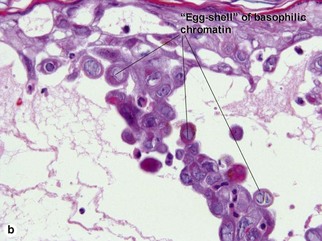
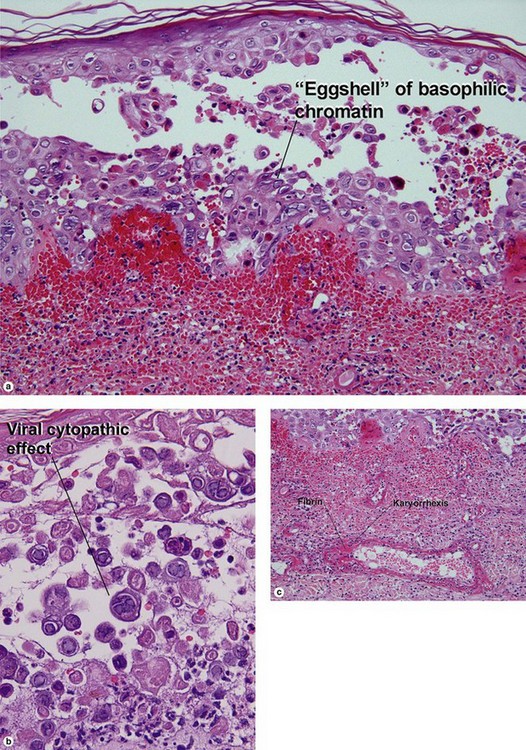
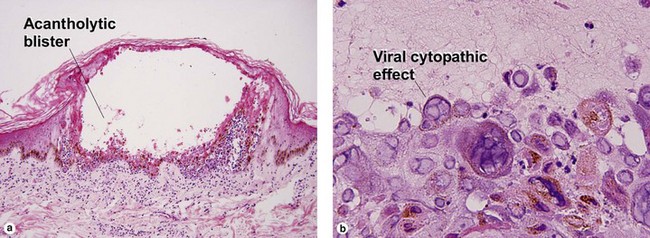
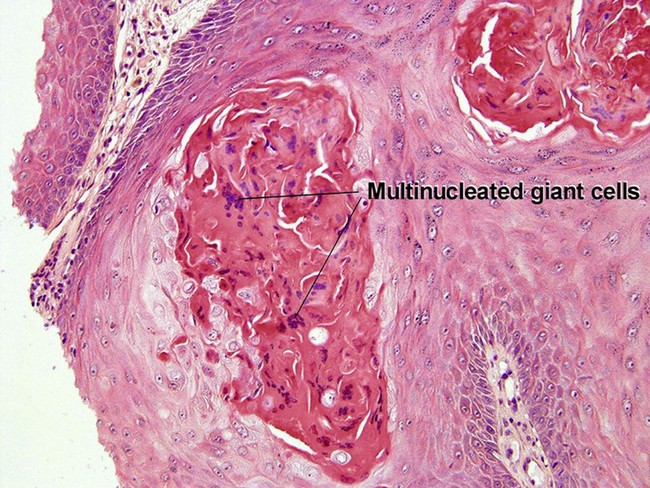
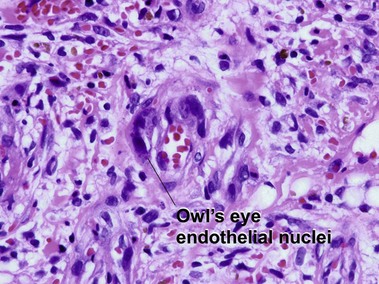
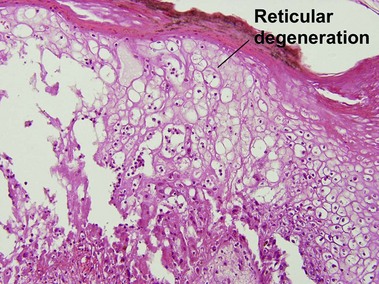
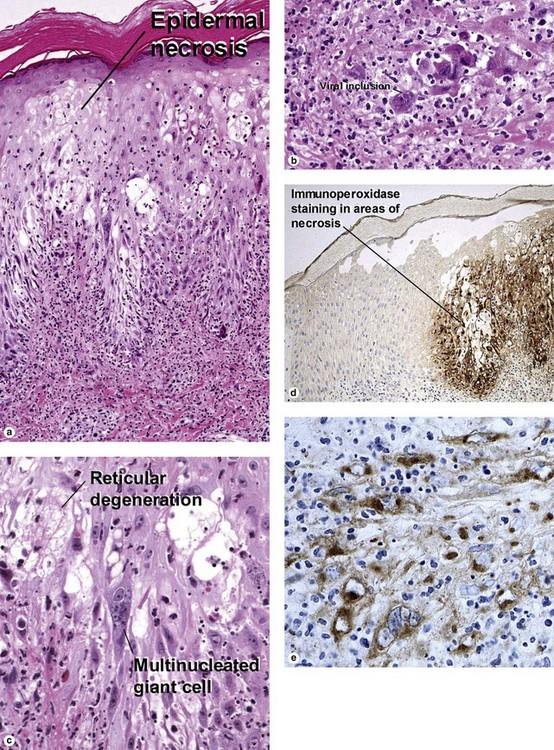
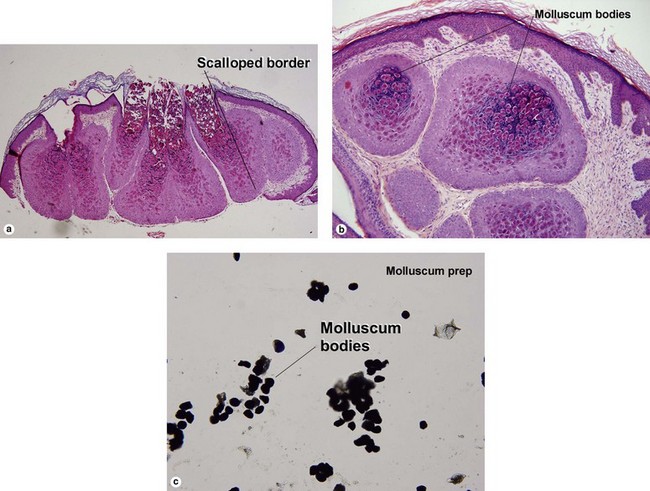
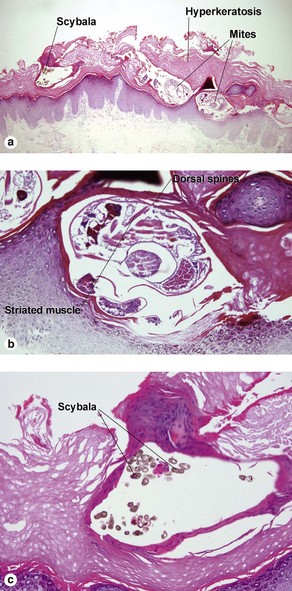
