T
T1 relaxation time (T1, spin-lattice relaxation time, longitudinal relaxation time) in magnetic resonance imaging, the time taken for the spins to give the energy obtained from the initial radio frequency impulse, back to the surrounding environment and return to equilibrium. It represents the time required for the longitudinal magnetization (Mz) to go from 0 to 63% of its final maximum value.
T2 relaxation time (transverse or spin-spin relaxation time) the time required for the transverse magnetization to decay to about 37% of its maximum value and is the characteristic time constant for loss of phase coherence among spins orientated at an angle to the static main magnetic field.
table incrementation time the time taken for the patient’s couch to move from one slice location to the next in sequential (non-spiral) CT scanning.
tabular grains are ‘flattened’ grains that are used only in sensitized film emulsions in screen film technology; they have a large surface area and small volume. The added dye can increase the amount of absorption resulting in a high-speed, high-resolution film with relatively low silver coating weights.
tachycardia excessively heart beat (in excess of 100 beats per minute in adults). Can occur following shock, haemorrhage, heart condition, hyperthermia or the action of certain drugs.
tachypnoea rapid, shallow respiration.
tactile relating to the sense of touch. See also taenia.
taenia coli three flat bands running the length of the large intestine and consisting of the longitudinal muscle fibres.
talipes any of a number of deformities of the foot and ankle.
talipes calcaneovalgus a condition usually caused by intrauterine posture. The foot has been fixed in an upturned position with the sole against the uterine wall. Improvement and usually complete recovery occurs with active movement after birth.
talipes equinovarus (club foot) the heel is drawn up, the foot inverted and the hindfoot adducted.
talus situated between the tibia proximally and the calcaneus distally, thus directly bearing the weight of the body. It is the second largest bone of the ankle.
tangential when a beam enters the body at an angle to avoid critical structures, for example, in the treatment technique for carcinoma of the breast.
target thin tungsten plate on the anode of an X-ray tube which, when bombarded with electrons, produces X-rays.
target angle the angle between the X-ray beam and the face of the target, the target of an X-ray tube is set at an angle to maximize the target area and minimize the geometric unsharpness.
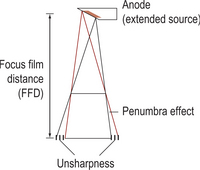
Target angle and geometric unsharpness.
From Radiographic imaging, 3rd edn, Chris Gunn, 2002, Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, with permission.
target organ the organ that a dose of radiation is calculated for.
tarsal bones short bones, the seven bones which lie between the metatarsal bones and the ankle joint in the foot.
tarsal coalition (peroneal spastic flat foot) an anomaly in which adjacent tarsal bones are fused together. Fusion may be bony or cartilaginous. The most common occurs between the calcaneus and the navicular with union across the mid-tarsal joint. Talocalcaneal coalition also occurs.
tarsometatarsal relating to the tarsal and metatarsal region.
tarsus the seven small bones of the foot. The dense connective tissue found in each eyelid, contributing to its form and support.
taste (gustation) a chemical sense closely linked with smell.
taste buds sensory receptors found on the tongue, epiglottis and pharynx.
tattoos permanent skin markings to facilitate accurate daily set up of patients during a course of radiotherapy.
TE (echo time) the time between the centre of the excitation pulse and the peak of the echo.
tears the secretion produced by the lacrimal gland. Tears contain the bactericidal enzyme lysozyme.
technetium (Tc) a radioactive element which is produced by irradiation of molybdenum, an isotope of technetium (99Tcm) is used in radionuclide imaging for brain scanning.
technetium generator used to produce radionuclides artificially by bombarding the nuclei of elements with particles. Molybdenum-98 is placed in a neutron stream and neutrons are absorbed to produce molybdenum-99 which results in the emission of gamma rays; the molybdenum decays to form technetium-99m and this is removed from the generator as sodium pertechnetate which is used for radionuclide imaging.
