third action that it exerts is to help stop bleeding through platelet stimulation. Vasopressin binds two types of receptors: V1 and V2. V1 is subtyped into V1a and V1b. V1 receptors are found in many locations of the body, including endothelium and many other sites. V2 receptors are located in the collecting ducts of the nephron.
Vasopressin binds two types of receptors: V1 and V2. V1 is subtyped into V1a and V1b. V1 receptors are found in many locations of the body, including endothelium and many other sites. V2 receptors are located in the collecting ducts of the nephron. At very low concentrations vasopressin acts on V2 receptors. Only at higher doses are the V1 receptors activated.
At very low concentrations vasopressin acts on V2 receptors. Only at higher doses are the V1 receptors activated. V1 receptors are located on vascular smooth muscle and produce a potent vasoconstrictor effect when stimulated. This occurs only at higher serum levels of vasopressin.
V1 receptors are located on vascular smooth muscle and produce a potent vasoconstrictor effect when stimulated. This occurs only at higher serum levels of vasopressin. The hemodynamic effects of vasopressin are similar to norepinephrine; the difference is that norepinephrine also possesses some β-agonist activity and therefore will increase heart rate and contractility, whereas vasopressin will not.
The hemodynamic effects of vasopressin are similar to norepinephrine; the difference is that norepinephrine also possesses some β-agonist activity and therefore will increase heart rate and contractility, whereas vasopressin will not. Filtrate that reaches the collecting duct in the kidney has been diluted by previous tubules. Therefore filtrate that is reabsorbed in the collecting duct is quite dilute and low in sodium.
Filtrate that reaches the collecting duct in the kidney has been diluted by previous tubules. Therefore filtrate that is reabsorbed in the collecting duct is quite dilute and low in sodium. V2 receptors are located in the collecting duct of the nephron. When stimulated, they activate pores called aquaporins (e.g., aquaporin 2). These pores usually are stored in intracellular vesicles and when stimulated by vasopressin will fuse with the luminal membrane and facilitate the reabsorption of water from the nephron lumen back into the body. In the absence of the vasopressin and the aquaporins, the collecting duct is impermeable to water and will not absorb any water.
V2 receptors are located in the collecting duct of the nephron. When stimulated, they activate pores called aquaporins (e.g., aquaporin 2). These pores usually are stored in intracellular vesicles and when stimulated by vasopressin will fuse with the luminal membrane and facilitate the reabsorption of water from the nephron lumen back into the body. In the absence of the vasopressin and the aquaporins, the collecting duct is impermeable to water and will not absorb any water. Desmopressin is a synthetic compound; it is more specific for V2 receptors and has a longer half-life than vasopressin. Compared with vasopressin, desmopressin (DDAVP) is 3000 times more selective for V2 receptors. Therefore desmopressin minimizes the potent vasoconstrictor effects associated with vasopressin.
Desmopressin is a synthetic compound; it is more specific for V2 receptors and has a longer half-life than vasopressin. Compared with vasopressin, desmopressin (DDAVP) is 3000 times more selective for V2 receptors. Therefore desmopressin minimizes the potent vasoconstrictor effects associated with vasopressin. Factor VIII and von Willebrand’s factor (vWF) bind together and then bind platelets, which causes platelet activation. A deficiency in either of these two factors will result in decreased platelet function and bleeding disorders (hemophilia A and von Willebrand’s disease).
Factor VIII and von Willebrand’s factor (vWF) bind together and then bind platelets, which causes platelet activation. A deficiency in either of these two factors will result in decreased platelet function and bleeding disorders (hemophilia A and von Willebrand’s disease). Vasopressin is administered by intravenous infusion. It has a short half-life and therefore is given by infusion.
Vasopressin is administered by intravenous infusion. It has a short half-life and therefore is given by infusion. Excessive vasoconstriction. The use of vasopressin should be restricted to physicians trained in critical care.
Excessive vasoconstriction. The use of vasopressin should be restricted to physicians trained in critical care. Water intoxication (hyponatremia): This is caused by the antidiuretic action and results in water retention leading to dilution of electrolytes, specifically Na+.
