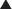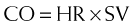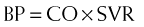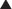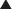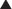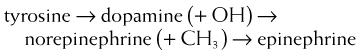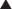Chapter 11 Cardiology
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors (ACEIs)
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
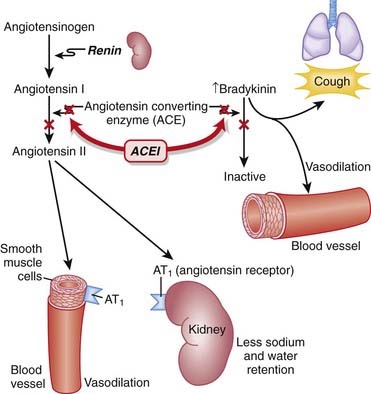
 Through inhibition of ACE with an ACEI, the following effects occur:
Through inhibition of ACE with an ACEI, the following effects occur:
 Net result: Because angiotensin II levels are lower and bradykinin levels are higher, there is more vasodilation; SVR (systemic vascular resistance) and afterload are lowered. Because aldosterone levels are lower, less Na and water are reabsorbed in the kidney; therefore preload is reduced (Figure 11-1).
Net result: Because angiotensin II levels are lower and bradykinin levels are higher, there is more vasodilation; SVR (systemic vascular resistance) and afterload are lowered. Because aldosterone levels are lower, less Na and water are reabsorbed in the kidney; therefore preload is reduced (Figure 11-1).Pharmacokinetics
Contraindications
Side Effects
 Dry cough: Attributed to increased bradykinin levels. Can be persistent enough to affect compliance and may lead to discontinuation.
Dry cough: Attributed to increased bradykinin levels. Can be persistent enough to affect compliance and may lead to discontinuation. Hyperkalemia: Particularly in combination with K+-sparing diuretics. Hyperkalemia occurs via the reduction in aldosterone but is usually clinically significant only with the addition of oral K+ or in patients with renal dysfunction.
Hyperkalemia: Particularly in combination with K+-sparing diuretics. Hyperkalemia occurs via the reduction in aldosterone but is usually clinically significant only with the addition of oral K+ or in patients with renal dysfunction. Hypotension: Caused by vasodilation from lower levels of angiotensin II. Patients with ventricular dysfunction (low ejection fraction) are at greater risk.
Hypotension: Caused by vasodilation from lower levels of angiotensin II. Patients with ventricular dysfunction (low ejection fraction) are at greater risk. Renal dysfunction: Angiotensin II plays an important role in maintaining glomerular filtration rate (GFR) by constricting the efferent (outgoing) arteriole of the glomerulus. This is particularly important when the blood flow to the kidneys has been compromised. ACEIs cause vasodilation of the efferent arteriole. This decreases the glomerular pressure and reduces GFR. Volume depletion amplifies this effect.
Renal dysfunction: Angiotensin II plays an important role in maintaining glomerular filtration rate (GFR) by constricting the efferent (outgoing) arteriole of the glomerulus. This is particularly important when the blood flow to the kidneys has been compromised. ACEIs cause vasodilation of the efferent arteriole. This decreases the glomerular pressure and reduces GFR. Volume depletion amplifies this effect. Angioedema: A rare but serious adverse effect, often attributed to the increased bradykinin levels, although a definitive mechanism has not been established. Angioedema is edema caused by pathologically leaky blood vessels. It can cause swollen lips or tongue, and death can also result from airway obstruction.
Angioedema: A rare but serious adverse effect, often attributed to the increased bradykinin levels, although a definitive mechanism has not been established. Angioedema is edema caused by pathologically leaky blood vessels. It can cause swollen lips or tongue, and death can also result from airway obstruction.Important Notes
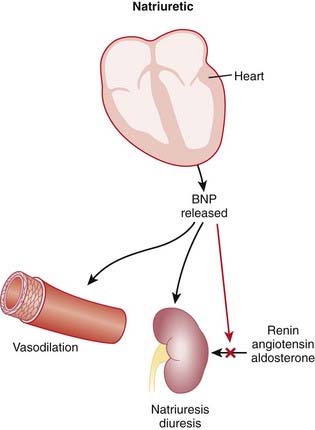
 The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) plays an important role in the body’s compensation for a failing heart. Activation of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) leads to the release of renin, which in turn increases vascular tone and sodium and water retention.
The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) plays an important role in the body’s compensation for a failing heart. Activation of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) leads to the release of renin, which in turn increases vascular tone and sodium and water retention. ACEIs might be of particular use in the management of HTN in the diabetic patient, as they may delay the development of diabetic nephropathy. This is primarily because of a reduction in intraglomerular pressure, through relaxation of the efferent arteriole and the overall reduction in systemic blood pressure (BP).
ACEIs might be of particular use in the management of HTN in the diabetic patient, as they may delay the development of diabetic nephropathy. This is primarily because of a reduction in intraglomerular pressure, through relaxation of the efferent arteriole and the overall reduction in systemic blood pressure (BP).Advanced
 In addition to the beneficial effects of RAS inhibitors in diabetic nephropathy, there is emerging evidence that RAS inhibitors may reduce the incidence of new-onset diabetes. Potential mechanisms for this effect include improvements in blood flow that improve the delivery of insulin and glucose to skeletal muscle, as well as effects on glucose transport and insulin signaling. If this preventative effect of RAS inhibition in diabetes becomes established, it could change the way these agents are used.
In addition to the beneficial effects of RAS inhibitors in diabetic nephropathy, there is emerging evidence that RAS inhibitors may reduce the incidence of new-onset diabetes. Potential mechanisms for this effect include improvements in blood flow that improve the delivery of insulin and glucose to skeletal muscle, as well as effects on glucose transport and insulin signaling. If this preventative effect of RAS inhibition in diabetes becomes established, it could change the way these agents are used. ONTARGET (Ongoing Telmisartan Alone and in Combination with Ramipril Global Endpoint Trial) was a large (approximately 8500 patients per arm), long-term (median follow-up of 56 months) study comparing an angiotensin-receptor blocker (ARB), an ACEI, and a combination of the two in patients with vascular disease or high-risk diabetes. The study found that the combination of ARB and ACEI failed to demonstrate benefit versus either agent alone, with an increased incidence of adverse events in this population.
ONTARGET (Ongoing Telmisartan Alone and in Combination with Ramipril Global Endpoint Trial) was a large (approximately 8500 patients per arm), long-term (median follow-up of 56 months) study comparing an angiotensin-receptor blocker (ARB), an ACEI, and a combination of the two in patients with vascular disease or high-risk diabetes. The study found that the combination of ARB and ACEI failed to demonstrate benefit versus either agent alone, with an increased incidence of adverse events in this population.Evidence
Hypertension
 A 2009 Cochrane review (24 trials, N = 58,040 participants) compared benefits and harms of first-line antihypertensives with those of placebo or no treatment over a minimum of 1 year in patients with hypertension. ACEIs (three trials) reduced mortality (relative risk [RR] 0.83), stroke (RR 0.65), coronary heart disease (RR 0.81), and cardiovascular events (RR 0.76).
A 2009 Cochrane review (24 trials, N = 58,040 participants) compared benefits and harms of first-line antihypertensives with those of placebo or no treatment over a minimum of 1 year in patients with hypertension. ACEIs (three trials) reduced mortality (relative risk [RR] 0.83), stroke (RR 0.65), coronary heart disease (RR 0.81), and cardiovascular events (RR 0.76).FYI Notes
 Brady means slow (e.g., bradycardia). Bradykinin is so named because it causes slow contractions of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
Brady means slow (e.g., bradycardia). Bradykinin is so named because it causes slow contractions of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs)
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
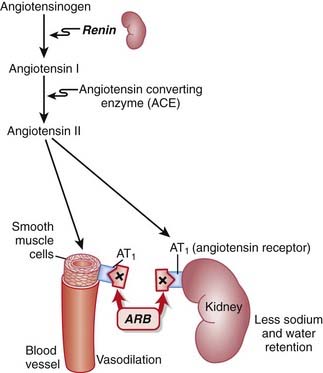
 ARBs are antagonists of the angiotensin-1 (AT1) receptor. Therefore they block the actions of angiotensin II.
ARBs are antagonists of the angiotensin-1 (AT1) receptor. Therefore they block the actions of angiotensin II. Angiotensin II is a vasoactive hormone that induces vasoconstriction and stimulates the secretion of aldosterone by the adrenal cortex, which results in sodium and water retention.
Angiotensin II is a vasoactive hormone that induces vasoconstriction and stimulates the secretion of aldosterone by the adrenal cortex, which results in sodium and water retention. Blocking AT1 results in vasodilation, natriuresis (renal loss of sodium), and diuresis (renal loss of water).
Blocking AT1 results in vasodilation, natriuresis (renal loss of sodium), and diuresis (renal loss of water). ACEIs block the degradation of bradykinins. ARBs have no effect on bradykinin levels. Because bradykinins are vasodilators, ARBs might not produce as much vasodilation as ACEIs.
ACEIs block the degradation of bradykinins. ARBs have no effect on bradykinin levels. Because bradykinins are vasodilators, ARBs might not produce as much vasodilation as ACEIs.Pharmacokinetics
Side Effects
Important Notes
 Perhaps because of the lack of increased bradykinin levels, ARBs are not typically associated with the side effect of cough, which can be a significant limitation to the use of ACEIs.
Perhaps because of the lack of increased bradykinin levels, ARBs are not typically associated with the side effect of cough, which can be a significant limitation to the use of ACEIs.Advanced
 In addition to the beneficial effects of RAS inhibitors in diabetic nephropathy, there is emerging evidence that RAS inhibitors may reduce the incidence of new-onset diabetes. Potential mechanisms for this effect include improvements in blood flow that improve the delivery of insulin and glucose to skeletal muscle, as well as effects on glucose transport and insulin signaling. If this preventative effect of RAS inhibition in diabetes becomes established, it could change the way these agents are used.
