Regulation of Cell Metabolism
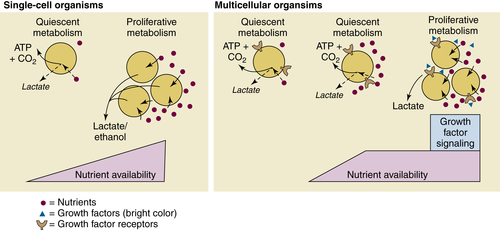
The Metabolic Profile of Cancer Cells
Aerobic Glycolysis: The Warburg Effect
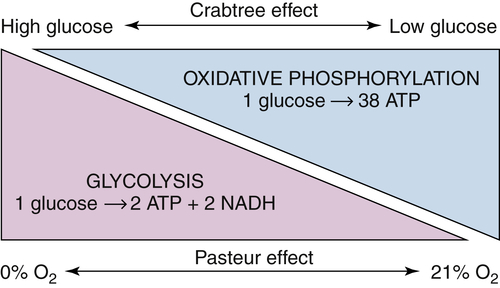
The Paradox of the Warburg Effect
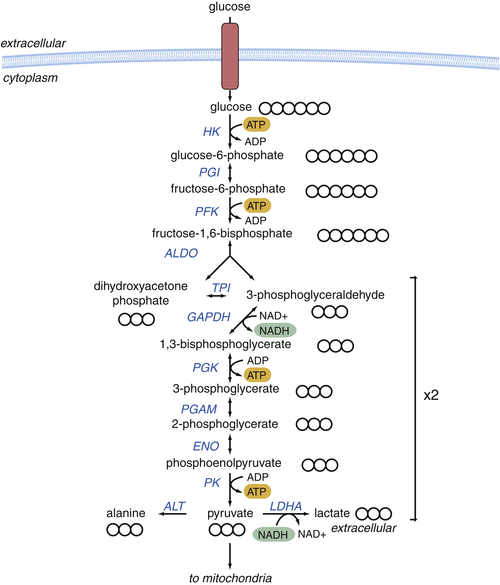
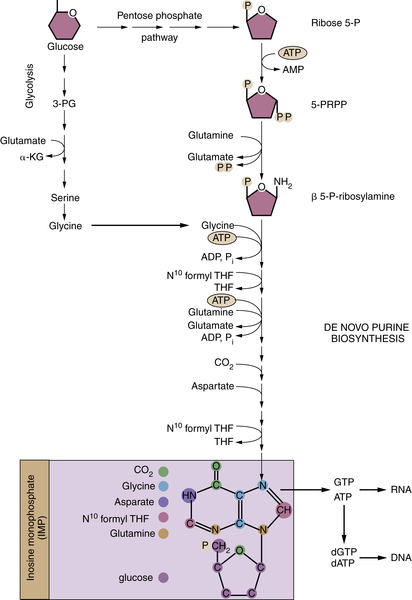
Glycolysis Provides Key Intermediates to Support Cell Growth
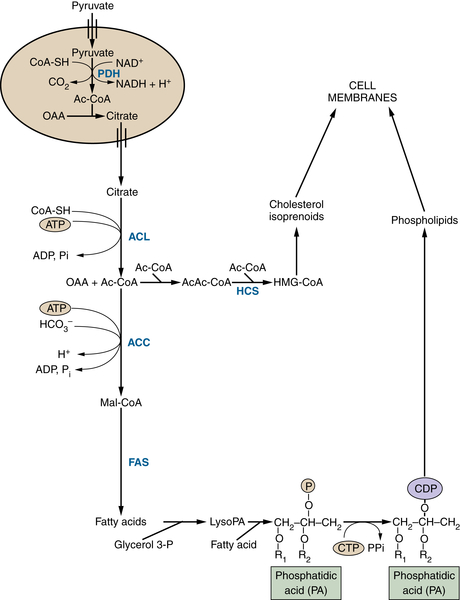
Glucose-Derived Metabolites Contribute to All Classes of Macromolecules
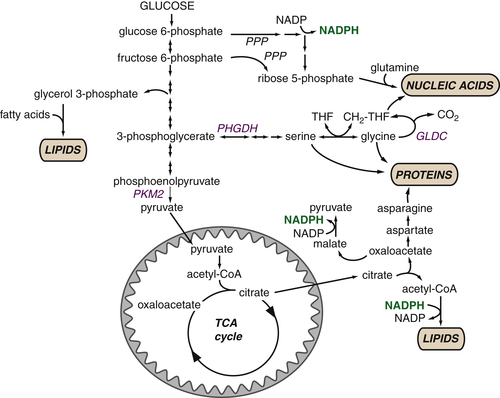
Macromolecular Synthesis, Not ATP, May Be the Major Purpose of Elevated Glycolysis in Cancer Cells
The TCA Cycle as a Biosynthetic Hub
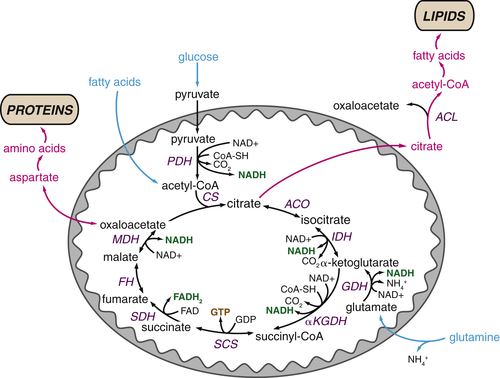
TCA Cycle Metabolites Are Required for Macromolecular Biosynthesis
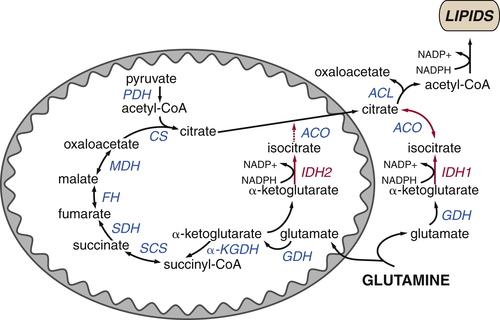
Glutamine Plays Several Roles Supporting the TCA Cycle and Anabolic Metabolism
TCA Cycle Rearrangements Highlight the Role of TCA Cycle Metabolites as Biosynthetic Precursors
Genetic Mechanisms Driving Cancer Cell Metabolism
Activation of the PI3K Pathway Promotes Metabolic Transformation
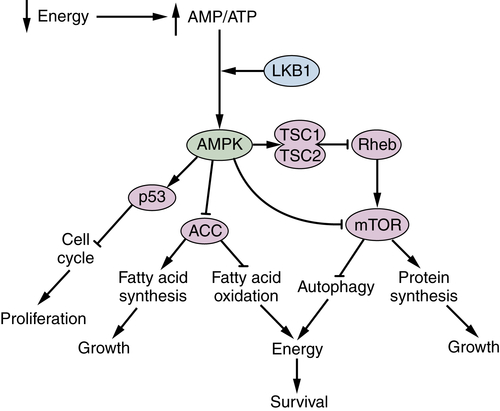
LKB1 and AMPK Are Metabolic Brakes That Circumvent Tumor Growth
The Transcription Factor HIF1 Controls Glycolytic Metabolism
c-Myc Coordinates Cellular Proliferation and Metabolism
Mutations in Metabolic Enzymes Can Influence Tumorigenesis
Clinical Implications of Metabolic Transformation
1. Understanding the Warburg effect: the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation . Science . 2009 ; 324 : 1029 – 1033 .
2. How cancer metabolism is tuned for proliferation and vulnerable to disruption . Nature . 2012 ; 491 : 364 – 373 .