Water intoxication (hyponatremia): This is caused by the antidiuretic action and results in water retention leading to dilution of electrolytes, specifically Na+. Hypotension (paradoxical to other analogues): If administered by the intravenous route, desmopressin must be given slowly.
Hypotension (paradoxical to other analogues): If administered by the intravenous route, desmopressin must be given slowly. Nephrogenic DI is a condition of nonresponsiveness of the kidney to normal circulating levels of ADH.
Nephrogenic DI is a condition of nonresponsiveness of the kidney to normal circulating levels of ADH. In DI there is too much water relative to Na+ in the blood. Therefore, hyponatremia exists. Furthermore, there is very little water in the urine and so the urine osmolality is very high.
In DI there is too much water relative to Na+ in the blood. Therefore, hyponatremia exists. Furthermore, there is very little water in the urine and so the urine osmolality is very high. Varices are abnormal blood veins: dilated, elongated, and tortuous. They are caused by abnormally high venous pressures. They are most commonly seen in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract (esophagus, anus) in patients with liver failure and portal hypertension and also in the legs when one-way valves in the upper leg fail to prevent backflow and pressure. Administration of vasopressin or other vasoconstricting analogues results in mesenteric vasoconstriction and reduced blood flow and thus reduced portal blood pressure. This is beneficial to patients with portal hypertension secondary to liver disease who have bleeding variceal vessels in the esophagus.
Varices are abnormal blood veins: dilated, elongated, and tortuous. They are caused by abnormally high venous pressures. They are most commonly seen in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract (esophagus, anus) in patients with liver failure and portal hypertension and also in the legs when one-way valves in the upper leg fail to prevent backflow and pressure. Administration of vasopressin or other vasoconstricting analogues results in mesenteric vasoconstriction and reduced blood flow and thus reduced portal blood pressure. This is beneficial to patients with portal hypertension secondary to liver disease who have bleeding variceal vessels in the esophagus. There are many subtypes of von Willebrand’s disease, depending on the levels of vWF in the body. Desmopressin is really effective in only the mild forms of the disease.
There are many subtypes of von Willebrand’s disease, depending on the levels of vWF in the body. Desmopressin is really effective in only the mild forms of the disease. V2 antagonists are the newest class of diuretics. These agents are referred to as aquaretics, because by blocking V2 receptors in the collecting duct they produce a water diuresis, with minimal loss of electrolytes. The first aquaretic, tolvaptan, has been approved in most jurisdictions for patients with volume overload and electrolyte problems that would be exacerbated by conventional diuretics.
V2 antagonists are the newest class of diuretics. These agents are referred to as aquaretics, because by blocking V2 receptors in the collecting duct they produce a water diuresis, with minimal loss of electrolytes. The first aquaretic, tolvaptan, has been approved in most jurisdictions for patients with volume overload and electrolyte problems that would be exacerbated by conventional diuretics.Desmopressin and Bedwetting (Enuresis) in Children
 A Cochrane review in 2002 (47 studies, 3448 children) demonstrated that desmopressin is effective at reducing bedwetting but that the effects do not persist when the drug is stopped. Using a wake-up alarm (the alarm goes off when the child gets wet) was just as effective as desmopressin but had better long-lasting effects.
A Cochrane review in 2002 (47 studies, 3448 children) demonstrated that desmopressin is effective at reducing bedwetting but that the effects do not persist when the drug is stopped. Using a wake-up alarm (the alarm goes off when the child gets wet) was just as effective as desmopressin but had better long-lasting effects.Desmopressin and Surgical Blood Loss in Patients without Bleeding Disorders
 A Cochrane review in 2004 (19 studies, 1387 patients) demonstrated that bleeding with desmopressin was statistically less compared with placebo (mean difference = 241 mL less). However, there was no difference in blood transfusions, and the volume of blood loss reduction is not a clinically significant amount.
