CHAPTER 5 Mapping and Identifying Genes for Monogenic Disorders
The identification of the gene associated with an inherited single gene (monogenic) disorder, as well as having immediate clinical diagnostic application, will enable an understanding of the developmental basis of the pathology with the prospect of possible therapeutic interventions. The molecular basis for more than 2700 disease phenotypes is now known.
In the 1990s a genome-wide set of microsatellites was constructed with approximately 1 marker per 10 centimorgans (cM). These 350 markers could be amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and facilitated genetic mapping studies that led to the identification of thousands of genes. This approach has been superseded by DNA microarrays or ‘single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) chips’. Although SNPs (p. 67) are less informative than microsatellites, they can be scored automatically and microarrays are commercially available with several million SNPs distributed throughout the genome.
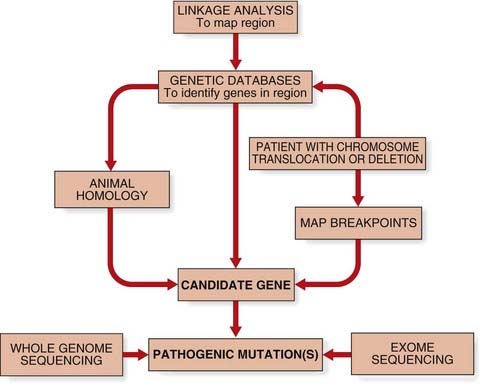
The common step for all approaches to identify human disease genes was the identification of a candidate gene (Figure 5.1). Candidate genes may be suggested from animal models of disease or by homology, either to a paralogous human gene (e.g., where multigene families exist) or to an orthologous gene in another species. With the sequencing of the human genome now complete, it is also possible to find new disease genes by searching through genetic databases (i.e., ‘in silico’).
Position-Independent Identification of Human Disease Genes
Functional Cloning
Functional cloning describes the identification of a human disease gene through knowledge of its protein product. From the amino-acid sequence of a protein, oligonucleotide probes could be synthesized to act as probes for screening complementary DNA (cDNA) libraries (p. 56).
Use of Animal Models
The recognition of phenotypic features in a model organism, such as the mouse, which are similar to those seen in persons affected with an inherited disorder, allowed the possibility of cloning the gene in the model organism to lead to more rapid identification of the gene responsible in humans. An example of this approach was the mapping of the gene responsible for the inherited disorder of pigmentation and deafness known as Waardenburg syndrome (p. 91) to the long arm of human chromosome 2. This region of chromosome 2 shows extensive homology, or what is known as synteny, to the region of mouse chromosome 1 to which the gene for the murine pigmentary mutant known as Splotch had been assigned. The mapping of the murine Pax3 gene, which codes for a transcription factor expressed in the developing nervous system, to this region suggested it as a positional candidate gene for the disorder. It was suggested that the pigmentary abnormalities could arise on the basis that melanocytes, in which melanin synthesis takes place, are derived from the neural crest. Identification of mutations in PAX3, the human homolog, confirmed it as the gene responsible for Waardenburg syndrome.
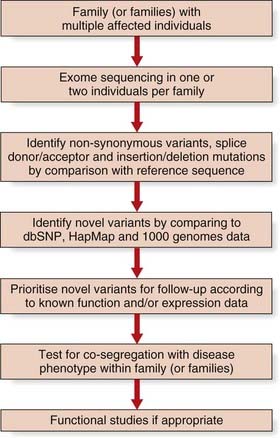
Next-Generation ‘Clonal’ Sequencing
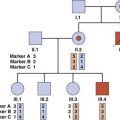
This new sequencing technology shows great promise for elucidating the remaining ~55% of single gene disorders where the genetic aetiology remains unknown (Figure 5.2). The first success was in the identification of mutations in the DHODH gene that cause Miller syndrome by ‘exome’ sequencing. Around 164,000 regions encompassing exons and their conserved splice sites (a total of 27 Mb) were sequenced in a pair of affected siblings and probands from two additional families. Non-synonymous variants, splice donor/acceptor, or coding insertion/deletion mutations were identified in nearly 5000 genes in each of the two affected siblings. Filtering these variants against public databases (dbSNP and HapMap) yielded novel variants in less than 500 genes. Analysis of pooled data from the four affected patients revealed just one gene, DHODH, which contained two mutated alleles in each of the four individuals.
