66
Human Papillomaviruses
Key Points
• Different genotypes cause different skin lesions (Table 66.1).
Table 66.1
Clinical manifestations of common human papillomavirus (HPV) types.
In clinical practice, subtyping is generally only performed routinely on Papanicolaou smears. Subtyping does not usually change management of cutaneous lesions.
| Skin Lesions | Frequently Detected HPV Type |
| Common, palmar, plantar, myrmecial warts | 1, 2, 4 |
| Flat warts | 3, 10 |
| Epidermodysplasia verruciformis | 5, 8* > others (e.g. 9, 20) |
| Condylomata acuminata (anogenital warts) | 6, 11 |
| High-grade squamous intraepithelial neoplasia (cervical lesions, bowenoid papulosis, erythroplasia of Queyrat) | 16, 18, 31, 33 > others (e.g. 35) |
| Cervical cancer | 16, 18 |
* Oncogenic, like HPV types 16, 18.
– Transmitted via person-to-person contact or contact with contaminated surfaces/objects.
– Prevalence of 20% in schoolchildren.
– A third or more self-regress within 1–2 years.
– Numerous warts or persistent/progressive warts should prompt consideration of immunosuppression, defects in cellular immunity, or other syndromes [e.g. HIV infection, epidermodysplasia verruciformis, WHIM syndrome (see Chapter 49)].
• Anogenital infection with HPV.
• Rx.
– If desired, focuses on destruction of visible lesions or induction of an immune response.
– Effective targeted antiviral treatments are not available.
Common Warts (Verrucae Vulgares)
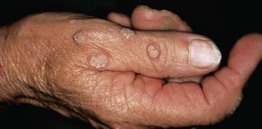
• Any site, but commonly on the fingers, dorsal hands, and/or sites prone to trauma (Figs. 66.1 and 66.2).
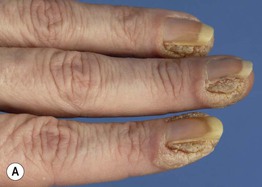
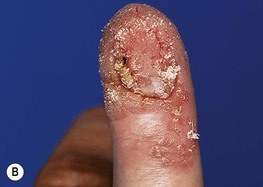
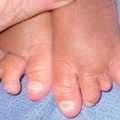
Fig. 66.2 Periungual common warts. Destruction of the nail matrix and bed can lead to partial (A) or complete (B) absence of the nail plate. Bowen’s disease may be considered in the differential diagnosis, especially for a single, recalcitrant digital wart. A, B, Courtesy, Reinhard Kirnbauer, MD, and Petra Lenz, MD.
• Hyperkeratotic, exophytic or dome-shaped papules or plaques with punctate black dots (thrombosed capillaries) that may require paring to see (Fig. 66.3).
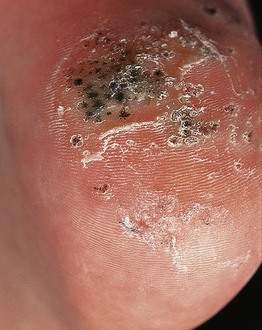
Fig. 66.3 Verrucae plantares (plantar warts). The photo was taken after shaving of the hyperkeratotic surface; the black dots represent thrombosed capillaries. Courtesy, Reinhard Kirnbauer, MD, and Petra Lenz, MD.
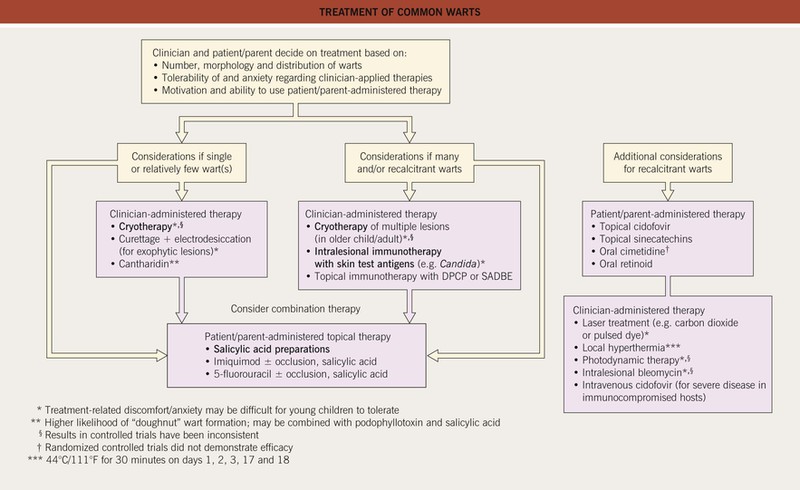
• Rx: outlined in Fig. 66.4; may regress spontaneously within 1–2 years; may be difficult to eradicate.
