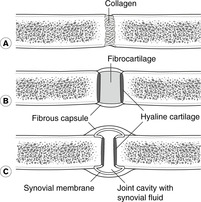
revision
Head and neck
Lateral aspect
| Position | Significance |
|---|---|
| Pterion: 4cm (about) above and anterior to pinna | Anterior division of middle meningeal vessels behind thinnest area of skull, extradural haemorrhages |
| Pterion: above and behind | Central sulcus of cerebral cortex separating motor cortex (anterior) and sensory cortex (posterior) |
| 2cm (about) above pinna | Auditory cortex Superficial temporal pulse (often visible) |
| Between pinna and mandible, extending below angle of mandible | Parotid gland |
| Anterior to pinna | Parotid nodes |
| Mastoid process | Mastoid lymph nodes |
| Temporomandibular joint, below and behind | Terminal branching of external carotid artery |
Anterior aspect
| Position | Significance |
|---|---|
| Bridge of the nose, above and behind | Cribriform plate: anterior cranial fossa fractures, anosmia, CSF rhinorrhoea |
| Supraorbital foramen | Supraorbital nerve (Va) and vessels: fractures |
| Infraorbital foramen | Infraorbital nerves (Vb) and vessels: fractures |
| Mental foramen | Mental nerve (Vc) and vessels: fractures |
Posterior aspect
| Position | Significance |
|---|---|
| External occipital protuberance, above | Visual cortex |
| External occipital protuberance | Confluence of sinuses |
| External occipital protuberance, below | Cerebellum |
Neck
| Position | Significance | Approx. vertebral level |
|---|---|---|
| Hyoid bone, angle of mandible | Tonsillar (jugulodigastric) node | C2 |
| Ear lobe (roughly) – sternoclavicular joint | Internal jugular vein, deep cervical chain of lymph (deep to sternocleidomastoid) | |
| Angle of mandible–midpoint of clavicle | External jugular vein | |
| Lateral to superior border of thyroid cartilage | Bifurcation of common carotid artery, carotid pulse | C3 |
| Behind, and slightly below thyroid prominence | Vocal cords | C4 |
| Cricothyroid membrane | Laryngotomy site | C5 |
| Cricoid cartilage | Cricopharyngeal sphincter, upper extent of oesophagus, trachea | C6 |
| Sternocleidomastoid, trapezius, clavicle | Boundaries of posterior triangle | |
| Posterior triangle: one-third of way down posterior border–one-third of way up anterior border | Accessory nerve (XI) |
Thorax
| Position | Significance | Approx. vertebral level |
|---|---|---|
| Sternoclavicular joint | Formation of brachiocephalic veins (from subclavian, internal jugular) | T2 |
| Suprasternal notch | Trachea | T2 |
| First intercostals space, anteriorly | Formation of superior vena cava | T3 |
| Sternal angle (of Louis) | Bifurcation of trachea, lower limit of arch of aorta | T4 |
| Hilum of lung | T5/6 |
Pleural cavities and reflections
2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12: 2cm above clavicle – sternoclavicular joint – second costal cartilage – fourth costal cartilage – sixth costal cartilage (more lateral on the left) – eighth rib, midclavicular line – tenth rib, midaxillary line – twelfth rib (or lower), midscapular line (behind) – side of vertebra L1.
Lungs
These are similar to the pleura except that lung tissue does not extend much below vertebral level T10.
• Oblique fissure (both sides): spine of vertebra T2 or T3–sixth costal cartilage.
• Horizontal fissure: level of fourth costal cartilage, sternal edge–line of oblique fissure.
• Chest drain: second intercostal space in midclavicular line or fourth or fifth space in midaxillary line.
Heart borders
2 × 3 = 6: second intercostal space, left sternal edge – third intercostal space, right sternal edge – sixth intercostal space, right sternal edge – fifth intercostal space, midclavicular line (normal apex) – back to top.
Heart valves
| Valve | Position | Best heard |
|---|---|---|
| Pulmonary | Retrosternal, level of 3rd rib | 2nd space just to left of sternal edge |
| Aortic | Retrosternal, level of 3rd space | 2nd space just to right of sternal edge |
| Mitral | Retrosternal, level of 4th rib | Apex (5th space, midclavicular line) |
| Tricuspid | Retrosternal, level of 4th space | Lower sternal edge, side depending upon the condition |
Abdomen and pelvis
Anterior abdominal wall
15
• Nine regions: see Figure 11.1 (p. 106). Of these:
– epigastrium: stomach, liver, aorta
– umbilical region: aorta is palpable above the umbilicus
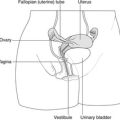
– hypogastrium or suprapubic region: uterus, bladder
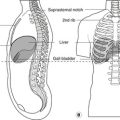
– right hypochondrium: liver and gall bladder
– left hypochondrium: enlarged spleen
– lumbar region: lower poles of the kidneys, colon
McBurney’s point: one-third of the way from the right anterior superior iliac spine to the umbilicus: base of appendix, caecum.
