•
Venoocclusive disease (VOD)
•
Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (SOS)
•
Stem cell transplantation and high-dose chemotherapy
•
Herbal medicines containing pyrrolizidine alkaloids
•
Rare complication of liver transplantation
•
Rare causes of sinusoidal obstruction: Sickle cell crisis,
Plasmodium falciparum malaria, extensive infiltration by neoplastic cells
•
Older age and poor performance status
•
HLA disparity in allogeneic stem cell transplant
•
Preexisting liver dysfunction
•
Prior abdominal radiation
•
Pretransplant use of acyclovir or vancomycin
•
High-dose busulphan and cyclophosphamide therapy
•
Injury to sinusoidal endothelial cells is important initial event; hence, preferred term is SOS
•
Major damage occurs in zone 3, which has high concentration of cytochrome P450 enzymes that metabolize many chemotherapeutic agents
•
Depletion of glutathione, also predominantly present in centrizonal location, plays role in hepatocyte necrosis
•
SOS in stem cell transplantation
Typically occurs in 1st 3 weeks
Triad of hyperbilirubinemia, weight gain, and painful hepatomegaly
Plasma levels of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 are often elevated
Attenuated or reverse flow in portal vein on Doppler ultrasound
Wedged hepatic venous pressure gradient (WHVPG) > 10 mmHg has 91% specificity and 52% sensitivity
Diagnosis often based on clinical criteria, biopsy reserved for unclear cases
•
Use of pharmacokinetics to monitor drug levels with intent of minimizing hepatic injury
•
Fibrinolytic agents such as recombinant tissue plasminogen activator and anticoagulants like heparin
•
Antiinflammatory agents such as ursodiol and pentoxifylline
•
Endothelial protective agents such as prostaglandin E1 and defibrotide
•
Glutathione and N-acetyl cysteine supplementation
•
Mild disease: No significant adverse effect from liver dysfunction with complete resolution
•
Moderate disease: Requiring therapy but with eventual complete resolution
•
Severe: Dismal outcome, mortality approaching 100%
•
Adverse prognostic factors: Ascites, multiorgan failure, WHVPG > 20 mmHg
•
Liver biopsy is done through transjugular route; percutaneous biopsy is contraindicated given high risk for bleeding
•
Changes can be patchy in early disease leading to false-negative results
•
Subendothelial edema, red cell extravasation, fibrin deposition in central vein and sinusoids
•
Narrowing of venular lumen leads to sinusoidal dilatation and hepatocyte necrosis
•
Fibrosis develops in sinusoids and venular wall
•
Eventually leads to venular obliteration, extensive hepatocellular necrosis, and widespread fibrosis
•
Also causes acute liver dysfunction after stem cell transplant
•
Bile duct damage and apoptosis are not seen in VOD
•
Centrizonal hepatocellular damage is not characteristic of GVHD
•
Venular luminal compromise, obliteration absent in hepatic venous outflow obstruction
1.Palladino, M, et al. Severe veno-occlusive disease after autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for high-grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma: report of a successfully managed case and a literature review of veno-occlusive disease. Clin Transplant . 2008; 22(6):837–841.
2.Karoui, M, et al. Influence of preoperative chemotherapy on the risk of major hepatectomy for colorectal liver metastases. Ann Surg . 2006; 243(1):1–7.
3.Kumar, S, et al. Hepatic veno-occlusive disease (sinusoidal obstruction syndrome) after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Mayo Clin Proc . 2003; 78(5):589–598.
4.Wadleigh, M, et al. Hepatic veno-occlusive disease: pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment. Curr Opin Hematol . 2003; 10(6):451–462.
5.Dhillon, AP, et al. Hepatic venular stenosis after orthotopic liver transplantation. Hepatology . 1994; 19(1):106–111.
Diagnostic Pathology Hepatobiliary and Pancreas
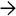 .