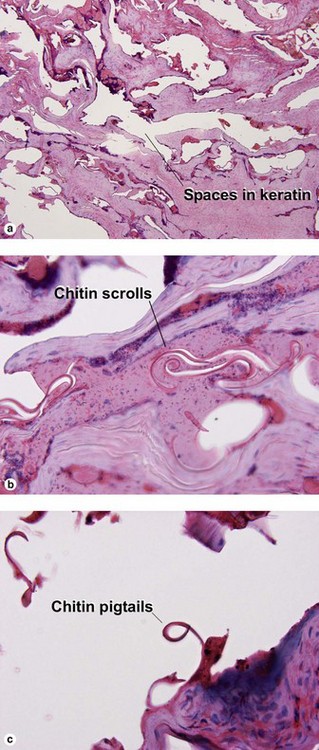
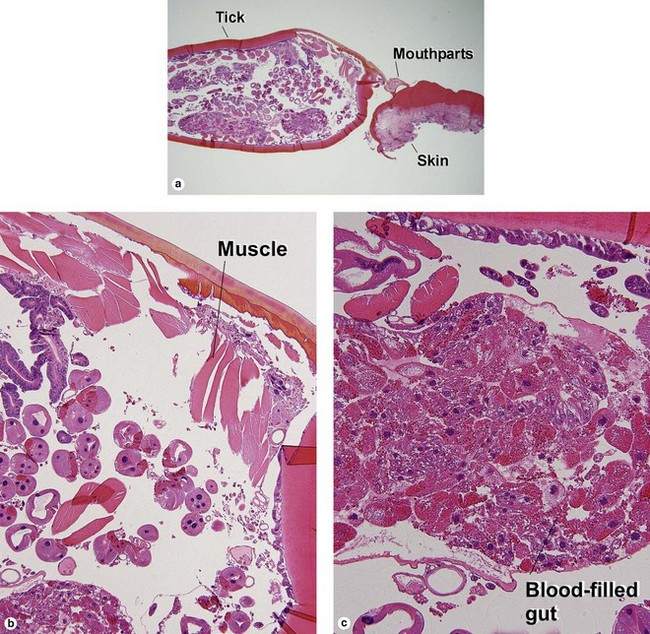
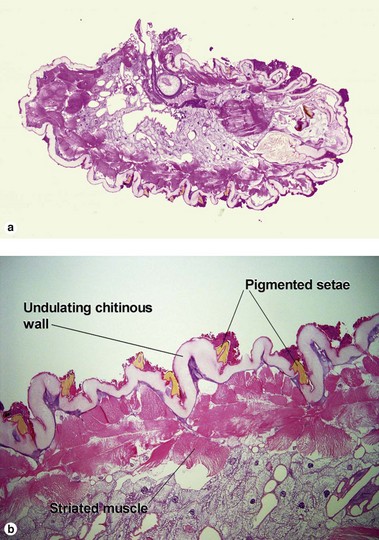
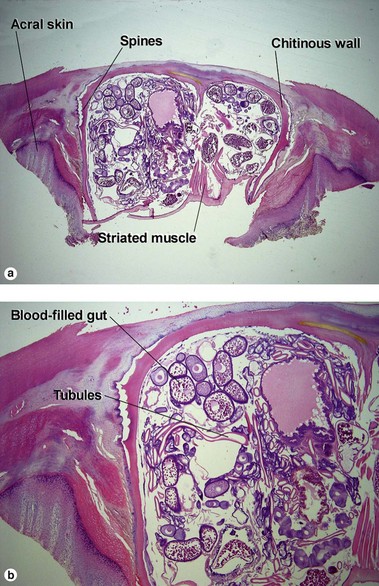
Viral infections, helminths, and arthropods
Viral infections
Warts
Condyloma acuminatum
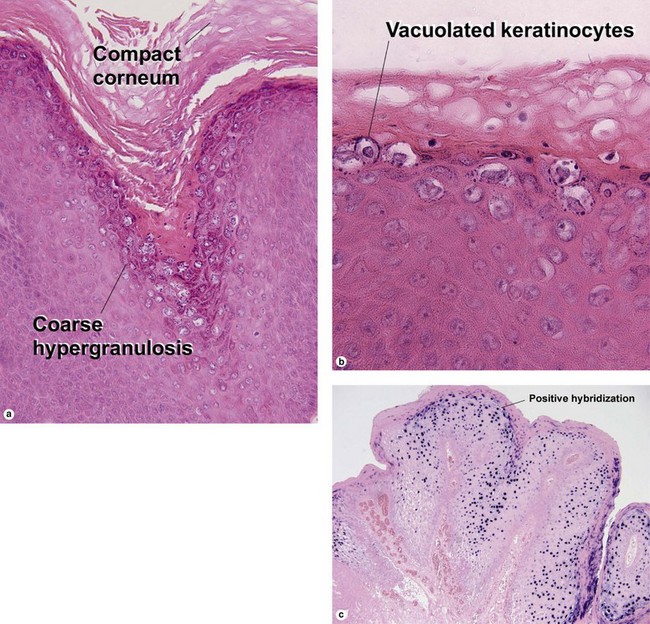
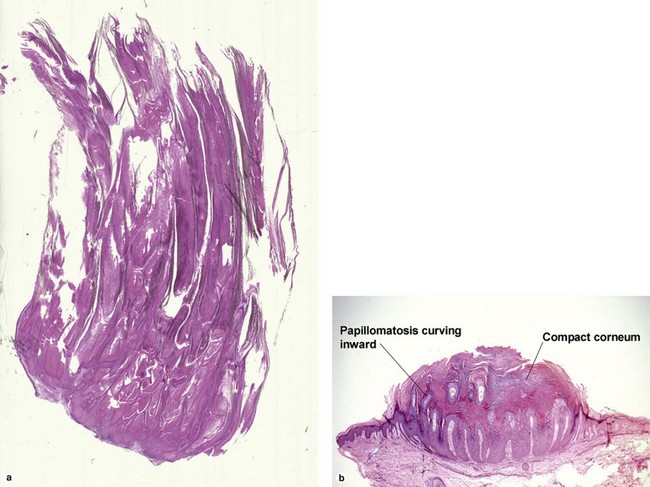
