U
ulcer an erosion or loss of continuity of the skin or mucous membrane.
ulcerative associated with or of the nature of an ulcer.
ulcerative colitis superficial inflammatory condition affecting the colon. It always involves the rectum and spreads continuously for a variable distance. Long-standing disease predisposes to colorectal cancer.
ulna the inner bone of the forearm.
ulnar associated with the ulna as in artery, vein and nerve.
ultrasonic relating to mechanical vibrations of very high frequency.
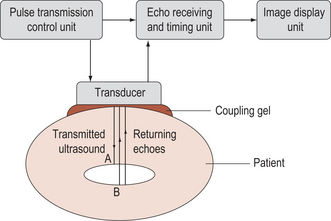
ultrasonography formation of a visible image from the use of ultrasound. A controlled beam of sound is directed into the relevant part of the body. The reflected ultrasound is used to build up an electronic image of the various structures of the body. Routinely offered during pregnancy to monitor progress and detect fetal and placental abnormalities. See also ultrasound, diagnostic ultrasonography, real-time ultrasonography.
ultrasound sound waves with a frequency of over 20000 Hertz, not audible to the human ear.
ultraviolet rays (UV) short wavelength electromagnetic rays outside the visible spectrum.
umbilical cord the cord connecting the fetus to the placenta. It contains a vein and two arteries.
umbilical hernia (omphalocele) protrusion of a portion of intestine through the area of the umbilical scar.
umbilicus (navel) the abdominal scar left by the separation of the umbilical cord after birth.
unconscious incapable of responding to sensory stimuli. That part of mental activity concealed from the consciousness by the psychological sensor.
undescended testis the testis remains within the bony pelvis or inguinal canal. See also cryptorchism.
uniaxial joint a joint with movement round one axis only, for example, flexion and extension.
unicellular consisting of only one cell.
uniformity the variations in count rate detected by a gamma camera when it is exposed to a regular source of gamma rays emitted from a radionuclide.
unilateral relating to or on one side only.
unit cost an average cost for a specific activity, for example, a surgical procedure, or a home visit. It is calculated by dividing the total cost of the service by the number of outputs.
univariate statistics descriptive statistics that analyse one variable, such as frequency distributions.
unrelated the whole groups of data are roughly matched but the individual samples are not.
unsharpness blurring on a radiograph (photographic unsharpness) which can be caused by movement unsharpness, screen unsharpness and/or geometric unsharpness.
upgrade an improvement to a computer system which allows the most recent information to be added to a programme.
upper motor neuron the cell is in the motor cortex and the axon terminates in the anterior horn of the spinal cord.
upper respiratory tract infection (URTI) the upper respiratory tract is the commonest site of infection in all age groups. The infections include rhinitis – usually viral – sinusitis, tonsillitis, adenoiditis, pharyngitis, otitis media and croup (laryngitis), often involving the tonsils and cervical lymph nodes. Such infections seldom require hospital treatment, but epiglottitis can be rapidly fatal.
uptake count for a particular organ, is expressed as a percentage of the total radiation administered to the patient for radionuclide imaging purposes.
urachus the stem-like structure connecting the bladder with the umbilicus in the fetus; after birth it becomes a fibrous cord situated between the apex of the bladder and the umbilicus, known as the median umbilical ligament.
uraemia an excess of urea, creatinine and nitrogenous end products of protein and amino acid metabolism in the blood. The entire complex of signs and symptoms of chronic renal failure.
urea the main nitrogenous end product of protein metabolism; produced in the liver it is excreted in the urine.
urease bacterial enzyme that splits urea.
ureter the tube passing from each kidney to the bladder for the conveyance of urine; its average length is 25–30cm.
ureterolith a calculus in the ureter.
ureterovaginal associated with the ureter and vagina.
ureterovesical associated with the ureter and urinary bladder.
urethra the passage from the bladder through which urine is excreted.
urethrography radiological examination of the urethra. Can be an inclusion with cystography either retrograde (ascending) or during micturition.
uric acid substance formed during purine metabolism which is present in nucleic acids and some foods and beverages. Uric acid is excreted in the urine and may give rise to kidney stones. High levels of uric acid in the blood may be due to faulty excretion of uric acid, excessive cell breakdown, or associated with high purine intake. See also gout.
urinal a vessel used for urination if a patient is unable to walk, a static unit for urination.
urinary associated with urine.
