Chapter 6 Intradural Extramedullary Malignant Tumors
MALIGNANT PERIPHERAL NERVE SHEATH TUMOR
EPIDEMIOLOGY
DISTRIBUTION
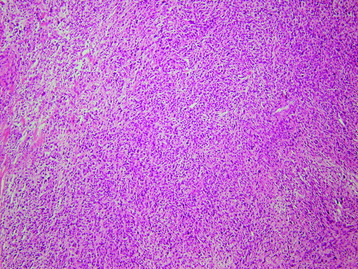
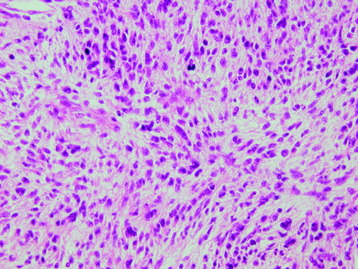
HISTOLOGY
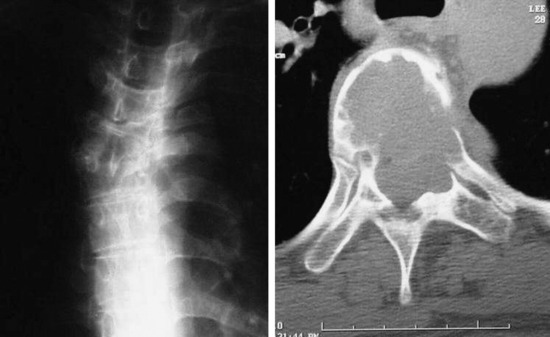
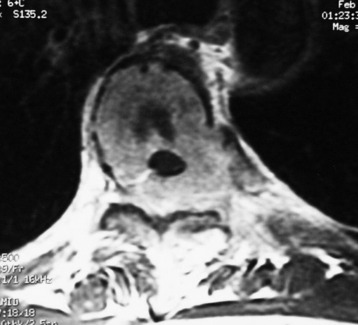
RADIOLOGY
HEMANGIOPERICYTOMA
EPIDEMIOLOGY
DISTRIBUTION
Only 39 cases of primary hemangiopericytoma have been reported in the spinal column, and only five have been intradural.7
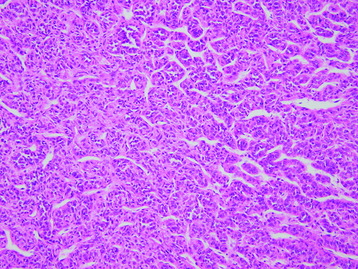
HISTOLOGY
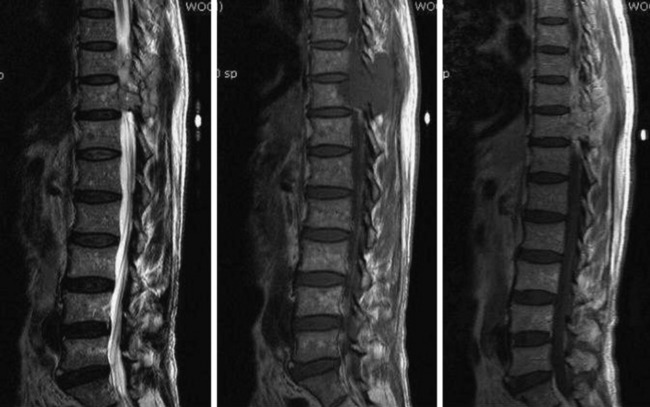
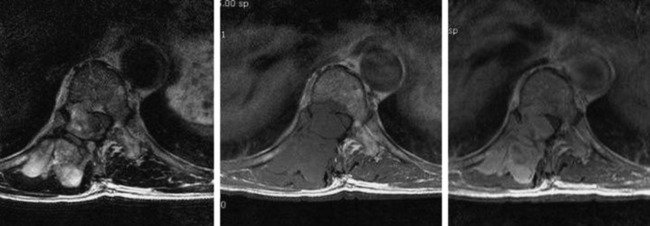
RADIOLOGY
CEREBROSPINAL FLUID DISSEMINATED METASTASIS—LEPTOMENINGEAL METASTASIS
EPIDEMIOLOGY
Table 6-1 Primary Tumors that Commonly Cause Leptomeningeal Metastasis8
| Primary Tumor | n (%) | Histology (n) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary brain tumors | 36 (23) | Glioblastoma (20) |
| Astrocytoma (4) | ||
| Oligodendroglioma (2) | ||
| Ependymoma (3) | ||
| Medulloblastoma (6) | ||
| Germinoma (1) | ||
| PCNSL | 14 (9) | High-grade NHL (14) |
| Lymphoreticular tumors | 17 (11) | Low-grade NHL (3) |
| Metastatic to the CNS | CLL (4) | |
| High-grade NHL (3) | ||
| ALL (1) | ||
| NHL nos (2) | ||
| Hodgkin’s lymphoma (1) | ||
| Langerhans’ histiocytosis (1) | ||
| Non-Langerhans’ histiocytosis (1) | ||
| AML (1) | ||
| Melanoma | 21 (14) | |
| Breast cancer | 30 (19) | |
| Lung cancer | 20 (13) | SCLC (8) |
| NSCLC (7) | ||
| nos (5) | ||
| Others | 8 (5) | Gastric cancer (2) |
| Ovarian cancer (1) | ||
| Endometrial carcinoma (1) | ||
| Prostate cancer (1) | ||
| Myosarcoma of the uterus (1) | ||
| Fibrous histiocytoma (1) | ||
| Mesothelioma (1) | ||
| CUP | 9 (6) |
PCNSL, primary central nervous system lymphoma; NHL, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma; NOS, not otherwise specified; CNS, central nervous system; CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukemia; CUP, carcinoma of unknown primary; ALL, Acute lymphoblastic leukemia; AML, acute myeloblastic leukemia; SCLC, small-cell lung cancer; NSCLC, non-small lung cell cancer.
