V
vacuum space entirely without matter.
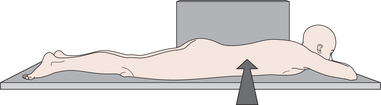
vacuum bag a sealed plastic bag containing small expanded polystyrene spheres, the patient is positioned on the bag which has the air pressure reduced until it is hardened. This mould can be used during radiotherapy to accurately immobilize the patient and enable daily reproducibility of positioning. See also patient immobilization.
vagal associated with the vagus nerve.
vagina literally, a sheath; the musculomembranous passage extending from the cervix uteri to the vulva.
vaginal speculum used to examine the vagina and cervix, for taking high vaginal swabs and cervical smears and for some treatments. Types include Cuscoe’s bivalve and Sim’s speculum.
vagus nerve the tenth cranial nerve, composed of both motor and sensory fibres, with a wide distribution in the neck, thorax and abdomen, sending important parasympathetic branches to the heart, lungs, stomach, etc.
valence band a band which contains the outer electrons of an atom and may be partially or completely full.
valency the ability of one atom to join another.
valency bond the electron linkage between two atoms.
valgus (valga, valgum) exhibiting angulation away from the midline of the body, e.g. hallux valgus.
validity (external) a term that indicates the degree to which research findings can be generalized to other populations and in other settings.
validity (internal) in research, a term that indicates the extent to which a method or test measures what it intends to measure.
Valsalva manoeuvre the maximum intrathoracic pressure achieved by forced expiration against a closed glottis; occurs in activities such as lifting heavy objects, changing position and during defecation: the glottis narrows simultaneously with contraction of the abdominal muscles.
value for money (VFM) a means of obtaining the best quality of service within the resource allocation. It involves economy, efficiency and effectiveness.
valve a fold of membrane in a passage or tube permitting the flow of contents in one direction only.
variable a research term that describes any factor or circumstance that is part of the study. confounding variable one that affects the conditions of the independent variables unequally. dependent variable one that depends on the experimental conditions. independent variable the variable conditions of an experimental situation, e.g. control or experimental. random variable background factors such as environmental conditions that may affect any conditions of the independent variables equally.
variance a mathematical term used in statistics. The distribution range of a set of results around the mean. See also standard deviation.
varicocele a swelling of the pampiniform venous complex of the spermatic cord.
varices dilated, tortuous vein.
varus (vara, varum) displaying displacement or angulation towards the midline of the body, for example coxa vara.
vas deferens (deferent duct) the excretory duct of the testis.
vasa vasorum the minute nutrient vessels of the artery and vein walls.
vascular supplied with vessels, especially referring to blood vessels.
vascularization the acquisition of a blood supply; the process of becoming vascular.
vasoconstriction narrowing of the lumen of a blood vessel.
vasodilation widening of the lumen of a blood vessel.
vasography the investigation of male infertility by injecting radiographic contrast agent into the vas deferens.
vasomotor relating to nerves and muscles that control vessel lumen size.
vasomotor centre (VMC) a centre, located in the medulla oblongata, concerned with controlling lumen size of peripheral arterioles, it operates through sympathetic activity in response to baroreceptor signals.
vasopressin formed in the hypothalamus and stored in the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland. It is the antidiuretic hormone (ADH).
vasospasm constricting spasm of vessel walls.
vasovagal shock shock caused by the loss of vascular tone and therefore dilatation of the blood vessels as a result of severe pain or fright. Used to be called neurogenic shock.
vein a vessel conveying blood from the capillaries back to the heart. It has the same three coats as an artery, the inner one modified to form valves.
velocity distance travelled in unit time in a given direction, unit metre per second.
vena cava one of two large veins emptying into the right atrium of the heart.
venepuncture insertion of a needle into a vein.
venesection surgical blood letting by opening a vein or introducing a wide-bore needle, performed on blood donors and to reduce the risk of thrombosis.
venography (phlebography) radiological examination of the venous system involving injection of an opaque medium. Mostly replaced by ultrasound.
venous associated with the veins.
venous haemorrhage the loss of blood from a vein.
ventilation the mechanical process of breathing, the supply of fresh air. See also pulmonary ventilation.
ventilation perfusion ratio (V/Q) the ratio between gases in the alveoli (alveolar ventilation) and blood flow in the pulmonary capillaries (pulmonary perfusion).
ventilator (life support machine) specialized equipment for mechanically inflating a patient’s lungs. Used to support or replace a patient’s own breathing.
ventral associated with the abdomen or the anterior surface of the body.
ventral decubitus radiograph the patient lies prone and the central ray passes through the body from side to side.
ventricle a small belly-like cavity.
ventricles of the brain four cavities filled with cerebrospinal fluid within the brain.
ventricles of the heart the two lower muscular chambers of the heart.
ventricular fibrillation fine, rapid twitching of the ventricles of the heart, if uncontrolled leads to circulatory arrest.
ventriculoatrial shunt creating a pathway between the atria of the heart and the cerebral ventricles to drain cerebrospinal fluid.
