Chapter 5. Physical Assessment
Guidelines for Inspection
▪ Inspection is a simple but highly skilled technique.
▪ Inspection involves the use of sight, hearing, and smell in a systematic assessment of infants and children.
▪ Inspection is essential at the beginning of the health assessment to detect obvious health concerns and to establish priorities.
▪ Inspection should be thorough and should involve each area of the body.
▪ Body parts are assessed for shape, color, symmetry, odor (Table 5-1), and abnormalities.
| Odor | Significance |
|---|---|
| Acetone or fruity odor | Might indicate diabetic acidosis |
| Ammonia | Might indicate urinary tract infection |
| Fecal odor (breath or diaper area) | Associated with soiled diapers, fecal incontinence, bowel obstruction |
| Foul-smelling stool | Might indicate gastroenteritis, cystic fibrosis, malabsorption syndromes |
| Halitosis | Associated with poor oral hygiene, dental caries or abscess, throat infection, sinusitus, constipation, foreign body in nasal passage |
| Musty odor | Associated with infection underneath a cast or dressing |
| Sweet, thick odor | Might indicate Pseudomonas infection |
▪ Careful inspection requires good lighting.
Guidelines for Palpation
▪ Palpation involves the use of fingers and palms to determine temperature, hydration, texture, shape, movement, and areas of tenderness. Palpation can be light or deep. Light palpation is used to assess skin temperature, texture, and hydration; overt, large, or superficial masses; fluid and muscle guarding; and superficial tenderness. Light palpation is performed with the dominant hand, fingers together. The fingerpads are placed on the skin in a plane parallel to the area and the skin is depressed gently and lightly (about 1 cm or 0.4 inches) in a circular motion. If the child is ticklish, lift the hand fully off the skin before moving to another area. Deep palpation is used to assess the position of organs or masses, as well as their consistency, shape, mobility, and areas of discomfort. It is frequently used in abdominal and reproductive assessments. Deep palpation involves depressing the skin to a depth of approximately 4 to 5 cm (1.5 to 2 inches).
▪ Warm hands before beginning palpation.
▪ Keep fingernails short.
▪ Palpate areas of tenderness or vulnerability last. If pain is experienced during palpation, discontinue palpation in that area immediately.
▪ Palpate with fingertips for pulsation, size, shape, texture, hydration, and mobility and consistency of organs.
▪ Palpate with palms for vibration.
▪ Palpate with back of hand for temperature.
▪ The nurse can assist the ticklish child by first placing the child’s hands on the skin and gradually sliding hands over those of the child or by having the child keep his or her hands over the nurse’s during examination.
▪ Move firmly and without hesitation.
Guidelines for Percussion
▪ Percussion involves the use of tapping to produce sound waves, which are characterized regarding intensity, pitch, duration, and quality (Table 5-2).
| Percussion Sound | Intensity | Pitch | Duration | Quality | Body Region Where Sound Might Be Heard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tympany | Loud | High | Moderate | Drumlike | Gastric bubble, air-filled intestine (simulate by tapping puffed-out cheeks) |
| Resonance | Moderate to loud | Low | Long | Hollow | Lungs |
| Hyperresonance | Very loud | Very low | Long | Booming | Lungs with trapped air, lungs of a young child |
| Dullness | Soft to moderate | High | Moderate | Thudlike | Liver, fluid-filled space (e.g., stomach) |
| Flatness | Soft | High | Short | Flat | Muscle |
▪ Percussion can be direct or indirect.
Direct percussion involves striking the body part directly with one or two fingers.
Indirect percussion involves a pleximeter and a plexor.
Place the middle finger (pleximeter) of the nondominant hand gently against child’s skin.
Strike the distal joint of the pleximeter with the tip of the middle finger (plexor) of the dominant hand (Figure 5-1).
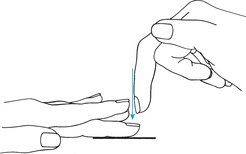 |
| Figure 5-1Percussion. Note position of fingers. |
The blow to the pleximeter should be crisp, and the plexor must be perpendicular.
The wrist movement is essential to percussion and must be a snapping motion.
The nail of the plexor should be short.
▪ Percuss from resonance to dullness.
Guidelines for Auscultation
▪ Auscultation is the process of listening for body sounds.
▪ The bell (cupped portion) of the stethoscope is used for low-pitched sounds (e.g., cardiovascular sounds), and the diaphragm (flat portion) is used for high-pitched sounds (e.g., those found in the lung and bowel).
▪ The diaphragm of the stethoscope is placed firmly against the wall of the body part. The examiner must avoid pressing too firmly, causing the skin to flatten and vibrations to decrease. Resting the heel of the hand on the child will assist in avoiding heavy pressure. Place the bell lightly on the skin surface. If it is placed too firmly, it stretches the skin, causing it to act like a diaphragm.
▪ The examiner should practice identifying normal sounds before trying to identify abnormal ones.