O
oat cell carcinoma histological subtype of small cell carcinoma most commonly of bronchogenic epithelium. It accounts for approximately 20% of all lung cancers and is characterized by rapid growth (doubling time approximately 29 days). The highest incidence is in smokers. The lung primary may present with cough, haemoptysis, recurrent pneumonia, increasing breathlessness and weight loss or may be an incidental finding on chest X-ray. Therapy generally does not include surgery, but 90% are sensitive to chemotherapy, which is usually the treatment of choice.
objective associated with things external to oneself.
objective signs those which the observer notes, as distinct from the symptoms of which the patient complains.
oblique fracture a break in bone continuity that is at an angle to the main shaft of the bone.
oblique incidence when a radiotherapy beam enters the patient at an angle other than 90° due to the curvature of the skin surface.
observational study research in which the researcher observes, listens and records the events of concern. Where the researcher participates and has a role it is termed a participant observational study. May be used in qualitative social science research.
obstetrician a qualified doctor who practices the science and art of obstetrics.
obstetrics the science dealing with the care of the pregnant woman during the antenatal, parturient and puerperal stages; midwifery.
obturator that which closes an aperture.
obturator foramen the opening in the innominate bone which is closed by muscles and fascia.
occipital associated with the back of the head.
occipital bone the bone forming the back and part of the base of the skull, characterized by a large hole through which the spinal cord passes.
occipitoanterior describes a presentation when the fetal occiput lies in the anterior half of the maternal pelvis.
occipitofrontal associated with the occiput and forehead.
occipitoposterior describes a presentation when the fetal occiput is in the posterior half of the maternal pelvis.
occiput the posterior region of the skull.
occlusal biting edge of the teeth.
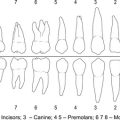
occlusal film a radiographic film in a waterproof envelope which the patient bites on, used to demonstrate either upper or lower 321123 on a single film.
occlusion the closure of an opening, especially of ducts or blood vessels. In dentistry, the contact of the upper and lower teeth in any jaw position. See also centric occlusion, traumatic occlusion.
occult blood blood that is not obvious on examination, detected by a chemical test, microscopic or spectroscopic examination.
occupational disease see industrial disease.
occupational exposure job-related risk of exposure to carcinogens.
occupational health the active and proactive management of health in the workplace.
OCR (Optical Character Recognition) a means of the computer directly reading printed or written characters.
ocular associated with the eye.
oculomotor the third pair of cranial nerves which innervate four of the extrinsic muscles and the upper eye lid. They also alter the shape of the lens and control pupil size.
odontoid process a peg-like projection of the axis (second cervical vertebra).
oedema abnormal infiltration of tissues with fluid. There are many causes, including reduced blood albumin, disease of the cardiopulmonary system, the urinary system and the liver. See also angio-oedema, ascites.
oesophageal associated with the oesophagus.
oesophageal atresia a narrowing of the oesophagus which is often associated with a tracheo-oesophageal fistula.
oesophageal ulcer ulceration of the oesophagus due to gastro-oesophageal reflux caused by hiatus hernia.
oesophageal varices varicosity of the veins in the lower oesophagus due to portal hypertension. These varices can bleed and may cause a massive haematemesis.
oesophagostomy a surgically established fistula between the oesophagus and the skin in the root of the neck. May be used temporarily for feeding after excision of the pharynx for malignant disease.
oesophagus the musculomembranous canal, 23cm in length, extending from the pharynx to the stomach.
oestradiol (estradiol) an endogenous oestrogen secreted by the corpus luteum.
oestriol (estriol) an endogenous oestrogen. Produced by the fetus and placenta. Oestriol levels in maternal blood or urine can be used to assess fetal well-being and placental function.
oestrogens (estrogens) a generic term referring to a group of steroid hormones, oestradiol, oestriol and oestrone. Produced by the ovaries, placenta, testes and, in smaller amounts, the adrenal cortex in both sexes. Oestrogens influence normal skeletal growth especially in puberty and are responsible for female secondary sexual characteristics and the development and proper functioning of the female genital organs. Used in the combined oral contraceptive and as hormone replacement.
oestrone (estrone) an endogenous oestrogen.
off-centre field of view in magnetic resonance imaging a field of view that is not centred at the isocentre of the magnet.
ohm the unit of electrical resistance equal to the resistance between two points on a conductor when a potential difference of one volt between the points, produces a current of one ampere.