ventriculoperitoneal shunt creating a pathway between the peritoneum and the cerebral ventricles to drain cerebrospinal fluid.
ventriculostomy an artificial opening into a ventricle. Usually refers to a drainage operation for hydrocephalus.
verification the process of confirming the accuracy of radiotherapy planning prior to treatment taking place.
vermiform appendix the vestigial, hollow, wormlike structure attached to the caecum.
vernix caseosa the fatty substance which covers and protects the skin of the fetus.
vertebra one of the irregular bones making up the spinal column.
vertebra prominens the seventh cervical vertebra.
vertebral column (spinal column) made up of 33/34 vertebrae, articulating with the skull above and the pelvic girdle below. The vertebrae are so shaped that they enclose a cavity (spinal canal, neural canal) which houses the spinal cord.
vertigo feeling of loss of balance. See also Menières syndrome.
vesical associated with the urinary bladder.
vesicle a small bladder, cell or hollow structure. A skin blister.
vesico-ureteric reflux the passing of urine backwards up the ureter during micturition.
vessel a tube, duct or canal, holding or conveying fluid, especially blood and lymph.
vestibule the middle part of the internal ear, lying between the semicircular canals and the cochlea. The triangular area between the labia minora. The area of the mouth between the lips and the gums/teeth.
vestibulocochlear relating to the vestibule and the cochlear.
vestibulocochlear nerve auditory nerve the eighth pair of cranial nerves. There are two branches: the vestibular, which transmits impulses from the vestibular apparatus of the ear to the cerebellum, and the cochlear, which transmits impulses from the cochlea in the ear to the auditory cortex situated in the temporal lobe of the cerebrum.
vestibulo-ocular reflex compensatory eye movement stimulated by head movement to stabilize gaze in space.
vibration syndrome cysts in the wrist or sometimes the hand, caused by using vibrating machinery.
videotext the interactive public information service broadcast on television, known as Prestel.
vignetting shading round an image.
villonodular synovitis a joint problem, usually affecting the hips or knees where the lining of the joint becomes swollen and extra synovial fluid is secreted causing swelling and pain.
villus a microscopic fingerlike projection; found in the mucosa of the small intestine or on the outside of the chorion of the embryonic sac.
virement financial term meaning to move money from one expenditure category to another.
virus a unique class of infectious agents, consisting of genetic material surrounded by protein and in some cases, with an outer membranous envelope. They cause many diseases including measles, AIDS, hepatitis and evidence suggests that some may be capable of causing cancer. A computer program designed to cause malfunction in a computer which often arrives as an attachment to an email and opening the attachment will release the virus to corrupt the main program.
visible spectrum the small part of the electromagnetic spectrum containing the range of wavelengths that can be seen by the human eye (see figure on p. 396).
visual acuity the ability of a person to see small objects.
visually handicapped a loss or reduction of sight.
vital capacity (VC) the amount of air expelled from the lungs after a deep inspiration.
vitallium an alloy used in the manufacture of nails, plates, etc., used in orthopaedic and other surgical procedures.
vitamins organic substance or group of substances that have specific biochemical functions in the body. They are either fat-soluble, vitamins A, D, E and K, or water-soluble, vitamin B complex and vitamin C. They are essential for normal metabolism and are provided by the diet. Some vitamins can also be synthesized in the body, e.g. vitamin D. Their absence causes deficiency diseases.
vitreous chamber the cavity inside the eyeball and behind the lens.
vitreous humour (body) the jelly-like substance contained in the vitreous chamber.
vocal cords membranous folds stretched anteroposteriorly across the larynx. They vibrate as air from the lungs passes between them to produce the voice.
Volkmann’s canals canals joining the haversian systems in compact bone.
volt (V) the derived SI unit (International System of Units) for electromotive force (also known as potential difference or electrical potential). It is the potential that exists at a point when 1 joule of work is done in moving coulomb of positive charge from infinity to that point; volt of potential difference exists between two points if 1 joule of work is done moving coulomb of positive charge from one point to the other.
voltage the number of volts in a circuit; in Britain the mains voltage is 240 volts for the domestic supply and 398 volts for a three-phase supply.
volumetric reconstruction the production of a three-dimensional image in CT scanning.
volvulus a loop of bowel causing an obstruction.
vomer a flat bone forming the postero-inferior aspect of the bony nasal septum.
vomiting centre a centre in the medulla oblongata that has overall control of vomiting. It responds to various stimuli such as those from the gastrointestinal organs.
Von Recklinghausen’s disease (Recklinghausen’s disease) describes two conditions: (a) osteitis fibrosa cystica – the result of hyperparathyroidism leading to decalcification of bones and formation of cysts; (b) multiple neurofibromatosis – the tumours can be felt beneath the skin along the course of nerves. There may be pigmented spots (caf° au lait) on the skin and neurofibroma in the endocrine glands and the gastrointestinal tract.
voxel a three-dimensional pixel.