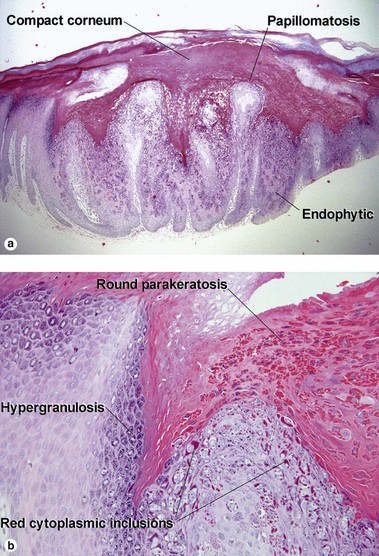
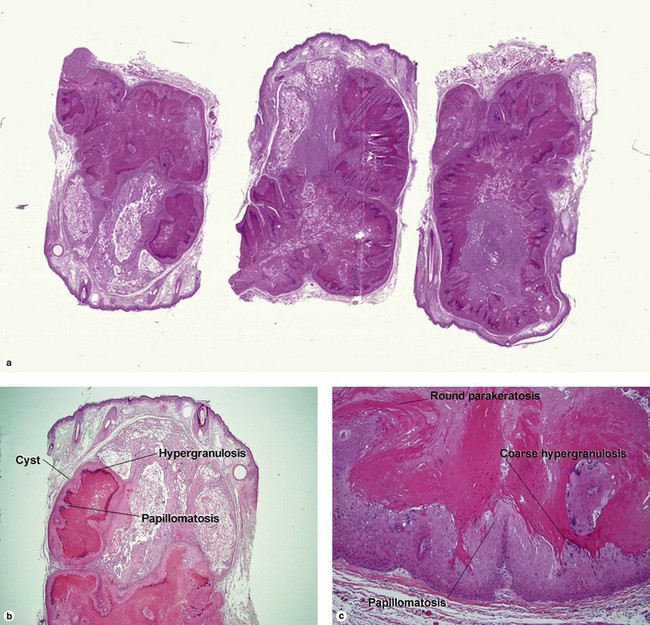
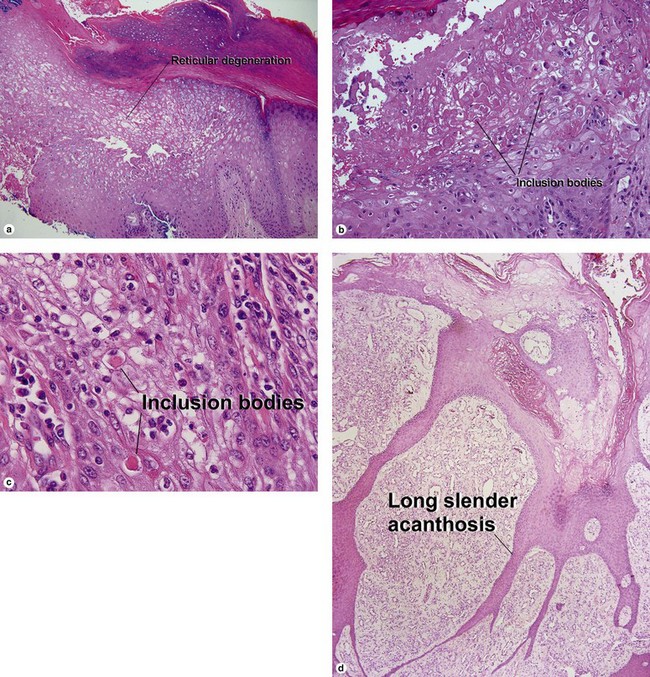
Fig 19-4 (a,b) Condyloma accuminatum. (c) Condyloma accuminatum in situ hybridization for low risk HPV (types 6 and 11)
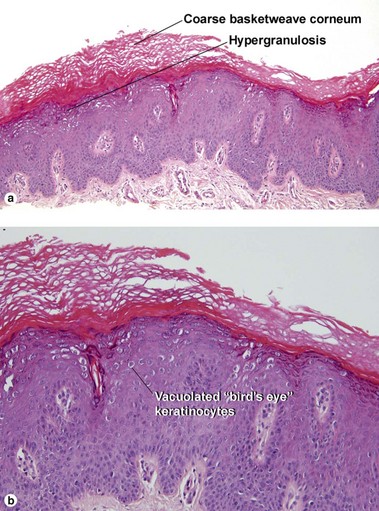
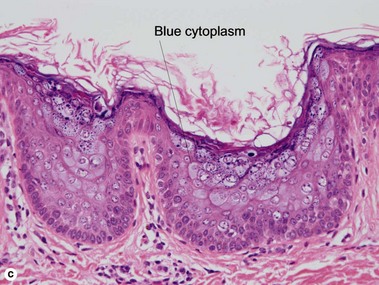
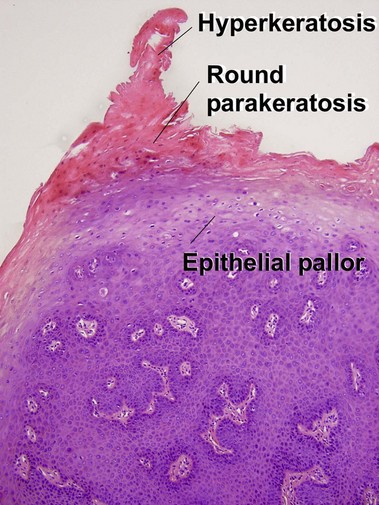
