CHAPTER 115 Basic Principles of Cranial Surgery for Brain Tumors
Preoperative Evaluation and Management
Preoperative Imaging Interpretation
Timing of Surgery
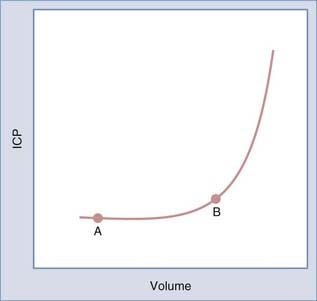
The timing of surgery is dictated by the type of symptoms and their pace. Progressive symptoms over a short period indicate that the tumor and edema are expanding faster than the brain is able to compensate. Recognition of this situation is critical because such patients are at risk for rapid deterioration. The Monro-Kellie principle, introduced to neurosurgery by Cushing, states that changes in brain volume cause reciprocal changes in the blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) compartments within the rigid cranial sphere to maintain intracranial pressure (ICP) within a normal range.1 As brain volume increases secondary to a mass such as a tumor, a compensatory decrease in CSF or blood volume occurs to maintain ICP within the normal range. As the tumor expands, ICP increases slowly until there is no further displaceable volume (i.e., CSF or blood). At this point, further increases in brain volume result in an accelerated increase in ICP. The relationship between volume and pressure is depicted by the volume-pressure curve in Figure 115-1. As a tumor grows and expands, a patient moves along the curve from point A to point B. During this time, compensatory changes occur, including displacement of CSF and blood, as well as compression of normal brain tissue, to maintain ICP in the normal range. At point B, the ability of the brain to further compensate is limited. Thus, a small additional increase in volume results in a larger increase in pressure. It is important to recognize patients who are approaching point B on the volume-pressure curve because they are at risk for a rapid increase in ICP with small additional increases in volume. This rapid increase in ICP can lead to rapid neurological decline.
Surgical Preparation
In general, patients respond within 24 hours of beginning steroid treatment. This clinical improvement parallels the increased compliance measured in patients 24 hours after beginning steroids. Investigative studies in patients and animals indicate that dexamethasone decreases tumor capillary permeability and tumor blood volume.2–4 These actions alter the configuration of the volume-pressure curve such that further increases in tumor volume result in a smaller increase in ICP.
Positioning
Positioning is an important but often overlooked part of the surgical procedure. The four body positions are supine, lateral, prone, and sitting. Sitting is rarely used today. In the past, the sitting position was used primarily for pineal tumors, but it has now been replaced by the prone Concorde position (see Chapter 126 for pineal tumors).
Tumor Removal
Intraoperative adjuvants that facilitate maximal safe surgical resection include intraoperative navigation with frameless stereotactic systems, intraoperative ultrasonography, and intraoperative MRI. These tools provide imaging feedback that the surgeon can use to evaluate the extent of resection. These tools should be used as adjuvants to complement the visual feedback that the surgeon is receiving from the gross appearance of the tumor. 5-Aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA) is a fluorescent marker that accumulates in malignant glioma tissue and can be used to evaluate the extent of resection. Intraoperative use of this marker guides the tumor resection such that studies have demonstrated more complete glioma resection, based on postoperative MRI, when 5-ALA was used than when it was not used.5
Cushing H. Studies in Intracranial Physiology and Surgery. London: Oxford University Press; 1926. 19-23
Leenders KL, Beaney RP, Brooks DJ, et al. Dexamethasone treatment of brain tumor patients: effects on regional cerebral blood flow, blood volume, and oxygen utilization. Neurology. 1985;35:1610-1616.
Tonn JC, Stummer W. Fluorescence-guided resection of malignant gliomas using 5-aminolevulinic acid: practical use, risks, and pitfalls. Clin Neurosurg. 2008;55:20-26.
Yamada K, Bremer AM, West CR. Effects of dexamethasone on tumor-induced brain edema and its distribution in the brain of monkeys. J Neurosurg. 1979;50:361-367.
Yamada K, Ushio Y, Hayakawa T, et al. Effects of methylprednisolone on peritumoral brain edema. J Neurosurg. 1983;59:612-619.
1 Cushing H. Studies in Intracranial Physiology and Surgery. London: Oxford University Press; 1926. 19-23
2 Yamada K, Ushio Y, Hayakawa T, et al. Effects of methylprednisolone on peritumoral brain edema. J Neurosurg. 1983;59:612-619.
3 Leenders KL, Beaney RP, Brooks DJ, et al. Dexamethasone treatment of brain tumor patients: effects on regional cerebral blood flow, blood volume, and oxygen utilization. Neurology. 1985;35:1610-1616.
4 Yamada K, Bremer AM, West CR. Effects of dexamethasone on tumor-induced brain edema and its distribution in the brain of monkeys. J Neurosurg. 1979;50:361-367.
5 Tonn JC, Stummer W. Fluorescence-guided resection of malignant gliomas using 5-aminolevulinic acid: practical use, risks, and pitfalls. Clin Neurosurg. 2008;55:20-26.