X
xanthine an intermediate product formed during the breakdown of nucleic acids to uric acid. It is excreted in the urine.
xanthogranuloma a tumour of granulation tissue.
xanthoma a benign, fatty, fibrous tumour that develops in the subcutaneous layers of skin, usually round a tendon.
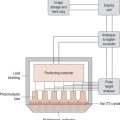
xeroradiography a method of image recording using a re-usable, electrically charged selenium plate which is sprayed with blue powder and the image is transferred to paper; was used for soft tissue imaging, including mammography. Now obsolete.
xerostomia dryness of the mouth caused by the inhibition of normal salivary secretions.
X-rays short wavelength, penetrating rays of electromagnetic spectrum, produced by electrical equipment. The word is popularly used to mean radiographs.
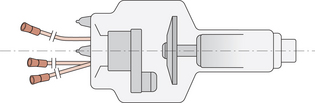
X-ray tube equipment formed by either a stationary or rotating anode and a cathode assembly in an evacuated glass envelope which is contained in an oil-filled, lead-lined housing.