Plantar/Palmar Warts
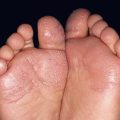
• Thick, exo- and endophytic hyperkeratotic papules and plaques (Fig. 66.5); coalescence of lesions can lead to extensive areas of involvement referred to as mosaic warts.
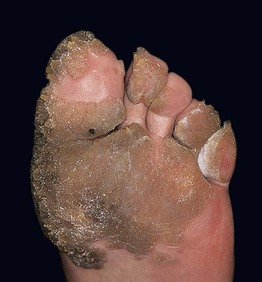
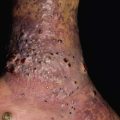
Fig. 66.5 Extensive and chronic verrucosis of the sole causing pain when walking. HPV-2a was isolated from the lesion of this otherwise immunocompetent and healthy patient. Courtesy, Reinhard Kirnbauer, MD, and Petra Lenz, MD.
• May see sloping sides and a central depression (the term myrmecia is used because it can resemble an anthill); tender with pressure (Fig. 66.6).
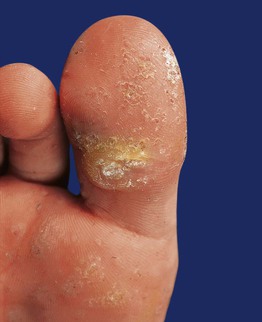
Fig. 66.6 Myrmecial wart. The wart at the base of the distal phalanx of the hallux is painful due to deep endophytic growth; in addition, there are confluent plaques of superficial warts (mosaic warts). Courtesy, Reinhard Kirnbauer, MD, and Petra Lenz, MD.
• DDx: corns (clavi; see Chapter 74), punctate palmoplantar keratoderma (see Table 47.1), arsenical keratoses, SCC, amelanotic melanoma.
Flat Warts (Verrucae Planae)
• Commonly on the dorsal hands, arms, and face, as well as the legs (exacerbated by shaving).
• Skin-colored to pink or brown (sometimes hypopigmented in darker skin), minimally elevated papules; the surface is smooth and often flat-topped (Fig. 66.7).
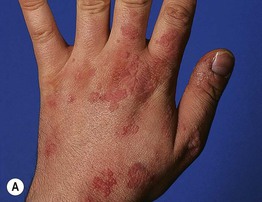
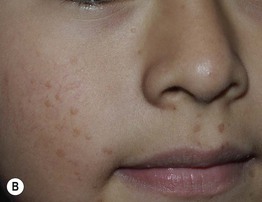
Fig. 66.7 Verrucae planae (flat warts). Multiple skin-colored or pink (A) to brown (B) smooth-surfaced, flat-topped papules. These lesions are typically caused by HPV-3 or -10. A, Courtesy, Reinhard Kirnbauer, MD, and Petra Lenz, MD; B, Courtesy, Julie V. Schaffer, MD.
• DDx: small seborrheic keratoses, common warts, Gottron’s papules of dermatomyositis, lichen nitidus, lichen planus, acrokeratosis verruciformis (see Chapter 48), epidermodysplasia verruciformis (see below).
• Rx.
– If a few lesions, destructive or ablative therapies (e.g. cryosurgery, trichloroacetic acid; see Fig. 66.4).
– If numerous, topical application of irritants (e.g. retinoids), immunotherapy (see Fig. 66.4), topical 5-fluorouracil.
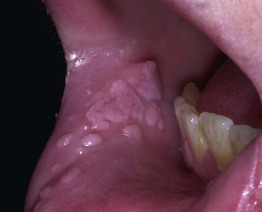
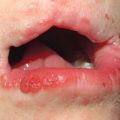
Oral Warts
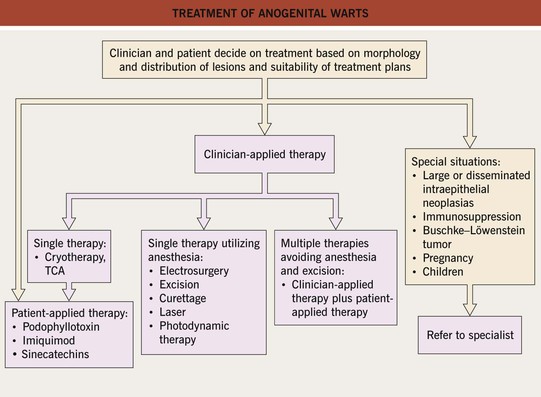
Condylomata Acuminata
• Involve primarily the anogenital region.
• Range from discrete, sessile, smooth-surfaced papillomas to large cauliflower-like lesions (Figs. 66.9 and 66.10).
