Chapter 10 Drugs Affecting the Parasympathetic Nervous System and Autonomic Ganglia
| Abbreviations | |
|---|---|
| AcCoA | Acetyl coenzyme A |
| ACh | Acetylcholine |
| AChE | Acetylcholinesterase |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| BuChE | Butyrylcholinesterase |
| ChAT | Choline acetyltransferase |
| ChE | Cholinesterase |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| Epi | Epinephrine |
| EPSP | Excitatory postsynaptic potential |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| 2-PAM | Pralidoxime |
| PNS | Peripheral nervous system |
| SNP | Single-nucleotide polymorphism |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
Therapeutic Overview
Drugs that block the actions of ACh at muscarinic receptors are termed muscarinic receptor antagonists, parasympatholytics, or cholinolytics, and are used to treat motion sickness, relieve some of the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease (see Chapter 28), dilate the pupils for ocular examination, reduce motility of the GI and urinary tracts, dilate the airways of the lung in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
| Therapeutic Overview |
|---|
| Muscarinic Receptor Agonists |
| Glaucoma |
| Postoperative ileus, congenital megacolon, and urinary retention |
| Cholinesterase (ChE) Inhibitors |
| Glaucoma |
| Postoperative ileus, congenital megacolon, urinary retention |
| Diagnosis and treatment of myasthenia gravis |
| Reversal of neuromuscular blockade following surgery |
| Alzheimer’s disease |
| Muscarinic Receptor Antagonists |
| Motion sickness |
| Examination of the retina and measurement of refraction; inflammatory uveitis |
| Excessive motility of GI and urinary tract; urinary incontinence; irritable bowel syndrome |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| Parkinson’s disease |
| Ganglionic Blockers |
| Hypertensive emergencies |
(see Chapter 16), and reduce acid secretion in individuals with peptic ulcer disease (see Chapter 18).
Drugs that antagonize the actions of ACh at ganglionic nicotinic receptors are referred to as ganglionic blockers and are used to treat hypertensive emergencies. Drugs that antagonize the actions of ACh at nicotinic receptors at the neuromuscular junction are termed neuromuscular blocking agents and are used to relax skeletal muscle (see Chapter 12).
Mechanisms of Action
The biochemistry and physiology of the autonomic nervous system, including a discussion of muscarinic and nicotinic cholinergic receptors, are presented in Chapter 9. Detailed information on receptors and signaling pathways are discussed in Chapter 1. This section covers topics that pertain specifically to cholinergic neurotransmission and its modulation by drugs.
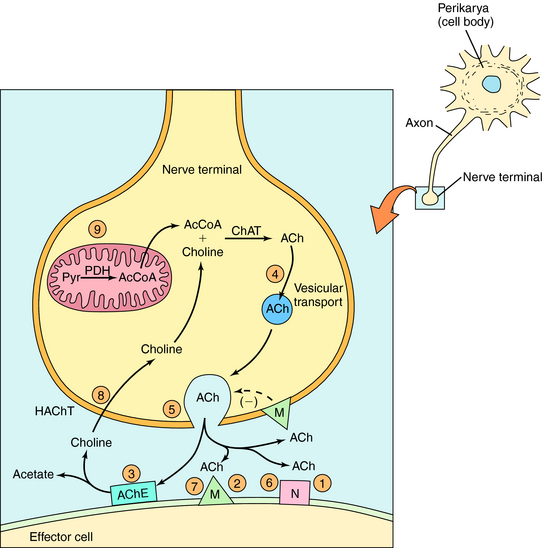
The neurochemical steps that mediate cholinergic neurotransmission are summarized in Figure 10-1. ACh is synthesized from choline and acetyl coenzyme A (AcCoA) by the enzyme choline acetyltransferase (ChAT). ChAT is not rate-limiting for ACh synthesis, and thus ChAT inhibitors have little or no effect on ACh concentrations. The AcCoA used for ACh synthesis is synthesized in mitochondria from its immediate precursor, pyruvate, and is transported out of mitochondria into the cytoplasm.
