Erosive pustular dermatosis
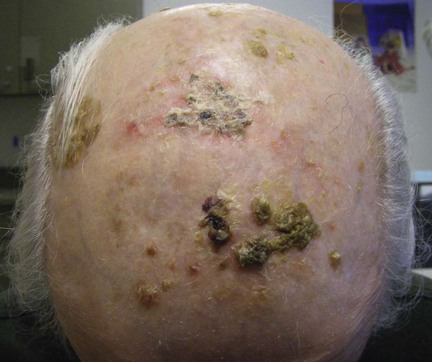
First-line therapy
Three series and 13 case reports exist for high potency topical cortisones in the literature.
Second-line therapies
Nine case reports exist for topical tacrolimus ointment in the literature.

Three series and 13 case reports exist for high potency topical cortisones in the literature.
Nine case reports exist for topical tacrolimus ointment in the literature.
