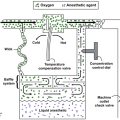
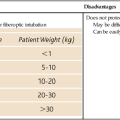
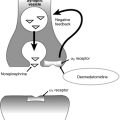
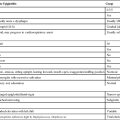
Principles of medical professional liability insurance
Exclusions—what is not covered?
Medical professional liability insurance policies generally contain exclusionary language expressly limiting coverage in specifically defined situations. Although the exclusionary language varies among different policies, most medical professional liability policies routinely exclude coverage for specific situations (Box 249-1).