Once formed in the cytosol, ACh is transported actively into synaptic vesicles by the vesicular ACh transporter. The arrival of an action potential at the nerve terminal causes Ca++ influx, triggering the release of ACh from storage vesicles. The toxin from Clostridium botulinum (botulinum toxin) prevents the exocytotic release of ACh from synaptic vesicles and blocks cholinergic neurotransmission. This mechanism underlies the clinical and cosmetic use of botulinum toxin in conditions that involve involuntary skeletal muscle activity or increased muscle tone including strabismus, blepharospasm, hemifacial spasm, and facial wrinkles (see Chapter 12). After release from the nerve terminal, ACh elicits cellular responses by activating postsynaptic muscarinic or nicotinic receptors. Muscarinic receptors are also located presynaptically, where they inhibit further neurotransmitter release. The effects of ACh are rapidly terminated by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE), which hydrolyzes ACh to acetate and choline. Choline is transported back into nerve terminals by the high-affinity choline transporter, where it can be reused for ACh synthesis.
Drugs can modify the effectiveness of parasympathetic nerve activity by increasing or decreasing cholinergic neurotransmission. Parasympathomimetics mimic cholinergic transmission by acting directly on postsynaptic receptors (muscarinic receptor agonists) or by prolonging the action of released ACh (AChE inhibitors). Drugs that block cholinergic transmission inhibit either the storage of ACh (vesamicol), vesicular exocytosis (botulinum toxin), or the high-affinity transport of choline (hemicholinium). Drugs can also block muscarinic receptors (muscarinic receptor antagonists). The sites of action of all these compounds are depicted in Figure 10-1.
Activation of Cholinergic Receptors
Drugs that activate cholinergic receptors may be classified as either directly or indirect-acting. Direct-acting compounds produce their effects by binding to and activating either muscarinic or nicotinic receptors and are termed muscarinic or nicotinic receptor agonists, respectively. Indirect-acting cholinomimetics produce their effects by inhibiting AChE, thereby increasing the concentration and prolonging the action of ACh at cholinergic synapses. The directly and indirect-acting cholinomimetics and their clinical uses are presented in Table 10-1.
TABLE 10–1 Direct- and Indirect-Acting Cholinomimetic Drugs and their Uses
| Action | Agent | Use |
|---|---|---|
| Direct-Acting (Muscarinic Receptor Agonists) | ||
| Pilocarpine | Glaucoma | |
| Carbachol | Glaucoma | |
| Bethanechol | Postoperative ileus, congenital megacolon, urinary retention | |
| ChE Inhibitors* | ||
| Physostigmine | Glaucoma | |
| Demecarium | Glaucoma | |
| Echothiophate | Glaucoma | |
| Isoflurophate | Glaucoma | |
| Neostigmine | Postoperative ileus, congenital megacolon, urinary retention, reversal of neuromuscular blockade | |
| Edrophonium | Diagnosis of myasthenia gravis, reversal of neuromuscular blockade, supraventricular tachyarrhythmias | |
| Ambenonium | Treatment of myasthenia gravis | |
| Pyridostigmine | Treatment of myasthenia gravis, reversal of neuromuscular blockade | |
* ChE inhibitors used for Alzheimer’s disease are listed in Chapter 28.
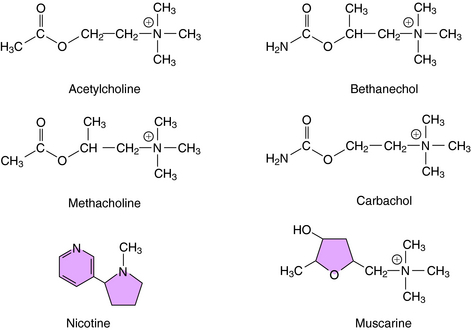
The structures of several direct-acting cholinergic agonists are shown in Figure 10-2. Introduction of a methyl group in the β position of ACh yields agonists selective for muscarinic receptors such as methacholine and bethanechol. In addition, substitution of an amino group for the terminal methyl group yields corresponding carbamic acid ester derivatives (i.e., carbachol and bethanechol), which render these compounds relatively resistant to hydrolysis by AChE, prolonging their action as compared with ACh.
