G
gag the reflex contraction of the pharyngeal muscles and elevation of the palate when the soft palate or posterior pharynx is stimulated. An instrument used to keep the mouth open.
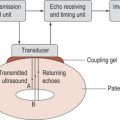
gain (swept gain) the amount of sound received back by an ultrasonic transducer, increasing the gain visualizes the organs further away from the probe.
gain correction a factor used to compensate for the variation in electrical signal for an absorbed intensity of radiation between detector channels in CT scanning.
gait a manner or style of walking. ataxic gait an incoordinate or abnormal gait. cerebellar gait reeling, staggering, lurching. scissors gait one in which the legs cross each other in progressing. spastic gait stiff, shuffling, the legs being held together. tabetic gait the foot is raised high then brought down suddenly, the whole foot striking the ground.
Galeazzi fracture–dislocation fracture of the distal radius with dislocation of the radioulnar joint.
gallbladder a pear-shaped bag on the undersurface of the liver, it concentrates and stores bile.
gallows traction see Bryant’s ‘gallows’ traction.
gallstones concentrations of cholesterol or other constituents of bile formed within the gallbladder or bile ducts; many small stones or one large stone may be formed.
galvanometer an instrument for measuring an electrical current.
gamete a female or male reproductive cell with the haploid (n) chromosome number; oocyte or spermatazoon.
gametogenesis production of gametes (oocytes and spermatozoa). See also oogenesis, spermatogenesis.
gamma the measure of the slope of a characteristic curve, the higher the gamma the higher the contrast on the radiographic film. See also average gradient, sensitometry.
gamma camera a large, stationery, scintillation counter, which records the activity over the whole field at the same time. Used to detect pathologies where the physiology of the structure is changed. The image is viewed on a cathode ray tube (see figure on p. 172).
gamma decay the emission of gamma rays from a nucleus which has excess energy.
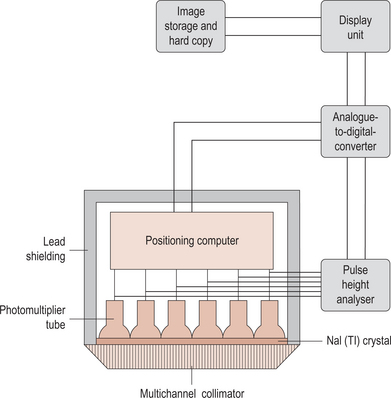
The main components of a gamma camera and its associated circuitry.
From Principles of radiological physics, 3rd edn, D T Graham, 1996, Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, with permission.
gamma encephalography a small dose of isotope is given which is concentrated in many cerebral tumours, the pattern of radioactivity is then measured.
gamma knife a method of treating tumours that are difficult to excise surgically by using multiple beams of radiation, focused at the tumour over a number of days.
gamma rays short wavelength, penetrating rays of the electromagnetic spectrum produced by disintegration of the atomic nuclei of radioactive elements.
ganglion a mass of nerve cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system such as those of the autonomic nervous system and those ganglia containing the cell bodies of sensory nerves. Localized cyst-like swelling near a tendon, sheath or joint. Sometimes occurs on the back of the wrist due to strain such as excessive use of a word processor. See also gasserian ganglion.
gangrene death of part of the tissues of the body. Usually the results of inadequate blood supply, but occasionally due to direct injury (traumatic gangrene) or infection (e.g. gas gangrene). Deficient blood supply may result from pressure on blood vessels (e.g. tourniquets, tight bandages and swelling of a limb); from obstruction within healthy vessels (e.g. arterial embolism, frostbite where the capillaries become blocked); from spasm of the vessel wall (e.g. ergot poisoning); or from thrombosis due to disease of the vessel wall (e.g. arteriosclerosis in arteries, phlebitis in veins). See also dry gangrene, moist gangrene.
gantry a structure or support, in CT scanning a structure in which the X-ray tube, detectors and associated electronics are housed.