Ohm’s law the current flowing through a conductor is proportional to the potential difference which exists across it providing other physical conditions remain constant.
olecranon process the large process at the upper end of the ulna; it forms the point of the elbow when the arm is flexed.
olfactory associated with the sense of smell.
olfactory nerve the first pair of cranial nerves. They carry sensory impulses from the olfactory epithelium of the nose to the brain.
oligodactyly a developmental absence of one or more digits (fingers or toes). There is total absence of all parts of the digit, for example, metatarsals and all phalanges.
oligodendrocyte a neuroglial cell of the central nervous system.
oligodendroglioma a slow-growing tumour most commonly of the frontal lobe of the brain, may become more aggressive after many years.
oligospermia a diminished output of spermatozoa.
omentum a sling-like fold of peritoneum. The functions of the omentum are support and protection, limiting infection and fat storage. greater omentum the fold which hangs from the lower border of the stomach and covers the front of the intestines. lesser omentum a smaller fold, passing between the transverse fissure of the liver and the lesser curvature of the stomach.
omphalocele congenital herniation of the gut through the abdominal wall around the umbilicus which is associated with chromosomal abnormality.
oncogene an altered gene that contributes to cancer development.
oncogenic capable of tumour production.
oncology the scientific study and therapy of neoplastic growths.
one-tailed hypothesis a theory that predicts a particular outcome.
oogenesis the formation of oocytes in the ovary. See also gametogenesis.
oophorectomy the surgical removal of an ovary.
oophoropexy the surgical fixation of a displaced ovary to the abdominal wall or the inferior body of the uterus, can be done prior to radiotherapy treatment so that the ovary can be protected from receiving a large dose of radiation.
opacity the incident light over the transmitted light and is a measure of the effect the radiograph has on the original light shining on it.
open (compound) fracture there is a wound permitting communication of broken bone end with air.
open reduction the realigning of fractures using a surgical procedure.
operational management the management of the day-to-day activities (operations) of an organization such as a district general hospital. See also strategic management.
ophthalmic applicator equipment which is sutured to the eye to hold the radioactive, source iodine-125, when treating the eye. The applicator should be handled with rubber-tipped forceps to prevent damage to the thin, active window, other radiation sources can be used.
ophthalmology the science that deals with the structure, function, diseases and treatment of the eye.
ophthalmoscope instrument for examining the interior of the eye, consisting of a mirror with a hole in it through which the observer looks. The retina is illuminated by light reflected from the mirror.
opportunity cost when a resource is used in a particular way, the opportunity to use it for another purpose is lost. This includes money, time and the activities which cannot be undertaken. An example in health care would be the decision to use money for an expensive cancer drug leading to a lost opportunity to spend the money for another service such as cataract surgery.
opportunistic infection a serious infection with a microorganism which normally has little or no pathogenic activity but causes disease where patient resistance is reduced by a serious disease, invasive treatments or drugs.
opposition describes the position of the thumb and fingers when objects are picked up or grasped between thumb and fingers.
opsins protein part of visual pigments found in cones and rods.
opsonin complement protein or an antibody which coats an antigen.
optic atrophy pathological whitening of the optic nerve head with loss of nerve axons.
optic chiasma the meeting of the two optic nerves; where the fibres from the medial or nasal half of each retina (supplying half the visual field in either eye) cross the middle line to join the optic tract of the opposite side.
optic disc the point where the optic nerve enters the eyeball.
optic nerves second pair of cranial nerves. They convey impulses from the rods and cones in the retina to the brain.
optic neuritis inflammation in the optic nerve that can be the first sign of multiple sclerosis.