Muscarinic receptors mediate cellular responses by interacting with heterotrimeric G proteins to affect ionic conductances and the cytosolic concentration of second messengers (see Chapters 1 9). As indicated in Chapter 9, five muscarinic receptor subtypes (M1 to M5) have been identified, with M1 receptors located in the CNS, peripheral neurons, and gastric parietal cells, M2 receptors located in the heart and on some presynaptic nerve terminals in the periphery and CNS, and M3 receptors located on glands and smooth muscle. M4 and M5 receptors are located in the CNS and are less well understood than the others.
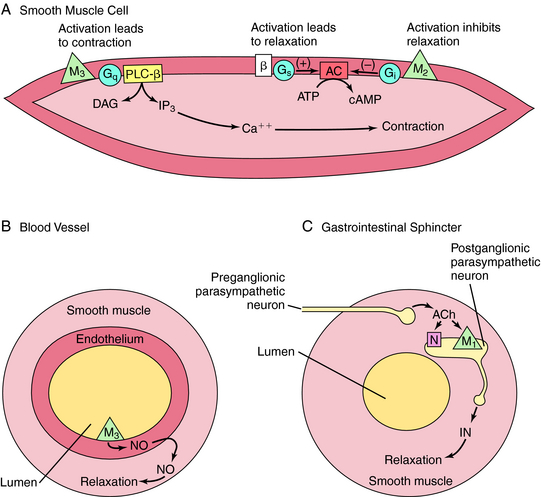
M1, M3, and M5 receptors are coupled to Gq proteins, and stimulation of these receptors activates phospholipase C, leading to increased phosphoinositide hydrolysis and the release of intracellular Ca++. In contrast, M2 and M4 receptors are coupled to Gi, and agonist activation leads to inhibition of adenylyl cyclase. The signaling pathways mediating the contraction of smooth muscle upon activation of M2 or M3 receptors is depicted in Figure 10-3, A. Activation of M3 receptors promotes smooth muscle contraction directly, whereas activation of M2 receptors promotes contraction by inhibiting the ability of β adrenergic receptor activation to relax smooth muscle. Activation of M3 receptors on the endothelium of blood vessels (see Fig. 10-3, B) increases the production of nitric oxide (NO), which diffuses and causes relaxation of the muscle, while activation of M1 receptors in parasympathetic ganglia (see Fig. 10-3, C) releases an inhibitory neurotransmitter such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP), NO, or vasoactive intestinal peptide to relax smooth muscle sphincters.
Most, but not all, peripheral effects of muscarinic receptor agonists resemble those elicited by the activation of parasympathetic nerves (see Chapter 9). These effects include: (1) constriction of the iris sphincter; (2) contraction of the ciliary muscle, resulting in accommodation of the lens; (3) constriction of the airways; (4) an increase in GI motility; (5) contraction of the bladder reservoir and relaxation of its outlet; (6) a decrease in heart rate; and (7) an increase in secretions of sweat glands, salivary glands, lacrimal glands, and glands of the trachea and GI mucosa. Although the ventricular myocardium and most peripheral blood vessels lack cholinergic innervation, they express muscarinic receptors. When activated by exogenously administered agonists, these receptors decrease the force of contraction in the heart and dilate peripheral blood vessels. Muscarinic receptor agonists also activate receptors throughout the CNS, and muscarinic receptors in the brain play an important role in learning, memory, control of posture, and temperature regulation. Excessive activation of central muscarinic receptors causes tremor, convulsions, and hypothermia.
The prototypic nicotinic receptor agonist, nicotine, is found in tobacco, cigarette smoke, some insecticides, and in transdermal patches used to ease withdrawal from smoking. Lobeline is another natural nicotinic receptor agonist that has actions similar to nicotine. The cholinomimetic carbachol has nicotinic as well as muscarinic receptor agonist activity. Nicotine activates nicotinic receptors at the neuromuscular junction, causing contraction followed by depolarization blockade and paralysis. Nicotine also activates sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia. As a consequence, because of differences in the predominant tone of autonomic systems (see Chapter 9), its effects on the vascular system are primarily sympathetic, whereas its effects on the GI tract are primarily parasympathetic. Nicotine elevates blood pressure and heart rate, with the latter opposed by reflex bradycardia. The sympathetic effects of nicotine are reinforced by stimulation of nicotinic receptors at the adrenal medulla, leading to the release of catecholamines. Nicotine also stimulates the GI and urinary tracts, causing diarrhea and urination. Nicotine readily enters the brain, and increasing doses cause alertness, vomiting, tremors, convulsions, and, ultimately, coma, and is a source of poisoning, especially in children.
