71 Hereditary Polyneuropathies
The hereditary motor and sensory neuropathies (HMSNs) account for approximately 40% of chronic neuropathies. There are now more than 40 known genes or loci for the various forms of HMSN, which are collectively known as Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease (CMT). About 1 in 2500 persons is affected by CMT. New genes or loci for CMT subtypes are identified very frequently. Less common inherited polyneuropathies are those associated with systemic genetic disorders and inborn errors of metabolism (Table 71-1). Advances in genetic characterization of the inherited neuropathies have afforded greater insight into their biologic basis, and there is increasing interest in therapeutic strategies for these disorders, which can cause lifelong morbidity related to weakness, sensory loss, and orthopedic complications.
Table 71-1 Classification of Inherited Polyneuropathies
| Inheritance | Neurophysiology | |
|---|---|---|
| Hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy type 1 | Autosomal dominant | Demyelinating |
| Hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy type 2 | Autosomal dominant Autosomal recessive |
Axonal |
| Hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy type 3 | Autosomal/de novo dominant | Demyelinating |
| Hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy type 4 | Autosomal recessive | Demyelinating |
| Intermediate CMT | Autosomal dominant | Mixed |
| X-linked CMT | X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive |
Mixed |
| Hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathies | Autosomal recessive | Axonal |
| Hereditary motor neuropathies | Autosomal dominant | Axonal |
| Hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsies | Autosomal dominant | Demyelinating |
| Other Inherited Neuropathies | ||
| Hereditary neuralgic amyotrophy | Autosomal dominant | Axonal |
| Familial amyloid polyneuropathy | Autosomal dominant | Axonal |
| Giant axonal neuropathy | Autosomal recessive | Axonal |
| Infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy | Autosomal recessive | Axonal |
| Andermann syndrome | Autosomal recessive | Axonal |
| Neuropathies Associated with Inborn Errors of Metabolism | ||
| Lipid Disorders | ||
| Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis | Autosomal recessive | Mixed |
| Abetalipoproteinemia, hypolipoproteinemia | Autosomal recessive | Demyelinating |
| Ataxia with vitamin E deficiency | Autosomal recessive | Demyelinating |
| Peroxisomal Disorders | ||
| Refsum disease | Autosomal recessive | Demyelinating |
| Adrenomyeloneuropathy | X-linked | Axonal |
| Mitochondrial Cytopathies | ||
| NARP | Autosomal recessive | Mixed |
| MNGIE | Autosomal recessive | Mixed |
| Leigh disease | Autosomal recessive | Mixed |
| Lysosomal Enzyme Diseases | ||
| Globoid cell leukodystrophy | Autosomal recessive | Demyelinating |
| Metachromatic leukodystrophy | Autosomal recessive | Demyelinating |
| Fabry disease | X-linked | Axonal |
| Tyrosinemia type 1 | Autosomal recessive | Axonal |
| Sphingomyelin Lipidoses | ||
| Niemann–Pick disease type C | Autosomal recessive | Demyelinating |
| Farber disease | Autosomal recessive | Demyelinating |
| Porphyrias | ||
| Acute intermittent porphyria | Autosomal dominant | Axonal |
| Hereditary coproporphyria | Autosomal dominant | Axonal |
| Variegate porphyria | Autosomal dominant | Axonal |
| Disorders with Defective DNA Synthesis or Repair | ||
| Ataxia telangiectasia | Autosomal recessive | Axonal |
| Cockayne syndrome | Autosomal recessive | Demyelinating |
| Neuropathies Associated with Spinocerebellar Ataxias | ||
| Friedreich ataxia, other SCAs | Autosomal recessive | Axonal |
| Neuroacanthocytosis | Autosomal recessive | Axonal |
MNGIE, mitochondrial neurogastrointestinal encephalopathy; NARP, neuropathy, ataxia, and retinitis pigmentosa; SCA, spinocerebellar ataxia.