In addition to the beneficial effects of RAS inhibitors in diabetic nephropathy, there is emerging evidence that RAS inhibitors may reduce the incidence of new-onset diabetes. Potential mechanisms for this effect include improvements in blood flow that improve the delivery of insulin and glucose to skeletal muscle, as well as effects on glucose transport and insulin signaling. If this preventative effect of RAS inhibition in diabetes becomes established, it could change the way these agents are used. ACEIs reduce the effect of both AT1 and AT2 receptors by lowering levels of angiotensin II; only AT1 receptors are inhibited by ARBs. Chronic stimulation of the AT2 receptor may be beneficial in providing neuroprotection in older patients with HTN and thus could mean that ARBs have a potential advantage in this patient subset.
ACEIs reduce the effect of both AT1 and AT2 receptors by lowering levels of angiotensin II; only AT1 receptors are inhibited by ARBs. Chronic stimulation of the AT2 receptor may be beneficial in providing neuroprotection in older patients with HTN and thus could mean that ARBs have a potential advantage in this patient subset. ONTARGET (Ongoing Telmisartan Alone and in Combination with Ramipril Global Endpoint Trial) was a large (approximately 8500 patients per arm), long-term (median follow-up of 56 months) study comparing an ARB, an ACEI, and a combination of the two in patients with vascular disease or high-risk diabetes. The study found that the combination of ARB and ACEI failed to demonstrate benefit versus either agent alone, with an increased incidence of adverse events in this population.
ONTARGET (Ongoing Telmisartan Alone and in Combination with Ramipril Global Endpoint Trial) was a large (approximately 8500 patients per arm), long-term (median follow-up of 56 months) study comparing an ARB, an ACEI, and a combination of the two in patients with vascular disease or high-risk diabetes. The study found that the combination of ARB and ACEI failed to demonstrate benefit versus either agent alone, with an increased incidence of adverse events in this population.Direct Renin Inhibitors
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
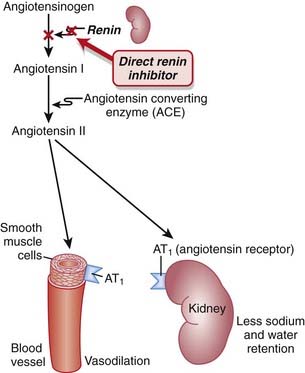
 Renin is an enzyme released from the kidneys that converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I. It is considered to be the rate-limiting step in the eventual formation of angiotensin II.
Renin is an enzyme released from the kidneys that converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I. It is considered to be the rate-limiting step in the eventual formation of angiotensin II. Renin and its inactive precursor, prorenin, are stored in the juxtaglomerular cells of the kidney. Renin is released in response to three different stimuli:
Renin and its inactive precursor, prorenin, are stored in the juxtaglomerular cells of the kidney. Renin is released in response to three different stimuli:
 Other agents that target the RAS, such as the ACEIs and ARBs, elicit a compensatory increase in plasma renin activity, resulting in increased binding of angiotensin II to AT1 receptors and other AT receptors.
Other agents that target the RAS, such as the ACEIs and ARBs, elicit a compensatory increase in plasma renin activity, resulting in increased binding of angiotensin II to AT1 receptors and other AT receptors.Evidence
Blood-Pressure Lowering Efficacy versus Placebo
 A 2008 Cochrane review (six trials, 3694 participants) compared the blood-pressure–lowering efficacy of renin inhibitors versus placebo in primary HTN. The authors found that aliskiren elicits a dose-dependent reduction in both systolic and diastolic pressure similar to that seen with ACEIs or ARBs. In the included trials, aliskiren did not increase withdrawals due to adverse events versus placebo.
A 2008 Cochrane review (six trials, 3694 participants) compared the blood-pressure–lowering efficacy of renin inhibitors versus placebo in primary HTN. The authors found that aliskiren elicits a dose-dependent reduction in both systolic and diastolic pressure similar to that seen with ACEIs or ARBs. In the included trials, aliskiren did not increase withdrawals due to adverse events versus placebo.FYI Notes
 Renin was first identified in 1898, when it was extracted from kidneys and discovered to have pressor properties. It would be another 40 years before it was determined that renin was an enzyme that catalyzed the formation of a pressor substance (angiotensin II), rather than being the pressor itself.
Renin was first identified in 1898, when it was extracted from kidneys and discovered to have pressor properties. It would be another 40 years before it was determined that renin was an enzyme that catalyzed the formation of a pressor substance (angiotensin II), rather than being the pressor itself. Although renin inhibitors were considered to be the most obvious target for inhibition of the RAS, it took several decades to develop the first direct renin inhibitor. Two main hurdles were finding an agent with sufficient bioavailability and an agent with high affinity for the active site of the renin enzyme.
Although renin inhibitors were considered to be the most obvious target for inhibition of the RAS, it took several decades to develop the first direct renin inhibitor. Two main hurdles were finding an agent with sufficient bioavailability and an agent with high affinity for the active site of the renin enzyme.Sodium Channel Blockers (Class I Antiarrhythmics)
Description
Na channel blockers are Vaughan Williams class I antiarrhythmics. There are three subclasses: Ia, Ib, and Ic. The use of Na channel blockers as local anesthetics is discussed in the discussion of local anesthetics in Chapter 21.
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
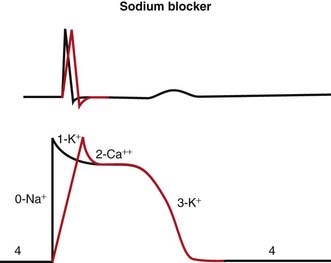
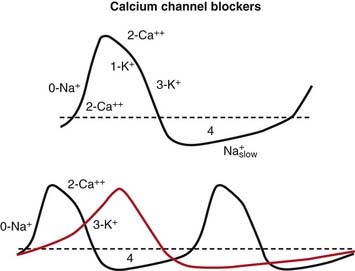
 Na channels are blocked, so Na ion movement during phase 0 of the action potential is inhibited. The result is a “slow” phase 0, which results in a wider (and slower) QRS wave on the electrocardiogram (ECG). The net result is slower conduction (Figure 11-4).
Na channels are blocked, so Na ion movement during phase 0 of the action potential is inhibited. The result is a “slow” phase 0, which results in a wider (and slower) QRS wave on the electrocardiogram (ECG). The net result is slower conduction (Figure 11-4). Phase 3 can be longer or shorter, depending on the subclass (a, b, or c). This is omitted in the diagram for simplicity.
Phase 3 can be longer or shorter, depending on the subclass (a, b, or c). This is omitted in the diagram for simplicity. Changing the duration of the action potential (not shown in diagram) influences the QT interval (distance from the QRS to the T wave). This distance can be thought of as the refractory period of the ECG. Therefore changing the action potential durations will change the refractory times of atrial, Purkinje or ventricular tissues.
Changing the duration of the action potential (not shown in diagram) influences the QT interval (distance from the QRS to the T wave). This distance can be thought of as the refractory period of the ECG. Therefore changing the action potential durations will change the refractory times of atrial, Purkinje or ventricular tissues. Because abnormal electrical circuits require a delicate balance between conduction speed and refractory times, changing these parameters will sometimes terminate dysrhythmias or create new ones.
Because abnormal electrical circuits require a delicate balance between conduction speed and refractory times, changing these parameters will sometimes terminate dysrhythmias or create new ones.Pharmacokinetics
Side Effects
 Proarrhythmic: As with all antiarrhythmics, changing the delicate balance of conduction speed and refractory times might provoke another area of the conducting system into developing a dysrhythmia.
Proarrhythmic: As with all antiarrhythmics, changing the delicate balance of conduction speed and refractory times might provoke another area of the conducting system into developing a dysrhythmia.Evidence
 Atrial fibrillation and prevention of recurrence: A Cochrane review in 2007 (45 studies, 12,559 patients) evaluated the efficacy and safety of multiple different antiarrhythmics in patients who had previously experienced atrial fibrillation (a very common arrhythmia). Class Ia antiarrhythmics were associated with increased mortality compared with controls (odds ratio [OR] 2.39; number needed to harm [NNH] 109). Class Ia and Ic were associated with reduced occurrences of atrial fibrillation (OR 0.19 to 0.6). There were many withdrawals from treatment because of side effects for all antiarrhythmics (NNH 17 to 36).
Atrial fibrillation and prevention of recurrence: A Cochrane review in 2007 (45 studies, 12,559 patients) evaluated the efficacy and safety of multiple different antiarrhythmics in patients who had previously experienced atrial fibrillation (a very common arrhythmia). Class Ia antiarrhythmics were associated with increased mortality compared with controls (odds ratio [OR] 2.39; number needed to harm [NNH] 109). Class Ia and Ic were associated with reduced occurrences of atrial fibrillation (OR 0.19 to 0.6). There were many withdrawals from treatment because of side effects for all antiarrhythmics (NNH 17 to 36).β Antagonists (β-Blockers)
Prototype and Common Drugs
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
To understand β-blockers, you must understand the effects of the adrenergic system and which effects are mediated via β receptors. β-Blockers competitively antagonize the action of catecholamines at β receptors. There are many cardiac and noncardiac consequences of β-blockade. More details on the autonomic nervous system are described in Chapter 3.
Hypertension
 Cardiac output (CO) is therefore reduced, which leads to a reduction in BP. Recall:
Cardiac output (CO) is therefore reduced, which leads to a reduction in BP. Recall:
where SVR = systemic vascular resistance.
 In addition, β1 antagonism leads to a reduction in renin secretion, which in turn reduces production of angiotensin II, a hormone that induces vasoconstriction and, via aldosterone, sodium retention.
In addition, β1 antagonism leads to a reduction in renin secretion, which in turn reduces production of angiotensin II, a hormone that induces vasoconstriction and, via aldosterone, sodium retention.Tachycardia and Arrhythmia
The properties of β-blockers that make them antitachycardics include the following:
 Catecholamine β1 stimulation results in an increase in the slow Na+ current (If) of the action potential phase 4 in the SA node. This results in a faster rising (and shorter) phase 4, a shorter time to the next heartbeat, and thus a faster HR. β-Blockers will oppose this action, slowing the SA pacemaker rate.