3. Mitochondria and cancer . Nat Rev Cancer . 2012 ; 12 : 685 – 698 .
4. A mitochondrial paradigm of metabolic and degenerative diseases, aging, and cancer: a dawn for evolutionary medicine . Annu Rev Genet . 2005 ; 39 : 359 – 407 .
5. Glutamine addiction: a new therapeutic target in cancer . Trends Biochem Sci . 2010 ; 35 : 427 – 433 .
6. Biochemistry . New York, NY : W.H. Freeman ; 2002 .
7. Regulation of cancer cell metabolism . Nat Rev Cancer . 2011 ; 11 : 85 – 95 .
8. Aerobic glycolysis: meeting the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation . Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol . 2011 ; 27 : 441 – 464 .
9. Metabolic reprogramming: a cancer hallmark even Warburg did not anticipate . Cancer Cell . 2012 ; 21 : 297 – 308 .
10. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation . Cell . 2011 ; 144 : 646 – 674 .
11. On the origin of cancer cells . Science . 1956 ; 123 : 309 – 314 .
12. Energy metabolism in tumor cells . FEBS J . 2007 ; 274 : 1393 – 1418 .
13. On respiratory impairment in cancer cells . Science . 1956 ; 124 : 269 – 270 .
14. The role of the Crabtree effect and an endogenous fuel in the energy metabolism of resting and proliferating thymocytes . Eur J Biochem . 1993 ; 212 : 95 – 99 .
15. High activity of mitochondrial glycerol phosphate dehydrogenase in insulinomas and carcinoid and other tumors of the amine precursor uptake decarboxylation system . Cancer Res . 1990 ; 50 : 7203 – 7205 .
16. Substrate-dependent utilization of the glycerol 3-phosphate or malate/aspartate redox shuttles by Ehrlich ascites cells . Biochem J . 1995 ; 310 ( Pt 2 ) : 665 – 671 .
