77
Xanthomas
Key Points
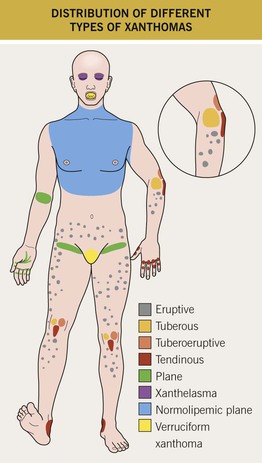
• Four major types of xanthomas: eruptive, tuberous, tendinous, and plane.
• The type of xanthoma and its anatomic location are clues to the specific lipid abnormality or associated disorder (Table 77.1; Figs. 77.1 and 77.2).
Table 77.1
Major types of hyperlipidemia.
apo, apolipoprotein; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; LPL, lipoprotein lipase; VLDL, very-low-density lipoprotein.
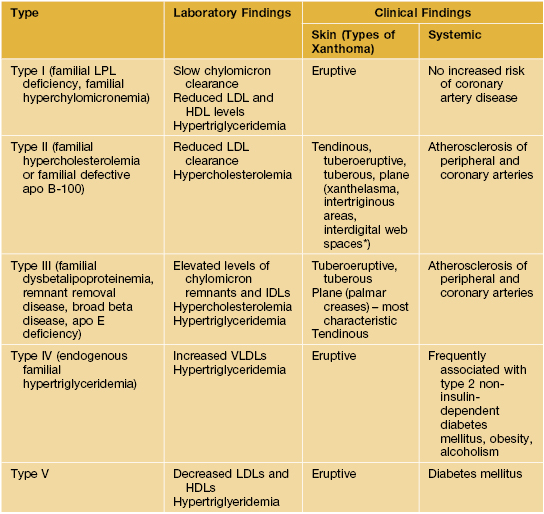
* Plane xanthomas in the interdigital web space are said to be pathognomonic for the homozygous state.
• DDx depends on the type of xanthoma (Table 77.2).
• In general, Rx is focused on correcting any underlying hyperlipidemia.
Xanthomas Associated with Hyperlipidemia
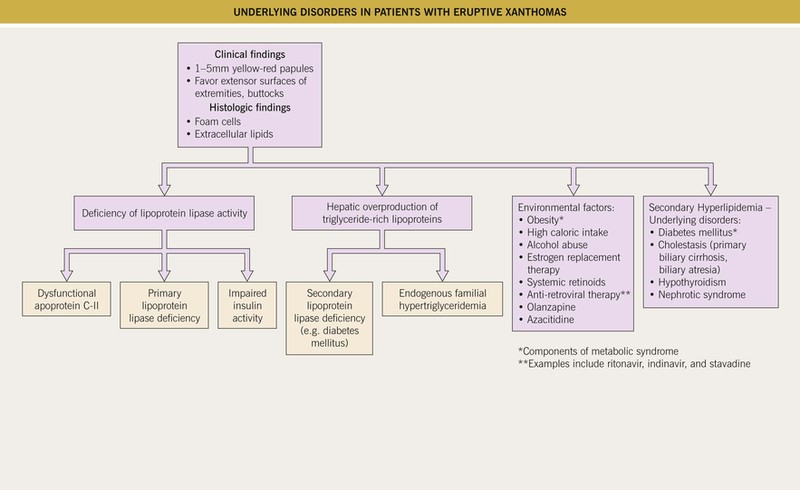
Eruptive Xanthomas
• Yellow-pink papules, 1–5 mm in diameter.
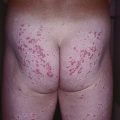
• May be widespread, but favor the extensor surfaces of the extremities and buttocks (Figs. 77.3 and 77.4).
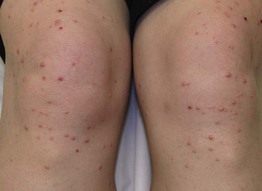
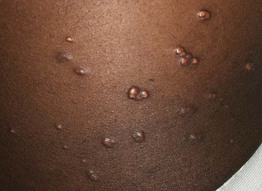
Fig. 77.3 Eruptive xanthomas due to hypertriglyceridemia. The lesions favored the extensor surface of the lower extremities, in particular the knees.
• An inflammatory halo, tenderness, and/or pruritus may be present.
• Associated with hypertriglyceridemia (often >3000–4000 mg/dl) (see Fig. 77.2).
Tuberous/Tuberoeruptive Xanthomas
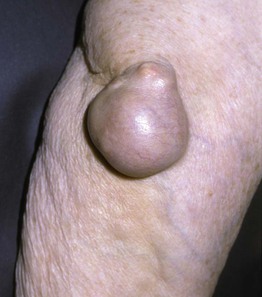
• Pink-yellow to yellow-brown papules (tuberoeruptive) or nodules (tuberous) on extensor surfaces, especially the elbows and knees (Figs. 77.5 and 77.6); tuberous xanthomas can be >3 cm in diameter.