urinary bladder a muscular distensible bag situated in the pelvis. It receives urine from the kidneys via two ureters and stores it until micturition occurs.
urinary catheter a catheter inserted into the urinary bladder to drain urine.
urinary system comprises two kidneys, two ureters, one urinary bladder and one urethra. The kidneys produce urine of variable content; the ureters convey the urine to the bladder, which stores it until there is sufficient volume to elicit reflex emptying or the desire to pass urine and it is then conveyed to the exterior by the urethra.
urinary tract infection (UTI) the second most prevalent infection in hospital, but the most common hospital-acquired infection. It occurs most frequently in the presence of an indwelling catheter. It is most commonly caused by the bacterium Escherichia coli, suggesting that self-infection via the periurethral route is a common pathway.
urine the clear straw-coloured fluid excreted by the kidneys. Urine contains water, nitrogenous waste and electrolytes. Normally adults produce about 1500mL every 24h, but this depends on fluid intake, activity and age. Usually slightly acidic (pH 6.0), but varies between 4.5 and 8.0. The specific gravity is usually within the range 1005–1030.
URL (Uniform Resource Locator) the address of internet files.
urobilin a brownish pigment excreted in the faeces. Formed by the oxidation of urobilinogen.
urobilinogen (stercobilinogen) a pigment formed from bilirubin in the intestine by bacterial action. It may be reabsorbed into the circulation and converted back to bilirubin in the liver and re-excreted in the bile or urine.
urodynamics the method used to study bladder function. See also cystometry.
urogenital (urinogenital) associated with the urinary and the genital organs.
urography radiographic visualization of the renal pelvis and ureter by injection of a contrast agent. The medium may be injected into the bloodstream whence it is excreted by the kidney (intravenous urography) or it may be injected directly into the renal pelvis or ureter by way of a fine catheter introduced through a cystoscope (retrograde or ascending urography). See also intravenous urography.
urokinase an enzyme which dissolves fibrin clot. It is used therapeutically in vitreous haemorrhage (eye), thrombosed arteriovenous shunts and other thromboembolic conditions.
urticaria (nettlerash, hives) skin eruption characterized by multiple, circumscribed, smooth, raised, pinkish, itchy weals, developing very suddenly, usually lasting a few days and leaving no visible trace. The cause is unknown in most cases. See also angio-oedema.
USB (Universal Serial Bus) a serial port on a computer used to attach hardware such as the mouse, keyboard or a scanner.
useful density range the range of densities, between 1.36 and 2.16 that make up a radiographic image; above and below this range it is not possible to determine differences visually between adjacent densities. See also useful exposure range.
useful exposure range the range of exposures that make up a radiographic image; above and below this range it is not possible to determine differ-ences visually between adjacent densities. To calculate the range the characteristic curve of the film is used at a particular kV, a vertical line is drawn from density 1.36 and 2.16, the antilogs of the range of values on the horizontal, log It, axis gives the useful exposure range in mAs. See also characteristic curve.
uterine associated with the uterus. uterine supports muscles of the pelvic floor, the peritoneum and various ligaments; pubocervical, round, transverse cervical (Mackenrodt’s or cardinal) and the uterosacral ligaments that hold the uterus in the correct anteverted and anteflexed position.
uterine cavity that of the uterus, the base extending between the orifices of the uterine tubes.
uterine tubes (fallopian tubes, oviducts) two tubes opening out of the upper part of the uterus. Each measures 10cm and the distal end is fimbriated and lies near the ovary. They are the site of fertilization and they convey the ovum to the uterus.
uteroplacental associated with the uterus and placenta.
uterorectal associated with the uterus and the rectum.
uterosacral associated with the uterus and sacrum.
uterosalpingography (hysterosalpingography) radiological examination of the uterus and uterine tubes involving retrograde introduction of an opaque contrast agent during fluoroscopy. Used to investigate patency of uterine (fallopian) tubes. Is being superseded by ultrasound examination.
uterovaginal associated with the uterus and the vagina.
uterovesical associated with the uterus and the urinary bladder.
uterus the womb, a hollow muscular organ into which the ovum is received through the uterine (fallopian) tubes and where it is retained during development, and from which the fetus is expelled through the vagina. See also bicornuate.
utricle a little sac or pocket. A fluid-filled sac in the internal ear. Part of the vestibular apparatus. See also saccule.
uvea the pigmented middle coat of the eye, includes the iris, ciliary body and choroid.
uvula the central tag hanging down from the free edge of the soft palate.