A Cochrane review in 2004 (19 studies, 1387 patients) demonstrated that bleeding with desmopressin was statistically less compared with placebo (mean difference = 241 mL less). However, there was no difference in blood transfusions, and the volume of blood loss reduction is not a clinically significant amount. From Latin:
From Latin:
 Aquaporin 1 is present in the proximal tubule and is responsible for water reabsorption in this part of the nephron. It is not responsive to AVP.
Aquaporin 1 is present in the proximal tubule and is responsible for water reabsorption in this part of the nephron. It is not responsive to AVP. Syndrome of inappropriate ADH (SIADH) is a condition of too much ADH. It is essentially the opposite of DI.
Syndrome of inappropriate ADH (SIADH) is a condition of too much ADH. It is essentially the opposite of DI. Oxytocin and vasopressin are structurally very similar. Therefore oxytocin and vasopressin agonists or antagonists can interact with either receptor.
Oxytocin and vasopressin are structurally very similar. Therefore oxytocin and vasopressin agonists or antagonists can interact with either receptor. The human bladder contains all five subtypes (M1 to M5) of muscarinic (M) receptors. Although M2 receptors are more abundant in this region, M3 receptors mediate contraction of the detrusor muscle in the bladder.
The human bladder contains all five subtypes (M1 to M5) of muscarinic (M) receptors. Although M2 receptors are more abundant in this region, M3 receptors mediate contraction of the detrusor muscle in the bladder. Detrusor muscle contraction facilitates emptying of the bladder (micturition). Abnormal contractions of the detrusor, also known as hyperreflexia, can lead to incontinence, specifically urge incontinence. Urge incontinence is defined as the inability to reach the toilet in time following the urge to urinate (Figure 25-5).
Detrusor muscle contraction facilitates emptying of the bladder (micturition). Abnormal contractions of the detrusor, also known as hyperreflexia, can lead to incontinence, specifically urge incontinence. Urge incontinence is defined as the inability to reach the toilet in time following the urge to urinate (Figure 25-5). Anticholinergics that antagonize the M3 receptor inhibit these detrusor contractions, easing the symptoms of urge incontinence.
Anticholinergics that antagonize the M3 receptor inhibit these detrusor contractions, easing the symptoms of urge incontinence. M1 receptors are found in the central nervous system (CNS), on glands (enteric and salivary), and on enteric nerves.
M1 receptors are found in the central nervous system (CNS), on glands (enteric and salivary), and on enteric nerves. Because of the wide distribution of M receptors, anticholinergics for OAB have an extensive side effect profile, and considerable research is going into localizing the effects of these agents to the detrusor.
Because of the wide distribution of M receptors, anticholinergics for OAB have an extensive side effect profile, and considerable research is going into localizing the effects of these agents to the detrusor. Most of the anticholinergics for OAB are lipophilic, meaning that they readily cross the blood-brain barrier. The exception is trospium, a polar molecule that does not cross into the brain.
Most of the anticholinergics for OAB are lipophilic, meaning that they readily cross the blood-brain barrier. The exception is trospium, a polar molecule that does not cross into the brain. The half-lives of these agents vary widely, and agents with short half-lives (oxybutynin, tolterodine) typically have extended-release (ER) preparations available.
The half-lives of these agents vary widely, and agents with short half-lives (oxybutynin, tolterodine) typically have extended-release (ER) preparations available. Oxybutynin is also marketed as a transdermal patch. The patch is applied twice weekly and delivers 3.9 mg of oxybutynin per day.
Oxybutynin is also marketed as a transdermal patch. The patch is applied twice weekly and delivers 3.9 mg of oxybutynin per day. Conditions in which cholinergic blockade would exacerbate an already serious condition, or patients at risk for the following:
Conditions in which cholinergic blockade would exacerbate an already serious condition, or patients at risk for the following:
 Typical anticholinergic side effects:
Typical anticholinergic side effects:
 CNS side effects are a concern with the use of anticholinergics, particularly in seniors and the elderly. Attempts have been made to develop compounds that either have limited penetration into the CNS (trospium) or that bind with lower affinity to M1 receptors (darifenacin), receptors that are thought to play an important role in cognition. However, although there is some evidence of reduced CNS side effects in older, otherwise-healthy patients, there is no definitive proof that these approaches are able to reduce the burden of CNS side effects in patients with OAB.