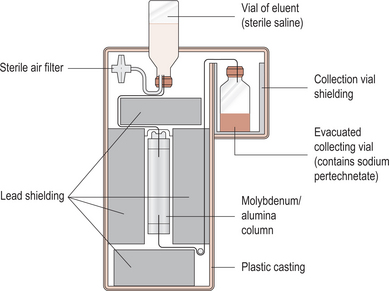
Principal features of a technetium-99m generator.
From Principles of radiological physics, 3rd edn, D T Graham, 1996, Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, with permission.
teeth the 32 adult (see figure on p. 370) or 20 childhood teeth lie in the alveolar ridge of the mandible and the maxilla.
teething lay term for the discomfort during the eruption of the primary dentition in babies.
tegument the skin or covering of the body.
telangiectasia the dilatation of thin-walled, superficial blood vessels.
teleisotope unit equipment containing a radioactive source producing X or γ rays for teletherapy.
telemetry the electronic transmission of data including clinical measurement between distant sites. May be used for cardiac monitoring.
teleradiology the electronic transfer of images and reports to remote centres, for example, general practitioner practices.
Teletex the sending of documents at high speed electronically.
Teletext the non-interactive public information service on television; BBC transmits Ceefax, the ITA transmits Oracle.
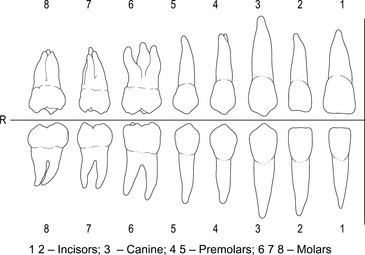
Permanent teeth right upper and lower quadrants.
From Bones and joints, 4th edn, Chris Gunn, 2002, Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, with permission.
teletherapy when an external source of radiation (X-rays or γ-rays) is directed to a tumour to give the maximum radiation dose to the tumour and the minimum dose to the surrounding healthy tissue.
temple that part of the head situated between the outer angle of the eye and the top of the pinna.
temporal relating to the temple.
temporal bones one on each side of the skull below the parietal bone, containing the middle ear.
temporomandibular relating to the temporal region or bone, and the lower jaw, such as the joint between the temporal bone and mandible.
temporomandibular joint (TMJ) syndrome pain in the region of the temporomandibular joint frequently caused by malocclusion of the teeth, resulting in malposition of the condylar heads in the joint and abnormal muscle activity, and by bruxism.
tendinitis inflammation of a tendon.
tendon a band of white, fibrous connective tissue that joins muscle to bone.
tenesmus a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bowel.
tennis elbow a painful condition affecting the extensor muscle of the forearm at the attachment of the lateral epicondyle of the humerus.
tension pneumothorax a valve-like wound or tear in the lung allows air to enter the pleural cavity with each inspiration, but not to escape on expiration, thus progressively increasing intrathoracic pressure and constituting an acute medical emergency. Signs are of hyperinflation, midline shift and increasing respiratory distress.
tenosynovitis inflammation of the thin synovial lining of a tendon sheath, as distinct from its outer fibrous sheath. It may be caused by mechanical irritation or by bacterial infection.
tenth-value thickness the thickness of a substance that will transmit exactly one-tenth of the intensity of radiation falling on it.
tentorium cerebelli a fold of dura mater between the cerebellum and cerebrum. Damage during birth may result in intracranial bleeding.
teratoma commonly a tumour of the testis or ovary. It is of embryonic origin and usually malignant. Some testicular tumours have both seminoma and teratoma components. The cure rate for germ cell tumours has increased 10-fold with use of platinum-based chemotherapy.
termination of pregnancy (TOP) see abortion.
tesla a unit for measuring the strength of a magnetic field. A magnetic flux density of 1 tesla exists if the force on a 1 metre long straight wire, carrying a current of 1 ampere, is 1 Newton and the wire is placed at right angles to the direction of magnetic flux.
testis a male gonad. One of the two glandular structures contained in the scrotum of the male; they produce spermatozoa and the male sex hormones. undescended testis the testis remains within the bony pelvis or inguinal canal. See also cryptorchism.
testosterone the major androgen, a steroid hormone produced by the testes. It is responsible for the development of the male secondary sexual characteristics and reproductive functioning.
tetradactylous having four digits on each limb.
tetraplegia (quadriplegia) paralysis of all four limbs.