Condylomata acuminata commonly have horn cysts and resemble seborrheic keratoses. The two are differentiated by areas of compact stratum corneum, round parakeratosis, coarse hypergranulosis, and vacuolated keratinocytes with large gray nuclei. In situ hybridization can identify the human papillomavirus (HPV) type.
Bowenoid papulosis
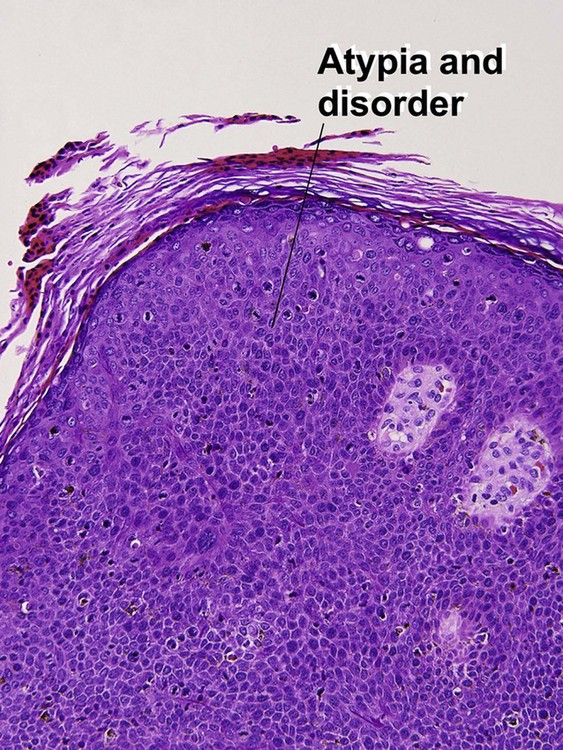
Bowenoid papulosis presents as discrete pink, brown, or gray lesions in the genitalia. They are typically sessile, rather than papillomatous or cauliflower-like. The histologic spectrum ranges from that of a condyloma with buckshot scatter of atypical cells to full-thickness atypia, indistinguishable from Bowen’s disease.