Two types of cholinesterase (ChE) enzymes are expressed in the body, AChE and butyrylcholinesterase (BuChE, also called plasma or pseudoChE), each with a different distribution and substrate specificity. AChE is located at synapses throughout the nervous system and is responsible for terminating the action of ACh. BuChE is located at non-neuronal sites, including plasma and liver, and is responsible for the metabolism of certain drugs, including ester-type local anesthetics (Chapter 13) and succinylcholine (Chapter 12). Most enzyme inhibitors used clinically do not discriminate between the two types of ChEs.
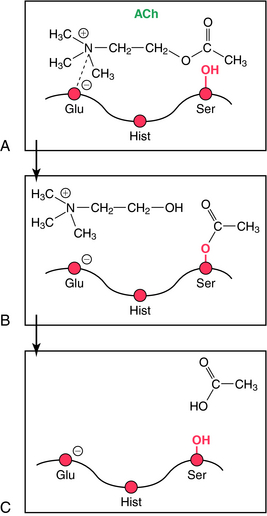
The mechanism involved in the hydrolysis of ACh explains the biochemical basis of the actions of ChE inhibitors (Fig. 10-4). AChE is a member of the serine hydrolase family of enzymes and contains a serine (ser)-glutamate (glu)-histidine (hist) triad at the active site. The enzyme has an anionic and a catalytic domain. When ACh binds to AChE, the quaternary nitrogen of ACh binds to the anionic site, positioning the ester group near the catalytic site. The ester moiety undergoes a nucleophilic attack by the serine of the catalytic site, resulting in the hydrolysis of ACh and binding of acetate to the serine of the catalytic domain (acetylation). The acetylated serine is rapidly hydrolyzed, and the free enzyme is regenerated. This enzymatic reaction is one of the fastest known; approximately 104 molecules of ACh are hydrolyzed per second by a single AChE molecule, requiring only about 100 μsec.
ChE inhibitors are divided into two main types, reversible and irreversible. Reversible inhibitors are further subdivided into noncovalent and covalent enzyme inhibitors. Noncovalent inhibitors, such as edrophonium, bind reversibly to the anionic domain of AChE. The duration of action is determined in part by the way in which the inhibitor binds. Edrophonium binds weakly and has a rapid renal clearance, resulting in a brief duration of action (approximately 10 minutes). Tacrine and donepezil are also noncovalent ChE inhibitors used to treat Alzheimer’s disease (Chapter 28); they have higher affinities and partition into lipids, giving longer durations of action.
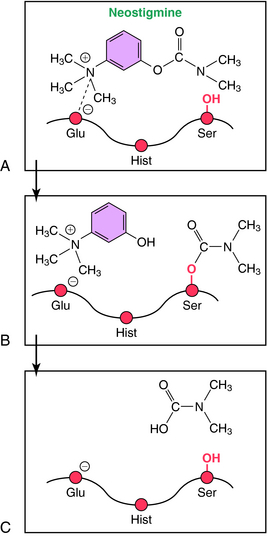
Covalent reversible ChE inhibitors, such as physostigmine and neostigmine, are sometimes referred to as carbamate inhibitors and are carbamic acid ester derivatives. These compounds bind to AChE and are hydrolyzed, but at a relatively slow rate (Fig. 10-5). The resultant carbamylated enzyme is more stable than the acetylated enzyme produced by the hydrolysis of ACh. Unlike the acetylated enzyme, which is deacetylated within seconds, the carbamylated enzyme takes 3 to 4 hours to decarbamylate, contributing to the moderate duration of action of these compounds in patients.