TFT (Thin Film Transistor) the technology used in laptop screens.
thalamus a collection of grey matter at the base of the cerebrum. Sensory impulses from the whole body pass through the thalamus en route to the cerebral cortex.
thalassaemia an inherited disease due to abnormal haemoglobin causing haemolytic anaemias.
thallium activator luminescent centres where about 10–15% of the energy deposited is converted to light energy. Used with sodium iodide as a scintillator crystal.
theca an enveloping sheath, especially of a tendon, or the dura mater.
thenar relating to the palm (hand) and the sole (foot). thenar eminence the palmar eminence below the thumb.
therapeutic ablation a dose of radiation given to destroy harmful tissue.
therapeutic abortion see abortion.
therapy verification film an X-ray film shielded by a lead sheet, which is placed behind the patient during one treatment to verify the area being treated. See also portal imaging.
thermal capacity the heat energy in joules which is required to raise the temperature of the body by 1 kelvin unit.
thermal effect of ultrasound the heating of tissue by breaking down the air bubbles and cavities in the tissues.
thermionic emission the process of releasing electrons from an emitter.
thermionic emitter a substance that releases electrons when heated.
thermographic printing utilizes a film containing silver behenate that when exposed to light the resultant heat activates the silver and produces the image. See also photo-thermographic printing.
thermography an investigation that detects minute temperature differences over different body areas by use of an infrared thermograph that is sensitive to radiant heat. The uses include the study of blood flow and detection of cancers, such as breast cancer.
thermoluminescence a substance that when irradiated stores energy, when heated photons of light are produced in proportion to the energy stored.
thermoluminescent dosimetry small disks containing lithium fluoride can be attached to a patient’s body, the disks are then heated and the amount of light produced is compared to a standard to ascertain the amount of radiation received by the patient. A badge containing two lithium fluoride disks worn by radiation workers to estimate the radiation dose they have received to the skin and the whole body dose.
thermometer equipment for measuring temperature.
thermostat equipment for controlling temperature.
thoracic associated with the thorax.
thoracic cage framework of bones that protects the thoracic structures and provides muscle attachments.
thoracic duct a channel conveying lymph (chyle) from the cisterna chyli in the abdomen to the left subclavian vein. thoracic inlet syndrome (cervical rib) a supernumerary rib in the cervical region, which may present no symptoms or it may press on nerves of the brachial plexus.
throracic vertebrae the 12 bones of the spine that articulate with the ribs.
Thoraeus filter see compound filters.
threatened miscarriage loss of pregnancy characterized by slight vaginal bleeding while the cervix remains closed.
three-dimensional reconstruction a digitally produced image that shows the depth, height and width of an object or objects.
three-dimensional ultrasound the creation of a computerized, reconstructed ultrasound image which represents the anatomical structure being investigated, for example, used to visualize the fetal face and the adult heart valves.
three phase a form of alternating current formed by three phases of current and voltage to enable more power to be supplied for static X-ray equipment. The line voltage is 398 volts in a three-phase supply.
threshold the point at which a film first shows a reaction to exposure. See also sensitometry.
thrombin the active enzyme formed from prothrombin. Thrombin is formed during both the extrinsic and intrinsic coagulation pathways; it converts fibrinogen to fibrin. See also coagulation, prothrombin, thromboplastin.
thrombocyte (platelet) plays a part in the clotting of blood. See also blood.
thrombocytopenia a reduction in the number of platelets in the blood.
thrombosis the unwanted, intravascular formation of a blood clot. See also coronary thrombosis, deep-vein thrombosis.