Flukes, tapeworms and roundworms
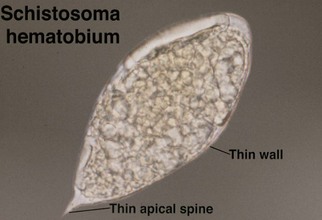
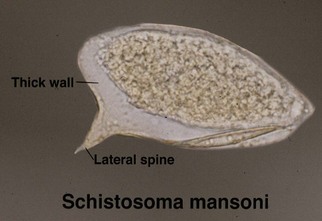
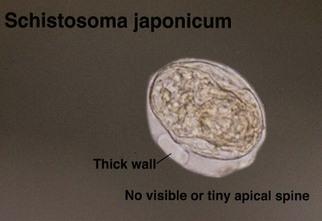
Schistosomiasis
Schistosomes are trematodes (flukes). When cutaneous involvement occurs, it usually involves genital skin. Schistosoma haematobium is typically implicated.
Flatworms
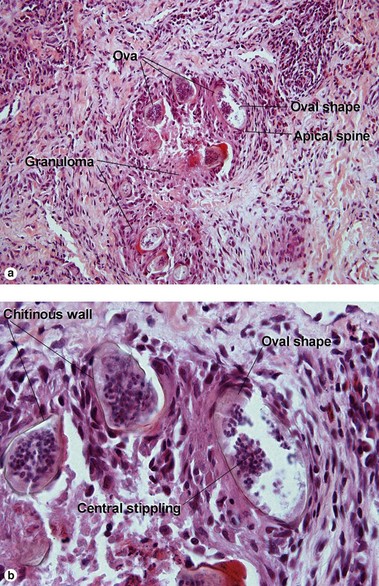
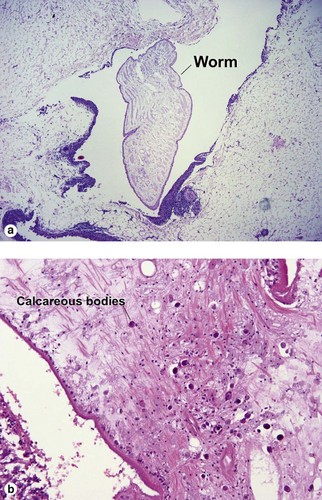
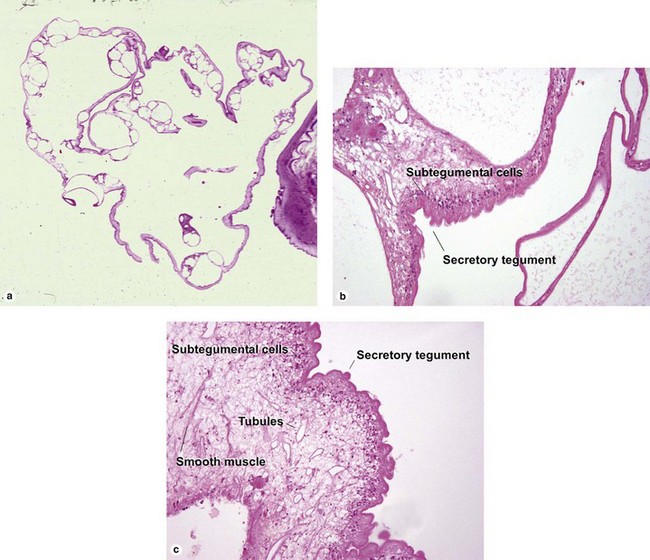
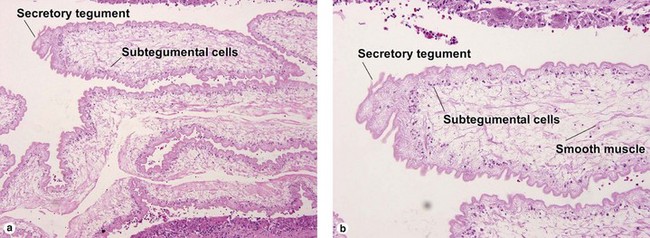
Spirometra worms, the cause of sparganosis, are typical cestodes. They lack a gut, and must absorb nutrients through the tegumental cells. They cannot excrete waste, and so calcify it internally as calcareous bodies.
