CHAPTER 29 Incisional surgery
Astigmatic keratotomy and limbal relaxing incisions
Epidemiologic consideration and terminology
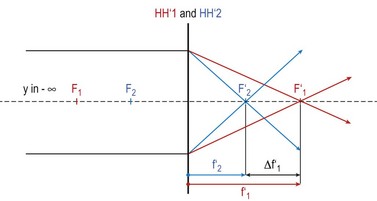
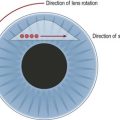
As opposed to a spherical cornea, where refractive power of all meridians is identical, regular toric corneas are defined by two perpendicular meridians with different (highest and lowest) refractive powers. This results in two longitudinal displaced orthogonal focus lines and a circle of least confusion between them instead of one focal point. Thus retinal images are blurred and drawn-out (Fig. 29.1).
Astigmatism with more than two meridians, non-perpendicular meridians, or no regular pattern at all is defined as irregular astigmatism. Influence of astigmatism on visual acuity is approximately half of the influence of a defocus aberration of the same magnitude1.
Fundamental principles
The principle of incisional astigmatism correction is the same in both procedures, LRI and AK. One or two arcuate and more or less peripheral incisions of different depth (according to the corneal thickness at the incision location) are performed perpendicular to the steep meridian. The biomechanical properties of the cornea this way induce a steepening of the flat meridian and a flattening of the steep meridian. This so called coupling effect is the ratio of flattening to steepening (coupling ratio, i.e. for AK: 0.85 ± 0.052). The effect increases with increasing incision length and depth as well as with decreasing distance from the central cornea. The predictability of refractive outcome, however, decreases with decreasing treatment radius. This is why AK may correct for larger astigmatism, e.g. after penetrating keratoplasty, but is predictability worse compared with LRI.
Indications for surgery
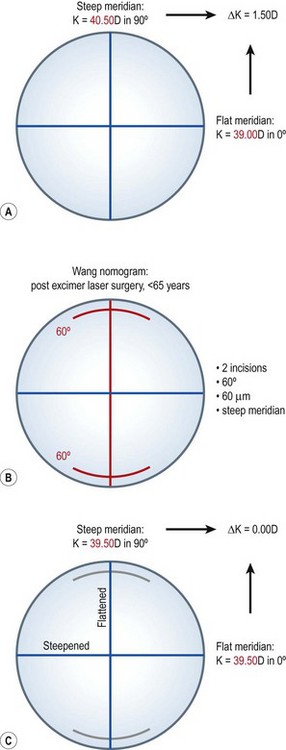
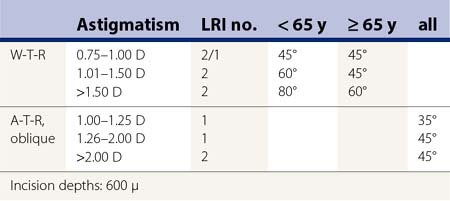
Typical cases where the application of LRIs is useful are procedures like the correction of a residual astigmatism after cataract surgery, refractive lens exchange, or phakic intraocular lens implantation with non-toric implants. Looking at the common LRI nomograms3,4 the correction of astigmatism between 0.75 D and 2.00 D (Table 29.1) (Fig. 29.2) is proven to be safe and effective.
Table 29.1 Nomogram for limbal relaxing incisions according to Wang et al.4 for cataract surgery
AK is especially indicated in large astigmatisms, i.e. after penetrating keratoplasty5,6. Incisions are placed on the transplant in this case.