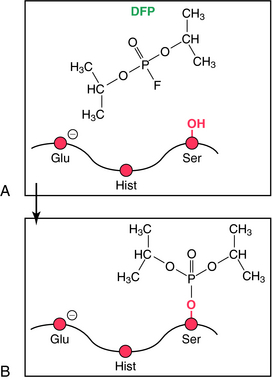
Irreversible ChE inhibitors phosphorylate the serine in the active site of AChE (Fig. 10-6). These compounds are organophosphorus molecules and include the toxic nerve gases sarin, soman, and tabun; the insecticides parathion and malathion; and the therapeutic agents echothiophate and isoflurophate. Collectively these compounds are termed organophosphorus ChE inhibitors. The phosphorylated enzyme formed with these compounds is extremely stable, unlike that formed from the hydrolysis of ACh. Dephosphorylation of the phosphorylated enzyme takes hours, if it occurs at all. In the case of secondary (isoflurophate) and tertiary (soman) alkyl-substituted phosphates, the phosphorylated enzyme is so stable that it is not dephosphorylated, and new enzyme molecules must be synthesized for enzyme activity to recover. Many organophosphorus ChE inhibitors also irreversibly phosphorylate and inactivate other serine hydrolases, including trypsin and chymotrypsin. Enzyme reactivation with oximes used in clinical practice such as pralidoxime (2-PAM) is used in conjunction with respiratory support and muscarinic receptor antagonists.
ChE inhibitors amplify the effects of ACh at all sites throughout the nervous system, which results in both therapeutic and adverse effects. Thus ChE inhibitors indirectly activate nicotinic receptors at the neuromuscular junction and at sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia. In skeletal muscle, low doses of ChE inhibitors tend to increase the force of contraction. This is not particularly noticeable in normal individuals, but it is the basis for the therapeutic effect of these compounds in patients with myasthenia gravis. Intermediate doses of ChE inhibitors elicit muscle fasciculations and fibrillations, and high doses cause depolarization blockade and muscle paralysis. ChE inhibitors indirectly activate muscarinic receptors at all postjunctional sites in the parasympathetic nervous system and sweat glands. In GI smooth muscle, ChE inhibitors increase motility by prolonging the action of ACh at muscarinic receptors on smooth muscle. ChE inhibitors also relax sphincters by enhancing neurotransmission through parasympathetic ganglia, causing the release of a noncholinergic inhibitory neurotransmitter that directly relaxes GI sphincter smooth muscle (see Fig. 10-3, C).
Most organophosphorus ChE inhibitors and tertiary amine carbamate inhibitors readily penetrate the blood-brain barrier and indirectly activate central nicotinic and muscarinic receptors. ChE inhibitors that penetrate the blood-brain barrier (see Chapter 2) have been specifically developed and used for Alzheimer’s disease (see Chapter 28).
Blockade of Cholinergic Receptors
Cholinergic receptor blockers are classified as muscarinic or nicotinic receptor antagonists.
Muscarinic Receptor Antagonists
Muscarinic receptor antagonists block muscarinic receptors competitively. Because the effects of these drugs resemble those of agents that block postganglionic parasympathetic nerves, these compounds are sometimes referred to as parasympatholytics. Included in this group are the naturally occurring belladonna alkaloids atropine and scopolamine.1 Muscarinic receptor antagonists and their clinical uses are presented in Table 10-2. Most antagonists used clinically are not selective for different muscarinic receptor subtypes.
| Agent | Use |
|---|---|
| Tertiary Amines | |
| Atropine | Treatment of anti-ChE poisoning |
| Scopolamine | Treatment of motion sickness |
| Homatropine | Mydriatic and cycloplegic; for mild uveitis |
| Dicyclomine | Alleviates GI spasms, pylorospasm, and biliary distention |
| Oxybutynin | Treatment of urinary incontinence |
| Oxyphencyclimine | Antisecretory agent for peptic ulcer |
| Cyclopentolate | Mydriatic and cycloplegic |
| Tropicamide | Mydriatic and cycloplegic |
| Benztropine | Treatment of Parkinson’s disease |
| Trihexyphenidyl | Treatment of Parkinson’s disease |
| Pirenzepine | Antisecretory agent for peptic ulcer |
| Quaternary Ammonium Derivatives | |
| Methylatropine | Mydriatic, cycloplegic and antispasmodic |
| Methylscopolamine | Antisecretory agent for peptic ulcer, antispasmodic |
| Ipratropium | Aerosol for COPD |
| Glycopyrrolate | Antisecretory agent for peptic ulcer, antispasmodic |
| Tolterodine | Treatment of urinary incontinence |
| Propantheline | GI antispasmodic |
| Tiotropium | Aerosol for COPD |
* Muscarinic antagonists used for Parkinson’s disease are also listed in Chapter 28.