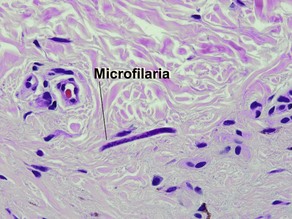
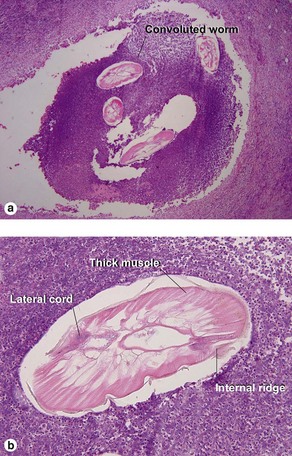
Dirofilariasis
Table 19-1
Ridge patterns of Dirofilaria species
| Species | Ridge pattern |
| D. tenuis | Wide/broken |
| D. repens | Narrow/sharp |
| D. ursi | Spaced far apart/round |
| D. immitis | None |
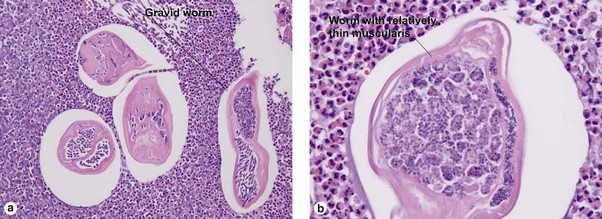
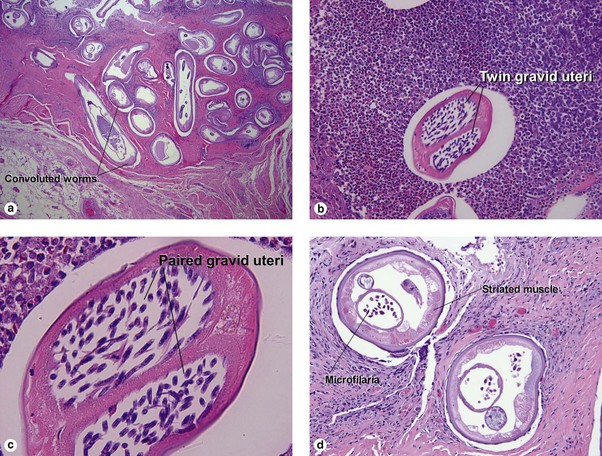
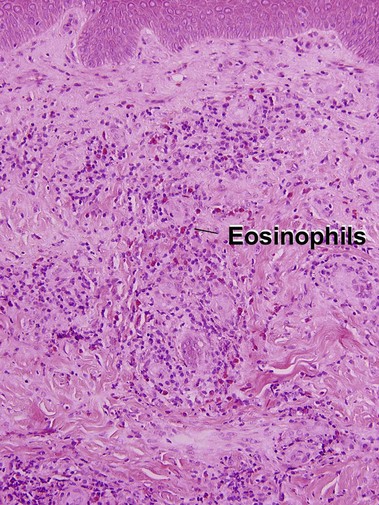
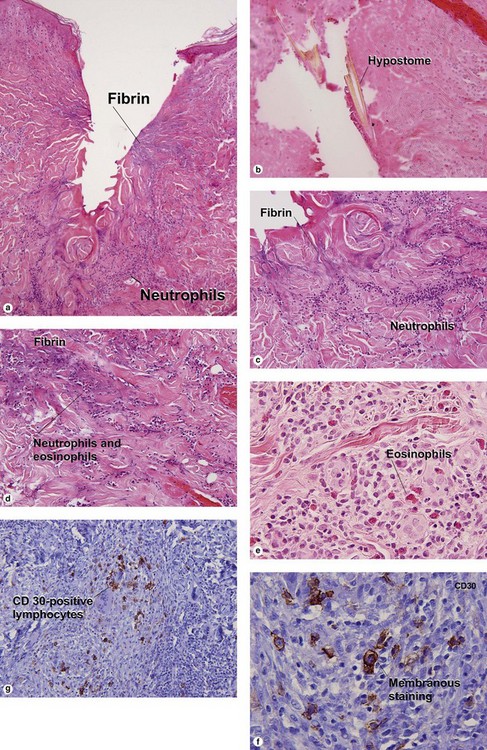
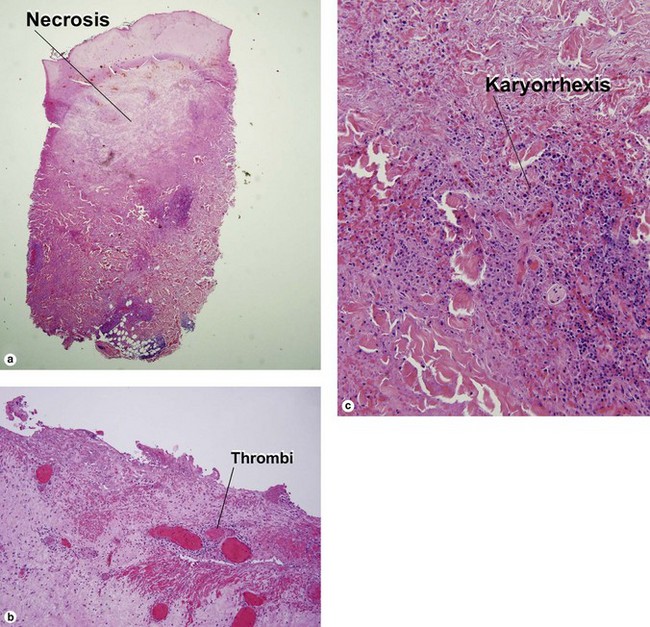
Early lesions may demonstrate abscesses with a mix of neutrophils and eosinophils. Later biopsies show a 1–3 cm granulomatous nodule surrounded by dense eosinophilic fibrin. Because humans are accidental hosts, there is only a single adult worm, and reproduction cannot occur. Microfilaria are not seen. Most human cases are associated with Dirofilaria tenuis. Aedes, Anopheles, and Culex mosquitoes act as vectors for most Dirofilaria. D. ursi is transmitted by Simulium blackflies.
Bayer-Garner, IB. Monkeypox virus: histologic, immunohistochemical and electron-microscopic findings. J Cutan Pathol. 2005; 32(1):28–34.
Brar, BK, Pall, A, Gupta, RR. Bullous scabies mimicking bullous pemphigoid. J Dermatol. 2003; 30(9):694–696.
Burch, JM, Krol, A, Weston, WL. Sarcoptes scabiei infestation misdiagnosed and treated as Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2004; 21(1):58–62.