Positional Cloning
Linkage Analysis
Genetic mapping, or linkage analysis (p. 137), is based on genetic distances that are measured in centimorgans (cM). A genetic distance of 1 cM is the distance between two genes that show 1% recombination, that is, in 1% of meioses the genes will not be co-inherited and is equivalent to approximately 1 Mb (1 million bases). Linkage analysis is the first step in positional cloning that defines a genetic interval for further analysis.
Linkage analysis can be performed for a single, large family or for multiple families, although this assumes that there is no genetic heterogeneity (p. 378). The use of genetic markers located throughout the genome is described as a genome-wide scan. In the 1990s, genome-wide scans used microsatellite markers (a commercial set of 350 markers was popular), but microarrays with several million SNPs now provide greater statistical power.
Autozygosity mapping (also known as homozygosity mapping) is a powerful form of linkage analysis used to map autosomal recessive disorders in consanguineous pedigrees (p. 269). Autozygosity occurs when affected members of a family are homozygous at particular loci because they are identical by descent from a common ancestor.
Linkage of cystic fibrosis (CF) to chromosome 7 was found by testing nearly 50 white families with hundreds of DNA markers. The gene was mapped to a region of 500 kilobases (kb) between markers MET and D7S8 at chromosome band 7q31-32, when it became evident that the majority of CF chromosomes had a particular set of alleles for these markers (shared haplotype) that was found in only 25% of non-CF chromosomes. This finding is described as linkage disequilibrium and suggests a common mutation from a founder effect (p. 378). Extensive physical mapping studies eventually led to the identification of four genes within the genetic interval identified by linkage analysis, and in 1989 a 3-bp deletion was found within the cystic fibrosis transmembrane receptor (CFTR) gene. This mutation (p.Phe508del) was present in approximately 70% of CF chromosomes and 2% to 3% of non-CF chromosomes, consistent with the carrier frequency of 1 in 25 in whites.
Chromosome Abnormalities
Occasionally, individuals are recognized with single-gene disorders who are also found to have structural chromosomal abnormalities. The first clue that the gene responsible for Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) (p. 307) was located on the short arm of the X chromosome was the identification of a number of females with DMD who were also found to have a chromosomal rearrangement between an autosome and a specific region of the short arm of one of their X chromosomes. Isolation of DNA clones spanning the region of the X chromosome involved in the rearrangement led in one such female to more detailed gene-mapping information as well as to the eventual cloning of the DMD or dystrophin gene (p. 307).
The occurrence of a chromosome abnormality and a single-gene disorder is rare, but identification of such individuals is important as it has led to the cloning of several other important disease genes in humans, such as tuberous sclerosis (p. 316) and familial adenomatous polyposis (p. 221).
Candidate Genes
Searching databases for genes with a function likely to be involved in the pathogenesis of the inherited disorder can also suggest what are known as candidate genes. If a disease has been mapped to a particular chromosomal region, any gene mapping to that region is a positional candidate gene. Data on the pattern of expression, the timing, and the distribution of tissue and cells types may suggest that a certain positional candidate gene or genes is more likely to be responsible for the phenotypic features seen in persons affected with a particular single-gene disorder. Several computer programs have been developed that can search genomic DNA sequence databases for sequence homology to known genes, as well as DNA sequences specific to all genes, such as the conserved intron–exon splice junctions, promoter sequences, polyadenylation sites and stretches of open reading frames (ORFs).