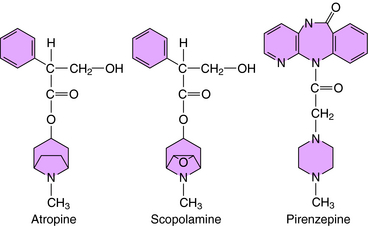
The structures of several muscarinic receptor antagonists are shown in Figure 10-7. The prototypical compound is atropine, which has been used for many years to define muscarinic responses. Scopolamine differs from atropine by the addition of an epoxide group that reduces the base strength and enables it to penetrate into the brain more readily than atropine. Other drugs, including some antihistamines, tricyclic antidepressants, and antipsychotics, are structurally similar to the muscarinic receptor antagonists and have prominent antimuscarinic side effects. The anticholinergic effects of these compounds are discussed in chapters specifically dealing with these drugs.
The effects of muscarinic receptor antagonists can be understood by knowledge of the distribution of muscarinic receptors throughout the body, as discussed in Chapter 9. For example, in the anterior segment of the eye, muscarinic receptor antagonists relax the iris sphincter and ciliary muscle, causing pupillary dilation (mydriasis) and a paralysis of the accommodation reflex (cycloplegia), resulting in blurred vision. Muscarinic receptor antagonists also relax nonvascular smooth muscle, including that in the lung airways, the GI tract, and the urinary bladder. Muscarinic receptor antagonists inhibit the secretion of substances from various exocrine glands, including sweat, salivary, lacrimal, and mucosal glands of the trachea and GI tract. In moderate to high doses, muscarinic receptor antagonists block the effects of ACh on the heart, resulting in an increased heart rate.
Muscarinic receptor antagonists that reach the brain (e.g., atropine and scopolamine) interfere with short-term memory and, in moderately high doses, cause delirium, excitement, agitation, and toxic psychosis. Quaternary amine versions of these compounds are available; they do not penetrate the blood-brain barrier very well, thereby reducing effects on the CNS (Chapter 2).
Pharmacokinetics
As indicated, many clinically used drugs that modify cholinergic function lack selectivity for receptor subtypes. Nevertheless, a degree of selectivity can be achieved in vivo, depending on the route of administration and tissue distribution of the drug. An important structural feature to keep in mind is whether a compound is or is not charged, because tertiary amines, unlike quaternary ammonium compounds, readily penetrate into the brain through the blood-brain barrier (see Chapter 2).
Highly lipophilic organophosphorus ChE inhibitors are well absorbed from the GI tract, lung, eye, and skin, making these compounds extremely dangerous and accounting for their use as nerve gases. The carbamate insecticides are not highly absorbed transdermally. The organophosphorus insecticides malathion and parathion are prodrugs, that is, they are inactive but can be metabolized to the active ChE inhibitors paraoxon and malaoxon. Malathion is relatively safe in mammals because it is hydrolyzed rapidly by plasma carboxylesterases. This detoxification occurs much more rapidly in birds and mammals than in insects. Malathion is available outside the United States in the form of a lotion or shampoo for the treatment of head lice.
The lipophilicity and degree of ionization of cholinergic antagonists also influences their absorption and distribution. Quaternary ammonium antagonists are poorly absorbed from the GI tract and do not penetrate readily into the CNS (Chapter 2). The passage of these agents across the blood-brain barrier is strongly influenced by their degree of ionization, even among the tertiary amines. Although atropine and scopolamine have a similar affinity for muscarinic receptors, scopolamine is approximately 10 times more potent at producing CNS effects. This is attributed to its weaker base strength (pKa = 7.53) relative to that of atropine (pKa = 9.65). Consequently, a greater fraction of scopolamine is present in a unionized form at physiological pH relative to that of atropine (see Chapter 2). The relatively low pKa of scopolamine facilitates its absorption through the skin, making the transdermal route of administration of the free base feasible, and has led to the therapeutic use of this agent to treat motion sickness. The selective M1 receptor antagonist pirenzepine contains three tertiary amine groups, with a resultant high degree of ionization, thereby preventing its entry into brain.