Gardner’s syndrome familial polyposis of the large bowel, with fibrous dysplasia of the skull, extra teeth, osteomas, fibroma and epidermal cysts.
gargoylism congenital disorder of mucopolysaccharide metabolism with recessive or sex-linked inheritance. The polysaccarides chondroitin sulphate ‘B’ and heparitin sulphate are excreted in the urine. Characterized by skeletal abnormalities, coarse features, enlarged liver and spleen, learning disability.
gas one of the three states of matter, the others being solid and liquid. A gas retains neither shape nor volume when released.
gas gangrene a serious wound infection caused by anaerobic organisms of the genus Clostridium, especially Clostridium perfringens (welchii), a soil microbe often present in the intestine of humans and animals. See also gangrene.
gasserian ganglion a mass of nerve cell bodies deeply situated within the skull, on the sensory root of the fifth cranial nerve. It is involved in trigeminal neuralgia.
gas transfer factor measurement of the lung’s ability to exchange gases. Particularly useful in the diagnosis and surveillance of interstitial lung diseases, sarcoidosis and emphysema.
gastrectomy surgical removal of all or part of the stomach.
gastrin a hormone secreted by the gastric mucosa on entry of food, which causes further gastric secretion.
gastritis inflammation of the stomach.
gastrocnemius the large two-headed muscle of the calf.
gastrocolic associated with the stomach and the colon.
gastrocolic reflex sensory stimulus when food enters the stomach, resulting in strong peristaltic waves in the colon.
gastroduodenal associated with the stomach and the duodenum.
gastroenteritis inflammation of the stomach and intestines.
gastrointestinal associated with the stomach and intestine.
gastro-oesophageal associated with the stomach and oesophagus.
gastro-oesophageal reflux disease caused by passage of gastric contents into the oesophagus, typically causes heartburn, complications include ulceration, strictures and Barrett’s oesophagus.
gastrophrenic associated with the stomach and diaphragm.
gastroschisis a portion of bowel appearing through a defect in the abdominal wall, near the umbilicus.
gastrulation in early embryonic development the immense changes occurring as the blastocyst becomes the gastrula. The three primary germ layers are formed and cells move to their appointed locations in readiness for the start of structural development.
gate a gate performs a single logical operation when subjected to a number of inputs. It is the basis of all computer operations.
Gauss an electromagnetic unit of magnetic induction now replaced by the Tesla (1 Tesla = 10000 Gauss).
Geiger counter a device for detecting and registering radioactivity.
Geiger–Muller counter a device for measuring radiation dosage, it has a glass envelope containing argon, a positively charged central electrode and a negatively charged mesh cylinder.
Geiger–Muller tube a radiation detector using an ionization chamber, used in personnel dosimetry and to detect the movement of gamma ray sources in brachytherapy.
gelatine a complex compound used in the emulsion layer of a radiographic film to allow the absorption of water during chemical processing, keeping the silver halide grains in suspension, during manufacture to allow the grains to grow and bind the emulsion to the base of the film, it assists with forming and stabilizing the image during and after exposure to electromagnetic radiation.
gemellus muscles muscles arising from the ischium.
general anaesthetic a drug which causes unconsciousness by inhalation or injection of the drug.
General Medical Council (GMC) the statutory body that regulates the practice of medicine in the UK. It oversees professional quality and continuing professional development standards for professional practice, discipline and conduct. It is responsible for the establishment and maintenance of a professional register for all doctors working in the UK, and has the power to remove individuals from the register in cases of professional misconduct, or in some cases to restrict practice or order specific training.
General Medical Services the medical services provided by family doctors.
general sales list medicines drugs that can be sold in shops and supermarkets under specific conditions.
genital associated with the organs of reproduction.
genitalia the external organs of reproduction.
genitocrural associated with the genital area and the legs.
genitourinary associated with the reproductive and urinary organs.
genitourinary medicine (GUM) specialty concerned with the management of sexually transmitted infections and other medical conditions of the genital tract.
genu valgum (bow legs) abnormal outward curving of the legs resulting in separation of the knees.
genu varum (knock knee) abnormal incurving of the legs so that there is a gap between the feet when the knees are in contact.
geometric unsharpness blurring of a radiographic image due to the size of the focal spot on the anode, and can be reduced by increasing the focus to film distance and the object film distance.
germicide any agent capable of killing microorganisms (germs).
gestation sac volume the volume of the sac which contains the fetus during pregnancy. Usually measured at 3 to 6 weeks using ultrasound.
ghosting in ultrasound a mirror image which is produced when the gain is too high or when imaging objects with high acoustic reflections.
giant cell an abnormally large tissue cell.