17. Alterations in the glycolytic and glutaminolytic pathways after malignant transformation of rat liver oval cells . J Cell Physiol . 1999 ; 181 : 136 – 146 .
18. High activity of mitochondrial glycerophosphate dehydrogenase and glycerophosphate-dependent ROS production in prostate cancer cell lines . Biochem Biophys Res Commun . 2005 ; 333 : 1139 – 1145 .
19. Why do cancers have high aerobic glycolysis? Nat Rev Cancer . 2004 ; 4 : 891 – 899 .
20. Acid-mediated tumor invasion: a multidisciplinary study . Cancer Res . 2006 ; 66 : 5216 – 5223 .
21. Bicarbonate increases tumor pH and inhibits spontaneous metastases . Cancer Res . 2009 ; 69 : 2260 – 2268 .
22. Targeting lactate-fueled respiration selectively kills hypoxic tumor cells in mice . J Clin Invest . 2008 ; 118 : 3930 – 3942 .
23. Attenuation of LDH-A expression uncovers a link between glycolysis, mitochondrial physiology, and tumor maintenance . Cancer Cell . 2006 ; 9 : 425 – 434 .
24. Phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase diverts glycolytic flux and contributes to oncogenesis . Nat Genet . 2011 ; 43 : 869 – 874 .
25. Functional genomics reveal that the serine synthesis pathway is essential in breast cancer . Nature . 2011 ; 476 : 346 – 350 .
26. Glycine decarboxylase activity drives non-small cell lung cancer tumor-initiating cells and tumorigenesis . Cell . 2012 ; 148 : 259 – 272 .
27. Pyruvate kinase type M2 and its role in tumor growth and spreading . Semin Cancer Biol . 2005 ; 15 : 300 – 308 .
28. Beyond aerobic glycolysis: transformed cells can engage in glutamine metabolism that exceeds the requirement for protein and nucleotide synthesis . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 2007 ; 104 : 19345 – 19350 .
29. ATP citrate lyase inhibition can suppress tumor cell growth . Cancer Cell . 2005 ; 8 : 311 – 321 .
30. ATP citrate lyase is an important component of cell growth and transformation . Oncogene . 2005 ; 24 : 6314 – 6322 .
31. Myc regulates a transcriptional program that stimulates mitochondrial glutaminolysis and leads to glutamine addiction . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 2008 ; 105 : 18782 – 18787 .
32. Deficiency in glutamine but not glucose induces MYC-dependent apoptosis in human cells . J Cell Biol . 2007 ; 178 : 93 – 105 .
33. Hypoxia promotes isocitrate dehydrogenase-dependent carboxylation of alpha-ketoglutarate to citrate to support cell growth and viability . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 2011 ; 108 : 19611 – 19616 .
34. Reductive glutamine metabolism by IDH1 mediates lipogenesis under hypoxia . Nature . 2012 ; 481 : 380 – 384 .
35. Reductive carboxylation supports growth in tumour cells with defective mitochondria . Nature . 2012 ; 481 : 385 – 388 .
36. Targeting PI3K signalling in cancer: opportunities, challenges and limitations . Nat Rev Cancer . 2009 ; 9 : 550 – 562 .
37. Transcriptional control of cellular metabolism by mTOR signaling . Cancer Res . 2011 ; 71 : 2815 – 2820 .
38. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease . Cell . 2012 ; 149 : 274 – 293 .
39. The LKB1-AMPK pathway: metabolism and growth control in tumour suppression . Nat Rev Cancer . 2009 ; 9 : 563 – 575 .
40. Hypoxia-inducible factors in physiology and medicine . Cell . 2012 ; 148 : 399 – 408 .
41. Defining the role of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in cancer biology and therapeutics . Oncogene . 2010 ; 29 : 625 – 634 .
42. Translational regulation of gene expression during conditions of cell stress . Mol Cell . 2010 ; 40 : 228 – 237 .
43. The transcription factor HIF-1alpha plays a critical role in the growth factor-dependent regulation of both aerobic and anaerobic glycolysis . Genes Dev . 2007 ; 21 : 1037 – 1049 .
44. Genetic and functional studies implicate HIF1alpha as a 14q kidney cancer suppressor gene . Cancer Discov . 2011 ; 1 : 222 – 235 .
45. Transcriptional regulation and transformation by Myc proteins . Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol . 2005 ; 6 : 635 – 645 .
46. The interplay between MYC and HIF in cancer . Nat Rev Cancer . 2008 ; 8 : 51 – 56 .
47. Global regulation of nucleotide biosynthetic genes by c-Myc . PLoS One . 2008 ; 3 : e2722 .
48. Cell-type independent MYC target genes reveal a primordial signature involved in biomass accumulation . PLoS One . 2011 ; 6 : e26057 .