CNS side effects are a concern with the use of anticholinergics, particularly in seniors and the elderly. Attempts have been made to develop compounds that either have limited penetration into the CNS (trospium) or that bind with lower affinity to M1 receptors (darifenacin), receptors that are thought to play an important role in cognition. However, although there is some evidence of reduced CNS side effects in older, otherwise-healthy patients, there is no definitive proof that these approaches are able to reduce the burden of CNS side effects in patients with OAB.Anticholinergics for Overactive Bladder
 A 2008 systematic review (83 trials) compared various anticholinergics in treating OAB. All the included anticholinergics (oxybutynin, tolterodine, fesoterodine, propiverine, solifenacin, darifenacin, and trospium) demonstrated efficacy in a variety of outcome measures related to incontinence (incontinence episodes, frequency, urgency) versus placebo.
A 2008 systematic review (83 trials) compared various anticholinergics in treating OAB. All the included anticholinergics (oxybutynin, tolterodine, fesoterodine, propiverine, solifenacin, darifenacin, and trospium) demonstrated efficacy in a variety of outcome measures related to incontinence (incontinence episodes, frequency, urgency) versus placebo. Although there were no definitive conclusions with respect to comparisons among agents, there was some indication that newer agents (solifenacin) may have greater efficacy than slightly older agents (tolterodine) for some outcomes. Oxybutynin was the only agent with a higher risk of withdrawals versus placebo. Tolterodine consistently had the most favorable safety and tolerability data compared with other agents.
Although there were no definitive conclusions with respect to comparisons among agents, there was some indication that newer agents (solifenacin) may have greater efficacy than slightly older agents (tolterodine) for some outcomes. Oxybutynin was the only agent with a higher risk of withdrawals versus placebo. Tolterodine consistently had the most favorable safety and tolerability data compared with other agents. Controversy still exists over the relative benefit to risk of anticholinergics for OAB, particularly in seniors and the elderly. Although these agents have demonstrated improved symptoms versus placebo, the clinical significance of these benefits is constantly being weighed against a considerable list of side effects.
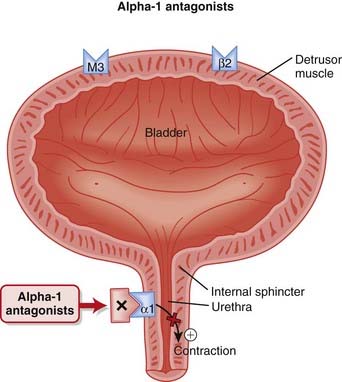
Controversy still exists over the relative benefit to risk of anticholinergics for OAB, particularly in seniors and the elderly. Although these agents have demonstrated improved symptoms versus placebo, the clinical significance of these benefits is constantly being weighed against a considerable list of side effects. Antagonism of α1 receptors on vascular smooth muscle induces vasodilation and decreases systemic vascular resistance (SVR).
Antagonism of α1 receptors on vascular smooth muscle induces vasodilation and decreases systemic vascular resistance (SVR). α1 Receptors are also found in the urinary sphincter (also smooth muscle) of the bladder. The sphincter controls the flow of urine out of the bladder (Figure 25-6).
α1 Receptors are also found in the urinary sphincter (also smooth muscle) of the bladder. The sphincter controls the flow of urine out of the bladder (Figure 25-6). In patients with an enlarged prostate, pressure exerted by the prostate on the sphincter can interfere with normal urine flow. Therefore patients with an enlarged prostate experience hesitancy (difficulty starting urination) and typically do not urinate much at a time but experience urinary frequency.