.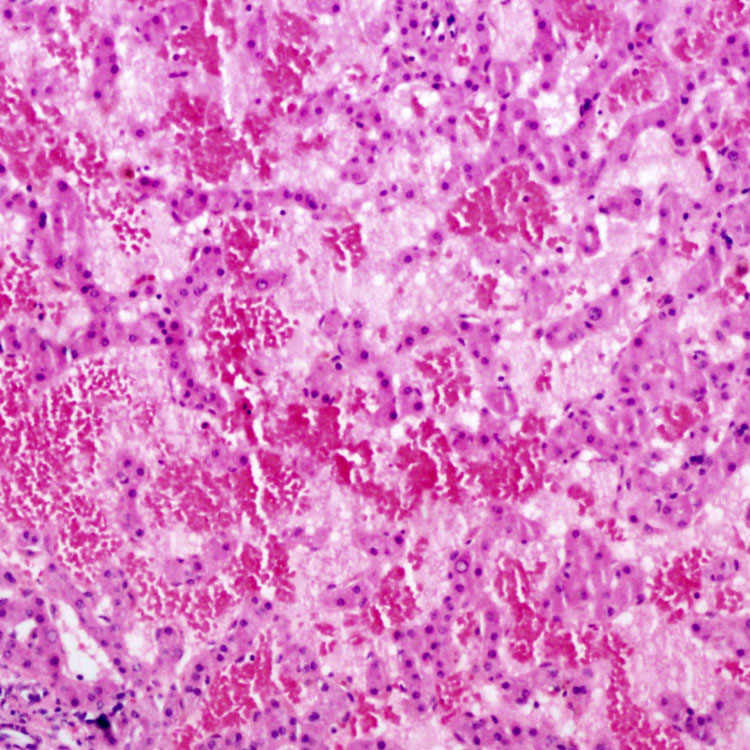
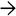 leads to partial occlusion of the lumen of a small hepatic vein in venoocclusive disease. These characteristic lesions may not be evident in biopsies.
leads to partial occlusion of the lumen of a small hepatic vein in venoocclusive disease. These characteristic lesions may not be evident in biopsies.
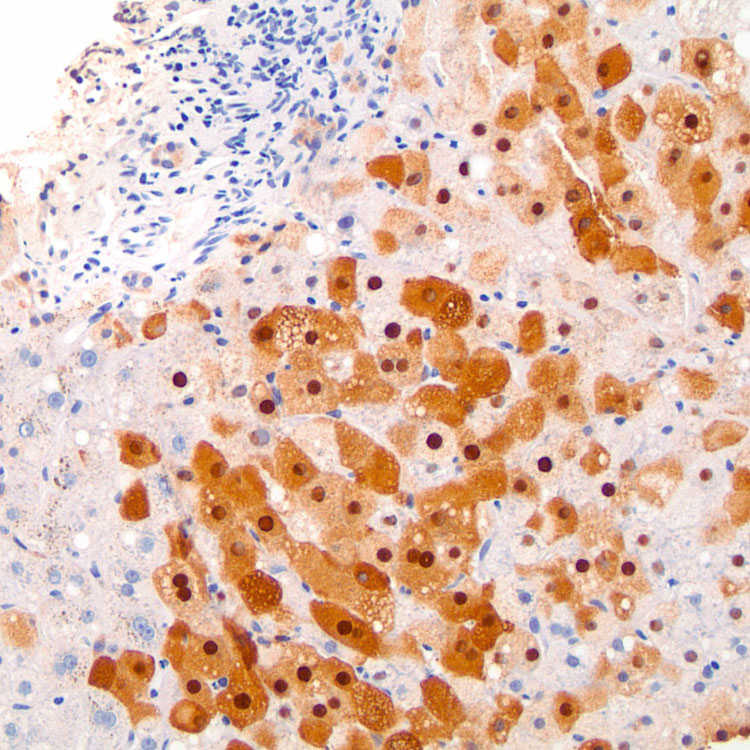
 in hepatic sickle cell crisis is shown. This is a rare phenomenon but can cause sinusoidal obstruction syndrome and present in an acute fashion.
in hepatic sickle cell crisis is shown. This is a rare phenomenon but can cause sinusoidal obstruction syndrome and present in an acute fashion.