Clinical Presentation
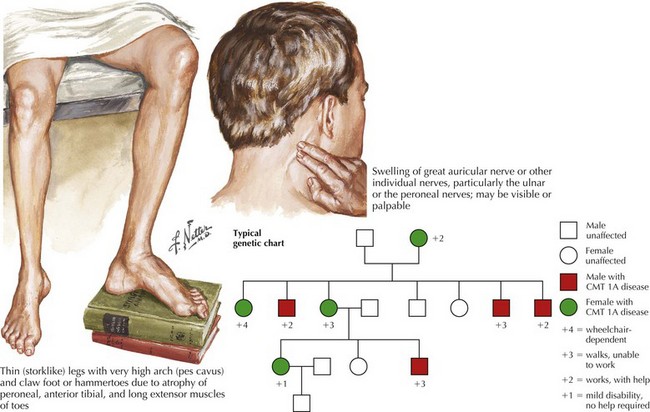
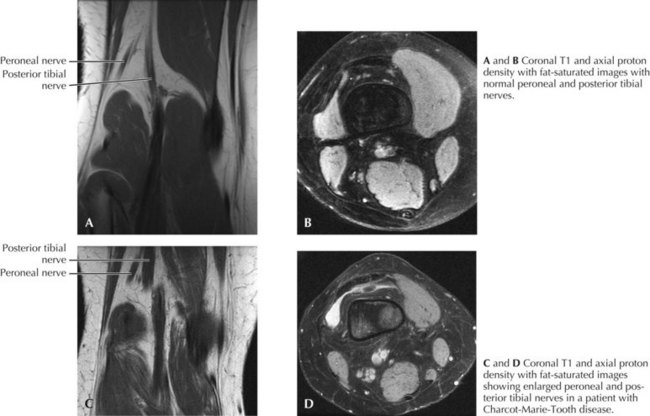
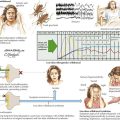
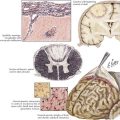
CMT generally first manifests in the first decade but progresses slowly, presenting in childhood or early adulthood with an abnormal gait or pes cavus. Less commonly, CMT presents in infancy with hypotonia and delayed motor milestones, or in late adulthood. The cardinal features of the genetic polyneuropathies are distal muscle wasting and weakness, loss of the deep tendon reflexes, and impaired distal sensation. The gait is high-stepping because of foot drop. Nerve hypertrophy may be palpable in the neck or at the elbow (Fig. 71-1) or nerve enlargement may be seen on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (Fig. 71-2).
Diagnostic Approach
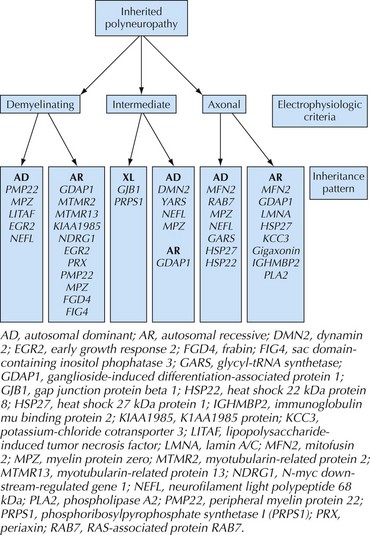
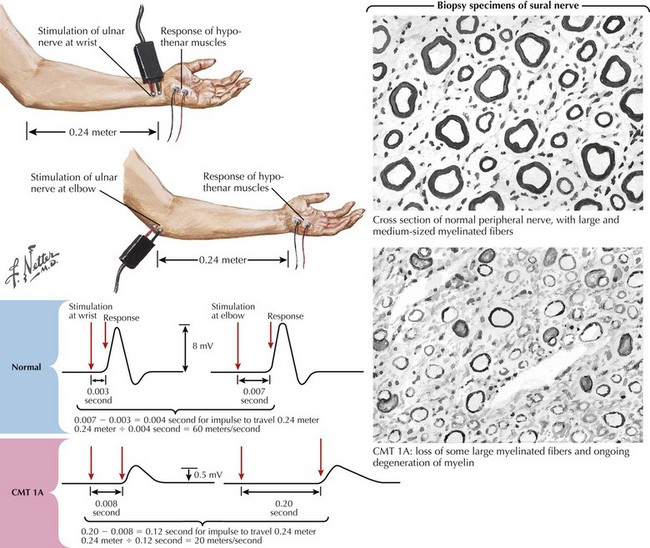
In patients with suspected neuropathies, the initial investigation will generally be nerve conduction studies and electromyography (Fig. 71-3). CMT is classified as demyelinating if the median nerve motor conduction velocity (MCV) is less than 38 m/s, or axonal (CMT2) if the median MCV is more than 38 m/s. Axonal (neuronal) neuropathies are also associated with low-amplitude sensory and motor responses. Intermediate forms of CMT have median MCVs in the 25–45 m/s range. In the hereditary demyelinating neuropathies, neurophysiologic abnormalities are generally homogeneous, with uniform slowing of motor and sensory nerve conduction. In contrast, the acquired demyelinating neuropathies (such as Guillain–Barré syndrome and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy) are characterized by patchy involvement of peripheral nerves with focal slowing, conduction block, and dispersion of motor responses (Fig. 71-4).
