Chapter 3 Inherited Forms of Bone Marrow Failure
Table 3-1 Inherited Bone Marrow Failure Syndromes:
Inheritance and Mutated Genes
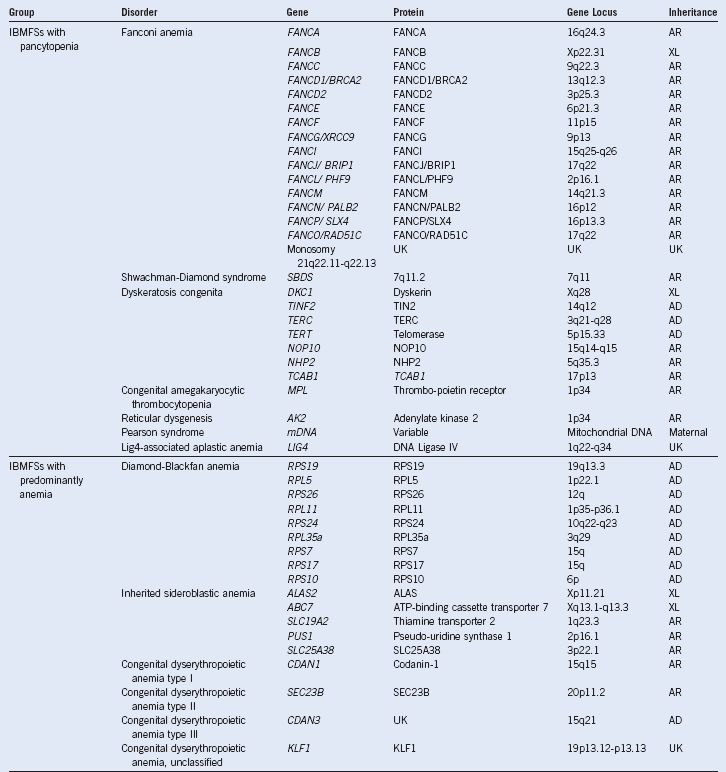
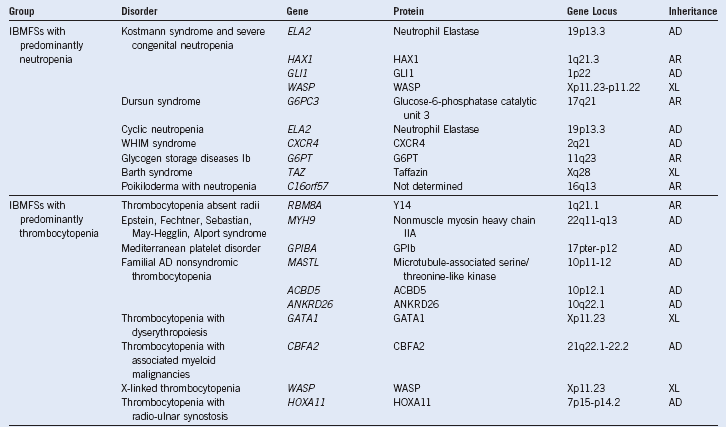
AD, Autosomal dominant; AR, autosomal recessive; IBMFSs, inherited bone marrow failure syndromes; UK, unknown; WHIM, warts, hypogammaglobulinemia, infections, and myelokathexis; X-L, X-linked recessive.
Modified from Dror Y: Inherited bone marrow failure syndromes: Genetic complexity of monogenic disorders. In Genetic Disorders. InTech Open Access Publisher. Available at http://www.intechweb.org.
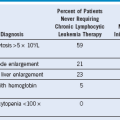
Table 3-2 Miscellaneous Inherited Thrombocytopenia Disorders and Their Major Hematologic Features
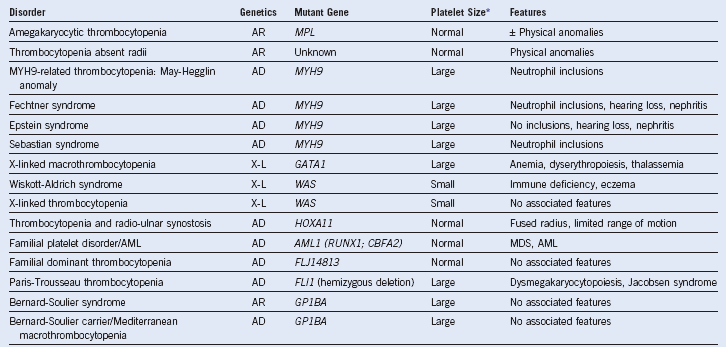
AD, Autosomal dominant; AML, acute myeloid leukemia; AR, autosomal recessive; MDS, myelodysplastic syndrome; MPV, mean platelet volume; X-L, X-linked recessive.
* Platelet size: small, MPV <7 fL; normal, MPV 7-11 fL; large or giant, MPV >11 fL.

