Inhalation anesthetic agents
Uptake
The uptake of an anesthetic agent from the lung into the bloodstream is dependent on three main factors (excluding the concentration and second-gas effects) (Box 64-1). The first is the alveolar–mixed venous partial pressure difference P(A − ![]() ). The next is the solubility of the anesthetic agent in the blood, defined as the blood-gas partition coefficient (λ), and the last is cardiac output (CO). Using these factors, a simple calculation can be used to help determine the uptake of any given inhaled anesthetic agent. From this equation, it is apparent that, if any of the three factors is increased, the result will be a larger uptake of the anesthetic agent:
). The next is the solubility of the anesthetic agent in the blood, defined as the blood-gas partition coefficient (λ), and the last is cardiac output (CO). Using these factors, a simple calculation can be used to help determine the uptake of any given inhaled anesthetic agent. From this equation, it is apparent that, if any of the three factors is increased, the result will be a larger uptake of the anesthetic agent: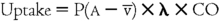
Blood-gas partition coefficient
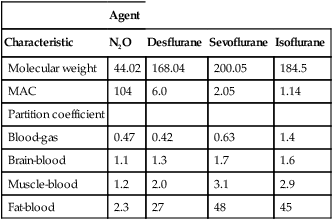
The λ describes the relative solubility of an anesthetic agent in blood, compared with its solubility in a gas (Table 64-1). Simply put, it is the concentration of anesthetic agent in the blood divided by the concentration in gas when the two phases are in equilibrium with one another. Soluble anesthetic agents, or ones that have a high λ, have higher concentrations in the blood phase than in the gas phase. Therefore, for a soluble anesthetic agent to exert a partial pressure in the blood phase equal to that of the gas phase, a relatively large number of molecules must be absorbed into the blood, translating into a slower rate of rise of the PA.
Table 64-1
Pharmacologic Characteristics of Inhalation Anesthetic Agents
| Agent | ||||
| Characteristic | N2O | Desflurane | Sevoflurane | Isoflurane |
| Molecular weight | 44.02 | 168.04 | 200.05 | 184.5 |
| MAC | 104 | 6.0 | 2.05 | 1.14 |
| Partition coefficient | ||||
| Blood-gas | 0.47 | 0.42 | 0.63 | 1.4 |
| Brain-blood | 1.1 | 1.3 | 1.7 | 1.6 |
| Muscle-blood | 1.2 | 2.0 | 3.1 | 2.9 |
| Fat-blood | 2.3 | 27 | 48 | 45 |
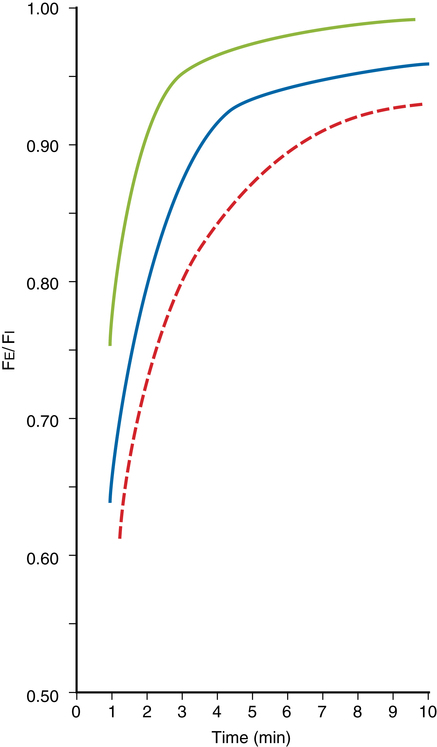
Concentration effect and second-gas effect
When anesthetic agents are combined, two phenomena—known as the concentration effect and second-gas effect—occur. When N2O is delivered in combination with other gases, the higher the inspired N2O concentration is, the faster the alveolar concentrations of N2O and the other gases will approach their respective inspired concentrations (PI concentration effect) (Figure 64-1). For example, patients receiving a PI of 80% N2O will experience a more rapid increase in their PA/PI ratio, as compared with patients receiving 60% N2O. As pulmonary capillary blood removes N2O from the alveoli, the gases in the anatomic dead space (e.g., bronchi) will be entrained into the alveoli, which results in an even faster rise in the alveolar concentration of the agent (second-gas effect).