In patients with an enlarged prostate, pressure exerted by the prostate on the sphincter can interfere with normal urine flow. Therefore patients with an enlarged prostate experience hesitancy (difficulty starting urination) and typically do not urinate much at a time but experience urinary frequency. Another rare use for α1 antagonists is in the management of pheochromocytoma. This is a tumor of the adrenal medulla that secretes catecholamines such as epinephrine and norepinephrine. α1 Antagonists such as phenoxybenzamine are used preoperatively and postoperatively to manage the symptoms of catecholamine excess.
Another rare use for α1 antagonists is in the management of pheochromocytoma. This is a tumor of the adrenal medulla that secretes catecholamines such as epinephrine and norepinephrine. α1 Antagonists such as phenoxybenzamine are used preoperatively and postoperatively to manage the symptoms of catecholamine excess. Prazosin has a short half-life and thus must be given twice daily. Longer-acting agents such as terazosin and doxazosin were developed to provide the advantage of once-daily administration.
Prazosin has a short half-life and thus must be given twice daily. Longer-acting agents such as terazosin and doxazosin were developed to provide the advantage of once-daily administration.Phentolamine and Phenoxybenzamine Only
 Orthostatic hypotension is common and can be quite significant, usually occurring within 90 minutes of the first dose of the drug. It can lead to dizziness and falls.
Orthostatic hypotension is common and can be quite significant, usually occurring within 90 minutes of the first dose of the drug. It can lead to dizziness and falls. Cardiovascular events: Although these agents are typically well tolerated, results of a recent study suggest that they may be associated with an increased risk, summarized in the Advanced section.
Cardiovascular events: Although these agents are typically well tolerated, results of a recent study suggest that they may be associated with an increased risk, summarized in the Advanced section. Compensatory sympathetic nervous system responses such as renin release and tachycardia are significant in the short term. However, in many cases these reflex responses subside, leaving a vasodilatory effect that predominates in the long term.
Compensatory sympathetic nervous system responses such as renin release and tachycardia are significant in the short term. However, in many cases these reflex responses subside, leaving a vasodilatory effect that predominates in the long term. Tamsulosin was developed to selectively target α1A receptors, which are found in the bladder sphincter and not in vascular smooth muscle. Therefore by antagonizing these α1A receptors selectively, it is believed that tamsulosin will be less likely to cause orthostatic hypotension and therefore less likely to cause dizziness and falls.
Tamsulosin was developed to selectively target α1A receptors, which are found in the bladder sphincter and not in vascular smooth muscle. Therefore by antagonizing these α1A receptors selectively, it is believed that tamsulosin will be less likely to cause orthostatic hypotension and therefore less likely to cause dizziness and falls. The use of α antagonists in hypertension was dealt a severe blow after treatment in the doxazosin arm of the landmark ALLHAT study had to be halted prematurely after observations of a significantly increased incidence of congestive heart failure, angina, and stroke in subjects treated with this α antagonist.
The use of α antagonists in hypertension was dealt a severe blow after treatment in the doxazosin arm of the landmark ALLHAT study had to be halted prematurely after observations of a significantly increased incidence of congestive heart failure, angina, and stroke in subjects treated with this α antagonist.Tamsulosin versus Placebo for Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy
 A 2002 Cochrane review (14 studies, N = 4122 participants) assessed tamsulosin for treatment of BPH. Tamsulosin improved symptoms and peak urine flow relative to placebo and was as effective as nonselective α antagonists. Men receiving a low dose of tamsulosin (0.2 mg) were less likely to discontinue treatment compared with men receiving terazosin. The adverse effects of terazosin increased markedly with increasing dose, compared with placebo. The most common adverse effects associated with tamsulosin were dizziness, rhinitis, and abnormal ejaculation.
