Dexmedetomidine
Dexmedetomidine—an intravenously administered α2-agonist with sedative, analgesic, sympatholytic, and anxiolytic properties—is relatively unique in its ability to preserve respiratory drive and airway reflexes. Dexmedetomidine has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for use in two situations: (1) as a short-term (<24 h) infusion in intubated and mechanically ventilated adults in the intensive care unit and (2) in nonintubated adults before or during operations or other procedures requiring sedation. Many off-label uses have also been reported (Box 86-1).
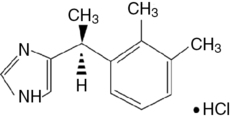
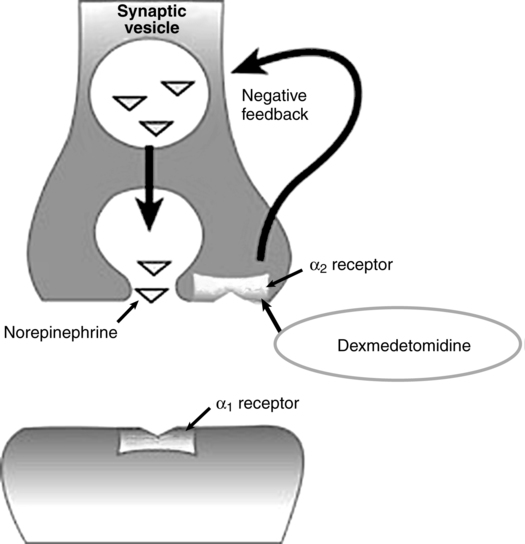
A water-soluble imidazole compound, dexmedetomidine is the pharmacologically active dextroisomer (S-enantiomer) of medetomidine (Figure 86-1). This highly selective α2-agonist has an eight times greater affinity for the α2-receptor than does clonidine and has α2:α1 activity of 1620:1. Presynaptic α2-adrenoceptor activation, primarily in the spinal cord, inhibits release of norepinephrine, terminating the propagation of pain signals. Postsynaptic α2-adrenoceptor activation in the central nervous system, primarily the locus coeruleus, both inhibits sympathetic activity and modulates vigilance (Figure 86-2). Combined, these effects produce analgesia, sedation, and anxiolysis and, similar to clonidine, may decrease blood pressure and heart rate.