GIF (Graphics Interchange Format) a compressed computer graphics file.
gigabyte one billion (109) bytes, a measure of the size of a computer hard disk and denotes the quantity of information that can be stored on the system.
gigantism abnormal overgrowth, especially in height, due to excess growth hormone in childhood prior to fusion of the epiphyses. Almost always due to a pituitary tumour.
gingiva the keratinized oral mucosa immediately surrounding a tooth, i.e. the gum.
gingival sulcus the pouch (invagination) made by the gingiva as it joins with the tooth surface.
gingivitis inflammation of the gums caused by dental plaque.
girdle usually a bony structure of oval shape such as the shoulder and pelvic girdles.
gland an organ or structure capable of making an internal or external secretion. See also endocrine, exocrine.
glans the bulbous termination of the clitoris and penis.
glass plasma display the technology used for early flat screen computer monitors comprising of neon gas cells between two electrodes. When the electrodes are activated the gas glows therefore forming an image.
Gleason score (grade) a method of grading prostate cancer based on the extent that tumour cells are arranged in recognizable glandular structures.
glenohumeral associated with the glenoid cavity of scapula and the humerus.
glenoid a cavity on the scapula into which the head of the humerus fits to form the shoulder joint.
glenoid labrum fibrocartilagenous rim round the glenoid to deepen the cavity.
gliding one articular surface sliding smoothly over another.
glioblastoma multiforme a malignant, rapidly growing tumour of the cerebrum or the spinal cord.
glioma a malignant tumour composed of neuroglial cells affecting the brain and spinal cord, typically an astrocytoma or oligodendroglioma. See also astrocyte, oligodendrocyte.
gliomyoma a tumour of nerve and muscle tissue.
globular grains the type of grains found in some radiographic film emulsions and have the characteristic that the light-absorbing ability of the grain depends only on its volume, they are used in blue-sensitive or monochromatic systems.
globulins a large group of proteins. Those in the plasma are classified as alpha and beta, which are concerned with substance transport, and gamma, which provides protection against infection. The gamma globulins comprise the immunoglobulins A, D, E, G and M.
globus pallidus literally pale globe; a mass of motor grey matter situated deep within the cerebral hemispheres, lateral to the thalamus. Part of the basal nuclei.
glomerular filtration rate (GFR) the volume of plasma filtered by the kidneys in 1 minute. It is usually about 120mL per minute.
glomerulus a coil of capillaries formed from a wide-bore afferent arteriole. It lies within the invaginated blind end of the renal tubule. Together with the renal tubule it forms a nephron. Part of the filtration membrane involved in the production of urine.
glossopharyngeal associated with the tongue and pharynx. The ninth pair of cranial nerves, they supply the tongue and pharynx.
glottis the opening between the abducted vocal folds in the larynx. It allows air to enter the respiratory tract and is involved in voice production.
glucagon hormone produced in the pancreatic islets of Langerhans. It causes the release of glucose from liver glycogen and thereby raises the blood glucose. Used by injection to reverse hypoglycaemia. See also insulin.
glucocorticoid any steroid hormone which promotes gluconeogenesis and which antagonizes the action of insulin. Occurring naturally in the adrenal cortex as cortisone and cortisol, and produced synthetically as, for example, prednisolone.
glucogenesis production of glucose.
gluconeogenesis the formation of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources, e.g. amino acids, lactate, etc.
glucuronic acid used in the liver for the conjugation of bile pigments.
glutathione a peptide needed for conjugation in the liver and for red cell integrity. Paracetamol overdose causes serious depletion.
gluteal associated with the buttocks.
gluteus muscles muscles of the buttock.
glycerol combines with fatty acids to form triglycerides (triacylglycerols) and phospholipids.
