1.Lai, CH, et al. Clonorchiasis-associated perforated eosinophilic cholecystitis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2007; 76(2):396–398.
2.Shakov, R, et al. Eosinophilic cholecystitis, with a review of the literature. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2007; 37(2):182–185.
3.Suzuki, M, et al. Churg-Strauss syndrome complicated by colon erosion, acalculous cholecystitis and liver abscesses. World J Gastroenterol. 2005; 11(33):5248–5250.
4.Jimenez-Saenz, M, et al. Biliary tract disease: a rare manifestation of eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Dig Dis Sci. 2003; 48(3):624–627.
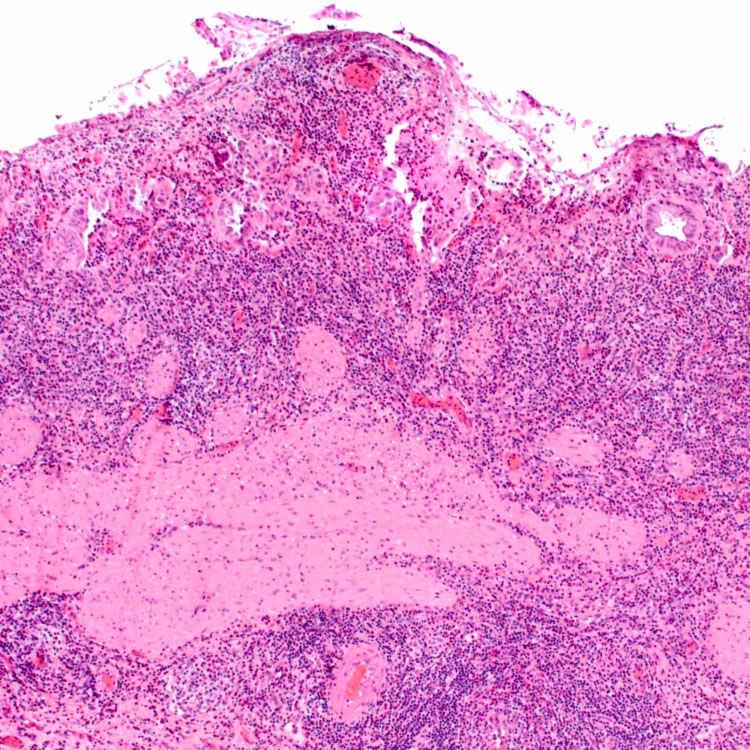
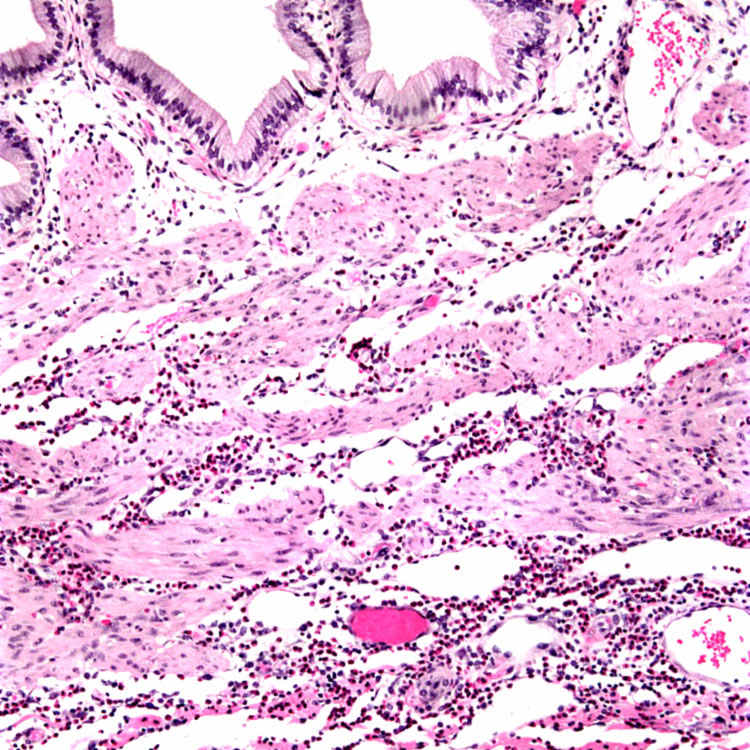
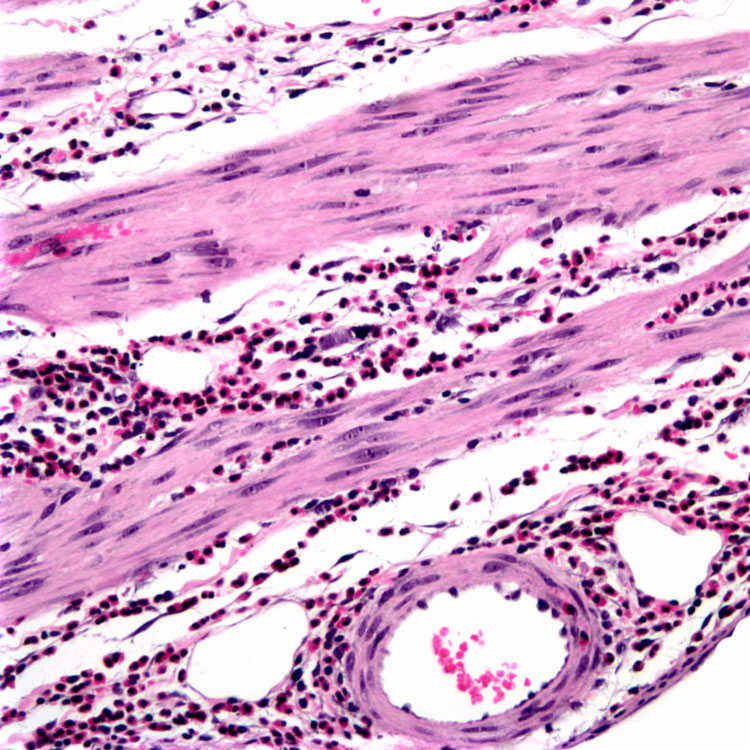
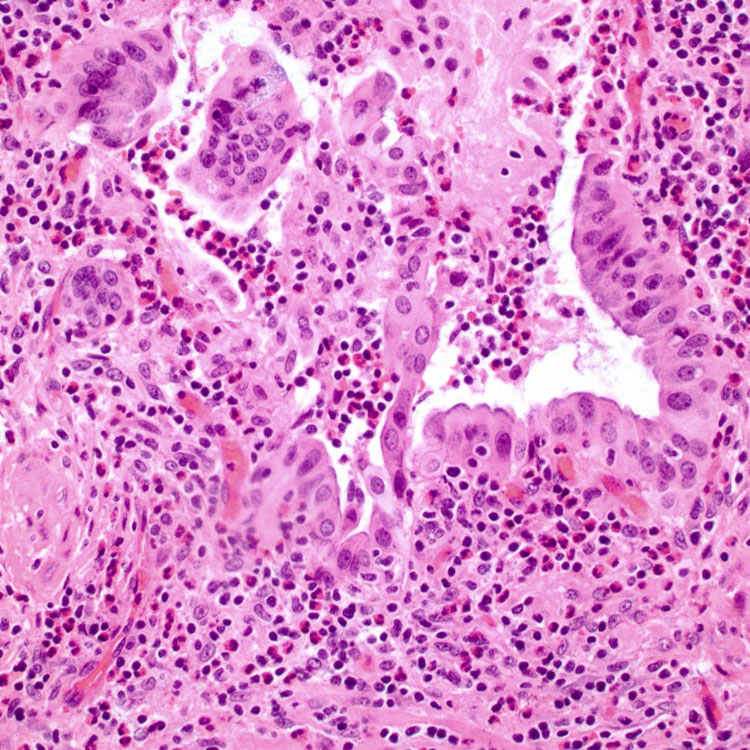
5.Dabbs, DJ. Eosinophilic and lymphoeosinophilic cholecystitis. Am J Surg Pathol. 1993; 17(5):497–501.
6.Parry, SW, et al. Acalculous hypersensitivity cholecystitis: hypothesis of a new clinicopathologic entity. Surgery. 1988; 104(5):911–916.
7.Kerstein, MD, et al. Eosinophilic cholecystitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1976; 66(4):349–352.