DISTRIBUTION
RADIOLOGY
CASE: BREAST CANCER WITH LEPTOMENINGEAL METASTASIS
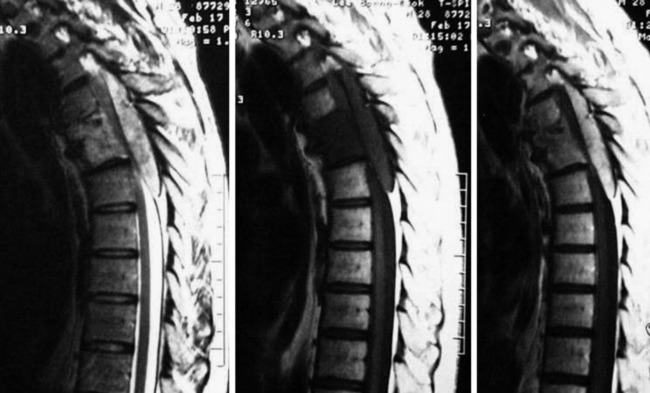
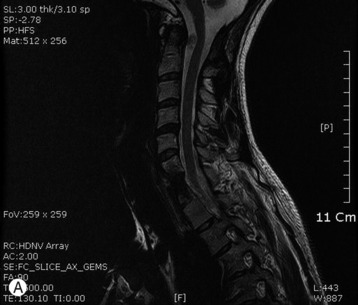
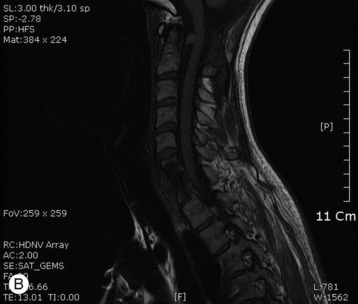
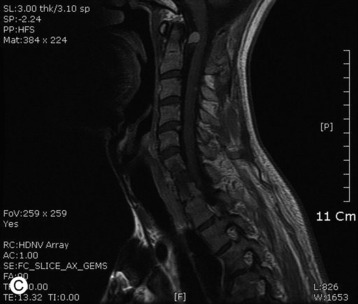
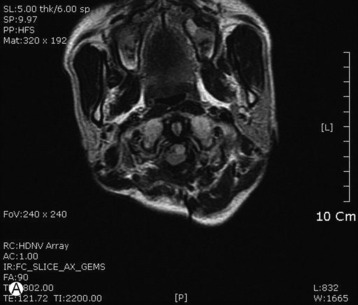
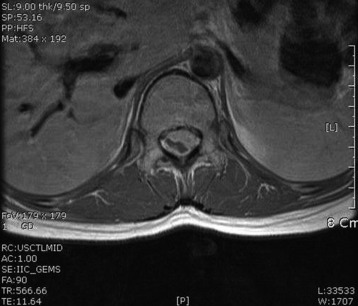
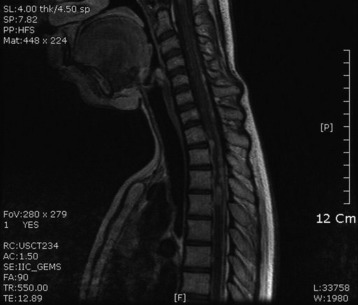
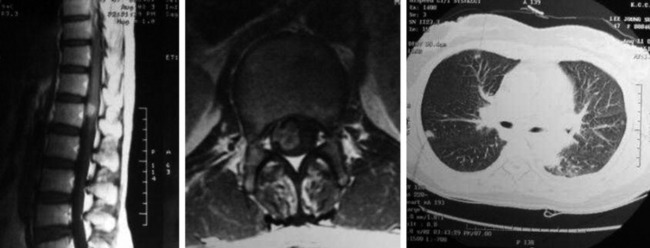
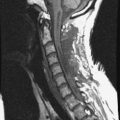
A 51-year-old female underwent breast cancer operation and received radiation therapy because of multiple lymph node metastases. She experienced weakness, in all four extremities 2 months before she was admitted to the hospital. On MRI a well-enhancing intradural extramedullary mass was found to constrict the spinal cord from C1 to C5 (Fig. 6-19). During operation the location of the tumor mass was identified to be intradural and external to the arachnoid membrane. The subarachnoid space was maintained. The consistency of the tumor mass was sticky and moderately hard.