• Quadrants:
– right upper quadrant (gall bladder, enlarged liver)
– left upper quadrant (enlarged spleen)
– right lower quadrant (appendix, caecum, etc.)
– left lower quadrant (sigmoid colon, etc.)
Abdomen, anterior aspect
| Position | Significance | Approx. vertebral level |
|---|---|---|
| Nipple, fourth intercostal space | Liver, upper limit | T7 |
| Xiphoid process | T10 | |
| Origin of coeliac artery | T12 | |
| Origin of superior mesenteric artery | T12/L1 | |
| Tip of 9th costal cartilage | Transpyloric plane: gall bladder, pylorus, duodenojejunal flexure, hilum of kidneys, head of pancreas | L1 |
| Subcostal plane | Origin of gonadal, inferior mesenteric artery (approximate) | L2/3 |
| Umbilicus, just below and to the left | Bifurcation of aorta | L3/4 |
| McBurney’s point: one-third of way between right anterior superior iliac spine and umbilicus | Base of appendix, caecum | L4 |
| Anterior superior iliac spine | Lateral cutaneous nerve of thigh, inguinal ligament attachment | L5 |
| Midinguinal point | Femoral pulse | |
| 2cm above midinguinal point | Deep inguinal ring | |
| Pubic tubercle, above | Superficial inguinal ring |
Abdomen, posterior aspect
| Position | Significance | Approx. vertebral level |
|---|---|---|
| Ribs 9, 10, 11 | Spleen | T11 |
| Rib 12 | Upper pole of kidneys, costodiaphragmatic recess | T12 |
| Hilum of kidney | L1/2 | |
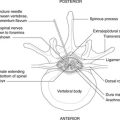
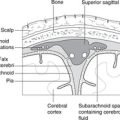
| Line between highest points of iliac crests | Lumbar puncture, extradural anaesthesia | L3/4 |
Upper limb
| Position | Structure, significance |
|---|---|
| Axilla | Axillary lymph nodes (breast cancer, etc.) |
| Arm: medial to biceps muscle | Brachial pulse |
| Cubital fossa | Biceps tendon |
| Cubital fossa: medial to biceps tendon | Brachial pulse |
| Cubital fossa: medial to brachial pulse | Median nerve |
| Wrist: radial side of (lateral to) tendon of flexor carpi ulnaris | Radial pulse |
| Wrist: ulnar side of (medial to) tendon of flexor carpi ulnaris | Ulnar pulse, ulnar nerve |
| Wrist: midline | Median nerve |
| Wrist: dorsum/radials side, between tendons of extensors pollicis longus and brevi | Anatomical snuff box, scaphoid (tenderness could signify fractured scaphoid) |
| Wrist: 2cm square distal to the distal wrist crease in midline | Flexor retinaculum |
| Palpable carpal bones | Pisiform, hamate (ulnar side); scaphoid, trapezium (radial side) |
| Fleshy muscle between thumb and index finger | First dorsal interosseous |
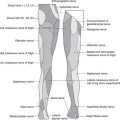
Lower limb
| Position | Structure, significance |
|---|---|
| Gluteal region: midway between posterior superior iliac spine and ischial tuberosity–midway between ischial tuberosity and greater trochanter | Sciatic nerve in gluteal region (to be avoided in injections) |
| Inguinal region: midpoint of inguinal ligament | Femoral pulse (arterial blood for blood gas estimations) |
| Inguinal region: medial to femoral pulse | Femoral vein |
| Inguinal region: lateral to femoral pulse | Femoral nerve |
| Inguinal region: about 2cm below and lateral to pubic tubercle | Saphenous opening, femoral hernia |
| Covering saphenous opening and medial part of inguinal ligament | Inguinal lymph nodes (perineal, lower limb disease) |
| Patella: | |
| Extending about 5cm above upper margin | Suprapatellar bursa |
| Anterior | Prepatellar bursa |
| Below | Infrapatellar bursa |
| Between biceps femoris, lateral head of gastrocnemius (laterally); semitendinosus, medial head of gastrocnemius (medially) | Popliteal fossa |
| Popliteal fossa: upper part, compress artery against popliteal surface of femur | Popliteal pulse (artery here is vulnerable in supracondylar femoral fracture) |
| Neck of fibula, biceps attachment | Common fibular nerve |
| Ankle: halfway between medial and lateral malleoli | Anterior tibial pulse |
| Ankle: anterior to medial malleolus | Saphenous vein and nerve at the ankle |
| Ankle: 2cm behind medial malleolus | Posterior tibial pulse, flexor retinaculum |
| Foot: between tendons of extensor hallucis longus and extensor digitorum longus on dorsum of foot | Dorsalis pedis pulse |
| Palpable foot bones | Head of talus, sustentaculum tali, navicular |