thromboxanes regulatory lipids derived from arachidonic acid (fatty acid). They are released from platelets and cause vasospasm and platelet aggregation during platelet plug formation. See also haemostasis.
thymocytes cells found in the dense lymphoid tissue of the thymus gland.
thymoma a tumour arising in the thymus.
thymopoietin peptide hormone secreted by the thymus gland.
thymosin peptide hormone secreted by the thymus gland.
thymus a lymphoid gland lying behind the sternum and extending upward as far as the thyroid gland. It is well developed in infancy and attains maximum size during puberty; and then the lymphatic tissue is replaced by fatty tissue. It produces thymic hormones (thymosins and thymopoietin) that ensure the proper development of T lymphocytes. The autoimmune condition myasthenia gravis results from pathology of the thymus gland.
thyratron a gas-filled device allowing current to flow in one direction only, containing an anode, a cathode and a grid. A negative potential on the grid can stop the electron flow and therefore can act as an on–off switch.
thyristor a solid-state replacement for a thyraton which can act as an electric switch.
thyroglobulin a colloid stored in the thyroid follicles used for the production of thyroxine.
thyroglossal associated with the thyroid gland and the tongue.
thyroglossal cyst a retention cyst caused by blockage of the thyroglossal duct: it appears on one or other side of the neck.
thyroglossal duct the embryonic passage from the thyroid gland to the back of the tongue. In this area thyroglossal cyst or fistula can occur.
thyroid associated with the thyroid gland.
thyroid antibody test the presence and severity of autoimmune thyroid disease is diagnosed by the levels of thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins in the blood.
thyroid gland a two-lobed endocrine gland, either side of the trachea. It secretes three hormones: triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) under pituitary control, which stimulate metabolism, and calcitonin from the follicular cells, which helps to regulate calcium and phosphate homeostasis. See also hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism.
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) pituitary hormone that stimulates the secretion of the thyroid hormones thyroxine and triiodothyronine. thyroid-stimulating hormone assay radioimmunoassay of the level of thyroid stimulating hormone in the serum. Used in the diagnosis of hypothyroidism.
thyrotoxicosis a disease of the thyroid gland resulting in the overproduction of thyroid hormones.
thyrotrophic describes any substance that stimulates the thyroid gland, for example, thyrotrophin (thyroid-stimulating hormone, TSH) secreted by the anterior pituitary gland.
thyroxine (T4) the principal hormone of the thyroid gland, it contains four atoms of iodine. It is essential for metabolism and development. Used in the treatment of hypothyroidism. See also triiodothyronine.
TI (inversion time) the time after the middle of a 180° radio frequency inverting pulse and the inversion recovery sequence to the middle of the 90° read pulse which monitors the amount of longitudinal magnetization.
tibia the shin bone; the larger of the two bones in the lower part of the leg; it articulates with the femur, fibula and talus.
tibial relating to the tibia, as in the artery and vein.
tibiofibular associated with the tibia and the fibula.
tidal air/volume (TV) the volume of air that passes in and out of the lungs in normal breathing.
tied numbers results of the same value.
TIFF (Tif, Tagged Information File Format) a graphics or picture computer file used for photographs. The file is not compressed and therefore the picture quality is good but the file size is very large.
time bomb a device used by some software suppliers to prevent piracy of programmes.
time gain control (TGC) a method of compensating for the attenuation of ultrasound as it passes through the tissues so that the deep echoes appear equally as reflective as superficial echoes.
time-of-flight angiography a technique in magnetic resonance imaging to enhance the blood flowing into a slice by ensuring that the blood does not become saturated by previous radio-frequency pulses.
time scale sensitometry a method of producing a characteristic curve by keeping all exposure factors constant, covering the film with a piece of lead rubber and exposing the film a number of times, moving the rubber to reveal more film for each exposure or producing darkened strips on the film by doubling the exposure time for each subsequent step.
tinnitus ringing or buzzing sound in the ears.