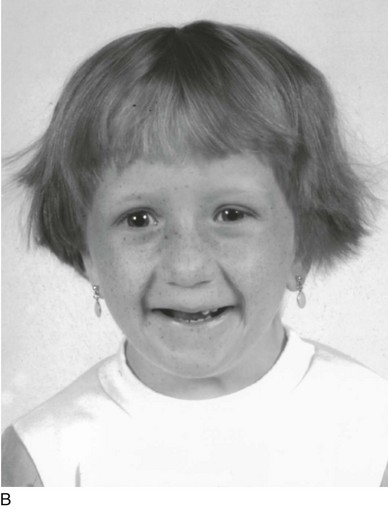
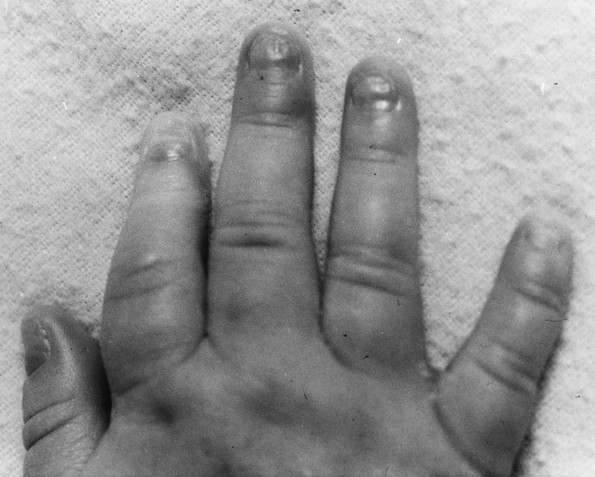
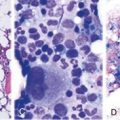
Figure 3-4 SIMILAR DIAMOND-BLACKFAN FACIES IN TWO UNRELATED GIRLS OF DIFFERENT ANCESTRIES CONSSTING OF A SMALL HEAD, ALMOND-SHAPED EYES WITH A SLIGHT ANTIMONGOLOID SLANT, A “FISH-LIKE” SMILE, AND A POINTED CHIN.
Table 3-3 Hematologic Features in Diamond-Blackfan Anemia at Diagnosis Based on Data on 21 Toronto Cases and on 41 Cases From the Canadian Inherited Marrow Failure Registry
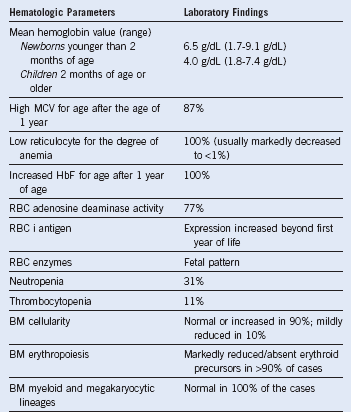
BM, Bone marrow; HbF, fetal hemoglobin; MCV, mean corpuscular volume; RBC, red blood cell.
Table 3-4 Distinguishing Features Between Diamond–Blackfan Anemia and Transient Erythroblastopenia of Childhood
| DBA | TEC | |
|---|---|---|
| Etiology | Genetic | Acquired |
| Immune mediated | None | Common |
| Family history | ≈10% | Occasional siblings with concurrent TEC |
| Antecedent history | None | Viral infection |
| Age at diagnosis | 90% by 1 year | 6 months-4 years |
| Physical anomalies | ≈50% | None |
| Neurologic findings | None | Occasional |
| Transfusion dependence | Yes, if steroid refractory | None |
| Course | Chronic | Full recovery |
| Risk of cancer | Increased | Not increased |
| Risk of MDS or leukemia | Increased | Not increased |
| Laboratory findings at diagnosis: | ||
| RBC size | Macrocytic | Normocytic |
| HbF | Increased | Normal* |
| i Antigen | Increased | Normal* |
| RBC enzyme activities | Fetal levels | Adult levels |
| RBC adenosine deaminase | Increased in 40%-90% | Normal |
DBA, Diamond–Blackfan Anemia; HbF, fetal hemoglobin; MDS, myelodysplastic syndrome; RBC, red blood cell; TEC, transient erythroblastopenia of childhood.
*During spontaneous recovery, values may be increased.
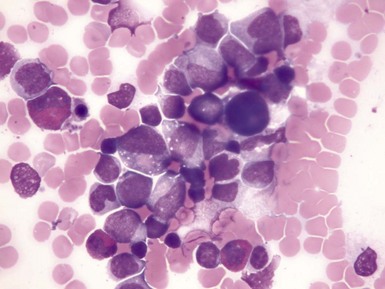
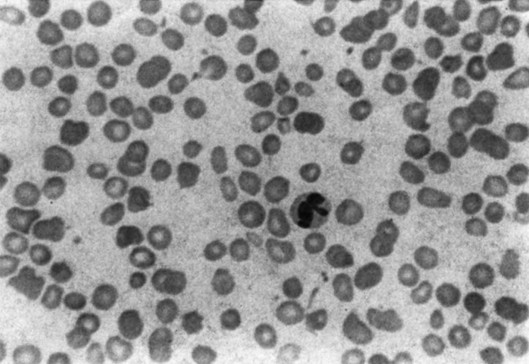
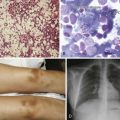
Figure 3-5 HIGH-POWER VIEW OF A BONE MARROW ASPIRATE FROM A PATIENT WITH KOSTMANN SYNDROME (CONGENITAL NEUTROPENIA) BEFORE GRANULOCYTE COLONY-STIMULATING FACTOR THERAPY.
(Photomicrograph prepared by Dr. Mohamed Abdelhaleem, Toronto.)
Table 3-5 Miscellaneous Inherited Neutropenia Disorders
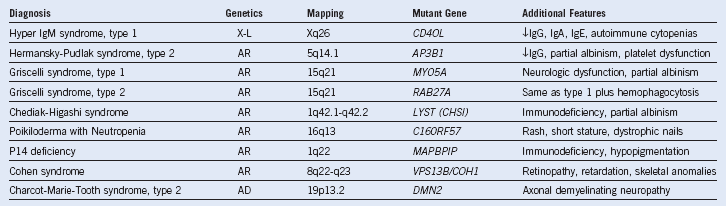
AD, Autosomal dominant; AR, autosomal recessive; Ig, immunoglobulin; X-L, X-linked recessive.
Data compiled from Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (http://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim).