Effects of common anesthetic agents on electroencephalograms
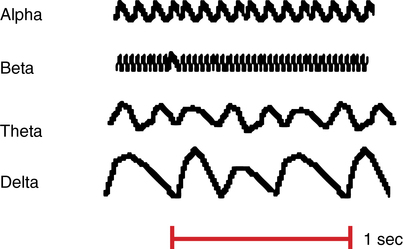
The electroencephalogram (EEG) is a depiction of the electrical activity occurring at the surface of the brain. This activity appears on the EEG recording as waveforms of varying frequency and amplitude measured in microvolts. Four categories of frequencies are the most clinically relevant (Table 43-1, Figure 43-1).
Table 43-1
Categories of the Most Clinically Relevant Electroencephalographic Frequencies
| Wave Pattern | Frequency Range (Hz) | Level of Consciousness |
| Delta | 0.5-4 | Deep sleep |
| Theta | 4-8 | Drowsiness (also first stage of sleep) |
| Alpha | 8-14 | Relaxed but alert |
| Beta | 14-30 | Highly alert and focused |