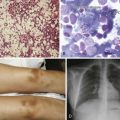
Chapter 31 Eosinophilia, Eosinophil-Associated Diseases, Chronic Eosinophil Leukemia, and the Hypereosinophilic Syndromes
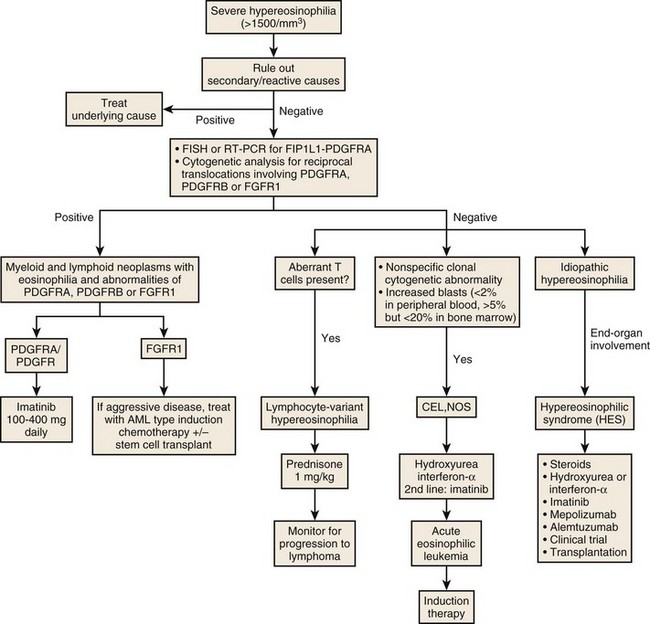
Diagnosis and Workup of Hypereosinophilic Syndrome
• Complete/detailed history and physical examination
• Review of all medications (including herbal medications and nutritional supplements); withdrawal of all noncritical medications
• Complete blood count with total eosinophil count and review of peripheral blood smear
• Hepatic and renal function tests, urine analysis
• Serologic assays: erythrocyte sedimentation rate, rheumatoid factor, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
• Quantitation of total IgE level
• Serologic assays for Strongyloides, Trichinella, Toxocara, Entamoeba histolytica, Echinococcus, filariasis, and schistosomiasis
• Bone marrow aspirate and biopsy
• Cytogenetics, FISH, and molecular analyses (PDGFRA, PDGFRB, FGFR1 fusion genes, BCR-ABL, JAK2 V617F, KIT D816V, clonal TCR gene rearrangement)
• T-cell phenotyping by flow cytometry
• Chest radiograph; computed tomographic scan of chest, abdomen, and pelvis
Diagnostic Criteria for HES/CEL
1. Persistent eosinophilia of greater than 1500 eosinophils/mm3 for more than 6 months
2. Exclusion of other potential “reactive” etiologies for the eosinophilia including parasitic, allergic, or other causes, and
3. Presumptive signs and symptoms of organ system dysfunction or involvement that appears related to the eosinophilia or is of unknown cause in the clinical presentation
Table 31-1 Diseases, Syndromes, and Conditions Commonly Associated With Peripheral Blood Eosinophilia and/or Tissue Eosinophilia
| INFECTIOUS AGENTS |
| Parasitic Infections |
Solid tumors (mucin-secreting, epithelial cell origin)
Idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndromes (HES)
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS)
Myelomonocytic leukemia with bone marrow eosinophilia (M4Eo, inversion 16)
Modified and updated from Mahanty S, Nutman, TB: Eosinophilia and eosinophil-related disorders. In Middleton EJ, Reed CE, Ellis EF, et al, editors: Allergy: Principles and practice, ed 4, St Louis, 1993, Mosby-Year Book, p 1077.
Table 31-2 Major Organ Involvement and Prominent Clinical Features of Patients With Hypereosinophilic Syndrome*
| PRIMARY ORGAN INVOLVEMENT† |
| CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS§ |
*Listed in order of frequency.
†Average percentage of 105 patients from American, French, and English studies combined.
‡Reproduced from Spry CJ: The hypereosinophilic syndrome: Clinical features, laboratory findings and treatment. Allergy 37:539, 1982.
§Reproduced from Weller PF, Bubley GJ: The idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. Blood 83:2759, 1994.
Table 31-3 Criteria for the Diagnosis of Idiopathic Hypereosinophilic Syndrome
| FACTORS FAVORING A DIAGNOSIS OF HES |
Reproduced with permission from Brito-Babapulle F: Clonal eosinophilic disorders and the hypereosinophilic syndrome. Blood Rev 11:129, 1997.
Table 31-4 End-Organ Damage Produced by Hypereosinophilia
| ORGAN/SYSTEM |
| Cardiac |
| Neurologic |
| Dermatologic |
| Pulmonary |
| Ocular |
| Gastrointestinal |
Reproduced from Brito-Babapulle F: Clonal eosinophilic disorders and the hypereosinophilic syndrome. Blood Rev 11:129, 1997.