Table 11-1
CDKs, Activating Cyclins, and Select Substrates
| CDK | Cyclin Partner | Substrate |
| CDKi (CDC2) | A and B | Lamins, histone Hi |
| CDK2 | E and A | Rb, P107, P130, Cdt1, CP110 |
| CDK3 | C | Rb |
| CDK4 | D | Rb, P107, P130, SMAD2, and SMAD3 |
| CDK6 | D | Rb, P107, P130, SMAD2, and SMAD3 |
| CDK7 (CAK) | H | CDK1-CDK6, RNA pol 11 |
CDK, Cyclin-dependent kinase.
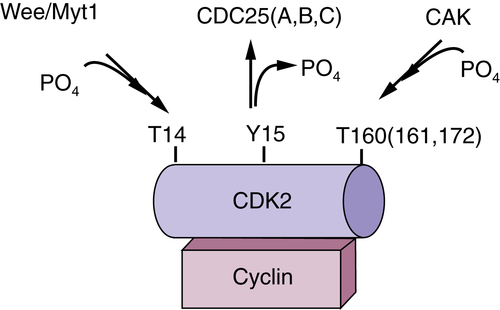
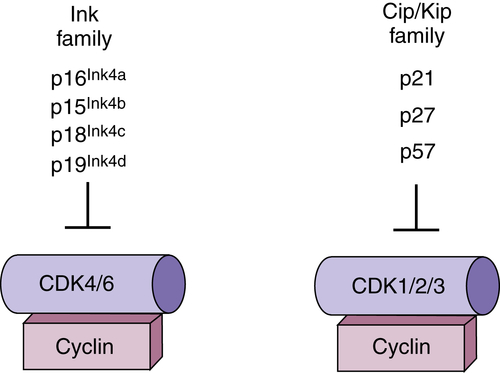
CDK Regulation by Small-Polypeptide Inhibitors
Ink4 Family
Cip/Kip Family
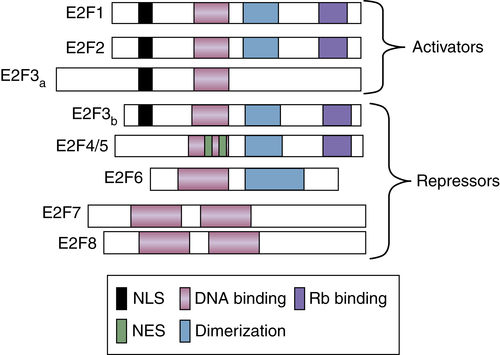
Transcriptional Regulation by the E2F Transcription Factors
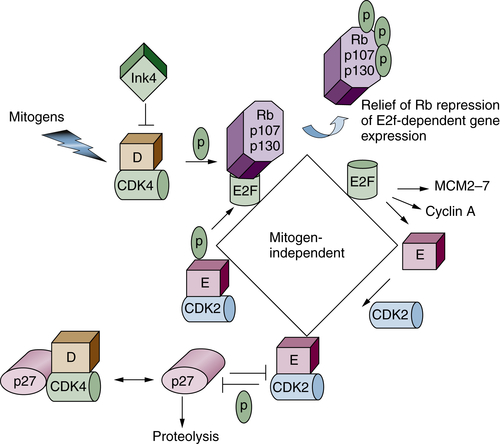
G1 Regulation/Restriction Point Control
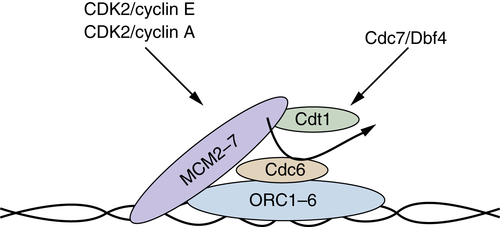
Regulation of DNA Replication (S Phase)
G2/M Transition Regulation
The Kinases of Mitosis
Table 11-2
Regulators of DNA Replication and Function
| Cdt1 | Associates with MCM2-MCM7 and, in concert with Cdc6, facilitates MCM loading on origins. |
| Cdc6 | Functions to recruit and load the MCM complex in an ATPase-dependent manner. |
| CdC45 | Associates with the MCM and is responsible for recruitment of DNA polymerase α, primase, and replication protein A. |
| MCM2-7 | Minichromosome maintenance proteins. Hetero-hexameric complex composed of six distinct but related proteins (MCM2-MCM7). The MCM complex functions as the putative replicative helicase. |
| MCM10 | Structurally distinct from MCM2-MCM7; functions to recruit CDC45. |
| Orc | Origin recognition complex. Hetero-hexameric complex that binds directly to DNA and functions as a protein landing pad on which the replication complexes form. |
| Origin | Functionally defined in mammalian cells as regions of chromatin where DNA replication initiates. |
| Cdc7/Dbf4 | The Cdc7 protein kinase, like cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), requires an allosteric activator, Dbf4. The Cdc7/Dbf4 kinase phosphorylates components of the replication complexes to initiate DNA replication. |
| Pre-RC | The prereplication forms during G1 and contains ORC1-ORC6, Cdc6, MCM2-7. Replication ensues at S phase on recruitment of DNA polymerase and phosphorylation by both the Cdc7/Dbf4 and CDK2-cyclin A protein kinases. |
MCM, Minichromosome maintenance; ORC, origin of replication complex.
Entry into Mitosis
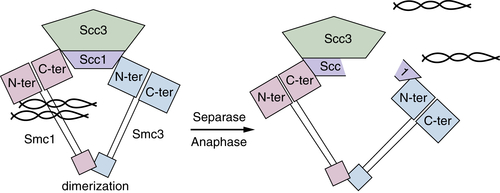
Chromosome Cohesion
Exit from Mitosis
Mitotic Checkpoint
Regulated Proteolysis in Cell Cycle Control
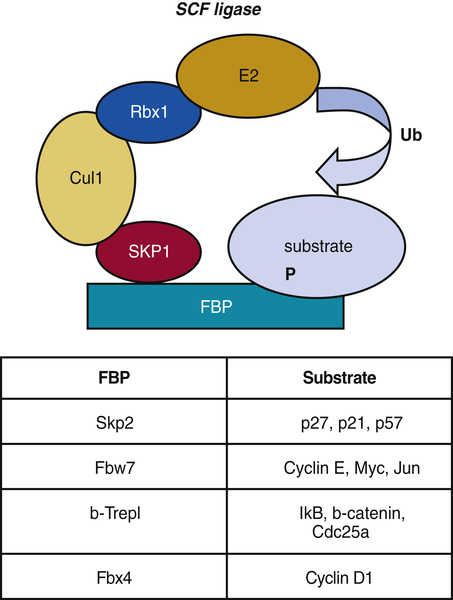
SCF Ligases
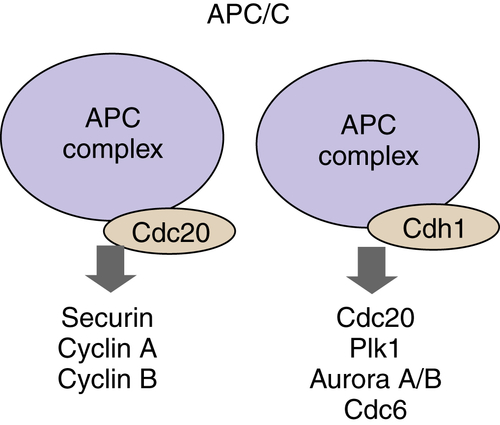
APC/C Ligase
Sumoylation
Integration of Growth Factor Signals During G1 Phase by the Ras Small GTP-Binding Protein
Deregulation of G1 Restriction Point Control in Cancer
Targeting the Cell Cycle as a Therapeutic Modality
Targeting CDKs
Targeting Cell Cycle Checkpoints
Targeting Regulators of Mitosis
Conclusions
1. Human cyclins A and B1 are differentially located in the cell and undergo cell cycle-dependent nuclear transport . J Cell Biol . 1991 ; 115 : 1 – 17 .
2. The crystal structure of cyclin A . Structure . 1995 ; 3 : 1235 – 1247 .
3. Mechanism of CDK activation revealed by the structure of a cyclinA-CDK2 complex . Nature . 1995 ; 376 : 313 – 320 .
4. A cyclin associated with the CDK-activating kinase MO15 . Nature . 1994 ; 371 : 254 – 257 .
5. Cdk-activating kinase complex is a component of human transcription factor TFIIH . Nature . 1995 ; 374 : 283 – 287 .
6. Relationship of CDK-activating kinase and RNA polymerase II CTD kinase TFIIH/TFIIK . Cell . 1994 ; 79 : 1103 – 1109 .
7. The Cdk-activating kinase (CAK) from budding yeast . Cell . 1996 ; 86 : 553 – 564 .
8. A cyclin-dependent kinase-activating kinase (CAK) in budding yeast unrelated to vertebrate CAK . Science . 1996 ; 273 : 1714 – 1717 .
9. Subcellular localisation of human wee1 kinase is regulated during the cell cycle. J Cell Sci . 108 Part . 1995 ; 6 : 2425 – 2432 .
10. Mechanisms of p34cdc2 regulation . Mol Cell Biol . 1993 ; 13 : 1675 – 1685 .
11. Requirement for tyrosine phosphorylation of Cdk4 in G1 arrest induced by ultraviolet irradiation . Nature . 1995 ; 376 : 358 – 362 .
12. Cell cycle regulation by the Cdc25 phosphatase family . Prog Cell. Cycle Res . 2000 ; 4 : 107 – 114 .
13. Reduction of Cdc25A contributes to cyclin E1-Cdk2 inhibition at senescence in human mammary epithelial cells . Oncogene . 2000 ; 19 : 5314 – 5323 .
14. Normal cell cycle and checkpoint responses in mice and cells lacking Cdc25B and Cdc25C protein phosphatases . Mol Cell Biol . 2005 ; 25 : 2853 – 2860 .
15. CDK inhibitors: positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression . Genes Dev . 1999 ; 13 : 1501 – 1512 .
16. A new regulatory motif in cell-cycle control causing specific inhibition of cyclin D/CDK4 . Nature . 1993 ; 366 : 704 – 707 .
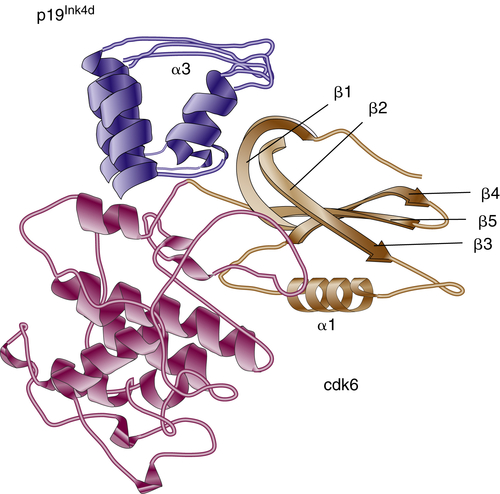
17. Crystal structure of the complex of the cyclin D-dependent kinase Cdk6 bound to the cell-cycle inhibitor p19INK4d . Nature . 1998 ; 395 : 244 – 250 .
18. Structural characterization of the tumor suppressor p16, an ankyrin-like repeat protein . Protein Sci . 1996 ; 5 : 1776 – 1784 .
19. Oncogenic ras provokes premature cell senescence associated with accumulation of p53 and p16INK4a . Cell . 1997 ; 88 : 593 – 602 .
20. Reciprocal Rb inactivation and p16INK4 expression in primary lung cancers and cell lines . Cancer Res . 1995 ; 55 : 505 – 509 .
21. Distinct versus redundant properties among members of the INK4 family of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors . FEBS Lett . 2000 ; 470 : 161 – 166 .
22. Alternative reading frames of the INK4a tumor suppressor gene encode two unrelated proteins capable of inducing cell cycle arrest . Cell . 1995 ; 83 : 993 – 1000 .