tissue a collection of cells or fibres of similar function, forming a structure, often in a background connective tissue.
tissue–air ratio the ratio of the dose rate at a point in the patient to that at the same point in air without the patient being present.
tissue compensator an attenuator placed in the primary beam during radiotherapy of irregular parts of the body, to maintain the dose distribution and the skin sparing effect.
tissue Doppler imaging the analysis of the Doppler signals from a moving structure, for example, the myocardium of the heart, exhibiting a large amplitude but low frequency.
tissue equivalent material a substance that interacts with ionizing radiation in the same way that a patient would interact with the radiation, it therefore has the same scattering and absorption properties of human tissue.
tissue harmonic imaging in ultrasound, using the secondary frequencies sent back to the probe by tissue or contrast media such as air bubbles to improve contrast and spatial resolution in larger subjects as the far field is improved. See also contrast, spatial resolution.
tissue phantom ratio the ratio of the axis dose rate at a depth d in a phantom to the axis dose rate at a reference depth in the same phantom.
TNM classification a description of the primary tumour, the nodal spread and the distant metastases which summarizes the extent of the malignancy in a patient (see box on p. 376).
token part of a computer network that indicates if a node can write to the network.
| T1–3 | Generally based on the size and/or extent of the primary |
| T4 | The most advanced local disease, often with invasion of adjacent structures |
| N0 | No nodes palpable |
| N1 | Mobile nodes on the same side as the primary |
| N1a | Nodes not considered to contain tumour |
| N1b | Nodes considered to contain tumour |
| N2 | Mobile nodes on the opposite side (N2a and N2b as above) |
| N3 | Fixed, involved nodes |
| M0 | No evidence of distant metastasis |
| M1 | Distant metastasis present |
token ring the circular computer network which carries the tokens enabling them to signal to the nodes.
tomography a radiographic technique to produce a sharp plane within the body by blurring the structures above and below the image by moving the X-ray tube and film around a fulcrum.
tone a quality of sound, or the normal, healthy state of tension.
tongue the mobile muscular organ situated in the mouth; it is concerned with mastication, swallowing, taste and speech.
tonsillopharyngeal relating to the tonsils and pharynx.
tonsils small aggregations of lymphoid tissue located around the pharynx. Forming part of body defences they contain macrophages and are a site for lymphocyte proliferation. There are lingual tonsils under the tongue, nasopharyngeal tonsils located on the posterior wall of the nasopharynx (called adenoids when enlarged) and the palatine tonsils found in the oropharynx, one on each side in the fauces between the palatine arch. See also Waldeyer’s ring.
tooth hard calcified structures in the mouth used for masticating food. Composed largely of dentine with enamel covering the crown and cementum covering the root surface. The pulp occupies the cavity at the core of the crown (pulp chamber) and the channel running along the length of the root (root canal). The primary (deciduous, milk) and secondary (permanent, adult) dentitions consist of 20 and 32 teeth, respectively.
tophus a small, hard concretion forming on the ear lobe, on the joints of the phalanges, etc. in gout.
topography a description of the regions of the body.
torsion the process of twisting.
total body imaging the radionuclide imaging of the whole of the body to detect metastatic spread from carcinomas.
total body irradiation (TBI) the aim of the treatment is to deliver a uniform dose to the whole body, using megavoltage photons and tissue compensation. Used prior to bone marrow transplants.
total efficiency the ability of a phosphor to produce light; it is dependent of its ability to absorb energy and convert it to light.
total linear attenuation coefficient (μ) the fraction of the X-rays removed from a beam per unit thickness of the attenuating material.
total mass attenuation coefficient graphs the sum of the individual mass attenuation processes, that is: energy spectrum of the X-ray beam, density and atomic number of the tissue passed through and the separation of the patient, plotted as a graph of energy against incidence.
total quality management (TQM) a whole organization approach to quality where all employees are expected to take responsibility for quality. It aims to ensure quality at every interface and improve effectiveness and flexibility throughout the organization.
total scanning time with multi-slice CT this is commonly reduced to the time of data acquisition as large volumes can be scanned in a single breath hold.
tourniquet equipment for compressing the blood vessels in a limb for the control of bleeding or the removal of blood from a vein.
trabeculae the septa or fibrous bands projecting into the interior of an organ, for example, the spleen.
tracer a substance or instrument used to gain information. Radioactive tracers are used in the diagnosis of some cancers, for example, brain, and thyroid disease.
trachea (windpipe) the fibrocartilaginous tube lined with ciliated mucosa passing from the larynx to the bronchi. It is about 115mm long and about 25mm wide.
tracheobronchial associated with the trachea and the bronchi.
tracheo-oesophageal associated with the trachea and the oesophagus.
tracheo-oesophageal fistula usually occurs in conjunction with esophageal atresia. The fistula usually connects the distal oesophagus to the trachea.
tracheostomy surgical opening between the front of the neck and the trachea to create an artificial airway. It is kept open with a tracheostomy tube.
tracheotomy a vertical slit in the anterior wall of the trachea at the level of the third and fourth cartilaginous rings.
traction a drawing or pulling on the patient’s body to overcome muscle spasm and to reduce or prevent deformity. A steady pulling exerted on some part (limb or head) by means of weights, pulleys and cords in conjunction with a variety of splints or frames. skeletal traction applied on a bone by means of a wire or pin passed through the lower fragment. skin traction or extension involves the application of weights to foam or extension plaster attached to the skin. See also beam, Braun’s frame, hoop traction, halopelvic traction.
tragus the projection in front of the external auditory meatus.
transabdominal through the abdomen.
transamniotic through the amniotic membrane and fluid, as a transamniotic transfusion of the fetus for haemolytic disease.
transcription first stage in protein synthesis where genetic information is transferred from DNA to mRNA. See also translation.
transducer (probe) device that converts one form of energy into another to facilitate its electrical transmission. A hand-held instrument composed of multiple elements of piezo-electric material each with its own electrodes, used in ultrasound imaging.
transferrin a protein that binds iron for safe transport in the blood.
transfer tubes tubes used to connect catheters to an afterloading machine.
transformer is a piece of equipment that either raises or lowers electric current in a circuit, a step-up transformer raises current, a step-down transformer reduces current.
transformer efficiency is the ratio of output power to input power of the transformer.
transfusion the introduction of fluid into the tissue or into a blood vessel. See also blood transfusion, intrauterine transfusion.
transhiatal across the opening.
transistor a solid-state replacement of a diode which consists of an emitter, a base and a collector; it allows current to flow in one direction only.
transjugular intrahepatic portasystemic stent shunting (TIPSS) a stent placed between the hepatic portal vein and the hepatic vein in the liver to reduce hepatic portal pressure by providing a shunt between the hepatic portal and systemic circulations. Performed to prevent further bleeding from oesophageal varices.
translation the second stage of protein synthesis in which tRNA and rRNA translate the base sequence required to make a new protein. The movement of a body or system in such a way that all points are moved in a parallel direction through equal distances. See also transcription.
translation table a method of modifying digital pixel values to adjust the contrast of a CT image; the table is loaded into the video interface of the display system.
translational movement along a path.
translumbar through the lumbar region. Route used for injecting aorta prior to aortography.
translumbar aortography the radiographic investigation of the aorta and its major branches by the direct injection of a contrast agent into the abdominal aorta.
transluminal angioplasty a method of dilating arterial narrowing by passing a guide wire through the lesion and then a catheter over the guidewire to dilate the artery.
transmethylation a process in which methyl groups are donated by amino acids and transferred to other compounds.
transmitted when photons pass through an object without interacting with it. See also transmitted light, transmitted beam.
transmitted beam the radiation leaving an object.
transmitted light the light seen by the viewer after it has passed through an X-ray film, used to calculate the opacity of the film. See also opacity.
transmitter bandwidth the range of frequencies within a radiofrequency pulse delivered by the transmitter in magnetic resonance imaging.
transoesophageal echo a tiny ultrasound probe on the end of an endoscope, used in cardiac work to examine the heart valves.
transonic a material that allows the passage of a beam of ultrasound without any reflection back to the transducer.
transport system the part of an automatic film processor that moves the film through the system and comprises a number of various diameter. See also hard roller, soft rollers.
transrectal through the rectum.
transrectal ultrasonography (TRUS) method used to perform an ultrasound examination of the prostate.
transthoracic across or through the chest, as in transthoracic needle biopsy of a lung mass.
transthoracic echo the examination of the heart through the thorax with the probe in the parasternal and apical positions.
transvaginal probe an ultrasound probe that is inserted into the vagina to allow imaging of the cervix, fallopian tubes, uterus, ovaries and related structures.
transverse fracture a horizontal break in a bone.
transverse plane a horizontal plane that divides the body into superior and inferior parts, it lies at right angles to the median sagittal plane. Also called the horizontal plane.
transverse relaxation time (T2 or spin-spin relaxation time) the time required for the transverse magnetization to decay to about 37% of its maximum value and is the characteristic time constant for loss of phase coherence among spins orientated at an angle to the static main magnetic field.
trapezium one of the eight carpal bones of the wrist; it lies under the base of the thumb.
trapezius large muscle of the neck and thorax.
trapezoid one of the eight carpal bones of the wrist.
traumatic occlusion any malocclusion resulting in damage to the teeth or periodontal tissues.
treated volume the volume of tissue inside an isodose surface that is appropriate to receive a radiation dose during radiotherapy treatment.
Trendelenburg’s position lying on an operating or examination table, where the patient is tilted so that the feet are higher than the head.
triceps the three-headed muscle on the back of the upper arm.
tricuspid having three cusps. tricuspid valve the right atrioventricular valve of the heart.
trigeminal triple; separating into three sections, for example, the trigeminal nerve, the fifth cranial nerve, which has three branches, ophthalmic, maxillary and mandibular.
triglyceride (triacylglycerol) a lipid with three fatty acids and a glycerol molecule. The major source of stored energy in the body.
trigone a triangular area, especially applied to the bladder base, bounded by the ureteral openings at the back and the urethral opening at the front.
triiodothyronine (T3) a thyroid hormone that plays a part in maintaining the body’s metabolic processes. It contains three iodine atoms and is formed from thyroxine.
trimester a period of 3 months. Applied especially to pregnancy.
triode a device allowing current to flow in one direction only, containing an anode, a cathode and a grid in a vacuum, a negative potential on the grid can stop the electron flow and therefore can act as an on–off switch.
triploidy a fetus with three sets of chromosomes instead of two, usually abort spontaneously in the first trimester.
triquetral one of the eight carpal bones of the wrist.
tritiated water when one hydrogen atom is replaced with tritium, an isotope of hydrogen-3. It is used to study electrolyte and water absorption problems.
Triton tumour a rare, benign tumour of the trigeminal nerve.
trocar a pointed rod which fits inside a cannula used for the introduction of a guide wire/catheter into a vessel. See also guidewire.
trochanters two processes, the larger one (greater trochanter) on the outer, the other (lesser trochanter) on the inner side of the femur between the neck and shaft; they provide attachment for muscles.
trochlea any part which is like a pulley in structure or function.
trochlear nerves the fourth pair of cranial nerves. They innervate the muscle that moves the eyeball in an outwards and downward direction.
trophic associated with nutrition.
tropomyosin one of the proteins located in the thin filaments of a muscle myofibril.
troponin one of the proteins present in a muscle myofibril.
true pelvis that part of the pelvis below the brim.
trypsin active proteolytic enzyme. See also trypsinogen.
trypsinogen inactive form of trypsin secreted by the pancreas. Activated by enterokinase (enteropeptidase).
t-test a statistical test used to compare two sets of results using a t-test table. If the results are equal to or greater than the value on the tables the results are significant.
tubal abortion see tubal miscarriage.
tubal ligation tying of both uterine (fallopian) tubes as a means of sterilization. tubal pregnancy. See also ectopic pregnancy.
tubal miscarriage an ectopic pregnancy that dies and is expelled from the fimbriated end of the uterine (fallopian) tube.
tube insert an evacuated tube which contains a negative cathode, which when heated produces a stream of electrons, and a positive anode or target that when bombarded by electrons produces a beam of radiation.
tubercle a small rounded prominence, usually on bone. The specific lesion produced by Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
tuberculide, tuberculid a small lump. Metastatic manifestation of tuberculosis, producing a skin lesion, for example, papulonecrotic tuberculide, rosacea-like tuberculide.
tuberculoma a caseous tubercle, usually large, its size suggesting a tumour.
tuberculosis (TB) chronic granulomatous infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (human type). Incidence, especially of multidrug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB), is increasing, in Asia and Africa, in association with poverty and homelessness, and in those who are immunocompromised. See also bovine tuberculosis.
tubo-ovarian associated with or involving both tube and ovary, for example, tubo-ovarian abscess.
tumor swelling: one of the five classic local signs and symptoms of inflammation, the others are calor, dolor, loss of function and rubor.
tumour a swelling. A mass of abnormal tissue which resembles the normal tissues in structure, but which fulfils no useful function and which grows at the expense of the body. Benign, simple or innocent tumours are encapsulated, do not infiltrate adjacent tissue or cause metastases and are unlikely to recur if removed. malignant tumour not encapsulated, infiltrates adjacent tissue and causes metastases. See also cancer.
tumour lysis syndrome (TLS) may occur following intensive chemotherapy treatment for some haematological malignancies. As cancer cells are destroyed there is release of cellular breakdown products. This results in metabolic problems (for example, hyperkalaemia, hypocalcaemia, hyperuricaemia, hyperphosphataemia) that may cause renal failure and possibly circulatory and respiratory failure.
tumour marker chemical detected in the serum that may be associated with a specific cancer or sometimes non-malignant diseases. They include: alphafetoprotein, CA-125, carcinoembryonic antigen and prostate specific antigen. They may be used for monitoring disease progress and efficacy of treatment, but are of limited use for population screening.
tumour necrosis factor (TNF) a cytokine that is toxic to cancer cells and activates other leucocytes. It causes profound metabolic effects that include inflammatory responses, pyrexia and weight loss.
tumourocidal dose a dose of radiation capable of destroying a tumour.
tumour suppressor gene a gene that, when it is absent or non-functioning in a cell, permits the abnormal development of the cell.
tunica a lining membrane; a coat.
tunica adventitia the outer coat of an artery or vein.
tunica intima the lining of an artery or vein.
tunica media the middle muscular coat of an artery or vein.
turbinate shaped like an inverted cone.
turbinate bones three on either side forming the lateral nasal walls. Also called nasal conchae.
Turner’s syndrome the absence of one X chromosome in women, resulting in ovarian failure, webbing of the neck, short metacarpals.
turnkey a term used to denote a company which will provide all the necessary software and hardware and back-up support to enable the user to ‘turn a key’ and use the equipment.
turtle a wheeled mechanical device, used for graphics, attached to a computer via cables.
two-tailed hypothesis a theory which predicts an outcome but does not state the direction it will take.
tylosis palmaris a scaling condition of the palms of the hands.
tylosis plantaris a scaling condition of the soles of the feet.
tympanic associated with the tympanum.
tympanic membrane (eardrum) separates the outer from the middle ear.
tympanic thermometer accurate body temperature recorded by means of an electronic probe introduced into the external auditory canal.
tympanum the cavity of the middle ear.
type I error (α error) in research, rejecting a null hypothesis that is true.
type II error (β error) in research, not rejecting a null hypothesis that is false.