glycogen the main carbohydrate (polysaccharide) storage compound in animals. Many glucose molecules are linked together in a process called glycogenesis occurring in the liver and skeletal muscle. The conversion of liver glycogen back to glucose is called glycogenolysis.
glycogenesis glycogen formation from blood glucose.
glycogenolysis the breakdown of glycogen to glucose.
glycogen storage disease a recessively inherited metabolic disorder caused by various enzyme deficiencies. Glycogen accumulates in organs and tissues, e.g. liver. Hypoglycaemia occurs, and the body tends to use fat rather than glucose, leading to ketosis and acidosis.
glycolysis a metabolic pathway where glucose is broken down to form pyruvic acid and some energy (ATP).
glyconeogenesis see gluconeogenesis.
glycoproteins large group of proteins conjugated with a carbohydrate, e.g. collagen, mucins.
glycosuria the presence of sugar in the urine.
gnathoplasty plastic surgery of the jaw or cheek.
goblet cells mucus-secreting cells, shaped like a goblet, found in the mucosa lining the gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts.
goitre an enlargement of the thyroid gland associated with a change of the level of thyroid function or a lack of iodine in the diet; may be smooth (simple) or nodular, and associated with normal or abnormal thyroid function; hyperthyroid with smooth enlargement in Graves’ disease, or nodular enlargement in toxic multinodular goitre; hypothyroid with glandular enlargement in Hashimoto’s disease.
gold (Au) The radioactive isotope gold-198 is sometimes used in the treatment of some malignant diseases.
golfer’s elbow inflammation of the medial epicondyle of the humerus associated with playing golf.
Golgi tendon organ specialized receptors in tendons that with skeletal muscle spindles monitor muscle stretching. Involved in proprioception.
Gompertzian growth curve a mathematical model explaining the relationship between age and the expected time of death.
gomphoses joints with minimal movement, for example, between the teeth and the jaw.
gonad the female or male primary reproductive structure, ovary, testis.
gonadotrophic having an affinity for, or influencing, the gonads.
gonadotrophin gonad-stimulating hormone. See also human chorionic gonadotrophin, luteinizing hormone.
gonad protection the use of lead rubber and/or collimation of the X-ray beam to reduce the radiation dosage to the reproductive system.
goose flesh contraction of the tiny muscles attached to the hair follicles causing the hair to stand on end: it is a reaction to either cold or fear.
gouge a chisel with a grooved blade for removing bone.
gout a form of metabolic disorder in which blood levels of uric acid are raised (hyperuricaemia). Acute arthritis can result from inflammation in response to urate crystals in the joint. The big toe is characteristically involved and becomes acutely painful and swollen. Drugs that reduce uric acid levels can control the disease. If gout is untreated deposition of urate crystals can cause chronic arthritis, nodules (e.g. in the ear) and kidney damage. See also pseudogout, tophus.
Graafian follicle a mature ovarian follicle. A minute vesicle in the ovarian stroma containing a single oocyte which is released when the vesicle ruptures at ovulation. After ovulation, the Graafian follicle forms the corpus luteum which, should fertilization occur, maintains the early pregnancy. In the absence of fertilization the corpus luteum only lasts for 12–14 days, after which it becomes the corpus albicans.
gracilis muscle muscle of the leg.
gradient coils magnetic coils that are designed to alter the main magnetic field by a few percent. The magnetic field gradient is controlled by the electrical current passing through the coil. They are used in magnetic resonance imaging to localize a slice and spatially encode slice information.
gradient echo a basic pulse sequence that only uses magnetic field gradient reversal to re-phase the transverse magnetization and produce echoes of the magnetic resonance signal. This allows shorter repetition times and therefore faster scanning and flip angles of less than 90°. See also flip angle.
grading a classification of cancers based on histopathological characteristics. The level of malignancy of the tissue is determined by comparing the amount of cellular abnormality and the rate of cell division with normal cells in the same tissue. Low-grade cancer generally has slow tumour growth and spread, whereas high-grade cancer is aggressive with rapid spread. The grade of the disease is more important (for some types of cancer) than the stage as an indicator of prognosis and effective treatment. See also differentiation, staging.
grain technology the shape of the silver halide crystals in a radiographic film emulsion are referred to as grains and have two main formats, globular and tabular. See also globular grains, tabular grains.
graininess random density patterns visible on a radiographic film due to the grains in the film being distributed in both area and depth and can be ‘clumped’ together due to the manufacturing process.