Catecholamine β1 stimulation results in an increase in the slow Na+ current (If) of the action potential phase 4 in the SA node. This results in a faster rising (and shorter) phase 4, a shorter time to the next heartbeat, and thus a faster HR. β-Blockers will oppose this action, slowing the SA pacemaker rate. Same mechanism as SA node: a decrease in the slow Na+ current (If) leaves the AV node in a refractory state longer.
Same mechanism as SA node: a decrease in the slow Na+ current (If) leaves the AV node in a refractory state longer. This mechanism is useful in making the AV node a protector of the ventricles. In situations (atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter) in which the AV node is bombarded by electrical signals from the atria, the depressed AV node can permit only a fraction of these signals to enter into the ventricular conducting system, controlling the ventricular rate.
This mechanism is useful in making the AV node a protector of the ventricles. In situations (atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter) in which the AV node is bombarded by electrical signals from the atria, the depressed AV node can permit only a fraction of these signals to enter into the ventricular conducting system, controlling the ventricular rate.Myocardial Ischemia and Infarction
Chronic Congestive Heart Failure
 Patients with a dysfunctional cardiovascular system have an inefficient system and thus require extra support; this support is in the form of increased levels of SNS activation, renin-angiotensin activity, endothelin activity, and many other compensatory mechanisms.
Patients with a dysfunctional cardiovascular system have an inefficient system and thus require extra support; this support is in the form of increased levels of SNS activation, renin-angiotensin activity, endothelin activity, and many other compensatory mechanisms.Pharmacokinetics
 Shorter half-lives (3 to 4 hours): propranolol, metoprolol (sustained-release forms with longer half-lives are available)
Shorter half-lives (3 to 4 hours): propranolol, metoprolol (sustained-release forms with longer half-lives are available)Contraindications
 Asthmatics should not use nonselective (β1, β2) β-blockers, as blocking β2 receptors may lead to bronchoconstriction. Stimulation of β2 receptors in the airways causes smooth muscle relaxation of the bronchioles and is the basis of bronchodilators that are β2 agonists.
Asthmatics should not use nonselective (β1, β2) β-blockers, as blocking β2 receptors may lead to bronchoconstriction. Stimulation of β2 receptors in the airways causes smooth muscle relaxation of the bronchioles and is the basis of bronchodilators that are β2 agonists.
 Second-degree heart block: It can be converted to third-degree heart block, resulting in very low HRs.
Second-degree heart block: It can be converted to third-degree heart block, resulting in very low HRs. Bradycardia: β-Blockers could make the already slow heart so slow that CO and BP fall below levels that are required by the body for adequate perfusion.
Bradycardia: β-Blockers could make the already slow heart so slow that CO and BP fall below levels that are required by the body for adequate perfusion. Acute heart failure: Note that chronic heart failure is an indication for β-blockers, and acute heart failure is a contraindication. In acute heart failure the patient is decompensated and probably being kept alive by the SNS being ramped up. Blocking the effects of the flight-or-fight response would further decompensate the patient and potentially kill him or her.
Acute heart failure: Note that chronic heart failure is an indication for β-blockers, and acute heart failure is a contraindication. In acute heart failure the patient is decompensated and probably being kept alive by the SNS being ramped up. Blocking the effects of the flight-or-fight response would further decompensate the patient and potentially kill him or her.Side Effects
 Raynaud’s phenomenon: Cold extremities (fingers in particular) may result from antagonism of β2 receptors, leading to vasoconstriction in the periphery.
Raynaud’s phenomenon: Cold extremities (fingers in particular) may result from antagonism of β2 receptors, leading to vasoconstriction in the periphery. Impotence: Erectile function is dependent on changes in blood flow and vasodilation in the corpora cavernosa, and these mechanisms can be blocked by β-blockers.
Impotence: Erectile function is dependent on changes in blood flow and vasodilation in the corpora cavernosa, and these mechanisms can be blocked by β-blockers. Hypoglycemia: Nonselective β-blockers may interfere with recovery from hypoglycemia in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes, as they antagonize the ability of catecholamines to promote glycogenolysis and mobilize glucose. Also, in diabetics, the β-blockade prevents symptoms caused by hypoglycemia and so masks early mild hypoglycemia, which can then deteriorate.
Hypoglycemia: Nonselective β-blockers may interfere with recovery from hypoglycemia in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes, as they antagonize the ability of catecholamines to promote glycogenolysis and mobilize glucose. Also, in diabetics, the β-blockade prevents symptoms caused by hypoglycemia and so masks early mild hypoglycemia, which can then deteriorate.Important Notes
 β-blockers should not be discontinued abruptly, because of a rebound effect that might result in tachycardia and exacerbate the symptoms of coronary artery disease or might induce a hypertensive effect. The rebound appears to be an overactivity of the SNS, caused perhaps by receptor up-regulation.
β-blockers should not be discontinued abruptly, because of a rebound effect that might result in tachycardia and exacerbate the symptoms of coronary artery disease or might induce a hypertensive effect. The rebound appears to be an overactivity of the SNS, caused perhaps by receptor up-regulation. The use of β-blockers for HTN is generally avoided in elderly patients, whereas younger hypertensive patients tend to respond well to these agents.
The use of β-blockers for HTN is generally avoided in elderly patients, whereas younger hypertensive patients tend to respond well to these agents. Not only might β-blockers impair the response to hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes, but the negative chronotropic effects of these agents may mask the tachycardia that normally provides an important indicator of hypoglycemia to the diabetic. Despite these concerns, β-blockers have proven effective in the treatment of people with type 1 diabetes who have experienced an MI, and thus the decision whether to use them is one of risk versus benefit in this population.
Not only might β-blockers impair the response to hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes, but the negative chronotropic effects of these agents may mask the tachycardia that normally provides an important indicator of hypoglycemia to the diabetic. Despite these concerns, β-blockers have proven effective in the treatment of people with type 1 diabetes who have experienced an MI, and thus the decision whether to use them is one of risk versus benefit in this population.Evidence
After Myocardial Infarction
 Evidence for the role of β-blockers in secondary prevention after an MI comes from several trials and was summarized in a 1999 systematic review (82 trials, N = 54,234 patients). There was a 23% reduction in the odds of death in long-term trials but only a 4% reduction in short-term trials. The review found that the number needed to treat (NNT) to avoid a fatality over the course of 2 years is 42. The greatest amount of evidence available was for propranolol, timolol, and metoprolol.
Evidence for the role of β-blockers in secondary prevention after an MI comes from several trials and was summarized in a 1999 systematic review (82 trials, N = 54,234 patients). There was a 23% reduction in the odds of death in long-term trials but only a 4% reduction in short-term trials. The review found that the number needed to treat (NNT) to avoid a fatality over the course of 2 years is 42. The greatest amount of evidence available was for propranolol, timolol, and metoprolol.Hypertension and Associated Stroke and Coronary Artery Disease
 A Cochrane review in 2007 (13 studies, N = 91,561 patients) compared β-blockers with other agents for HTN. Atenolol was the β-blocker most frequently used. The authors found that β-blockers had only weak effects in reducing stroke and no effect on coronary heart disease versus placebo. There was also a trend toward worse outcomes when compared with calcium channel blockers (CCBs), RAS inhibitors, and thiazides, prompting the authors to suggest that β-blockers should not be considered as first-line agents for HTN.
A Cochrane review in 2007 (13 studies, N = 91,561 patients) compared β-blockers with other agents for HTN. Atenolol was the β-blocker most frequently used. The authors found that β-blockers had only weak effects in reducing stroke and no effect on coronary heart disease versus placebo. There was also a trend toward worse outcomes when compared with calcium channel blockers (CCBs), RAS inhibitors, and thiazides, prompting the authors to suggest that β-blockers should not be considered as first-line agents for HTN.Obstructive Airway Disease (Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
 A Cochrane review in 2002 (29 studies, N = 381 patients) examined the impact of single-dose or short-term selective β1-blockers in patients with mild to moderate obstructive airway disease. There were no differences in pulmonary flow measurements compared with placebo except for a small decrease in FEV1 after the first treatment—an effect that disappeared with subsequent doses.
A Cochrane review in 2002 (29 studies, N = 381 patients) examined the impact of single-dose or short-term selective β1-blockers in patients with mild to moderate obstructive airway disease. There were no differences in pulmonary flow measurements compared with placebo except for a small decrease in FEV1 after the first treatment—an effect that disappeared with subsequent doses.Potassium Channel Blockers (Class III Antiarrhythmics)
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 Blocking K channels in phase 3 of the action potential slows the efflux of K back out of the myocyte, which slows the rate at which the cell repolarizes and therefore lengthens the plateau phase of the action potential. This increases the refractory period of atrial, ventricular, and Purkinje cells. This also increases the QT interval on the ECG (Figure 11-5).
Blocking K channels in phase 3 of the action potential slows the efflux of K back out of the myocyte, which slows the rate at which the cell repolarizes and therefore lengthens the plateau phase of the action potential. This increases the refractory period of atrial, ventricular, and Purkinje cells. This also increases the QT interval on the ECG (Figure 11-5).Pharmacokinetics
 Drug interactions:
Drug interactions:
 Amiodarone and dronedarone are metabolized by and are inhibitors of CYP3A4; this is important because other drugs used in the control of dysrhythmias, including verapamil and diltiazem, are also metabolized by CYP3A4, and drug levels can be increased when drugs are coadministered.
Amiodarone and dronedarone are metabolized by and are inhibitors of CYP3A4; this is important because other drugs used in the control of dysrhythmias, including verapamil and diltiazem, are also metabolized by CYP3A4, and drug levels can be increased when drugs are coadministered.Side Effects
Evidence
 Atrial fibrillation (AF) and multiple outcomes: A Cochrane review in 2007 (45 studies, 12,559 patients) evaluated the efficacy and safety of multiple different antiarrhythmics in patients who had previously experienced atrial fibrillation (the most common arrhythmia).
Atrial fibrillation (AF) and multiple outcomes: A Cochrane review in 2007 (45 studies, 12,559 patients) evaluated the efficacy and safety of multiple different antiarrhythmics in patients who had previously experienced atrial fibrillation (the most common arrhythmia).
