Physiologic determinants of cardiac output
< ?xml:namespace prefix = "mml" />
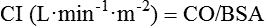
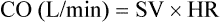
Stroke volume
Preload
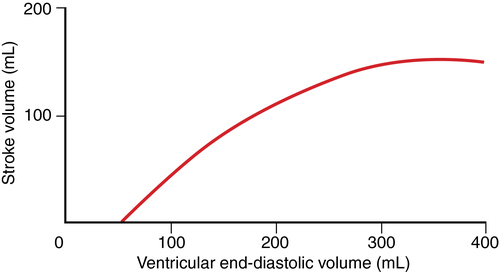
Preload is directly proportional to end-diastolic myocardial fiber length, often represented as end-diastolic volume (EDV, with a normal value of ∼120 mL). During normal cardiac muscle contraction, the sarcomere length is relatively short, but if EDV increases, the length of the sarcomere increases, and during subsequent contractions, more force is generated, the maximum rate of pressure development (dP/dt) increases, and SV increases proportionately (Figure 34-1).
Contractility
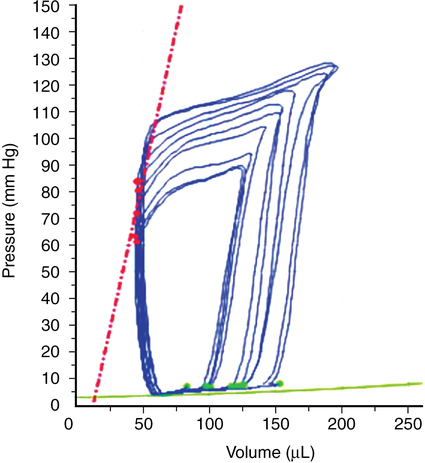
Contractility refers to the intrinsic ability of the myocardium to generate force at given end-diastolic fiber length and is closely related to the availability of intracellular calcium. Contractility is relatively easy to understand conceptually but difficult to define; measurements of cardiac performance include the dP/dt (Figure 34-2), isolated papillary muscle shortening, and the work generated by isolated or whole-heart preparations, but these definitions are not clinically useful.