Confirmatory Testing that a Candidate Gene Is a Disease Gene
Mutations in candidate genes can be screened for by a variety of methods (p. 59) and confirmed by DNA sequencing (p. 61). Finding loss-of-function mutations or multiple different mutations that result in the same phenotype provides convincing evidence that a potential candidate gene is associated with a disorder. For example, in the absence of functional data to demonstrate the effect of the p.Phe508del mutation on the CFTR protein, confirmation that mutations in the CFTR gene caused cystic fibrosis was provided by the nonsense mutation p.Gly542X.
The Human Gene Map
The rate at which single-gene disorders and their genes are being mapped in humans is increasing exponentially (see Figure 1.6, p. 7). Many of the more common and clinically important monogenic disorders have been mapped to produce the ‘morbid anatomy of the human genome’ (Figure 5.3).
FIGURE 5.3 A gene map of the human genome with examples of some of the more common or important single genes and disorders.
| α1-AT | 14q32 | α1-Antitrypsin deficiency |
| ABO | 9q34 | ABO blood group |
| ACTH | 2p25 | Adrenocorticotrophic hormone deficiency |
| ADA | 20q13.11 | Severe combined immunodeficiency, ADA deficiency |
| AHP | 9q34 | Acute hepatic porphyria |
| AIP | 11q23.3 | Acute intermittent porphyria |
| AKU | 3q2 | Alkaptonuria |
| ALD | Xq28 | Adrenoleukodystrophy |
| APKD1 | 16p13 | Adult polycystic kidney disease, locus 1 |
| APKD2 | 4q21–23 | Adult polycystic kidney disease, locus 2 |
| APOB | 2p24 | Apolipoprotein B |
| APOE | 19q.13.2 | Apolipoprotein E |
| ARG1 | 6q23 | Arginase deficiency, argininemia |
| ARSB | 5q11–13 | Mucopolysaccharidosis type VI, Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome |
| AS | 15q11–13 | Angelman syndrome |
| ATA | 11q22.3 | Ataxia telangiectasia |
| ATIII | 1q23–25 | Antithrombin III |
| ATRX | Xq13 | α-Thalassemia mental retardation |
| AZF | Yq11 | Azoospermia factor |
| BBS2 | 16q21 | Bardet–Biedl syndrome |
| BLM | 15q26.1 | Bloom syndrome |
| BRCA1 | 17q21 | Familial breast/ovarian cancer, locus 1 |
| BRCA2 | 13q12.3 | Familial breast/ovarian cancer, locus 2 |
| BWS | 11p15.4 | Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome |
| C3 | 19p13.2-13.3 | Complement factor 3 |
| C5 | 9q34.1 | Complement factor 5 |
| C6 | 5p13 | Complement factor 6 |
| C7 | 5p13 | Complement factor 7 |
| C9 | 5p13 | Complement factor 9 |
| CAH1 | 6p21.3 | Congenital adrenal hyperplasia, 21-hydroxylase |
| CBS | 21q22.3 | Homocystinuria |
| CEP | 10q25.2-26.3 | Congenital erythropoietic porphyria |
| CFTR | 7q31.2 | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator |
| CKN2 | 10q11 | Cockayne syndrome 2, late onset |
| CMH1 | 14q12 | Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy type 1 |
| CMH2 | 1q3 | Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy type 2 |
| CMH3 | 15q22 | Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy type 3 |
| CMT1A | 17p11.2 | Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease type 1A |
| CMT1B | 1q22 | Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease type 1B |
| CMT2 | 1p35–36 | Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease type 2 |
| COL1A1 | 17q21.31-22 | Collagen type I, α1 chain, osteogenesis imperfecta |
| COL1A2 | 7q22.1 | Collagen type I, α2 chain, osteogenesis imperfect |
