Intermittent noninvasive blood pressure monitoring
Methods of obtaining blood pressure
Palpation
Oscillometry
Oscillometry has become the most common method to measure arterial BP in the operating room.
Oscillometry operation and function
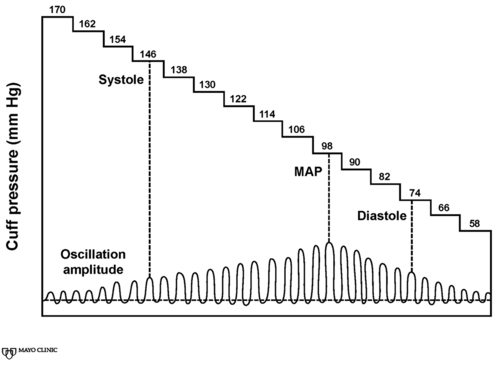
Most intermittent noninvasive BP monitors use oscillometry to measure BP. In most situations, a BP cuff is applied above the patient’s elbow of either the left or right upper extremity. The cycle begins with the cuff inflating to a pressure above the measurable arterial systolic BP. The cuff is then deflated slowly in a stepwise or linear manner until oscillations (arterial pressure pulsations) begin to be detected. The oscillations initially increase to a maximum and then decrease to an immeasurable level. After the final oscillation is detected, the cuff quickly bleeds out the remaining air. The point of maximum amplitude of the oscillations corresponds with the mean arterial pressure (Figure 17-1). The device then calculates the systolic and diastolic BP by an empirically derived algorithm; because the algorithms are proprietary, the systolic and diastolic BP measurements may vary from one device to another, depending on the manufacturer’s algorithm. In contrast, direct arterial BP monitoring via arterial catheter measures both the systolic and diastolic pressures and calculates the mean.