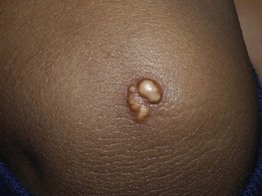
Fig. 77.5 Tuberoeruptive xanthomas on the elbow of a child with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Note the yellowish hue. Courtesy, Julie V. Schaffer, MD.
• Associated with hypercholesterolemia (type II or III hyperlipidemia).
• May be slow to regress with cholesterol-lowering agents (e.g. ‘statins’).
Tendinous Xanthomas
• Firm, smooth, skin-colored nodules due to lipid deposits within the Achilles tendons and the extensor tendons of the hands, knees, and/or elbows (Figs. 77.7 and 77.8).
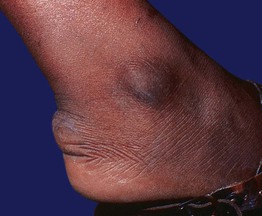
Fig. 77.7 Tendinous xanthoma. Linear swelling of the Achilles area, representing a tendinous xanthoma in a patient with dysbetalipoproteinemia. Courtesy, W. Trent Massengale, MD, and Lee T. Nesbitt, Jr., MD.
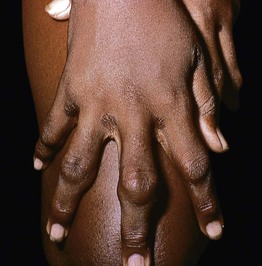
Fig. 77.8 Tendinous xanthomas of the fingers in a patient with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Note interdigital plane xanthomas of the web spaces. Courtesy, W. Trent Massengale, MD, and Lee T. Nesbitt, Jr., MD.
• Can serve as an early clue to the presence of type II hyperlipidemia.
• Rarely form as a consequence of accumulation of cholestanol (cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis) or plant sterols (β-sitosterolemia).
Plane Xanthomas and Xanthelasma
• Yellow to orange macules and patches or thin papules and plaques.
– Intertriginous – antecubital fossae, finger web spaces, and palmar creases (Figs. 77.9 and 77.10).
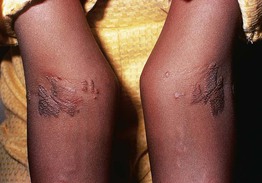
Fig. 77.9 Plane xanthomas of the antecubital fossae. This young patient had dysbetalipoproteinemia. Courtesy, W. Trent Massengale, MD, and Lee T. Nesbitt, Jr., MD.
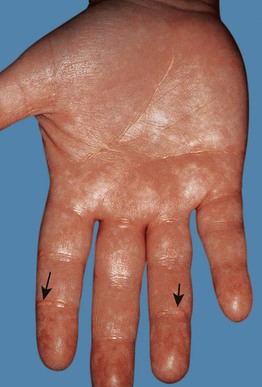
Fig. 77.10 Plane xanthomas of the palmar creases (arrows) in a patient with dysbetalipoproteinemia. They are seen in approximately two-thirds of patients with this disorder. Plane xanthomas are also seen in the setting of cholestasis, e.g. biliary atresia or primary biliary cirrhosis. Courtesy, W. Trent Massengale, MD, and Lee T. Nesbitt, Jr., MD.
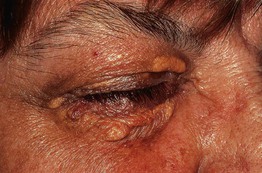
– Eyelids (xanthelasma), especially the medial aspect of the upper eyelid (Fig. 77.11).
Laboratory evaluation for suspected hyperlipidemia is outlined in Table 77.3.
Table 77.3
Laboratory evaluation of suspected hyperlipidemia.

* If elevated serum lipids, evaluate for systemic disease (see Table 77.1).
** If elevated serum alkaline phosphatase and bilirubin, evaluate for biliary disease.
Normolipemic Xanthomas
Plane Xanthomas Associated with Monoclonal Gammopathy
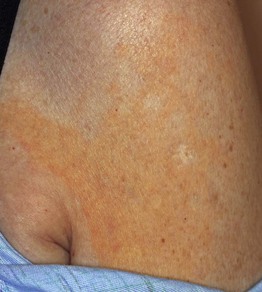
• In contrast to plane xanthomas due to hyperlipidemia, these yellow-orange patches and thin plaques are usually larger in size and have a more extensive distribution pattern; the latter often includes the trunk (Fig. 77.12).
Verruciform Xanthoma
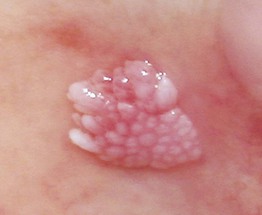
• Asymptomatic verrucous plaque, 1 to 2 cm in diameter (Fig. 77.13).
For further information see Ch. 92. From Dermatology, Third Edition.