Preoperative assessment
Preoperative assessment includes keratometry, subjective refraction, and topography. The last two are mainly used to exclude secondary pathologies or irregular astigmatism. Depending on the corneal astigmatism (K values) and the initial pathology either LRI (0.75 D–2.00 D, post-refractive or cataract surgery) or AK (>2.00 D, post-penetrating keratoplasty) is performed. Nomograms given by Wang et al.4 and Nichamin et al.3 (Table 29.1) show options for localization, length, and depth of LRI. Hoffart et al.5 present results for AK applicability; however, there is still a lack of reliable nomograms for AK. Therefore, and for the inter-individual difference in surgical approaches, it is important for surgeons to record their procedures and results, to modify their individual nomograms, for both LRI and AK. Over-correction of astigmatism is the optical worst-case-scenario and should be avoided by conservative planning of surgery. Under-correction of astigmatism is tolerated much better by patients than over-correction and resulting 90° switch of axes. Eventually existing, residual postoperative astigmatism can be corrected with other procedures of refractive surgery like toric intraocular lenses or corneal refractive surgery. Glasses and contact lenses are an option as well.
Due to the lack of predictability, AK is hardly ever used in refractive surgery today.
Operation techniques
The classical instrument for incisional refractive surgery is a diamond knife. Compared with the femtosecond laser, which might be used as well, it is an instrument that enables fast surgery and may be used even in blurred corneas. However, femtosecond lasers have some other advantages that should be taken into consideration. Localization, length, and depth of incisions are of higher precision with the laser, resulting in a better predictability of refractive outcomes5.
During LRI one or two approximately 600 µm deep arcuate incisions are placed parallel to the limbus and perpendicular to the steep corneal meridian4. Incisions are usually performed with a diamond knife. The applicability of a femtosecond laser in LRI is very limited, if indicated at all. The reason for this is the localization of the incisions near the limbus. Limbal vascularizations or other pathologic artifacts decrease the cornea’s transparency, which is a basic requirement for the femtosecond laser to perform cutting.
Postoperative complications
Postoperative complications of incisional surgery are often optical ones, over-correction and under-correction being the most frequent. Further on, the formation of irregular astigmatism can be a complication. AK is especially known for inducing irregular astigmatism and, for reasons of low treatment diameters, increased postoperative glare disability. In general, predictability of AK is not as good as in LRI7; further on fluctuations in postoperative refraction may occur8.
Assessment of surgery: self-evaluation; result of surgery
Results of incisional astigmatic surgery are most often reported as postoperative corrected and uncorrected high contrast visual acuity, induced and absolute subjective or keratometric astigmatism, and vectorial analyses of astigmatism9. Surgically induced astigmatism is considered to be the main outcome measure, as this shows the results of surgery in the easiest way. From these metrics, several other parameters may be calculated in order to have a closer look at single effects of incisional astigmatic surgery. These metrics vary a lot, depending on the publication and the purpose of the trials.
1 Naeser K, Hjortdal J. Optimal refraction with monofocal intraocular lenses: no beneficial effect of astigmatism. Acta Ophthalmol. 2011;89:111-115.
2 Faktorovich EG, Maloney RK, Price FWJr. Effect of astigmatic keratotomy on spherical equivalent: results of the Astigmatism Reduction Clinical Trial. Am J Ophthalmol. 1999;127:260-269.
3 Nichamin LD. Modified astigmatism correction nomogram. J Refract Surg. 2008;24:562-563.
4 Wang L, Misra M, Koch DD. Peripheral corneal relaxing incisions combined with cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2003;29:712-722.
5 Hoffart L, Proust H, Matonti F, et al. Correction of postkeratoplasty astigmatism by femtosecond laser compared with mechanized astigmatic keratotomy. Am J Ophthalmol. 2009;147:779-787. 87 e1
6 Kymionis GD, Yoo SH, Ide T, et al. Femtosecond-assisted astigmatic keratotomy for post-keratoplasty irregular astigmatism. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009;35:11-13.
7 Oshika T, Shimazaki J, Yoshitomi F, et al. Arcuate keratotomy to treat corneal astigmatism after cataract surgery: a prospective evaluation of predictability and effectiveness. Ophthalmology. 1998;105:2012-2016.
8 Lindstrom RL, Lindquist TD. Surgical correction of postoperative astigmatism. Cornea. 1988;7:138-148.
9 Alpins NA. A new method of analyzing vectors for changes in astigmatism. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1993;19:524-533.