Gram stain the method of staining microorganisms and therefore classifying them.
grand mal the commonest type of epileptic seizure with loss of consciousness and generalized convulsions.
granulocyte a cell containing granules in its cytoplasm. Describes the polymorphonuclear leucocytes, neutrophil, eosinophil and basophil.
granuloma a tumour formed of granulation tissue.
graph a diagrammatical representation of two or more groups of data.
graphics computerized ‘drawing’, known as CAD (computer-aided drawing). The ability of the computer to produce preprogrammed graphic characters. The mode the computer has to be placed in prior to drawing graphics.
graphics tablet a piece of equipment that can digitize drawing or graphs ready for input into the computer.
Graves’ disease an autoimmune disorder characterized by hyperthyroidism, and exophthalmos.
Graves’ ophthalmopathy a disease of the eye associated with Graves’ disease.
gravid pregnant; carrying fertilized eggs or a fetus.
gravity weight. See also specific gravity.
Grawitz’s tumour a renal cell adenocarcinoma.
gray (Gy) the derived SI unit (International System of Units) for the absorbed dose of radiation. It has replaced the rad.
greater omentum the fold which hangs from the lower border of the stomach and covers the front of the intestines.
greenstick fracture a partial break in bone continuity occurring in young children when the bone appears bent.
Greinacher circuit comprises of two rectifiers connected in series, and two capacitors connected in series to produce a fully rectified waveform with a ripple effect on the tube voltage but a constant tube current.
grey matter unmyelinated nerve fibres and nerve cell bodies situated in the central nervous system. See also white matter.
grey scale a method of showing the texture of tissue on an ultrasound display, the amplitude of each echo is represented by varying shades of grey, white outline from specular surfaces, mottled grey from various tissue areas and black from collections of fluid. The variation of shades of grey in which a CT image may be represented on screen.
grid a device constructed of strips of high atomic number material (e.g. lead) which absorbs the scattered radiation and low atomic number material which allows the primary beam to pass through thus improving radiographic contrast of the image.
grid lattice the number of lines of lead per centimetre in a secondary radiation grid.
grid ratio the ratio of the height of the lead strips to the width of the spaces between them in a secondary radiation grid.
groin the junction of the thigh with the abdomen.
grommet ventilation tube inserted into the tympanic membrane. Frequently used in the treatment of glue ear in children.
gross tumour volume (GTV) the total visible or palpable extent of a malignant growth.
grounded theory research study where a hypothesis is elicited from the data gathered.
ground state when the inner orbits of an atom are filled and therefore the atom is at its lowest energy state.
growth hormone (GH, somatotrophin) hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary gland under the influence of two hypothalamic hormones, growth hormone releasing hormone, and growth hormone release inhibiting hormone (somatostatin). Growth hormone has widespread effects on body tissues and influences the metabolism of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. See also acromegaly, dwarfism, gigantism.
growth scan when 2 or 3 measurements are taken of the abdomen, head and femur of a fetus in the second and third trimester using ultrasound imaging. The weight of the fetus is calculated by using charts.
guidewire a device used to position an intravenous catheter, endotracheal tube, central venous line or gastric feeding tube.
gumboil the opening on the gum of an abscess at the root of a tooth, dento-alveolar abscess.
Gurney Mott theory theory of latent image formation stating that electrons are trapped and then escape several times before another electron is trapped forming a stable two-atom silver speck called the latent sub-image centre, this attracts further electrons causing a build up of silver atoms which eventually destroys the crystal lattice and allows development to take place. See also Mitchell theory.
gut the intestines, large and small.
gut decontamination the use of non-absorbable antibiotics to prevent endogenous infection in patients having intestinal surgery or those who are immunocompromised because of drugs or neutropenia.
gynaecomastia enlargement of the male breast.
gyromagnetic ratio (γ) is a proportionality constant and is fixed for the nucleus, for example 42.6MHz/Tesla for hydrogen.