Anatomy of the posterior fossa
Boundaries
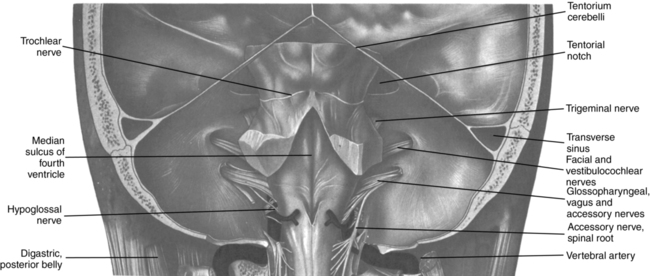
The posterior fossa is bounded (1) in front by the dorsum sellae, the clivus, the posterior aspects of the sphenoid bone, and the basilar part of the occipital bone; (2) behind by the lower part of the occipital squama below the sulci for the transverse sinuses and internal occipital protuberance; (3) laterally by the petrous and mastoid parts of the temporal bones and lateral parts of the occipital bone; and (4) above and behind by the mastoid angles of the parietal bones. It contains all structures caudal to the tentorium cerebelli (Figure 56-1). The foramen magnum is in the floor of the posterior fossa.
Structures
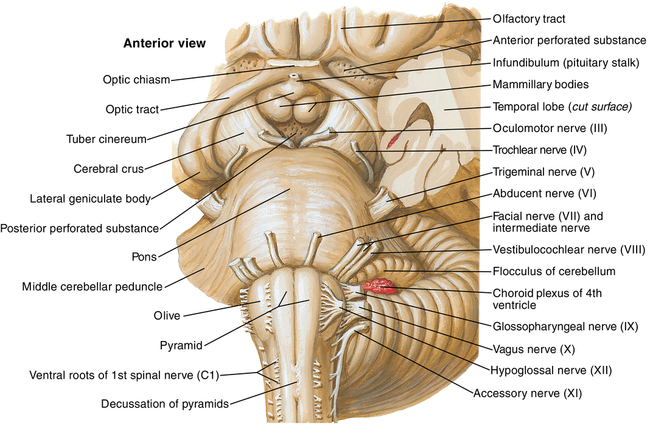
In addition to the aforementioned cerebellum, midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata, the fourth ventricle also lies within the posterior fossa (Figure 56-2). The nuclei of many cranial nerves and the cardiovascular and respiratory centers lie close to the anterior floor of the fourth ventricle.
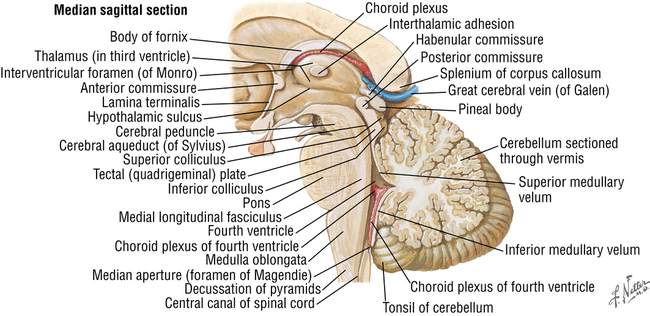
Cranial nerves IV through XII either traverse or are contained within the posterior fossa (Figure 56-3).
Veins
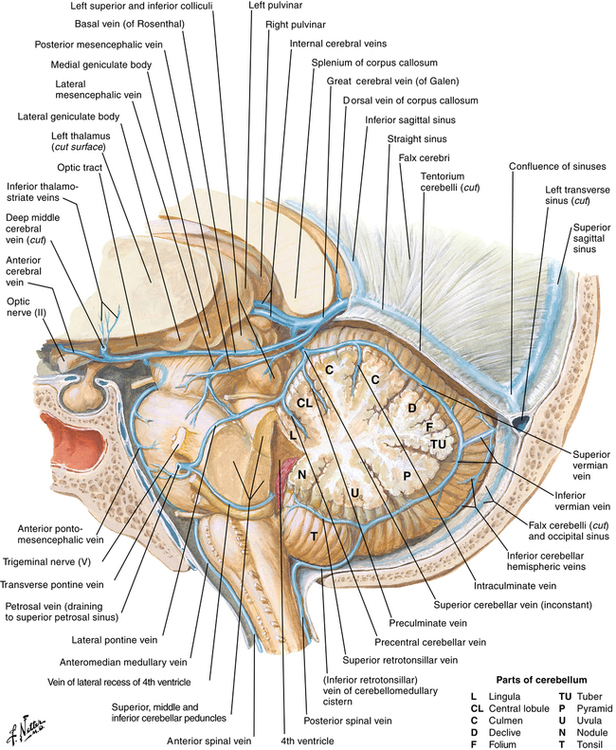
The veins of the posterior fossa drain the cerebellum and brainstem and may be the source of bleeding, hematoma, or venous air embolism. As seen in Figure 56-4, the major venous structures include the great cerebral vein of Galen, petrosal vein, superior petrosal sinus, straight sinus, left and right transverse sinuses, lateral sinus, and occipital sinus.
Arteries
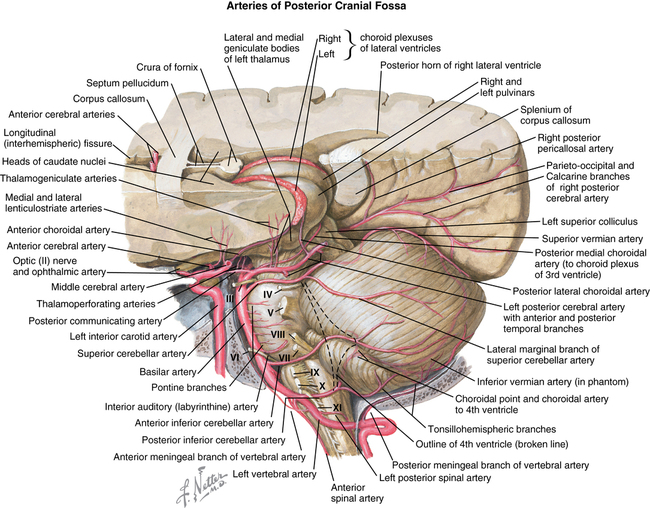
Arteries arising from the vertebrobasilar system (Figure 56-5) supply the pons, medulla, and cerebellum. Major arteries include the left and right vertebral arteries, basilar artery (formed from vertebrals), posterior inferior cerebellar artery, anterior inferior cerebellar artery, superior cerebellar artery, labyrinthine (internal auditory) artery, and posterior cerebral artery.