Chapter 52 Transfusion Therapy for Coagulation Factor Deficiencies
Table 52-1 Dosing Regimens for Bleeding and Prophylaxis in Hemophilia
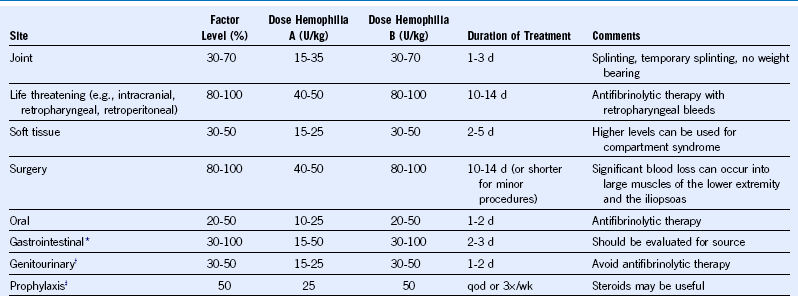
qod, Every other day.
Data from DiMichele D: Hemophilia 1996. New approach to an old disease. Pediatr Clin North Am 43:709, 1996; Mannucci PM: Haemophilia treatment protocols around the world: Towards a consensus. Haemophilia 4:421, 1998; and Lusher J: Treatment of congenital coagulopathies, 1999, AABB Press.
1-Deamino 8-D Arginine Vasopressin Trial
1. Collect citrated plasma from the patient immediately before DDAVP infusion for testing with the postinfusion blood specimen.
2. Administer DDAVP intravenously (0.3 µg/1 kg) in 25 to 50 mL normal saline.
3. Wait approximately 30 minutes after the infusion, carefully observing the patient for possible adverse side effects (increased blood pressure, facial flushing, signs or symptoms of hyponatremia).
4. Collect post-DDAVP infusion specimen in sodium citrate at 60, 120, and 240 minutes.
5. Compare the pre- and post-DDAVP FVIII : C and vWF : Ag levels to confirm a therapeutic response, threefold increase from baseline (for mild or moderate hemophilia, response is defined as twofold increase in FVIII : C levels or an absolute level above 0.31 U/mL at 1 hour).1
Treatment of Life-Threatening Bleeding Episodes in Patients With Inhibitors Against Factor VIII or Factor IX
Concentrates
1. Factor VIII containing concentrates in high doses (as high as 150-200 IU/kg) if inhibitor titer is low (<5-10 BU) or if neutralization can be demonstrated with high doses. High-dose continuous infusion of factor VIII (≈10 IU/kg/hour) after a high-dose bolus may be useful.
2. Recombinant factor VIIa. Dose is 90 µg/kg (or a dose up to 320 µg/kg) administered every 2 hours. Risk of thrombosis exists with this product.
3. Activated PCCs at a dose of 50 to 75 IU/kg every 8 to 12 hours. Risk of thrombosis exists with this product.
Conservative Measures
3. Local application of hemostatic agents
5. Avoid venipunctures, intramuscular injections, arterial puncture, and lumbar punctures
6. Avoid use of medications that inhibit platelet function
7. DDAVP may be effective in some patients with low titer inhibitors
Table 52-2 Other Coagulation Deficiencies
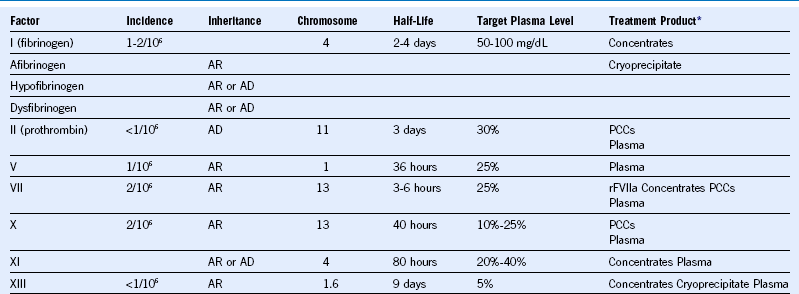
AD, Autosomal dominant; AR, autosomal recessive; PCC, prothrombin complex concentrates.
* Products are listed in order of viral safety.
Data from Cohen AJ and Kessler: Treatment of inherited coagulation disorders. Am J Med 99:675, 1995.