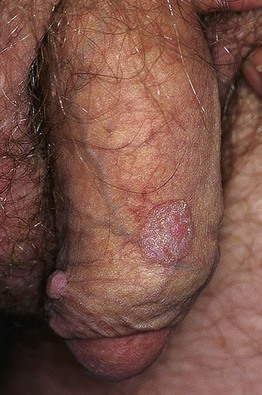
Fig. 66.9 Penile condylomata acuminata (genital warts). Both sessile and exophytic warts are present. Courtesy, Reinhard Kirnbauer, MD, and Petra Lenz, MD.
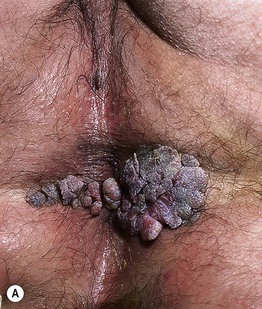
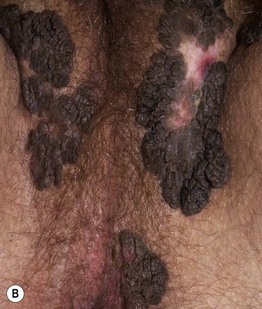
Fig. 66.10 Condylomata acuminata. A Perianal papillomas that are macerated due to moisture from occlusion. B Confluent lesions forming hyperpigmented plaques in the perineal region and along the inguinal fold. A depigmented scar is seen at the site of treatment with liquid nitrogen. A, B, Courtesy, Reinhard Kirnbauer, MD, and Petra Lenz, MD.
• Skin-colored to pink to brown.
• If present in children, especially those >3 years of age, the possibility of sexual abuse should be considered (see Chapter 75).
• DDx: seborrheic keratosis, skin tag, molluscum contagiosum, Bowenoid papulosis, SCC, pearly penile papules (see Chapter 95), free sebaceous glands, condyloma lata of secondary syphilis.
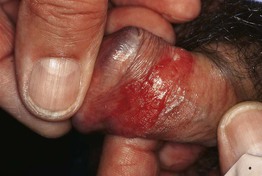
Bowenoid Papulosis (Intraepithelial Neoplasia-3; High-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion)
• Similar to condylomata acuminata, primarily in the anogenital region.
• Multiple pink to red-brown smooth to warty papules or plaques (Fig. 66.12; see Fig. 60.9).
Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ (Intraepithelial Neoplasia-3 or High-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion If Anogenital; Bowen’s Disease If Periungual; Historically Erythroplasia of Queyrat If Penile)
• Favors the glabrous skin of the vulva or penis and the periungual region.
Verrucous Carcinoma
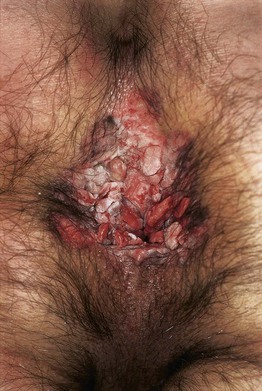
– Buschke–Löwenstein tumor (Fig. 66.14) – anogenital region; fistulas and/or abscesses may be present.
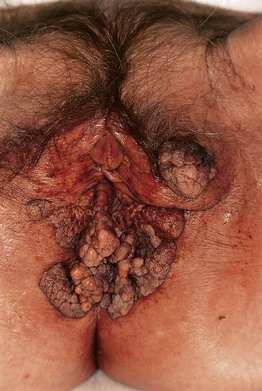
Fig. 66.14 Giant condylomata acuminata (Buschke–Löwenstein tumor). Cauliflower-like, deeply infiltrating giant condylomata acuminata in an older woman. Courtesy, Reinhard Kirnbauer, MD, and Petra Lenz, MD.
– Oral florid papillomatosis – oral mucosa or perinasal sinuses – pebbly confluence of whitish papillomas.
Epidermodysplasia Verruciformis (EDV)
• Cutaneous infection with particular HPV types in patients with an inherited predisposition [mutations in TMC6 (EVER1), TMC8 (EVER2)] or acquired immunosuppression (e.g. HIV infection); see Table 66.1.
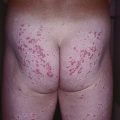
• Lesions vary in color from white to pink to brown and can resemble flat warts or tinea versicolor (Fig. 66.15).
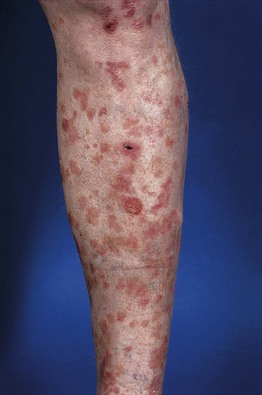
Fig. 66.15 Epidermodysplasia verruciformis. Generalized erythematous macules and plaques are seen. Lesions tested positive for HPV-8 and -36. Courtesy, Reinhard Kirnbauer, MD, and Petra Lenz, MD.
For further information see Ch. 79. From Dermatology, Third Edition.