A 2002 Cochrane review (14 studies, N = 4122 participants) assessed tamsulosin for treatment of BPH. Tamsulosin improved symptoms and peak urine flow relative to placebo and was as effective as nonselective α antagonists. Men receiving a low dose of tamsulosin (0.2 mg) were less likely to discontinue treatment compared with men receiving terazosin. The adverse effects of terazosin increased markedly with increasing dose, compared with placebo. The most common adverse effects associated with tamsulosin were dizziness, rhinitis, and abnormal ejaculation.Terazosin versus Other α-Blockers for Treatment of Benign Prostatic Obstruction
 A 2000 Cochrane review (17 studies, N = 5151 participants) assessed terazosin versus placebo (10 trials), α-blockers (seven trials), or the 5α-reductase inhibitor finasteride (one trial) for benign prostatic obstruction. Terazosin improved symptom scores and urine flow rates more than placebo or finasteride and similarly to other α antagonists. The proportion of men discontinuing treatment was higher than the proportion of men receiving other α antagonists and was comparable to what was seen with placebo and finasteride. Adverse effects occurring more often than with placebo included dizziness, asthenia, headache, and postural hypotension.
A 2000 Cochrane review (17 studies, N = 5151 participants) assessed terazosin versus placebo (10 trials), α-blockers (seven trials), or the 5α-reductase inhibitor finasteride (one trial) for benign prostatic obstruction. Terazosin improved symptom scores and urine flow rates more than placebo or finasteride and similarly to other α antagonists. The proportion of men discontinuing treatment was higher than the proportion of men receiving other α antagonists and was comparable to what was seen with placebo and finasteride. Adverse effects occurring more often than with placebo included dizziness, asthenia, headache, and postural hypotension. Phenoxybenzamine is an irreversible antagonist of α1 receptors, whereas other α1 antagonists are reversible.
Phenoxybenzamine is an irreversible antagonist of α1 receptors, whereas other α1 antagonists are reversible. Phentolamine antagonizes both α1 and α2 receptors. Through antagonism of presynaptic α2 receptors, it increases presynaptic noradrenaline release, which in turn stimulates the heart.
Phentolamine antagonizes both α1 and α2 receptors. Through antagonism of presynaptic α2 receptors, it increases presynaptic noradrenaline release, which in turn stimulates the heart. Yohimbine is an α2 antagonist with limited antagonism of α1 receptors. It is not widely used, but as with phentolamine, it can promote norepinephrine release and can be used in patients with orthostatic hypotension. It was also once used to treat erectile dysfunction, although it has been effectively replaced by the phosphodiesterase inhibitors (e.g., sildenafil).
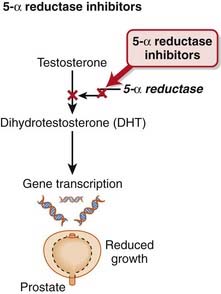
Yohimbine is an α2 antagonist with limited antagonism of α1 receptors. It is not widely used, but as with phentolamine, it can promote norepinephrine release and can be used in patients with orthostatic hypotension. It was also once used to treat erectile dysfunction, although it has been effectively replaced by the phosphodiesterase inhibitors (e.g., sildenafil). The 5α-reductase enzyme is the last step in the synthesis of DHT, the active form of testosterone (Figure 25-7).
The 5α-reductase enzyme is the last step in the synthesis of DHT, the active form of testosterone (Figure 25-7). Prostate cells depend on stimulation by DHT for their growth. Reducing levels of DHT will therefore slow growth of the prostate.
Prostate cells depend on stimulation by DHT for their growth. Reducing levels of DHT will therefore slow growth of the prostate. Selective or nonselective blockade of this enzyme results in decreased formation of DHT, inhibiting the growth-stimulating effects of this androgen.
Selective or nonselective blockade of this enzyme results in decreased formation of DHT, inhibiting the growth-stimulating effects of this androgen. No drug interactions of clinical significance have been detected with finasteride. Dutasteride is metabolized by CYP3A4; thus the potential for drug interactions with inhibitors or inducers of this isozyme does exist.
No drug interactions of clinical significance have been detected with finasteride. Dutasteride is metabolized by CYP3A4; thus the potential for drug interactions with inhibitors or inducers of this isozyme does exist. Pregnancy: Women of childbearing age should not use 5α-reductase inhibitors. They are strictly contraindicated in pregnancy. Testosterone is essential for development of genitalia in males; therefore these agents can lead to abnormal development. Pregnant women are advised not only to avoid taking the medication but also to avoid even handling the pills.