23. Tumor surveillance via the ARF-p53 pathway . Genes Dev . 1998 ; 12 : 2984 – 2991 .
24. Role of the INK4a locus in tumor suppression and cell mortality . Cell . 1996 ; 85 : 27 – 37 .
25. Separate domains of p21 involved in the inhibition of Cdk kinase and PCNA . Nature . 1995 ; 374 : 386 – 388 .
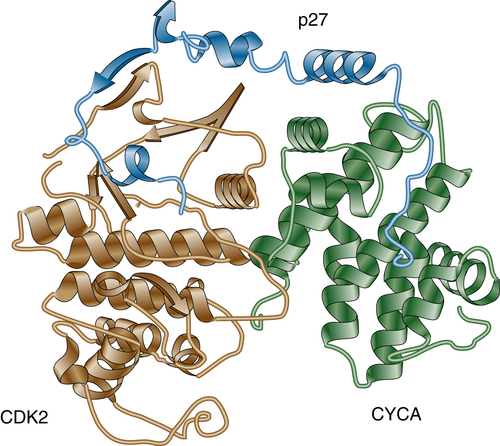
26. Crystal structure of the p27Kip1 cyclin-dependent-kinase inhibitor bound to the cyclin A-Cdk2 complex . Nature . 1996 ; 382 : 325 – 331 .
27. p27Kip1, a cyclin-Cdk inhibitor, links transforming growth factor-beta and contact inhibition to cell cycle arrest . Genes Dev . 1994 ; 8 : 9 – 22 .
28. PAX3-FOXO1 controls expression of the p57Kip2 cell-cycle regulator through degradation of EGR1 . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 2007 ; 104 : 18085 – 18090 .
29. A role of p73 in mitotic exit . J Biol Chem . 2005 ; 280 : 30354 – 30360 .
30. Role of an adenovirus E2 promoter binding factor in E1A-mediated coordinate gene control . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 1987 ; 84 : 2180 – 2184 .
31. Promoter interaction of the E1A-inducible factor E2F and its potential role in the formation of a multi-component complex . EMBO J . 1987 ; 6 : 2061 – 2068 .
32. Expression of transcription factor E2F1 induces quiescent cells to enter S phase . Nature . 1993 ; 365 : 349 – 352 .
33. Regulation of the cyclin E gene by transcription factor E2F1 . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 1995 ; 92 : 12146 – 12150 .
34. Differential activities of E2F family members: unique functions in regulating transcription . Mol Carcinog . 1998 ; 22 : 190 – 198 .
35. Direct binding of cyclin D to the retinoblastoma gene product (pRb) and pRb phosphorylation by the cyclin D-dependent kinase CDK4 . Genes Dev . 1993 ; 7 : 331 – 342 .
36. The DP-E2F-like gene DEL1 controls the endocycle in Arabidopsis thaliana . Curr Biol . 2005 ; 15 : 59 – 63 .
37. Synergistic function of E2F7 and E2F8 is essential for cell survival and embryonic development . Dev Cell . 2008 ; 14 : 62 – 75 .
38. Regulation of CYL/cyclin D genes by colony-stimulating factor 1 . Ciba Found Symp . 1992 ; 170 : 209 – 219; discussion 219-226 .
39. MCM proteins in DNA replication . Annu Rev Biochem . 1999 ; 68 : 649 – 686 .
40. Phosphorylation of MCM3 on Ser-112 regulates its incorporation into the MCM2-7 complex . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 2008 ; 105 : 8079 – 8084 .
41. Integrating DNA replication with trans-lesion synthesis via Cdc7 . Cell Cycle . 2010 ; 9 : 4818 – 4823 .
42. The SCF(Skp2) ubiquitin ligase complex interacts with the human replication licensing factor Cdt1 and regulates Cdt1 degradation . J Biol Chem . 2003 ; 278 : 30854 – 30858 .
43. The histone H4 Lys 20 methyltransferase PR-Set7 regulates replication origins in mammalian cells . Nat Cell Biol . 2010 ; 12 : 1086 – 1093 .
44. Analysis of model replication origins in Drosophila reveals new aspects of the chromatin landscape and its relationship to origin activity and the prereplicative complex . Mol Biol Cell . 2011 ; 23 : 200 – 212 .