Burroughs, RF, Elston, DM. What’s eating you? Human Dirofilaria infections. Cutis. 2003; 72(4):269–272.
Elston, DM, Eggers, JS, Schmidt, WE, et al. Histological findings after brown recluse spider envenomation. Am J Dermatopathol. 2000; 22(3):242–246.
Fagan, WA, Collins, PC, Pulitzer, DR. Verrucous herpes virus infection in human immunodeficiency virus patients. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1996; 120(10):956–958.
Groves, RW, Wilson-Jones, E, MacDonald, DM. Human orf and milkers’ nodule: a clinicopathologic study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991; 25(4):706–711.
Mukherjee, A, Ahmed, NH, Samantaray, JC, et al. A rare case of cutaneous larva migrans due to Gnathostoma sp. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2012; 30(3):356–358.
Nikkels, AF, Snoeck, R, Rentier, B, et al. Chronic verrucous varicella zoster virus skin lesions: clinical, histological, molecular and therapeutic aspects. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1999; 24(5):346–353.
Soyer, HP, Schadendorf, D, Cerroni, L, et al. Verrucous cysts: histopathologic characterization and molecular detection of human papillomavirus-specific DNA. J Cutan Pathol. 1993; 20(5):411–417.
Uthida-Tanaka, AM, Sampaio, MC, Velho, PE, et al. Subcutaneous and cerebral cysticercosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004; 50:S14.
Yang, Y, Ellis, MK, McManus, DP. Immunogenetics of human echinococcosis. Trends Parasitol. 2012; 28(10):447–454.