| COL2A1 | 12q13.11-13.2 | Collagen type II, Stickler syndrome |
| COL3A1 | 2q31 | Collagen type III, α1 chain, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV |
| CYP11B1 | 8q21 | Congenital adrenal hyperplasia, 11β-hydroxylase |
| DAZ | Yq11 | Deleted in azoospermia |
| DFNB1/A3 | 13q12 | Non-syndromic sensorineural deafness, first recessive, third dominant locus |
| DM | 19q13.2-13.3 | Myotonic dystrophy |
| DMD/BMD | Xp21.2 | Dystrophin, Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy |
| DRPLA | 12p13.1-12.3 | Dentatorubropallidoluysian disease |
| EDSVI | 1p36.2-36.3 | Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VI |
| EYA1 | 8q13.3 | Brachio-otorenal syndrome |
| F5 | 1q23 | Coagulation protein V |
| F7 | 13q34 | Coagulation protein VII |
| F8 | Xq28 | Coagulation protein VIII, hemophilia A |
| F9 | Xq27.1-27.2 | Coagulation protein IX, Christmas disease, hemophilia B |
| F10 | 13q34 | Coagulation protein X |
| F11 | Xq27.1-27.2 | Coagulation factor XI |
| F12 | 5q33-qter | Coagulation factor XII |
| FAP | 5q21-22 | Familial adenomatous polyposis, Gardner syndrome |
| FBN1 | 15q21.1 | Fibrillin-1, Marfan syndrome |
| FBN2 | 5q23-31 | Fibrillin-2, contractural arachnodactyly |
| FGFR1 | 8p11.1-11.2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1, Pfeiffer syndrome |
| FGFR2 | 10q26 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2, Crouzon, Pfeiffer, Apert syndrome |
| FGFR3 | 4p16.3 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3, achondroplasia, thanatophoric dysplasia |
| FH | 19p13.1-13.2 | Familial hypercholesterolemia |
| FRAXA (FMR1) | Xq27.3 | Fragile X mental retardation |
| FRDA | 9q13–21.1 | Friedreich ataxia |
| FSHMD | 4q35 | Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy |
| GAL | 9p13 | Galactosemia |
| GAP | 9q31 | Basal cell nevus syndrome, Gorlin syndrome |
| GLB1 | 3p21.33 | GM1 gangliosidosis |
| G6PD | Xq28 | Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| GUSB | 7q21.11 | Mucopolysaccharidosis type VII, Sly syndrome |
| HbB | 11p15.5 | β-Globin gene |
| HD | 4p16.3 | Huntington disease |
| HEXA | 15q23–24 | Hexosaminidase A, Tay-Sachs disease |
| HEXB | 5q13 | Hexosaminidase B, Sandhoff disease |
| HFE | 6p21.3 | Hemochromatosis |
| HGPRT | Xq26-27.2 | Hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl transferase, Lesch-Nyhan syndrome |
| HLA | 6p21.3 | Major histocompatibility locus |
| HPE3 | 7q36 | Holoprosencephaly |
| IDUA | 4p16.3 | Mucopolysaccharidosis type I, Hurler syndrome |
| IGKC | 2p12 | Immunoglobulin κ light chain |
| IGLC1 | 22q11 | Immunoglobulin λ light chains |
| INS | 11p15.5 | Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus type 2 |
| KRT5 | 12q11-13 | Epidermolysis bullosa simplex, Koebner type |
| LGMD7 | 5q31 | Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy |
| MCAD | 1p31 | Acyl coenzyme-A dehydrogenase, medium chain |
| MDS | 17p13.3 | Miller-Dieker lissencephaly syndrome |
| MEN1 | 11q13 | Multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 1 |
| MHS | 19q13.1 | Malignant hyperpyrexia susceptibility, locus 1 |
| MITF | 3p14.1 | Waardenburg syndrome type 2 |
| MJD | 14q24.3-31 | Machado-Joseph disease, spinocerebellar ataxia type 3 |
| MPS VI | 5q11-13 | Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome |
| MSH2 | 2p15-16 | Hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer type 1 |
| NCF2 | 1q25 | Chronic granulomatous disease, neutrophil cytosolic factor-2 deficiency |
| NF1 | 17q11.2 | Neurofibromatosis type I, von Recklinghausen disease |
| NF2 | 22q12.2 | Neurofibromatosis type II, bilateral acoustic neuroma |
| NP | 11p15.1-15.4 | Niemann-Pick disease type A and B |
| NPC | 18q11-12 | Niemann-Pick disease type C |
| NPS | 9q43 | Nail-patella syndrome |
| OTC | Xp21.1 | Ornithine transcarbamylase |
| p53 | 17p13.1 | p53 protein, Li-Fraumeni syndrome |
| PKU | 12q24.1 | Phenylketonuria |
| PROC | 2q13-14 | Protein C, coagulopathy disorder |
| PROS | 3p11.1-q11.2 | Protein S, coagulopathy disorder |
| PRNP | 20p12-pter | Prion disease protein |
| PWS | 15q11 | Prader-Willi syndrome |
| PXMP1 | 1p21–22 | Zellweger syndrome type 2 |
| RB | 13q14.1-14.2 | Retinoblastoma |
| RET | 10q11.2 | Familial medullary thyroid carcinoma, MEN 2A and 2B, familial Hirschsprung disease |
| RH | 1p34–36.2 | Rhesus null disease, Rhesus blood group |
| RP1 | 8p11-q21 | Retinitis pigmentosa, locus 1 |
| RP2 | Xp11.3 | Retinitis pigmentosa, locus 2 |
| RP3 | Xp21.1 | Retinitis pigmentosa, locus 3 |
| rRNA | Ribosomal RNA | |
| SCA1 | 6p23 | Spinocerebellar ataxia, locus 1 |
| SCA2 | 12q24 | Spinocerebellar ataxia, locus 2 |
| SPH1 | 14q22-23.2 | Spherocytosis type I |
| SMA | 5q12.2-13.3 | Spinal muscular atrophy |
| SOD1 | 21q22.1 | Superoxide dismutase, familial motor neuron disease |
| SRY | Yp11.3 | Sex-determining region Y, testis-determining factor |
| TBX5 | 12q21.3-22 | Holt-Oram syndrome |
| TCOF1 | 5q32-33.1 | Treacher-Collins syndrome |
| TRPS1 | 8q24.12 | Trichorhinophalangeal syndrome |
| TSC1 | 9q34 | Tuberous sclerosis, locus 1 |
| TSC2 | 16p13.3 | Tuberous sclerosis, locus 2 |
| TYR | 11q14-21 | Oculocutaneous albinism |
| USH1A | 14q32 | Usher syndrome type IA |
| USH1B | 11q13.5 | Usher syndrome type IB |
| USH1C | 11p15.1 | Usher syndrome type IC |
| USH2 | 1q41 | Usher syndrome type II |
| VWS | 1q32 | van der Woude syndrome |
| VHL | 3p25–26 | von Hippel-Lindau syndrome |
| VWF | 12p13.3 | von Willebrand disease |
| WD | 13q14.3-21.1 | Wilson disease |
| WRN | 8p11.2-12 | Werner syndrome |
| WS1 | 2q35 | Waardenburg syndrome type 1 |
| WT1 | 11p13 | Wilms tumor 1 gene |
| ZWS1 | 7q11.23 | Zellweger syndrome type 1 |

The Human Genome Project
Beginning and Organization of the Human Genome Project
The concept of a map of the human genome was proposed as long ago as 1969 by Victor McKusick (see Figure 1.5, p. 7), one of the founding fathers of medical genetics. Human gene mapping workshops were held regularly from 1973 to collate the mapping data. The idea of a dedicated human genome project came from a meeting organized by the US Department of Energy at Sante Fe, New Mexico, in 1986. The US Human Genome Project started in 1991 and is estimated to have cost around 2.7 billion US dollars. Other nations, notably France, the UK, and Japan, soon followed with their own major national human genome programs and were subsequently joined by a number of other countries. These individual national projects were all coordinated by the Human Genome Organization, which has three centers, one for the Americas based in Bethesda, Maryland, one for Europe located in London, and one for the Pacific in Tokyo.
