Paravertebral nerve blocks
Indications
PVBs can be utilized to provide anesthesia and analgesia for a variety of procedures (Box 126-1). PVBs provide excellent analgesia after thoracotomy and have unique advantages in patients with anatomic abnormalities, such as kyphoscoliosis and ankylosing spondylitis, in which thoracic epidural placement may be difficult or impossible. PVBs provide better deafferentation than does a thoracic epidural technique, which may help explain why PVBs result in better preservation of pulmonary function, compared with epidural analgesia. There is also evidence that the intensive deafferentation provided by PVBs may attenuate chronic pain and, when used during surgery for resection of (breast) malignancy, may decrease the incidence of metastasis.
Regional anatomy
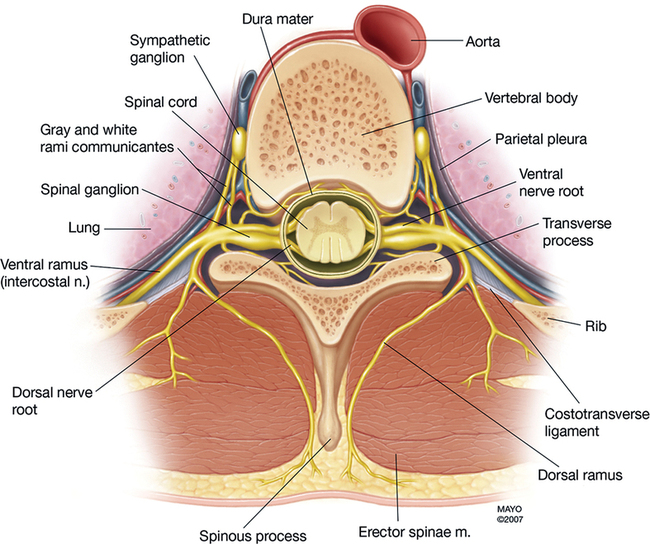
The paravertebral space is a wedge-shaped anatomic compartment adjacent to the vertebral bodies. The space is defined anterolaterally by the parietal pleura; posteriorly by the superior costotransverse ligament (thoracic levels); medially by the vertebra, vertebral disk, and intervertebral foramina; and superiorly and inferiorly by the heads of the ribs. Within this space, the spinal root emerges from the intervertebral foramen and divides into dorsal and ventral rami (Figure 126-1).
Anatomic technique
Position
Landmarks
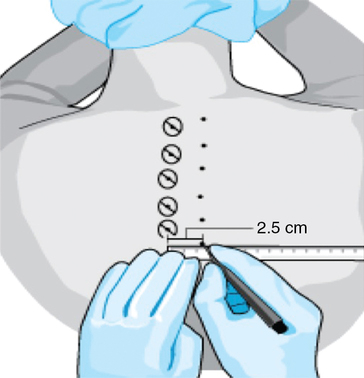
The spinous process of each level is identified, and a mark is placed at the most superior aspect. From the midpoint of these marks, a needle-entry site is marked 2.5 cm laterally (Figure 126-2). In the thoracic area, these marks should overlie the transverse process of the immediately caudal vertebra (because of the extreme angulation of the thoracic spinous processes). In the lumbar area, the transverse process is at the same level as the spinous process or even one level above the spinous process.