Genetic testing is available for the more common forms of CMT, but for less common phenotypes is often performed only on a research basis. Specific genetic diagnoses enable evaluation of relatives, prognostication and prediction of recurrence risk, and antenatal testing. Classification and clinical assessment are complicated by the fact that a single phenotype is often caused by different genes, and that mutations in a gene may present with a variety of phenotypes (see Fig. 71-3).
Classification of Cmt
CMT Type 1
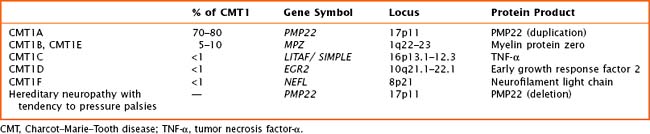
Autosomal dominant demyelinating CMT—CMT type 1—is the most common form of CMT in most populations. Five genes for CMT1 are known (Table 71-2). Most patients present with the “classical” CMT phenotype in the first two decades of life, with a steppage gait, frequent falls, and development of pes cavus. Distal sensory loss is generally mild. There is marked slowing of motor conduction (<38 m/s), and sensory nerve action potentials (SNAPs) are generally lost. Nerve biopsy is usually not required for diagnosis, but if performed shows a hypertrophic demyelinating neuropathy with onion bulb formation. The most common form, CMT1A, is caused by duplications in the peripheral myelin protein 22 gene on chromosome 17. Deletions in the same gene cause hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsies (HNPP), which presents with recurrent mononeuropathies after minor compressive stresses. Other forms of CMT1 are very uncommon. Genes implicated in CMT type 1 can also cause Déjerine–Sottas syndrome, a severe demyelinating neuropathy that presents before the age of 2 years.
CMT Type 2
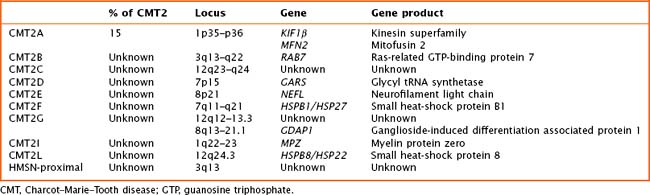
Axonal forms of CMT—CMT type 2—are relatively uncommon and can be difficult to distinguish from sporadic axonal neuropathies. CMT2 has been linked to at least 13 loci and 10 genes (Table 71-3). The most common form, CMT2A, is caused by mutations in the gene for a mitochondrial fusion protein, mitofusin 2 (MFN2). Mutations in MFN2 can cause the classic CMT phenotype or can be associated with early-onset severe weakness, long-tract signs, and/or optic atrophy. Other forms of type 2 CMT may be associated with prominent sensory loss and a mutilating arthropathy, early involvement of the distal upper extremities, and pyramidal signs.
Evidence and Additional Resources
Burns TM, Ryan MM, Darras BT, Jones HRJr. Therapeutic options for neuropathies associated with inborn errors of metabolism in childhood: an update. Mayo Clin Proc. 2003;78:858-868.
Hahn AF, Bolton CF, White CM, et al. Genotype/phenotype correlations in X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1999;883:366-382.
Nicholson GA. The dominantly inherited motor and sensory neuropathies: clinical and molecular advances. Muscle Nerve. 2006;33(5):589-597.
Ouvrier RA, Geevasinga N, Ryan MM. Autosomal recessive and X-linked forms of hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy in childhood. Muscle Nerve. 2007;36:131-143.
Passage E, Norreel JC, Noack-Fraissignes P, et al. Ascorbic acid treatment corrects the phenotype of a mouse model of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Nat Med. 2004;10:396-401.
Shy ME, Jani A, Krajewski K, et al. Phenotypic clustering in MPZ mutations. Brain. 2004;127:371-384.
Zuchner S, Mersiyanova IV, Muglia M, et al. Mutations in the mitochondrial GTPase mitofusin 2 cause Charcot–Marie–Tooth neuropathy type 2A. Nat Genet. 2004;36:449-454.