optic neuropathy disease of the optic nerve.
optical aberration imperfect focus of light rays by a lens.
optical disk a disk, usually a DVD or a CD that uses light in the form of a laser to burn data onto the disk and also to read information from the disk.
optical sensitizing increasing the spectral sensitivity of the film by adding impurities to the film emulsion, because it is done by adding coloured dyes and therefore can be called dye sensitizing, colour sensitizing or spectral sensitizing.
oral associated with the mouth.
oral cavity (buccal cavity) the mouth.
oral cholecystography the radiographic investigation of the biliary tract following the ingestion of a contrast agent, now superseded by ultrasound techniques.
oral medicine branch of dentistry concerned with the management of diseases of the oral mucosa and related structures, including oral manifestations of systemic diseases.
oral rehydration solution (ORS) a solution for the treatment of diarrhoeal dehydration. It contains glucose and electrolytes such as sodium chloride.
oral rehydration therapy (ORT) administration of oral rehydration solution by mouth to correct dehydration.
oral surgery branch of dentistry concerned with minor surgery to the teeth and jaws.
orbicular resembling a globe; spherical or circular.
orbit the bony socket containing the eyeball and its appendages.
orbitomeatal baseline a line joining the outer canthus of the eye to the mid point of the external auditory meatus (see figure on p. 278).
orchidectomy the surgical removal of a testis.
ordinal data categorical data that can be ordered or ranked, for example, general condition – good, fair or bad, or size in general terms, as in ‘smaller than’. See also nominal data.
ordinal scale the numbers allotted to the ranking or ordering data in a rough sequence.
organ an assembly of different tissues to form a distinct functional unit, for example, liver, uterus, able to perform specialized functions.
organ of Corti sited in the cochlea of the internal ear it contains the auditory receptors of the cochlear branch of the vestibulocochlear nerve.
organism a living cell or group of cells differentiated into functionally distinct parts which are interdependent.
organs at risk the organs of the body that are more sensitive to radiation and therefore may influence treatment planning or prescribed dose, for example eyes, spinal cord and gonads.
origin the commencement or source of anything. origin of a muscle the end that remains relatively fixed during contraction of the muscle.
ornithine an amino acid, obtained from arginine during the urea cycle.
orogenital associated with the mouth and the external genital area.
oropharyngeal associated with the mouth and pharynx.
oropharyngeal airway a flexible oval tube, such as a Guedel airway, which can be placed along the upper surface of the tongue to prevent a flaccid tongue from resting against the posterior pharyngeal wall, thereby obstructing the airway, and is commonly used during general anaesthesia. Also used during cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
oropharynx that portion of the pharynx which is below the level of the soft palate and above the level of the hyoid bone.
orthochromatic emulsions film emulsions that have a spectral sensitivity up to and including the green part of the visible spectrum tend to be used with rare earth intensifying screens.
orthodontic device device used to move teeth by the controlled application of force. May be removable, myofunctional (functional) or fixed.
orthodontics a branch of dentistry concerned with the prevention and correction of irregularities and malocclusion of the teeth.
orthognathic surgery surgery aimed at correcting abnormalities in position of the jaw to improve function and appearance.
orthogonal radiographs radiographs taken at 90 degrees to one another to localize the treatment area or to verify the relative positions of radioactive sources with reference to the associated anatomy.
orthopaedics formerly a specialty devoted to the correction of deformities in children. It is now a branch of surgery dealing with all conditions affecting the locomotor system.
orthopantomograph specialist dental, tomographic equipment for imaging the upper and lower teeth on one projection.
orthosis external device utilized to correct, control or counteract the effect of an actual or developing deformity. They include braces, callipers and splints.
Ortolani’s sign a test performed shortly after birth for the diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip (congenital dislocation of the hip). It should always be undertaken by an experienced clinician. Often used in conjunction with Barlow’s sign/test.
os a mouth. For example, external os, the opening of the cervix into the vagina, internal os, the opening of the cervix into the uterine cavity.
oscilloscope an instrument with a cathode ray tube, which displays a visual representation of electrical variations produced by a beam of electrons hitting the screen.
