Chapter 18. Lymphatic System
Rationale
The most common causes of visible lymphoid activity are infection and neoplasms. Infection is the most common cause of lumps in children’s necks. An understanding of which areas are drained by the nodes is useful in further assessment of present or past infections. Detection of enlarged nodes and an enlarged spleen can be critical to the early diagnosis and treatment of serious disorders.
Anatomy and Physiology
The lymphoid system is a system of lymph fluid, collecting ducts, and tissues. Although the specific functions of lymphoid tissue are still not fully understood, the system is thought to play an important role in the production of lymphocytes and antibodies and in phagocytosis. The system also transports lymph fluids, microorganisms, and protein back to the cardiovascular system and absorbs fat and fat-soluble substances from the intestine.
Lymph enters open-ended ducts called capillaries. The capillaries form larger collecting ducts, which drain into tissue centers or nodes. Lymph from the nodes eventually drains into the venous system by way of even larger ducts.
Lymph nodes, the most numerous element in the lymphatic system, rarely occur singly, but usually in chains or clusters. The lymph nodes that are closer to the center of the body are usually smaller; thus cervical nodes are larger than axillary nodes. The spleen is composed of lymphoid and reticuloendothelial cells. It is found under the ribs in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen. The amount of lymphoid tissue and the size of the lymph nodes vary with age. Infants have a small amount of palpable lymphatic tissue, which gradually increases until middle childhood, when the volume of lymphatic tissue reaches its peak. By middle adolescence the volume of lymphatic tissue begins to diminish, until it reaches the adult level of 2% to 3% of total body weight. Children are more likely to develop generalized adenopathy in response to disease, and even mild infections result in swollen nodes or “swollen glands.”
Equipment for Assessment of Lymphatic System
▪ Ruler
Preparation
Inquire about recent contact with persons with infectious diseases. Ask if the child has been experiencing weakness, easy fatigability, fever, bruising, bone pain, or chronic or recurrent infection. Ask if there is a family history of blood disorders or cancer.
Assessment of Lymph Nodes
| Assessment | Findings | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
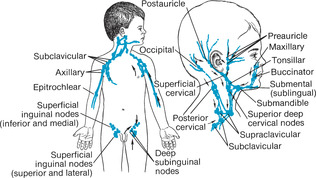
Using the distal portion of the fingers and gentle but firm circular motions, palpate the head, neck, axillae, and groin to detect enlarged lymph nodes (Figure 18-1). Note the color, size, location, mobility, temperature, consistency, and tenderness of enlarged nodes.
Tender nodes should be assessed last. Measure enlarged nodes.
To palpate nodes in the areas anterior and posterior to the sterno-cleidomastoid muscle, move the fingertips against the muscle.
|
Small (less than 1 cm, or 0.5 in), movable, nontender nodes are normal in young children.
Clinical Alert
Nodes that are enlarged because of infection are firm, warm, fluctuant, and movable, and their borders are diffuse. Redness can overlie nodes that are enlarged because of infection.
Enlargement of preauricular nodes commonly suggests eye infection.
Enlargement of the preauricular, mastoid, and deep cervical nodes can indicate infection of the ear.
Enlargement of nodes in the jaw area can signify infections of the tongue or mouth.
|
| Assessment | Findings |
|---|---|
|
To palpate nodes in the head and neck, have the child flex the head forward or bend toward the side being examined.
To palpate nodes in the axillae, roll the tissues against the chest wall and muscles of the axillae. Have the child hold the arms in a relaxed, slightly abducted position at the sides.
To palpate nodes in the inguinal area, place the child in a supine position.
|
Enlargement of nodes in the supraclavicular region often indicates metastases from the lungs or abdominal structures.
Bilateral lymph node enlargement can indicate infectious mononucleosis.
Nodes enlarged as a result of cancer are usually nontender, fixed, hard, of variable size, and matted. No discoloration is present.
Enlarged nodes can also indicate metabolic disorders, hypersensitivity reactions, and primary hematopoietic disorders.
|
| Assessment | Findings |
|---|---|
| With the child supine, place one hand under the child’s back and the other hand on the left upper quadrant of the child’s abdomen. Ask the child to “Suck in your breath.” The spleen tip can be felt during inspiration on deep palpation. |
The spleen can be palpated 1 to 2 cm (0.4 to 0.8 in) below the left costal margin in infants and children.
Clinical Alert
A spleen that extends more than 2 cm (0.8 in) below the costal margin can indicate leukemia, thalassemia major, sickle cell anemia, or infectious mononucleosis.
|
Related Nursing Diagnoses
Activity tolerance: related to generalized weakness.
Compromised family coping: related to situational crisis, knowledge deficit.
Hyperthermia: related to illness.
Altered protection: related to abnormal blood profiles.
Risk for infection: related to immunosuppression, inadequate secondary defenses.
Altered parenting: related to physical illness.
Risk for altered body temperature: related to illness.