49. The landscape of somatic copy-number alteration across human cancers . Nature . 2010 ; 463 : 899 – 905 .
50. MYC on the path to cancer . Cell . 2012 ; 149 : 22 – 35 .
51. Targeting mitochondrial glutaminase activity inhibits oncogenic transformation . Cancer Cell . 2010 ; 18 : 207 – 219 .
52. Glucose-independent glutamine metabolism via TCA cycling for proliferation and survival in B cells . Cell Metab . 2012 ; 15 : 110 – 121 .
53. Revisiting the TCA cycle: signaling to tumor formation . Trends Mol Med . 2011 ; 17 : 641 – 649 .
54. Succinate links TCA cycle dysfunction to oncogenesis by inhibiting HIF-alpha prolyl hydroxylase . Cancer Cell . 2005 ; 7 : 77 – 85 .
55. HIF overexpression correlates with biallelic loss of fumarate hydratase in renal cancer: novel role of fumarate in regulation of HIF stability . Cancer Cell . 2005 ; 8 : 143 – 153 .
56. Cell-permeating alpha-ketoglutarate derivatives alleviate pseudohypoxia in succinate dehydrogenase-deficient cells . Mol Cell Biol . 2007 ; 27 : 3282 – 3289 .
57. Germline mutations in FH predispose to dominantly inherited uterine fibroids, skin leiomyomata and papillary renal cell cancer . Nat Genet . 2002 ; 30 : 406 – 410 .
58. Renal cyst formation in Fh1-deficient mice is independent of the Hif/Phd pathway: roles for fumarate in KEAP1 succination and Nrf2 signaling . Cancer Cell . 2011 ; 20 : 524 – 537 .
59. The glycolytic shift in fumarate-hydratase-deficient kidney cancer lowers AMPK levels, increases anabolic propensities and lowers cellular iron levels . Cancer Cell . 2011 ; 20 : 315 – 327 .
60. Haem oxygenase is synthetically lethal with the tumour suppressor fumarate hydratase . Nature . 2011 ; 477 : 225 – 228 .
61. Cancer-associated IDH1 mutations produce 2-hydroxyglutarate . Nature . 2009 ; 462 : 739 – 744 .
62. The common feature of leukemia-associated IDH1 and IDH2 mutations is a neomorphic enzyme activity converting alpha-ketoglutarate to 2-hydroxyglutarate . Cancer Cell . 2010 ; 17 : 225 – 234 .
63. Leukemic IDH1 and IDH2 mutations result in a hypermethylation phenotype, disrupt TET2 function, and impair hematopoietic differentiation . Cancer Cell . 2010 ; 18 : 553 – 567 .
64. IDH1 mutation is sufficient to establish the glioma hypermethylator phenotype . Nature . 2012 ; 483 : 479 – 483 .
65. Oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate is a competitive inhibitor of alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases . Cancer Cell . 2011 ; 19 : 17 – 30 .
66. IDH mutation impairs histone demethylation and results in a block to cell differentiation . Nature . 2012 ; 483 : 474 – 478 .
67. The oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate inhibits histone lysine demethylases . EMBO Rep . 2011 ; 12 : 463 – 469 .
68. Metabolic regulation of epigenetics . Cell Metab . 2012 ; 16 : 9 – 17 .
69. Effective use of PI3K and MEK inhibitors to treat mutant Kras G12D and PIK3CA H1047R murine lung cancers . Nat Med . 2008 ; 14 : 1351 – 1356 .
70. Measurement of clinical and subclinical tumour response using [18F]-fluorodeoxyglucose and positron emission tomography: review and 1999 EORTC recommendations. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) PET Study Group . Eur J Cancer . 1999 ; 35 : 1773 – 1782 .
71. Targeting cancer metabolism: a therapeutic window opens . Nat Rev Drug Discov . 2011 ; 10 : 671 – 684 .
72. Small-molecule inhibition of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase activity suppresses glycolytic flux and tumor growth . Mol Cancer Ther . 2008 ; 7 : 110 – 120 .
73. c-Myc transactivation of LDH-A: implications for tumor metabolism and growth . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 1997 ; 94 : 6658 – 6663 .
74. Glioblastoma cells require glutamate dehydrogenase to survive impairments of glucose metabolism or Akt signaling . Cancer Res . 2009 ; 69 : 7986 – 7993 .
75. Inhibition of fatty acid synthesis delays disease progression in a xenograft model of ovarian cancer . Cancer Res . 1996 ; 56 : 1189 – 1193 .
76. Fatty acid synthase as a potential therapeutic target in cancer . Future Oncol . 2010 ; 6 : 551 – 562 .