Osgood–Schlatter disease see Schlatter’s disease.
osmosis the passage of pure solvent across a semipermeable membrane under the influence of osmotic pressure. It is the movement of a dilute solution into a more concentrated solution.
osseous relating to or resembling bone.
ossicles small bones, particularly those contained in the middle ear; the malleus, incus and stapes.
ossification the conversion of cartilage, etc. into bone. Also known as osteogenesis.
osteitis inflammation of bone.
osteitis deformans see Paget’s disease.
osteitis fibrosa cavities form in the interior of bone. The cysts may be solitary or the disease may be generalized. This second condition may be the result of excessive parathyroid secretion and absorption of calcium from bone.
osteoarthritis sometimes termed degenerative arthritis, although the disease process is much more than simply ‘wear and tear’; may be primary, or may follow injury or disease involving the articular surfaces of synovial joints. The articular cartilage becomes worn, osteophytes form at the periphery of the joint surface and loose bodies may result.
osteoarthropathy a condition where the bones of the forearms and shins become inflamed and painful, often associated with lung cancer.
osteoblast a bone-forming cell.
osteoblastoma a small, benign, tumour of poorly formed bone and fibrous tissue, seen in children and young adults.
osteochondritis originally an inflammation of bone cartilage. Usually applied to non-septic conditions, especially avascular necrosis involving joint surfaces, for example, osteochondritis dissecans in which a portion of joint surface may separate to form a loose body in the joint. See also Scheuermann’s disease, K°hler’s disease.
osteochondroma a benign bony and cartilaginous tumour.
osteochondrosis an idiopathic disease characterized by a disorder of the ossification of hyaline cartilage (endochondral). It encompasses a group of syndromes classified on the basis of their anatomical location. Primary articular epiphysis – Freiberg’s disease and K°hler’s disease. Secondary articular epiphysis – osteochondritis dissecans of the talus. Non-articular epiphysis (apophyseal injury) – Sever’s disease. The osteochondroses occur during the years of rapid growth. Aetiology has been linked to hereditary factors, trauma, nutritional factors and ischaemia. The articular osteochondroses such as Freiberg’s, K°hler’s and osteochondritis dissecans are characterized by fragmentation with a centre of ossification.
osteoclasis the therapeutic fracture of a bone.
osteoclast cell that resorbs bone.
osteoclastoma a tumour of the osteoclasts. May be benign, locally recurrent, or malignant. The usual site is near the end of a long bone.
osteodystrophy faulty growth of bone.
osteogenesis bone formation. See also ossification.
osteogenesis imperfecta a hereditary disorder usually caused by an autosomal dominant gene. It may be present at birth or develop during childhood. The congenital form is much more severe and may lead to early death. The bones are extremely fragile and may fracture following minimal trauma.
osteogenic bone-producing. osteogenic sarcoma malignant tumour that originates from bone-producing cells.
osteolysis the degeneration and dissolution of bone caused by disease, infection and ischaemia.
osteolytic destructive of bone, for example, osteolytic malignant deposits in bone.
osteoma a benign tumour of bone which may arise in the compact tissue (ivory osteoma) or in the cancellous tissue. May be single or multiple.
osteomalacia demineralization of the mature skeleton, with softening and bone pain. It is commonly caused by insufficient dietary intake of vitamin D or lack of sunshine, or both.
osteomyelitis inflammation commencing in the marrow of bone.
osteonecrosis the death of bone due to an impaired blood supply.
osteopathy an established clinical discipline. It is concerned with the inter-relationship between structure and function of the body. Osteopathy may be effective for the relief or improvement of a wide variety of conditions, for example, digestive disorders, as well as mechanical problems. Osteopathy is one of only a few complementary therapies to have achieved statutory self-regulation on a par with healthcare professions such as medicine.
osteopetrosis (Albers–Sch°nberg disease, marble bones) a congenital abnormality giving rise to very dense bones which fracture easily.
osteophyte a bony outgrowth or spur, usually at the margins of joint surfaces, for example, in osteoarthritis.
osteoplasty reconstructive operation on bone.
osteoporosis loss of bone density caused by excessive absorption of calcium and phosphorus from the bone, due to progressive loss of the protein matrix of bone which normally carries the calcium deposits. Associated with ageing in both men and women. Common cause of fractures, particularly fractures of the wrist, crush fractures of the spine and neck of femur fractures.
osteosarcoma a malignant tumour growing from bone cells (osteoblasts).
osteosclerosis increased density or hardness of bone.
osteotomy division of bone followed by realignment of the ends to encourage union by healing. See also McMurray’s osteotomy.
ostium the opening or mouth of any tubular structure.
otitis inflammation of the ear.
otitis externa inflammation of the skin of the external auditory canal.
otitis media inflammation of the middle ear cavity. The effusion can be serous, mucoid or purulent. Non-purulent effusions in children are often called glue ear. See also grommet.
otoliths tiny calcareous deposits within the utricle and saccule of the internal ear.
otosclerosis abnormal bone formation affecting primarily the footplate of the stapes. A common cause of progressive conductive deafness.
otoscope an instrument for examining the ear, usually incorporating both magnification and illumination. Also called an auriscope.
outcome measures scales developed to measure health outcome from clinical interventions: generic measures encompassing dimensions of physical, mental and social health; disease-specific scales detecting the effects of treatment of specific conditions. See also quality adjusted life years.
output data and information leaving a computer, which can then be sent to a display screen, printer or another computer.
ova the female gametes (reproductive cells). More correctly known as a secondary oocyte until penetration by a spermatozoon.
ovarian relating to the ovaries.
ovarian cycle the changes occurring in the ovary during the development of the follicle and oogenesis. It has two phases: follicular (days 1–14) when ovulation occurs, and luteal (days 15–28) when the corpus luteum develops. The cycle is controlled by follicle stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone.
ovarian cyst a tumour of the ovary, usually containing fluid – may be benign or malignant.
ovary a female gonad. One of two small oval bodies situated on either side of the uterus on the posterior surface of the broad ligament. Controlled by pituitary hormones they produce oocytes and oestrogen and progesterones.
overheads the cost of services that contribute to the general upkeep and running of the organization, for example, grounds maintenance, that cannot be linked directly to the core activity of a department.
oviduct uterine or fallopian tubes.
ovulation the maturation and rupture of a Graafian follicle with the discharge of an oocyte.
oxidation the act of oxidizing or state of being oxidized. It involves the addition of oxygen, for example, formation of oxides, or the loss of electrons or the removal of hydrogen. A part of metabolism, whereby energy is released from fuel molecules.
oxidative phosphorylation a mitochondrial energy-producing metabolic process, whereby adenosine diphosphate (ADP) is converted to adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by the addition of a phosphate group.
oxygen (O) a colourless, odourless, gaseous element; necessary for life and combustion. Constitutes 20% of atmospheric air. Used therapeutically as an inhalation to increase blood oxygenation. Delivered as part of a general anaesthetic to maintain life. See also hyperbaric.
oxygen concentrator a device for removing nitrogen from the air to provide a high concentration of oxygen for use by patients requiring many hours of oxygen therapy each day at home.
oxygen enhancement ratio the ratio of radiation doses needed to produce a given biological effect in the presence or absence of oxygen.
oxygen mask a facial mask which allows oxygen to be mixed with air before being administered to a patient.
oxygen tent a large plastic canopy that encloses the patient in a controlled environment used for oxygen therapy.
oxyhaemoglobin (oxygenated haemoglobin) an unstable compound formed from haemoglobin on contact with air in the alveoli.
oxyntic producing acid. oxyntic cells the cells in the gastric mucosa which produce hydrochloric acid.
oxytocin a hormone released from the posterior pituitary. It contracts the uterine muscle and milk ducts and is involved in reflex milk ejection.