CASE: LUNG CANCER WITH LEPTOMENINGEAL METASTASIS
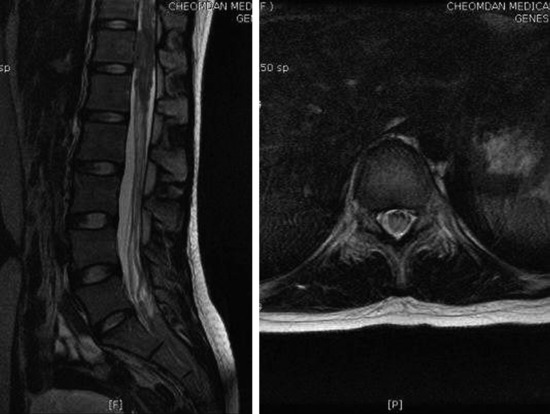
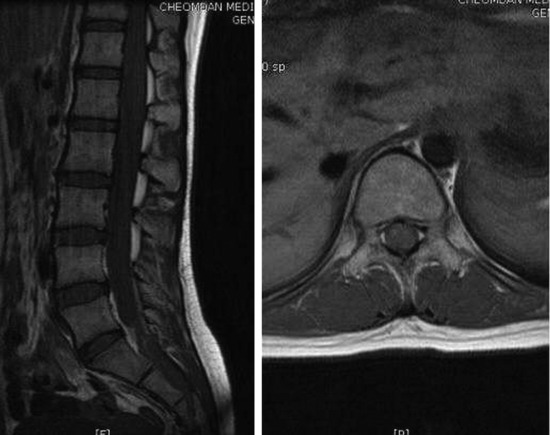
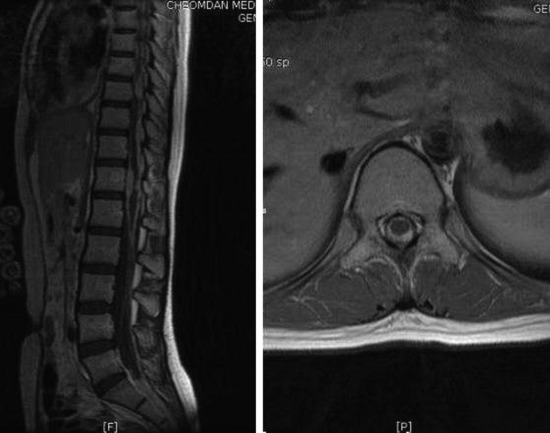
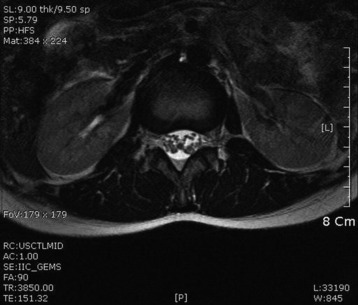
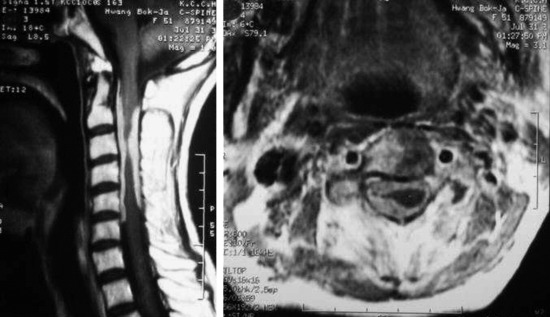
A 47-year-old-female patient presented with right lower extremity radiating pain and foot drop that had persisted for 3 months. MRI showed conglomerated nodular enhancement along the conus and cauda equina (Fig. 6-20). The mass was partially removed.