Human Gene Maps and Mapping of Human Inherited Diseases
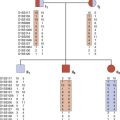
Designated genome mapping centers with ear-marked funding were involved in the coordination and production of genetic or recombination and physical maps of the human genome. The genetic maps initially involved the production of fairly low-level resolution index, skeleton or framework maps, which were based on polymorphic variable-number di-, tri-, and tetranucleotide tandem repeats (p. 17) spaced at approximately 10-cM intervals throughout the genome.
The mapping information from these genetic maps was integrated with high-resolution physical maps (Figure 5.4). Access to the detailed information from these high-resolution genetic and physical maps allowed individual research groups, often interested in a specific or particular inherited disease or group of diseases, rapidly and precisely to localize or map a disease gene to a specific region of a chromosome.
Sequencing of the Human Genome
Although sequencing of the entire human genome would have been seen to be the obvious main focus of the Human Genome Project, initially it was not the straightforward proposal it seemed. The human genome contains large sections of repetitive DNA (p. 15) that were technically difficult to clone and sequence. In addition, it would seem a waste of time to collect sequence data on the entire genome when only a small proportion is made up of expressed sequences or genes, the latter being most likely to be the regions of greatest medical and biological importance. Furthermore, the sheer magnitude of the prospect of sequencing all 3 × 109 base pairs of the human genome seemed overwhelming. With conventional sequencing technology, as was carried out in the early 1990s, it was estimated that a single laboratory worker could sequence up to approximately 2000 bp per day.
Although the Human Genome Sequencing Project is complete, a number of new projects have been initiated as a direct consequence, including the Cancer Genome, HapMap (p. 148), and 1000 Genomes (p. 150) projects.
Development of Bioinformatics
These developments in bioinformatics now allow the prospect of identifying coding sequences and determining their likely function(s) from homologies to known genes, leading to the prospect of identifying a new gene without the need for any laboratory experimental work, or what has been called ‘cloning in silico’.
Functional Genomics
The ability to introduce targeted mutations in specific genes, along with the production of transgenic animals (p. 102), for example in the mouse, allows the production of animal models to study the pathodevelopmental basis for inherited human disorders, as well as serve as a test system for the safety and efficacy of gene therapy and other treatment modalities (p. 350). Strategies using different model organisms in a complementary fashion, taking into account factors such as the ease or complexity of producing transgenic organisms and the generation times of different species, allow the possibility of relatively rapid analysis of gene expression, function and interactions in providing an understanding of the complex pathobiology of inherited diseases in humans.
Botstein D, White RL, Skolnick M, Davis RW. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1980;32:314-331.
Kerem B, Rommens JM, Buchanan JA, et al. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene. Genetic analysis. Science. 1989;245:1073-1080.
Original paper describing cloning of the cystic fibrosis gene.
McKusick VA. Mendelian inheritance in man, 12th ed. London: Johns Hopkins University Press; 1998.
Ng SB, Buckingham KJ, Lee C, et al. Exome sequencing identifies the cause of a mendelian disorder. Nat Genet. 2010;42:30-35.
Royer-Pokora B, Kunkel LM, Monaco AP, et al. Cloning the gene for an inherited human disorder—chronic granulomatous disease—on the basis of its chromosomal location. Nature. 1985;322:32-38.
Strachan T, Read AP. Human molecular genetics, 4th ed. London: Garland Science; 2011.
Sulston J. The common thread: a story of science, politics, ethics and the human genome. London: Joseph Henry Press; 2002.
Elements