 Mortality: When compared with controls, amiodarone showed no significant difference in mortality. Compared with class I drugs, amiodarone showed a significant reduction in mortality (OR 0.39, NNT 17).
Mortality: When compared with controls, amiodarone showed no significant difference in mortality. Compared with class I drugs, amiodarone showed a significant reduction in mortality (OR 0.39, NNT 17).Calcium Channel Blockers
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
Hypertension
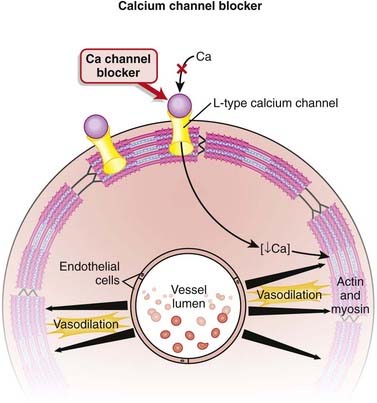
 Calcium channels are designated as L-, T-, P/Q-, N-, and R-type, depending on kinetics and receptor specificity. L means long duration, and T means transient.
Calcium channels are designated as L-, T-, P/Q-, N-, and R-type, depending on kinetics and receptor specificity. L means long duration, and T means transient. L-type calcium channels are located on the heart, skeletal muscle, neurons, vascular smooth muscle, and uterus.
L-type calcium channels are located on the heart, skeletal muscle, neurons, vascular smooth muscle, and uterus. All CCBs are antagonists of L-type calcium channels. By blocking the influx of calcium through L-type channels, these agents inhibit contraction of smooth muscle (Figure 11-6).
All CCBs are antagonists of L-type calcium channels. By blocking the influx of calcium through L-type channels, these agents inhibit contraction of smooth muscle (Figure 11-6). The dihydropyridine (DHP) CCBs have greater selectivity for the vasculature than either diltiazem or verapamil, the non-DHP CCBs.
The dihydropyridine (DHP) CCBs have greater selectivity for the vasculature than either diltiazem or verapamil, the non-DHP CCBs. DHPs have little effect on the recovery of the calcium channel and thus minimal effects on cardiac Ca channels involved with automaticity (HR), conduction speed, and refractory periods (important with regard to the AV node).
DHPs have little effect on the recovery of the calcium channel and thus minimal effects on cardiac Ca channels involved with automaticity (HR), conduction speed, and refractory periods (important with regard to the AV node).Tachycardia and Arrhythmia
The non-DHPs (but not the DPHs) are also class IV antiarrhythmics.
Blocking Ca+2 channels in phase 0 of the action potential lengthens the depolarizing current in SA and AV nodal cells. This results in more time before the next action potential. In the SA node, the result is a slower pacemaker. In the AV node, the result is a longer refractory period (Figure 11-7).
Pharmacokinetics
 Amlodipine has a slow onset and much longer half-life (40 hours) than nifedipine (4 hours). This slow onset helps to mitigate the reflex tachycardia commonly seen with these agents, particularly nifedipine.
Amlodipine has a slow onset and much longer half-life (40 hours) than nifedipine (4 hours). This slow onset helps to mitigate the reflex tachycardia commonly seen with these agents, particularly nifedipine.Contraindications
Nondihydropyridines
 Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome: In WPW the accessory pathway (bundle of Kent) is not blocked by Ca+2 channel blockers, but the AV node is. Therefore the use of Ca+2 channel blockers will promote conduction through the accessory pathway. Because the accessory pathway does not have a conduction delay as the AV node does, conduction through the accessory pathway can result in very high ventricular rates in the presence of atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter.
Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome: In WPW the accessory pathway (bundle of Kent) is not blocked by Ca+2 channel blockers, but the AV node is. Therefore the use of Ca+2 channel blockers will promote conduction through the accessory pathway. Because the accessory pathway does not have a conduction delay as the AV node does, conduction through the accessory pathway can result in very high ventricular rates in the presence of atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter.Important Notes
 Vasodilation results in lower BP, and low BP often induces a baroreceptor-mediated reflex tachycardia. An important clinical consequence of DHPs is that they can indirectly induce tachycardia, which can be very dangerous in conditions in which tachycardia is contraindicated (e.g., coronary artery disease).
Vasodilation results in lower BP, and low BP often induces a baroreceptor-mediated reflex tachycardia. An important clinical consequence of DHPs is that they can indirectly induce tachycardia, which can be very dangerous in conditions in which tachycardia is contraindicated (e.g., coronary artery disease).Evidence
As First-Line Agents in Hypertension
 A 2009 Cochrane review (24 trials, N = 58,040 participants) compared benefits and harms of first-line antihypertensives with those of placebo or no treatment over a minimum of 1 year. Only one randomized controlled trial (RCT) was found that included a CCB, and in this trial it reduced stroke (RR 0.58) but not coronary heart disease or mortality. Thiazides (19 trials) reduced mortality (RR 0.89), stroke (RR 0.63), and coronary heart disease (RR 0.84).
A 2009 Cochrane review (24 trials, N = 58,040 participants) compared benefits and harms of first-line antihypertensives with those of placebo or no treatment over a minimum of 1 year. Only one randomized controlled trial (RCT) was found that included a CCB, and in this trial it reduced stroke (RR 0.58) but not coronary heart disease or mortality. Thiazides (19 trials) reduced mortality (RR 0.89), stroke (RR 0.63), and coronary heart disease (RR 0.84).For Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
 A 2007 Cochrane review (16 studies, N = 3361 patients) examined whether DHP calcium antagonists alone or combined with magnesium sulfate (three studies) improved outcomes in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Overall, calcium antagonists reduced the risk of poor outcomes (death or disability), with an NNT of 19 (1 to 51). When separated by individual calcium antagonists, only oral nimodipine was statistically significant versus control. Calcium antagonists also reduced the risk of secondary ischemia.
A 2007 Cochrane review (16 studies, N = 3361 patients) examined whether DHP calcium antagonists alone or combined with magnesium sulfate (three studies) improved outcomes in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Overall, calcium antagonists reduced the risk of poor outcomes (death or disability), with an NNT of 19 (1 to 51). When separated by individual calcium antagonists, only oral nimodipine was statistically significant versus control. Calcium antagonists also reduced the risk of secondary ischemia.FYI Notes
 Patients have been known to take advantage of the interaction between felodipine and grapefruit juice to save themselves a few dollars on the drug cost. They will reduce their dose of felodipine by consuming grapefruit juice on a consistent basis. The bioflavonoids are found in the peel, however, so patients who grind their own juice may find they are not getting adequate drug levels if they do not include the peel.
Patients have been known to take advantage of the interaction between felodipine and grapefruit juice to save themselves a few dollars on the drug cost. They will reduce their dose of felodipine by consuming grapefruit juice on a consistent basis. The bioflavonoids are found in the peel, however, so patients who grind their own juice may find they are not getting adequate drug levels if they do not include the peel.Anticholinergics
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 Anticholinergics block the activity of acetylcholine (ACh) of the parasympathetic system at muscarinic receptors (M).
Anticholinergics block the activity of acetylcholine (ACh) of the parasympathetic system at muscarinic receptors (M). With respect to the cardiovascular system, this effect is most pronounced on the SA node and AV node, resulting in increased pacemaker rates of the SA node and sometimes increased conduction through the AV node. The primary result is a faster HR. The effect of AV node conduction is not clinically important unless a conduction block such as first-, second-, or third-degree AV block is present.
With respect to the cardiovascular system, this effect is most pronounced on the SA node and AV node, resulting in increased pacemaker rates of the SA node and sometimes increased conduction through the AV node. The primary result is a faster HR. The effect of AV node conduction is not clinically important unless a conduction block such as first-, second-, or third-degree AV block is present. Another (less clinically important) cardiovascular effect is reversal of vasodilation of some vascular beds, such as the mesentery (intestinal) vessels. ACh liberates NO from the endothelium, and atropine counteracts this.
Another (less clinically important) cardiovascular effect is reversal of vasodilation of some vascular beds, such as the mesentery (intestinal) vessels. ACh liberates NO from the endothelium, and atropine counteracts this.| Heart | Increased heart rate |
| Airways | Bronchodilation |
| Secretions | Reduced |
| Pupils | Dilated |
| Urinary function | Decreased |
| Gastrointestinal motility | Decreased |
| Central nervous system | Increased temperature, confusion |
Important Notes
FYI Notes
 One chemical used in a form of chemical warfare is an anticholinesterase. An anticholinesterase blocks cholinesterase, which is an enzyme that degrades ACh. The result is too much ACh, which mimics an overactive parasympathetic system and can even cause paralysis from overstimulation of the nicotinic receptor in the neuromuscular junction. Atropine is the antidote.
One chemical used in a form of chemical warfare is an anticholinesterase. An anticholinesterase blocks cholinesterase, which is an enzyme that degrades ACh. The result is too much ACh, which mimics an overactive parasympathetic system and can even cause paralysis from overstimulation of the nicotinic receptor in the neuromuscular junction. Atropine is the antidote. One class of anesthetic drug is a neuromuscular blocking reversal drug. It is an anticholinesterase and is used to increase the concentration of ACh in the neuromuscular junction. However, in addition to increased ACh in the neuromuscular junction, increased ACh at all other muscarinic receptors also occurs, leading to muscarinic side effects. Usual side effects of a normal dose include bradycardia and bronchorrhea (bronchial secretions). Antimuscarinic drugs including atropine and glycopyrrolate are used to minimize the side effects of these medications.
One class of anesthetic drug is a neuromuscular blocking reversal drug. It is an anticholinesterase and is used to increase the concentration of ACh in the neuromuscular junction. However, in addition to increased ACh in the neuromuscular junction, increased ACh at all other muscarinic receptors also occurs, leading to muscarinic side effects. Usual side effects of a normal dose include bradycardia and bronchorrhea (bronchial secretions). Antimuscarinic drugs including atropine and glycopyrrolate are used to minimize the side effects of these medications. A massive outpouring of parasympathetic activity (via the vagus nerve) caused by stress or fear is called a vasovagal attack. It results in bradycardia and hypotension and sometimes loss of consciousness.