Pregnancy: Women of childbearing age should not use 5α-reductase inhibitors. They are strictly contraindicated in pregnancy. Testosterone is essential for development of genitalia in males; therefore these agents can lead to abnormal development. Pregnant women are advised not only to avoid taking the medication but also to avoid even handling the pills. Sexual dysfunction: Decreased libido, ejaculation disorders, and erectile dysfunction are caused by the antiandrogenic effects.
Sexual dysfunction: Decreased libido, ejaculation disorders, and erectile dysfunction are caused by the antiandrogenic effects.Finasteride versus Placebo for Prevention of Prostate Cancer
 A 2008 Cochrane review (nine trials, N = 34,410 males) examined the effectiveness and harms of 5α-reductase inhibitors in preventing prostate cancer. Finasteride reduced the risk of prostate cancer by 2.9% (incidence of 6.3% in finasteride versus 9.2% in placebo). Impaired erectile function or endocrine effects were more common with finasteride than with placebo. However, the risk of high-grade disease may be increased with finasteride therapy. The authors recommended that future studies examine the impact of 5α-reductase inhibitors on mortality and also further examine the risk associated with development of high-grade cancers.
A 2008 Cochrane review (nine trials, N = 34,410 males) examined the effectiveness and harms of 5α-reductase inhibitors in preventing prostate cancer. Finasteride reduced the risk of prostate cancer by 2.9% (incidence of 6.3% in finasteride versus 9.2% in placebo). Impaired erectile function or endocrine effects were more common with finasteride than with placebo. However, the risk of high-grade disease may be increased with finasteride therapy. The authors recommended that future studies examine the impact of 5α-reductase inhibitors on mortality and also further examine the risk associated with development of high-grade cancers. Because of their lowering effects on prostate serum antigen (PSA), there is concern that 5α-reductase inhibitors may mask elevations in PSA associated with a malignancy of the prostate. This could lead to a delay in the diagnosis of prostate cancer because of false-negative screening test results.
Because of their lowering effects on prostate serum antigen (PSA), there is concern that 5α-reductase inhibitors may mask elevations in PSA associated with a malignancy of the prostate. This could lead to a delay in the diagnosis of prostate cancer because of false-negative screening test results. The 5α-reductase inhibitors have not performed well in comparative trials with α antagonists for treatment of BPH. This is thought to result from, at least in part, the fact that the beneficial effects of 5α-reductase inhibitors are more gradual, whereas symptomatic improvement with α antagonists occurs rapidly.
The 5α-reductase inhibitors have not performed well in comparative trials with α antagonists for treatment of BPH. This is thought to result from, at least in part, the fact that the beneficial effects of 5α-reductase inhibitors are more gradual, whereas symptomatic improvement with α antagonists occurs rapidly. As a means of overcoming the delayed effects of 5α-reductase inhibitors, consideration has been given to combining α antagonists with these agents. The Medical Therapy of Prostatic Symptoms (MTOPS) trial found that the combination of doxazosin and finasteride performed better than either agent alone in a variety of key clinical indicators of BPH progression, over the course of 4.5 years.
As a means of overcoming the delayed effects of 5α-reductase inhibitors, consideration has been given to combining α antagonists with these agents. The Medical Therapy of Prostatic Symptoms (MTOPS) trial found that the combination of doxazosin and finasteride performed better than either agent alone in a variety of key clinical indicators of BPH progression, over the course of 4.5 years.






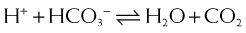
















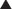



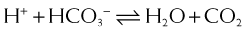



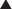
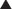
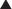







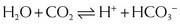 and that decreased H+ will drive the equation to the right and cause increased HCO3−.
and that decreased H+ will drive the equation to the right and cause increased HCO3−.