45. New histone incorporation marks sites of UV repair in human cells . Cell . 2006 ; 127 : 481 – 493 .
46. Human Asf1 and CAF-1 interact and synergize in a repair-coupled nucleosome assembly pathway . EMBO Rep . 2002 ; 3 : 329 – 334 .
47. A model for mitotic inheritance of histone lysine methylation . EMBO Rep . 2012 ; 13 : 60 – 67 .
48. TrxG and PcG proteins but not methylated histones remain associated with DNA through replication . Cell . 2012 ; 150 : 922 – 933 .
49. Principles of CDK regulation . Nature . 1995 ; 374 : 131 – 134 .
50. Regulation of APC activity by phosphorylation and regulatory factors . J Cell Biol . 1999 ; 146 : 791 – 800 .
51. Identification and cloning of a protein kinase-encoding mouse gene, Plk, related to the polo gene of . Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 1993 ; 90 : 4882 – 4886 .
52. Sister-chromatid separation at anaphase onset is promoted by cleavage of the cohesin subunit Scc1 . Nature . 1999 ; 400 : 37 – 42 .
53. Separating sister chromatids . Trends Biochem Sci . 1999 ; 24 : 98 – 104 .
54. A topological interaction between cohesin rings and a circular minichromosome . Cell . 2005 ; 122 : 849 – 860 .
55. Condensins, chromosome condensation protein complexes containing XCAP-C, XCAP-E and a Xenopus homolog of the Drosophila Barren protein . Cell . 1997 ; 89 : 511 – 521 .
56. Plk is an M-phase-specific protein kinase and interacts with a kinesin-like protein, CHO1/MKLP-1 . Mol Cell Biol . 1995 ; 15 : 7143 – 7151 .
57. Tension, microtubule rearrangements, and the proper distribution of chromosomes in mitosis . Chromosoma . 1989 ; 98 : 33 – 39 .
58. Microtubule attachment and spindle assembly checkpoint signalling at the kinetochore . Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol . 2013 ; 14 : 25 – 37 .
59. Mutations of mitotic checkpoint genes in human cancers . Nature . 1998 ; 392 : 300 – 303 .
60. Ub in charge: regulating E2 enzyme nuclear import . Nat Cell Biol . 2005 ; 7 : 12 – 14 .
61. Regulation of the cell cycle by SCF-type ubiquitin ligases . Semin Cell Dev Biol . 2005 ; 16 : 323 – 333 .
62. E3 ubiquitin ligase that recognizes sugar chains . Nature . 2002 ; 418 : 438 – 442 .
63. Targeted disruption of Skp2 results in accumulation of cyclin E and p27(Kip1), polyploidy and centrosome overduplication . EMBO J . 2000 ; 19 : 2069 – 2081 .
64. A CDK-independent function of mammalian Cks1: targeting of SCF(Skp2) to the CDK inhibitor p27Kip1 . Mol Cell . 2001 ; 7 : 639 – 650 .
65. Defective cardiovascular development and elevated cyclin E and Notch proteins in mice lacking the Fbw7 F-box protein . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 2004 ; 101 : 3338 – 3345 .
66. Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of SCF(Fbx4) dimerization and activity involves a novel component, 14-3-3varepsilon . Oncogene . 2011 ; 30 : 1995 – 2002 .
67. Mutations in Fbx4 inhibit dimerization of the SCF(Fbx4) ligase and contribute to cyclin D1 overexpression in human cancer . Cancer Cell . 2008 ; 14 : 68 – 78 .
68. Multiplex mutation screening by mass spectrometry in gastrointestinal stromal tumours . Pathology . 2012 ; 44 : 460 – 464 .
69. The Fbx4 tumor suppressor regulates cyclin D1 accumulation and prevents neoplastic transformation . Mol Cell Biol . 2011 ; 31 : 4513 – 4523 .
70. Ubiquitin ligases: cell-cycle control and cancer . Nat Rev Cancer . 2006 ; 6 : 369 – 381 .
71. SUMO-modified nuclear cyclin D1 bypasses Ras-induced senescence . Cell Death Differ . 2006 ; 18 : 304 – 314 .
72. Induction of cyclin D1 overexpression by activated ras . Oncogene . 1994 ; 9 : 3627 – 3633 .
73. Cyclin D1 and c-myc internal ribosome entry site (IRES)-dependent translation is regulated by AKT activity and enhanced by rapamycin through a p38 MAPK- and ERK-dependent pathway . J Biol Chem . 2005 ; 280 : 10964 – 10973 .
74. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta regulates cyclin D1 proteolysis and subcellular localization . Genes Dev . 1998 ; 12 : 3499 – 3511 .
75. Cyclins and breast cancer . Breast Cancer Res Treat . 1998 ; 52 : 17 – 28 .
76. Genetic alterations of cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, and Cdk inhibitors in human cancer . Adv Cancer Res . 1996 ; 68 : 67 – 108 .
77. Phosphorylation-dependent ubiquitination of cyclin D1 by the SCF(FBX4-alphaB crystallin) complex . Mol Cell . 2006 ; 24 : 355 – 366 .
78. AlphaB-crystallin is mutant B-RAF regulated and contributes to cyclin D1 turnover in melanocytic cells . Pigment Cell Melanoma Res . 2011 ; 23 : 201 – 209 .
79. AlphaB-crystallin as a marker of lymph node involvement in breast carcinoma . Cancer . 2004 ; 100 : 2543 – 2548 .
80. SCF(Fbx4/alphaB-crystallin) E3 ligase: when one is not enough . Cell Cycle . 2008 ; 7 : 2983 – 2986 .
81. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation . Cell . 2011 ; 144 : 646 – 674 .
82. Targeting the cell cycle: a new approach to cancer therapy . J Clin Oncol . 2005 ; 23 : 9408 – 9421 .
83. Selective killing of transformed cells by cyclin/cyclin-dependent kinase 2 antagonists . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A . 1999 ; 96 : 4325 – 4329 .
84. A phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of AT7519, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor in patients with refractory solid tumors . Ann Oncol . 2011 ; 22 : 2137 – 2143 .
85. Selective CDK4/6 inhibition with tumor responses by PD0332991 in patients with mantle cell lymphoma . Blood . 2012 ; 119 : 4597 – 4607 .
86. Phase I, dose-escalation trial of the oral cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor PD 0332991, administered using a 21-day schedule in patients with advanced cancer . Clin Cancer Res . 2012 ; 18 : 568 – 576 .
87. Phase I study of PD 0332991, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, administered in 3-week cycles (Schedule 2/1) . Br J Cancer . 2011 ; 104 : 1862 – 1868 .
88. Treatment of growing teratoma syndrome . N Engl J Med . 2009 ; 360 : 423 – 424 .
89. G1 cell-cycle control and cancer . Nature . 2004 ; 432 : 298 – 306 .
90. DNA repair dysregulation from cancer driver to therapeutic target . Nat Rev Cancer . 2012 ; 12 : 801 – 817 .
91. A phase II study of cell cycle inhibitor UCN-01 in patients with metastatic melanoma: a California Cancer Consortium trial . Invest New Drugs . 2012 ; 30 : 741 – 748 .
92. A Phase 1 study of UCN-01 in combination with irinotecan in patients with resistant solid tumor malignancies . Cancer Chemother Pharmacol . 2011 ; 67 : 1225 – 1237 .
93. A phase I trial of UCN-01 and prednisone in patients with refractory solid tumors and lymphomas . Cancer Chemother Pharmacol . 2010 ; 65 : 383 – 389 .
94. Anticancer therapy with checkpoint inhibitors: what, where and when? Trends Pharmacol Sci . 2011 ; 32 : 308 – 316 .
95. Aurora kinase inhibitor patents and agents in clinical testing: an update (2009-10) . Expert Opin Ther Pat . 2011 ; 21 : 857 – 884 .
96. Polo-like kinase (PLK) inhibitors in preclinical and early clinical development in oncology . Oncologist . 2009 ; 14 : 559 – 570 .
97. Kinesins and cancer . Nat Rev Cancer . 2012 ; 12 : 527 – 539 .
98. Living with or without cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases . Genes Dev . 2004 ; 18 : 2699 – 2711 .