A massive outpouring of parasympathetic activity (via the vagus nerve) caused by stress or fear is called a vasovagal attack. It results in bradycardia and hypotension and sometimes loss of consciousness.Adenosine
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 These ionic actions hyperpolarize the cell (i.e., make the inside of the cell more negative because there are fewer positive ions inside the cell) and render it refractory for a prolonged period (a few seconds or more).
These ionic actions hyperpolarize the cell (i.e., make the inside of the cell more negative because there are fewer positive ions inside the cell) and render it refractory for a prolonged period (a few seconds or more). Essentially, the AV node is completely turned off for a brief period of time, creating a third-degree heart block for a few seconds. Through this action, tachycardias that originate in the atria can be diagnosed more easily because all the QRSs are absent from the ECG for a few seconds.
Essentially, the AV node is completely turned off for a brief period of time, creating a third-degree heart block for a few seconds. Through this action, tachycardias that originate in the atria can be diagnosed more easily because all the QRSs are absent from the ECG for a few seconds.Pharmacokinetics
Side Effects
Important Notes
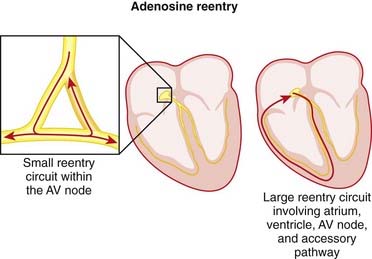
 Diagnostic for SVT: If the HR is so fast that you cannot determine what the underlying rhythm is, then adenosine will temporarily shut down the AV node, which will block conduction that leads to ventricular activity. This gives the observer an opportunity to assess the underlying atrial activity.
Diagnostic for SVT: If the HR is so fast that you cannot determine what the underlying rhythm is, then adenosine will temporarily shut down the AV node, which will block conduction that leads to ventricular activity. This gives the observer an opportunity to assess the underlying atrial activity. Treatment for reentry tachycardias: When adenosine is given, the AV node is turned off for a few seconds. This is usually sufficient to completely abolish a reentry tachycardia (which almost always uses the AV node as part of its pathway).
Treatment for reentry tachycardias: When adenosine is given, the AV node is turned off for a few seconds. This is usually sufficient to completely abolish a reentry tachycardia (which almost always uses the AV node as part of its pathway). If a patient’s heart converts to sinus rhythm after the administration of adenosine, then a diagnosis of reentry tachycardia is confirmed.
If a patient’s heart converts to sinus rhythm after the administration of adenosine, then a diagnosis of reentry tachycardia is confirmed.Evidence
Adenosine versus Verapamil for Supraventricular Tachycardia
 A Cochrane review in 2006 (eight trials, N = 577 patients) found that both drugs were 90% effective in treating SVTs and that there were no differences in efficacy; however, adenosine converted heart rhythm to sinus rhythm a little bit faster than verapamil did. Adenosine caused unpleasant side effects in about 10% of patients, and verapamil caused hypotension in 2% of patients.
A Cochrane review in 2006 (eight trials, N = 577 patients) found that both drugs were 90% effective in treating SVTs and that there were no differences in efficacy; however, adenosine converted heart rhythm to sinus rhythm a little bit faster than verapamil did. Adenosine caused unpleasant side effects in about 10% of patients, and verapamil caused hypotension in 2% of patients.Digoxin
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
Digoxin has two mechanisms of action:
 Through the action of Na/K/ATP ion pump blockade (Figure 11-9), the following sequence of ionic events occurs:
Through the action of Na/K/ATP ion pump blockade (Figure 11-9), the following sequence of ionic events occurs:
 In addition to the indirect reduction of the SNS as outlined previously, there is a direct increase in the parasympathetic system.
In addition to the indirect reduction of the SNS as outlined previously, there is a direct increase in the parasympathetic system. Digoxin sensitizes arterial baroreceptors in the carotid sinus and activates the vagal nuclei (in the brainstem). These baroreceptors induce a response via the vagus nerve that decreases HR and causes vasodilation when the receptors are stretched (which occurs with high BP). HR decreases owing to increased parasympathetic tone of the SA and AV nodes. By this mechanism on the AV node, digoxin is useful in patients with atrial fibrillation.
Digoxin sensitizes arterial baroreceptors in the carotid sinus and activates the vagal nuclei (in the brainstem). These baroreceptors induce a response via the vagus nerve that decreases HR and causes vasodilation when the receptors are stretched (which occurs with high BP). HR decreases owing to increased parasympathetic tone of the SA and AV nodes. By this mechanism on the AV node, digoxin is useful in patients with atrial fibrillation.Pharmacokinetics
 The therapeutic index is very low. The therapeutic range for digoxin is 0.5 to 2.5 nmol/L (in the blood). The probability of toxicity is significant when the level is > 2.6, and toxicity is virtually guaranteed when the level is >3. Contrast this to acetaminophen (Tylenol), in which the toxic oral dose is 10 times the normal dose.
The therapeutic index is very low. The therapeutic range for digoxin is 0.5 to 2.5 nmol/L (in the blood). The probability of toxicity is significant when the level is > 2.6, and toxicity is virtually guaranteed when the level is >3. Contrast this to acetaminophen (Tylenol), in which the toxic oral dose is 10 times the normal dose. Signs or symptoms of toxicity may not correlate well with digoxin levels. A normal level of digoxin does not rule out toxicity.
Signs or symptoms of toxicity may not correlate well with digoxin levels. A normal level of digoxin does not rule out toxicity. Clearance is via the kidneys. Renal dysfunction increases the elimination half-time, which increases digoxin levels and increases the risk of toxicity. The dose must be reduced accordingly.
Clearance is via the kidneys. Renal dysfunction increases the elimination half-time, which increases digoxin levels and increases the risk of toxicity. The dose must be reduced accordingly.Side Effects (Toxicity)
Inhibitors of Cholesterol Synthesis: Statins
Description
Statins are designed to reduce low-density–lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and raise HDL cholesterol.
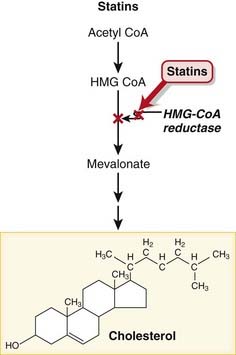
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 These drugs are HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. HMG-CoA reductase mediates the first step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol.
These drugs are HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. HMG-CoA reductase mediates the first step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol. Reduced biosynthesis of cholesterol causes an increase in the number of LDL receptors, through the actions of sterol regulatory element binding proteins (SREBPs). Additional LDL receptors increase the catabolic rate of LDL, and the liver’s extraction of LDL precursors. These actions reduce the plasma pool of LDL (Figure 11-11).
Reduced biosynthesis of cholesterol causes an increase in the number of LDL receptors, through the actions of sterol regulatory element binding proteins (SREBPs). Additional LDL receptors increase the catabolic rate of LDL, and the liver’s extraction of LDL precursors. These actions reduce the plasma pool of LDL (Figure 11-11).Side Effects
 Myalgia: muscle pain and associated weakness. The pathophysiology is not fully understood, and it is probable that this is a very mild form of myositis. This occurs in about 10% of patients.
Myalgia: muscle pain and associated weakness. The pathophysiology is not fully understood, and it is probable that this is a very mild form of myositis. This occurs in about 10% of patients.Rare, Serious Side Effects
 Myositis and rhabdomyolysis are rare (1% for myositis) but serious adverse effects of statin therapy, which tend to occur at higher doses or when a drug interaction is present.
Myositis and rhabdomyolysis are rare (1% for myositis) but serious adverse effects of statin therapy, which tend to occur at higher doses or when a drug interaction is present.
 Myositis is inflammation of muscle cells and is associated with a 10 times increase in CK levels in the blood.
Myositis is inflammation of muscle cells and is associated with a 10 times increase in CK levels in the blood. Rhabdomyolysis is an extreme form of myositis and results in lysis of skeletal muscle cells and release of myoglobin in high quantities, which results in damage to renal glomeruli and renal failure. This condition usually occurs in the presence of other risk factors in addition to statin administration, such as coadministration with cyclosporine (an immunosuppressant) or gemfibrozil (another lipid-lowering agent).
Rhabdomyolysis is an extreme form of myositis and results in lysis of skeletal muscle cells and release of myoglobin in high quantities, which results in damage to renal glomeruli and renal failure. This condition usually occurs in the presence of other risk factors in addition to statin administration, such as coadministration with cyclosporine (an immunosuppressant) or gemfibrozil (another lipid-lowering agent). Hepatotoxicity: Increases in serum aminotransferase have been observed in <1% of patients. As long as the elevations are not too great, patients who have no other risk factors for liver impairment can continue taking the statin without undue risk for liver injury, provided close monitoring is maintained.
Hepatotoxicity: Increases in serum aminotransferase have been observed in <1% of patients. As long as the elevations are not too great, patients who have no other risk factors for liver impairment can continue taking the statin without undue risk for liver injury, provided close monitoring is maintained.Important Notes
 Statins can be used in combination with other agents such as bile acid sequestrants or inhibitors of cholesterol absorption. Fibrates and niacin (other drugs used to achieve a more favorable lipid profile) should be used with caution, as both can interact with statins.
Statins can be used in combination with other agents such as bile acid sequestrants or inhibitors of cholesterol absorption. Fibrates and niacin (other drugs used to achieve a more favorable lipid profile) should be used with caution, as both can interact with statins. Ezetimibe is a cholesterol-lowering agent that is used in combination with the statins. Unlike the statins, which lower cholesterol by inhibiting its synthesis, ezetimibe reduces the absorption of cholesterol from the intestine. The fact that these two classes use distinct and complementary strategies to lowering cholesterol has made them a natural fit for combination therapy.
Ezetimibe is a cholesterol-lowering agent that is used in combination with the statins. Unlike the statins, which lower cholesterol by inhibiting its synthesis, ezetimibe reduces the absorption of cholesterol from the intestine. The fact that these two classes use distinct and complementary strategies to lowering cholesterol has made them a natural fit for combination therapy.Advanced
 Statins are being studied for their potential role in neuroprotection, with indications such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, stroke, and multiple sclerosis (MS). Statins appear to activate neuroprotective pathways and also may play a role in neurogenesis. The mechanisms of all these effects are still being worked out; however, some researchers believe that the use of statins may become even more widespread than it is today.
Statins are being studied for their potential role in neuroprotection, with indications such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, stroke, and multiple sclerosis (MS). Statins appear to activate neuroprotective pathways and also may play a role in neurogenesis. The mechanisms of all these effects are still being worked out; however, some researchers believe that the use of statins may become even more widespread than it is today.Evidence
Patients with Cardiac Risk Factors But Without Cardiac Disease (Primary Prevention)
 A 2009 systematic review (10 studies, N = 70,388 participants) examined the use of statins in people without established cardiovascular disease but with cardiovascular risk factors. The included studies had a mean follow-up of 4.1 years. Statins reduced the risk of all-cause mortality (OR 0.88), major coronary events (OR 0.70), and major cerebrovascular events (OR 0.81).
A 2009 systematic review (10 studies, N = 70,388 participants) examined the use of statins in people without established cardiovascular disease but with cardiovascular risk factors. The included studies had a mean follow-up of 4.1 years. Statins reduced the risk of all-cause mortality (OR 0.88), major coronary events (OR 0.70), and major cerebrovascular events (OR 0.81).Prevention of Stroke Recurrence (Secondary Prevention)
 A 2009 Cochrane review (eight studies, N ≈10,000 participants) examined the effect of altering serum lipids for prevention of subsequent cardiovascular disease and stroke in patients with a history of stroke. Statins marginally reduced subsequent cerebrovascular events (OR 0.88) but not all-cause mortality or sudden deaths. Three trials showed a subsequent reduction in serious vascular events (OR 0.74).
A 2009 Cochrane review (eight studies, N ≈10,000 participants) examined the effect of altering serum lipids for prevention of subsequent cardiovascular disease and stroke in patients with a history of stroke. Statins marginally reduced subsequent cerebrovascular events (OR 0.88) but not all-cause mortality or sudden deaths. Three trials showed a subsequent reduction in serious vascular events (OR 0.74).Fibrates
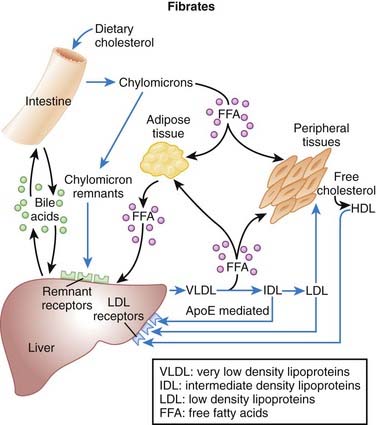
MOA (Mechanism of Action) (Figure 11-12)
 Transcription factors are proteins that bind DNA and increase or decrease transcription (production of RNA and thus proteins) of selected genes.
Transcription factors are proteins that bind DNA and increase or decrease transcription (production of RNA and thus proteins) of selected genes. Fibrates activate transcription factors called peroxisome proliferator–activated receptors (PPARs). These are nuclear hormone receptors that respond to lipid based ligands, including hormones, vitamins, and fatty acids.
Fibrates activate transcription factors called peroxisome proliferator–activated receptors (PPARs). These are nuclear hormone receptors that respond to lipid based ligands, including hormones, vitamins, and fatty acids.Pharmacokinetics
Drug Interactions
 Gemfibrozil competes for the same glucuronosyltransferases that metabolize statins. This is important because statins are used for the same indication (high cholesterol) as fibrates are, and both drugs can cause muscle breakdown and muscle pain (rhabdomyositis). Coadministration can result in increased levels of both drugs and an increase in the risk for this side effect.
Gemfibrozil competes for the same glucuronosyltransferases that metabolize statins. This is important because statins are used for the same indication (high cholesterol) as fibrates are, and both drugs can cause muscle breakdown and muscle pain (rhabdomyositis). Coadministration can result in increased levels of both drugs and an increase in the risk for this side effect.Important Notes
 Fibrates are usually administered in combination with statins and are not frequently first-line single agents.
Fibrates are usually administered in combination with statins and are not frequently first-line single agents.Evidence
FYI Notes
 Although the word fibrate is suggestive of fiber, the fibrates do not act as GI lipid-absorbing fiber resins. This mechanism of action belongs to a class of drug called bile acid sequestrants.
Although the word fibrate is suggestive of fiber, the fibrates do not act as GI lipid-absorbing fiber resins. This mechanism of action belongs to a class of drug called bile acid sequestrants.Bile Acid Sequestrants
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
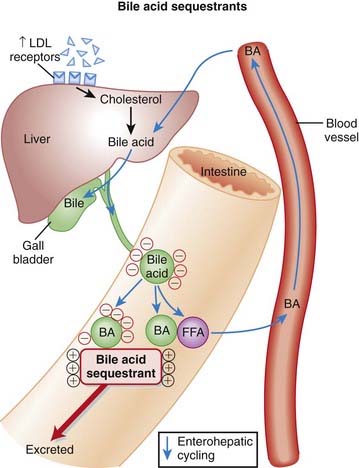
 Bile acids facilitate the digestion and absorption of dietary fats. The bile acids are normally enterohepatically recycled, which means they are secreted into the GI tract through the bile duct and then reabsorbed and transported back to the liver for the cycle to repeat (Figure 11-13).
Bile acids facilitate the digestion and absorption of dietary fats. The bile acids are normally enterohepatically recycled, which means they are secreted into the GI tract through the bile duct and then reabsorbed and transported back to the liver for the cycle to repeat (Figure 11-13). Bile acid binding resins carry a large positive charge and are therefore attracted to and bind negatively charged bile acids in the gut. The resins are large and therefore not absorbed, so the bound bile acids are excreted with the resins in the feces.
Bile acid binding resins carry a large positive charge and are therefore attracted to and bind negatively charged bile acids in the gut. The resins are large and therefore not absorbed, so the bound bile acids are excreted with the resins in the feces. The binding of bile acids by the resins therefore interrupts the process of enterohepatic recycling, depleting the pool of bile acids. With a deficiency of recycled bile acids the liver must synthesize more.
The binding of bile acids by the resins therefore interrupts the process of enterohepatic recycling, depleting the pool of bile acids. With a deficiency of recycled bile acids the liver must synthesize more. Cholesterol is a precursor of bile acids, so to create more bile acids the liver must obtain more cholesterol. It does this by increasing the number of LDL receptors, which in turn leads to a lowering of plasma LDL and total cholesterol.
Cholesterol is a precursor of bile acids, so to create more bile acids the liver must obtain more cholesterol. It does this by increasing the number of LDL receptors, which in turn leads to a lowering of plasma LDL and total cholesterol.Pharmacokinetics
 Cholestyramine and colestipol are available in powdered dosage forms, which are administered by suspending in water and drinking.
Cholestyramine and colestipol are available in powdered dosage forms, which are administered by suspending in water and drinking. The bile acid binding resins are not absorbed, and they exert their actions only within the GI tract.
The bile acid binding resins are not absorbed, and they exert their actions only within the GI tract. Binding to negatively charged molecules can interfere with the absorption of a number of different negatively charged drugs. Some of the more notable examples include thiazide diuretics, furosemide, propranolol, digoxin, and warfarin. Because of the large number of drugs that may be affected by this interaction, it is typically recommended that the administration of bile acid resins be separated from administration of other drugs by at least 1 hour if taken before the resin, or by 3 hours if taken after the resin.
Binding to negatively charged molecules can interfere with the absorption of a number of different negatively charged drugs. Some of the more notable examples include thiazide diuretics, furosemide, propranolol, digoxin, and warfarin. Because of the large number of drugs that may be affected by this interaction, it is typically recommended that the administration of bile acid resins be separated from administration of other drugs by at least 1 hour if taken before the resin, or by 3 hours if taken after the resin.Side Effects
 GI: constipation is the most common side effect. Others can include bloating, gas, nausea, and upper abdominal pain.
GI: constipation is the most common side effect. Others can include bloating, gas, nausea, and upper abdominal pain.Serious Side Effects
 Hyperchloremic acidosis (rare): The bile acid binding resins are chloride salts and in susceptible individuals (typically children) may increase chloride levels enough to induce acidosis. Chloride and bicarbonate are the primary anions in the blood, and if one goes up, the other usually goes down to maintain electrical neutrality. Dropping bicarbonate results in metabolic acidosis.
Hyperchloremic acidosis (rare): The bile acid binding resins are chloride salts and in susceptible individuals (typically children) may increase chloride levels enough to induce acidosis. Chloride and bicarbonate are the primary anions in the blood, and if one goes up, the other usually goes down to maintain electrical neutrality. Dropping bicarbonate results in metabolic acidosis.Important Notes
 To compensate for the actions of the bile acid binding resins, upregulation occurs in the activity of the HMG-CoA reductase enzyme, which is the rate-limiting enzyme in the production of cholesterol. This is the rationale for using the statins, which are HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, in combination with the bile acid binding resins.
To compensate for the actions of the bile acid binding resins, upregulation occurs in the activity of the HMG-CoA reductase enzyme, which is the rate-limiting enzyme in the production of cholesterol. This is the rationale for using the statins, which are HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, in combination with the bile acid binding resins. Interruption of enterohepatic recycling by the bile acid binding resins leads to an increase in plasma triglyceride levels. This is because the activity of the enzyme phosphatidic acid phosphatase, which is involved in triglyceride formation, is suppressed when the enterohepatic recycling system is functioning normally. When enterohepatic recycling is interrupted, it can lead to problematic increases in triglyceride levels, and patients who have preexisting problems with hypertriglyceridemia should avoid taking these agents.
Interruption of enterohepatic recycling by the bile acid binding resins leads to an increase in plasma triglyceride levels. This is because the activity of the enzyme phosphatidic acid phosphatase, which is involved in triglyceride formation, is suppressed when the enterohepatic recycling system is functioning normally. When enterohepatic recycling is interrupted, it can lead to problematic increases in triglyceride levels, and patients who have preexisting problems with hypertriglyceridemia should avoid taking these agents. The GI side effects of the powdered formulations may be reduced by allowing the suspension to sit, refrigerated, for several hours before consumption.
The GI side effects of the powdered formulations may be reduced by allowing the suspension to sit, refrigerated, for several hours before consumption.Inotropes and Pressors
Metabolism
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
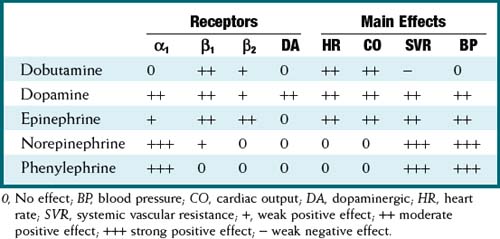
 These drugs all exert their actions via the autonomic nervous system α and β receptors. In addition to these receptors, dopamine (and only dopamine) also acts via dopaminergic (DA) receptors.
These drugs all exert their actions via the autonomic nervous system α and β receptors. In addition to these receptors, dopamine (and only dopamine) also acts via dopaminergic (DA) receptors. Drugs that are β1 agonists are inotropes; drugs that are α1 agonists are pressors. Activation of DA receptors results in mesenteric and renal vasodilation. Note: β2 agonists are vasodilators (on skeletal muscle).
Drugs that are β1 agonists are inotropes; drugs that are α1 agonists are pressors. Activation of DA receptors results in mesenteric and renal vasodilation. Note: β2 agonists are vasodilators (on skeletal muscle). Most drugs are agonists to both the α and β receptors. However, each drug has different potencies for the receptors. Thus at low doses some drugs are primarily agonists for one receptor. At higher doses, both receptors will be stimulated, but one receptor will be more stimulated. The exception to this rule is phenylephrine. It is a pure α1 agonist.
Most drugs are agonists to both the α and β receptors. However, each drug has different potencies for the receptors. Thus at low doses some drugs are primarily agonists for one receptor. At higher doses, both receptors will be stimulated, but one receptor will be more stimulated. The exception to this rule is phenylephrine. It is a pure α1 agonist. Stimulation of a β receptor activates the class of proteins called G proteins. This results in increased cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) levels, which then stimulate protein kinases, which result in increased intracellular calcium. Calcium enhances the actin-myosin interaction and results in increased myocardial contractile force.
Stimulation of a β receptor activates the class of proteins called G proteins. This results in increased cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) levels, which then stimulate protein kinases, which result in increased intracellular calcium. Calcium enhances the actin-myosin interaction and results in increased myocardial contractile force. Stimulation of an α1 receptor results in increased inositol triphosphate (IP3), which results in increased smooth muscle intracellular calcium, resulting in increased contractile force and increased vascular tone (vasoconstriction).
Stimulation of an α1 receptor results in increased inositol triphosphate (IP3), which results in increased smooth muscle intracellular calcium, resulting in increased contractile force and increased vascular tone (vasoconstriction).Pharmacokinetics
Important Notes
 A thorough assessment to determine the specific cause(s) of hypotension or shock must always be performed, and the primary cause of the problem must be corrected. For example, a patient who is bleeding and has hypotension has a preload (volume) problem, and therefore the preload should be corrected before the contractility or afterload is manipulated.
A thorough assessment to determine the specific cause(s) of hypotension or shock must always be performed, and the primary cause of the problem must be corrected. For example, a patient who is bleeding and has hypotension has a preload (volume) problem, and therefore the preload should be corrected before the contractility or afterload is manipulated.FYI Notes
 A mnemonic for the nor of norepinephrine is “no radical.” Remember that a radical is a CH group. Therefore, adding a CH3 group to norepi produces epi.
A mnemonic for the nor of norepinephrine is “no radical.” Remember that a radical is a CH group. Therefore, adding a CH3 group to norepi produces epi. Oxymetazoline and xylometazoline are both α1-agonist decongestants but are not used systemically; they are prepared as nasal sprays and function to decrease nasal stuffiness and congestion by vasoconstricting vessels in the nasal mucosa. However, frequent use of these medications results in a rebound congestion when they are stopped, and therefore they must be used sparingly. They are more commonly recognized by their brand names, which in North America include Otrivin and Dristan.
Oxymetazoline and xylometazoline are both α1-agonist decongestants but are not used systemically; they are prepared as nasal sprays and function to decrease nasal stuffiness and congestion by vasoconstricting vessels in the nasal mucosa. However, frequent use of these medications results in a rebound congestion when they are stopped, and therefore they must be used sparingly. They are more commonly recognized by their brand names, which in North America include Otrivin and Dristan.Phosphodiesterase-3 Inhibitors
MOA (Mechanism of Action) (Figure 11-14)
 PDE inhibitors therefore result in increased intracellular cAMP and cGMP, which cause increased intracellular calcium. Which cell or tissue type is affected will dictate the effect of the PDE inhibitor.
PDE inhibitors therefore result in increased intracellular cAMP and cGMP, which cause increased intracellular calcium. Which cell or tissue type is affected will dictate the effect of the PDE inhibitor. PDE3 is distributed in the body primarily in cardiac tissue, vascular smooth muscle, and platelets; thus its effects primarily involve these cell and tissue types.
PDE3 is distributed in the body primarily in cardiac tissue, vascular smooth muscle, and platelets; thus its effects primarily involve these cell and tissue types. Increased cAMP results in increased intracellular calcium, which causes increased inotropy (contraction).
Increased cAMP results in increased intracellular calcium, which causes increased inotropy (contraction). PDE3 inhibitors also have intracellular actions that should theoretically improve diastolic function:
PDE3 inhibitors also have intracellular actions that should theoretically improve diastolic function:
Pharmacokinetics
 The half-life is about 6 hours. This is important because it is administered as an intravenous infusion. Most cardiovascular drugs (e.g., dopamine, nitroglycerin [NTG]) that are administered as intravenous infusions (to optimize BP and CO) have half-lives of 3 to 5 minutes. Therefore, milrinone is less titratable than these other drugs, and the drug levels can become unexpectedly high.
The half-life is about 6 hours. This is important because it is administered as an intravenous infusion. Most cardiovascular drugs (e.g., dopamine, nitroglycerin [NTG]) that are administered as intravenous infusions (to optimize BP and CO) have half-lives of 3 to 5 minutes. Therefore, milrinone is less titratable than these other drugs, and the drug levels can become unexpectedly high.Side Effects
 Hypotension secondary to vasodilation: This is a very important side effect. Because of the relatively long half-life of milrinone and the fact that it is administered as an infusion, the potential for steadily increasing serum levels of drug over a period of many hours after the start of the infusion, especially in patients with renal dysfunction, results in hypotension being a frequent side effect. Hypotension induced by PDE3 infusions is treated with vasoconstrictors (usually norepinephrine) and by decreasing the infusion rate. With the longer half-life, hypotension usually persists for many hours even after the infusion is decreased.
Hypotension secondary to vasodilation: This is a very important side effect. Because of the relatively long half-life of milrinone and the fact that it is administered as an infusion, the potential for steadily increasing serum levels of drug over a period of many hours after the start of the infusion, especially in patients with renal dysfunction, results in hypotension being a frequent side effect. Hypotension induced by PDE3 infusions is treated with vasoconstrictors (usually norepinephrine) and by decreasing the infusion rate. With the longer half-life, hypotension usually persists for many hours even after the infusion is decreased.Important Notes
 Milrinone is not used for chronic heart failure. It is used only in select patients with severe acute heart failure.
Milrinone is not used for chronic heart failure. It is used only in select patients with severe acute heart failure. PDE3 inhibitors have a physiologic effect similar to that of β agonists because β agonists also result in increased cAMP, leading to:
PDE3 inhibitors have a physiologic effect similar to that of β agonists because β agonists also result in increased cAMP, leading to:
 However, there are important clinical differences between the two PDE3 inhibitors and β agonists:
However, there are important clinical differences between the two PDE3 inhibitors and β agonists:
 PDE3 inhibitors are not direct positive chronotropes (increased HR), whereas β agonists are. Lack of a chronotropic effect can be a benefit when the patient is already tachycardic or has disease in which tachycardia would be undesirable (e.g., coronary artery disease).
PDE3 inhibitors are not direct positive chronotropes (increased HR), whereas β agonists are. Lack of a chronotropic effect can be a benefit when the patient is already tachycardic or has disease in which tachycardia would be undesirable (e.g., coronary artery disease). PDE3 inhibitors do not use β receptors, which are frequently down-regulated or often already maximally stimulated by endogenous catecholamines, rendering them virtually unresponsive to additional exogenous β stimulation. Thus PDE3 inhibitors usually are clinically much stronger drugs in the setting of acute decompensated heart failure.
PDE3 inhibitors do not use β receptors, which are frequently down-regulated or often already maximally stimulated by endogenous catecholamines, rendering them virtually unresponsive to additional exogenous β stimulation. Thus PDE3 inhibitors usually are clinically much stronger drugs in the setting of acute decompensated heart failure. PDE3 inhibitors are frequently used with a pulmonary artery catheter in a critical care setting, and the cardiac index (which is CO divided by body mass index) is used for titrating the dose and for determining when the patient can be weaned off the drug.
PDE3 inhibitors are frequently used with a pulmonary artery catheter in a critical care setting, and the cardiac index (which is CO divided by body mass index) is used for titrating the dose and for determining when the patient can be weaned off the drug. PDE3 inhibitors increase myocardial work via increased contractility but decrease myocardial work via afterload reduction through vasodilation. The net effect on total myocardial work is difficult to predict but is usually about neutral.
PDE3 inhibitors increase myocardial work via increased contractility but decrease myocardial work via afterload reduction through vasodilation. The net effect on total myocardial work is difficult to predict but is usually about neutral.Advanced
 PDE3 breaks down both cAMP and cGMP. The subtype of PDE determines the ratio of activity against cAMP versus cGMP. PDE3 preferentially acts on cAMP 10 times more than it does cGMP. The changes in cAMP and cGMP in different cells dictate the clinical effects seen in either the heart or the vasculature.
PDE3 breaks down both cAMP and cGMP. The subtype of PDE determines the ratio of activity against cAMP versus cGMP. PDE3 preferentially acts on cAMP 10 times more than it does cGMP. The changes in cAMP and cGMP in different cells dictate the clinical effects seen in either the heart or the vasculature.FYI Notes
 cAMP was first identified in 1958 by Earl Sutherland, for which he received the 1971 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine “for his discoveries concerning the mechanisms of the action of hormones.”
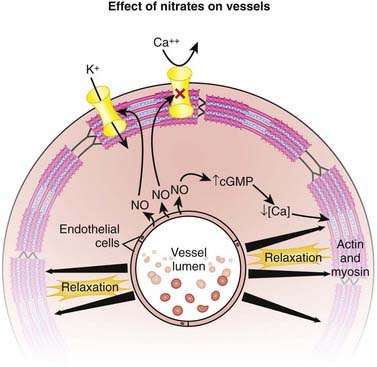
cAMP was first identified in 1958 by Earl Sutherland, for which he received the 1971 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine “for his discoveries concerning the mechanisms of the action of hormones.”Nitrates
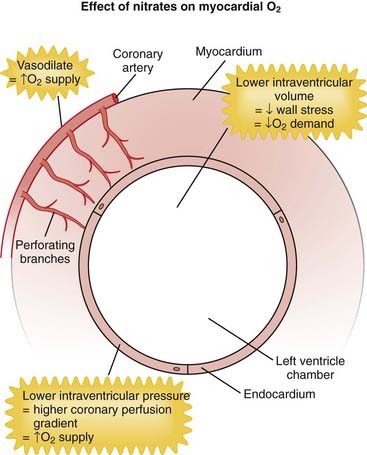
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 NO, also known as endothelium-derived relaxing factor (EDRF), induces vasodilation primarily on the venous side of the circulation (venodilation). It does this by activating guanylyl cyclase, an enzyme that produces cGMP, which decreases Ca+ entry into cells and causes relaxation of vascular smooth muscle (Figure 11-15).
NO, also known as endothelium-derived relaxing factor (EDRF), induces vasodilation primarily on the venous side of the circulation (venodilation). It does this by activating guanylyl cyclase, an enzyme that produces cGMP, which decreases Ca+ entry into cells and causes relaxation of vascular smooth muscle (Figure 11-15). This venodilatory effect produces a pooling of blood in the venous capacitance vessels, resulting in a reduction in venous return, preload, and end diastolic pressure, which:
This venodilatory effect produces a pooling of blood in the venous capacitance vessels, resulting in a reduction in venous return, preload, and end diastolic pressure, which:
 At higher doses, nitrates can have a vasodilatory (arterial) effect; however, this is not the major mechanism in the management of stable angina. The vasodilation reduces afterload, again reducing ventricular wall tension and oxygen demand.
At higher doses, nitrates can have a vasodilatory (arterial) effect; however, this is not the major mechanism in the management of stable angina. The vasodilation reduces afterload, again reducing ventricular wall tension and oxygen demand. To a minor extent, these agents also dilate coronary arteries, although this is again of secondary importance in their antianginal effects. It is important to realize that atherosclerotic plaques do not dilate in response to drugs, but that collateral coronary vessels might provide an increase in blood flow to an ischemic myocardium that is downstream from such a blockage.
To a minor extent, these agents also dilate coronary arteries, although this is again of secondary importance in their antianginal effects. It is important to realize that atherosclerotic plaques do not dilate in response to drugs, but that collateral coronary vessels might provide an increase in blood flow to an ischemic myocardium that is downstream from such a blockage.Pharmacokinetics
 NTG has very low oral bioavailability and therefore is administered topically (patch or ointment), sublingually (pill or spray), or intravenously.
NTG has very low oral bioavailability and therefore is administered topically (patch or ointment), sublingually (pill or spray), or intravenously.Important Notes
 The drug interaction with PDE5 inhibitors (vasodilators used for treatment of erectile dysfunction) is significant. Many men with erectile dysfunction are older and have heart problems, such as angina. Both classes of drugs increase intracellular cGMP, and the hypotension that develops from the profound vasodilation can be severe and refractory to treatment. Hence there is great potential for this interaction to occur and for potentially serious consequences if it does occur.
The drug interaction with PDE5 inhibitors (vasodilators used for treatment of erectile dysfunction) is significant. Many men with erectile dysfunction are older and have heart problems, such as angina. Both classes of drugs increase intracellular cGMP, and the hypotension that develops from the profound vasodilation can be severe and refractory to treatment. Hence there is great potential for this interaction to occur and for potentially serious consequences if it does occur. NTG can relax any and all smooth muscle. Esophageal spasm can mimic angina. NTG will relax the esophagus and trick the healthcare provider into thinking that the patient does indeed have cardiac ischemia when the “angina equivalent” is relieved.
NTG can relax any and all smooth muscle. Esophageal spasm can mimic angina. NTG will relax the esophagus and trick the healthcare provider into thinking that the patient does indeed have cardiac ischemia when the “angina equivalent” is relieved.Evidence
FYI Notes
 The tolerance that has become a characteristic feature of nitrate therapy was discovered accidentally. TNT stands for trinitrotoluene and has three nitrate groups. Munitions workers exposed to high levels of nitrates found that the headaches they experienced diminished as the work week progressed, only to reappear with intensity after the start of each new week. These “Monday morning headaches” were originally attributed to heavy drinking over the weekend. It was later determined that the workers were actually experiencing side effects of nitrates at the start of the week and then developed tolerance during the course of the week. The tolerance wore off during the weekend, when no exposure occurred.
The tolerance that has become a characteristic feature of nitrate therapy was discovered accidentally. TNT stands for trinitrotoluene and has three nitrate groups. Munitions workers exposed to high levels of nitrates found that the headaches they experienced diminished as the work week progressed, only to reappear with intensity after the start of each new week. These “Monday morning headaches” were originally attributed to heavy drinking over the weekend. It was later determined that the workers were actually experiencing side effects of nitrates at the start of the week and then developed tolerance during the course of the week. The tolerance wore off during the weekend, when no exposure occurred.Vasodilators
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 The underlying mechanism of vasodilation of arteriolar smooth muscle by the direct vasodilators is still not confirmed, but theories include interference with the release of Ca+2 from the SR and activation of potassium channels.
The underlying mechanism of vasodilation of arteriolar smooth muscle by the direct vasodilators is still not confirmed, but theories include interference with the release of Ca+2 from the SR and activation of potassium channels.Pharmacokinetics
Contraindications
FYI Notes
 These agents are rarely ever prescribed anymore because significant compensatory responses and numerous side effects limit their usefulness in the management of HTN.
These agents are rarely ever prescribed anymore because significant compensatory responses and numerous side effects limit their usefulness in the management of HTN. The iron (Fe) molecule in hemoglobin is normally in the Fe2+ state and can bind O2 appropriately. If the iron is oxidized to Fe3+, then the hemoglobin is called methemoglobin. Methemoglobin is unable to bind oxygen. In normal humans, about 0.5% of hemoglobin is in the form of methemoglobin. Methemoglobinemia reduces the oxygen carrying capacity of blood.
The iron (Fe) molecule in hemoglobin is normally in the Fe2+ state and can bind O2 appropriately. If the iron is oxidized to Fe3+, then the hemoglobin is called methemoglobin. Methemoglobin is unable to bind oxygen. In normal humans, about 0.5% of hemoglobin is in the form of methemoglobin. Methemoglobinemia reduces the oxygen carrying capacity of blood.Natriuretic Peptides
MOA (Mechanism of Action)
 A number of hormonal and neurologic mechanisms are activated in heart failure, of which natriuretic factors (peptides) are one.
A number of hormonal and neurologic mechanisms are activated in heart failure, of which natriuretic factors (peptides) are one. Endogenous natriuretic factors are increased during heart failure in response to atrial stretch and ventricular stretch, when the chambers are volume overloaded because of heart failure.
Endogenous natriuretic factors are increased during heart failure in response to atrial stretch and ventricular stretch, when the chambers are volume overloaded because of heart failure. BNP binds to BNP receptors on blood vessels and kidneys, which activates the cGMP system, resulting in the following effects:
BNP binds to BNP receptors on blood vessels and kidneys, which activates the cGMP system, resulting in the following effects:
Pharmacokinetics
Important Notes
 Endogenous BNP is elevated in patients with heart failure. Most systems that are activated in heart failure (such as the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and the SNS) result in vasoconstriction and water retention, which is the opposite effect of BNP. Therefore BNP acts as a counterbalancing hormone system in heart failure.
Endogenous BNP is elevated in patients with heart failure. Most systems that are activated in heart failure (such as the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and the SNS) result in vasoconstriction and water retention, which is the opposite effect of BNP. Therefore BNP acts as a counterbalancing hormone system in heart failure.Evidence
 A meta-analysis in 2005 (three trials, N = 862 patients) showed a possibility of increased death and renal dysfunction in patients with acute decompensated heart failure treated with nesiritide. All studies were double blinded. However, another meta-analysis in 2006 (seven trials, N = 1717 patients) did not show increased mortality or renal failure in patients with acute heart failure treated with nesiritide. Two of the trials were not blinded.
A meta-analysis in 2005 (three trials, N = 862 patients) showed a possibility of increased death and renal dysfunction in patients with acute decompensated heart failure treated with nesiritide. All studies were double blinded. However, another meta-analysis in 2006 (seven trials, N = 1717 patients) did not show increased mortality or renal failure in patients with acute heart failure treated with nesiritide. Two of the trials were not blinded. A third meta-analysis in 2009 (14 trials, N = 934 patients) evaluating the effect of nesiritide on renal function in patients immediately after cardiac surgery demonstrated reduced need for dialysis in patients treated with nesiritide (OR = 0.32). However, all studies included were small and underpowered to provide statistical significance on their own.
A third meta-analysis in 2009 (14 trials, N = 934 patients) evaluating the effect of nesiritide on renal function in patients immediately after cardiac surgery demonstrated reduced need for dialysis in patients treated with nesiritide (OR = 0.32). However, all studies included were small and underpowered to provide statistical significance on their own.