Relationship of Mechanisms of Action to Clinical Response
Both muscarinic receptor agonists and antagonists are used in the treatment of several neurodegenerative disorders. Muscarinic receptor antagonists, such as trihexyphenidyl and benztropine, are used for Parkinson’s disease with some benefit, and centrally acting ChE inhibitors have been noted to improve the cognitive deficits in Alzheimer’s disease without halting the underlying progression of the disease. These agents and uses are discussed in Chapter 28.
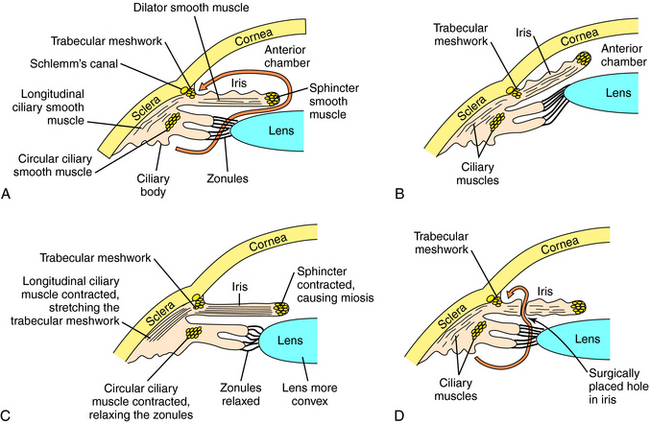
When left unchecked, high intraocular pressure (glaucoma) damages the optic nerve and retina, resulting in blindness. Usually, glaucoma is caused by impaired drainage of aqueous humor produced by the ciliary epithelium in the posterior chamber of the eye. Normally, aqueous humor flows into the anterior chamber by first passing between the lens and iris and then out through the pupil (Fig. 10-8, A). It leaves the anterior chamber by flowing through the fenestrated trabecular meshwork and into Schlemm’s canal, which lies at the vertex of the angle formed by the intersection of the cornea and the iris. This region is known as the ocular angle. In primary angle-closure glaucoma, pressure from the posterior chamber pushes the iris forward, closing the ocular angle and preventing the drainage of aqueous humor (Fig. 10-8, B). People with narrow angles are predisposed to closed-angle glaucoma. In primary open-angle glaucoma, the ocular angle remains open, but abnormalities in the trabecular meshwork cause the outflow of aqueous humor to be impeded. In secondary glaucoma, inflammation, trauma, or various ocular diseases can cause intraocular pressure to increase.
Glaucoma is treated with directly- and indirectly-acting cholinergic agonists. Open-angle glaucoma is also treated with carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, β receptor blockers, and epinephrine (Epi).2 When applied topically to the eye, cholinomimetics constrict the pupil, contract the ciliary muscles, and decrease intraocular pressure. In open-angle glaucoma, the contraction of the longitudinal ciliary muscle decreases intraocular pressure by stretching the trabecular meshwork and opening its tubules. In closed-angle glaucoma, pupillary constriction lowers the intraocular pressure by pulling the iris away from the trabeculum and opening the angle (see Fig. 10-8, C). Closed-angle glaucoma is a medical emergency that is corrected surgically by placing a hole in the peripheral portion of the iris to release pressure in the posterior chamber (see Fig. 10-8, D). Cholinomimetics are used acutely to treat closed-angle glaucoma until surgery can be performed. Occasionally, patients with closed-angle glaucoma exhibit a paradoxical increase in intraocular pressure in response to cholinomimetics because constriction of the pupil causes the iris to be pressed against the lens, thereby blocking the flow of aqueous humor into the anterior chamber. Cholinomimetics are also used to treat a variety of noninflammatory secondary glaucomas.
Muscarinic receptor antagonists dilate the pupil and relax the ciliary muscle, making them useful for examination of the retina and measurement of refractive errors of the lens, which often requires complete paralysis of the ciliary muscle. Choice of a mydriatic depends on its effectiveness and duration of action. Young children have a powerful accommodation reflex, requiring a highly potent and long-acting mydriatic such as atropine to cause complete blockade (cycloplegia). In contrast, shorter-acting agents such as tropicamide are used in older children and adults. The muscarinic receptor antagonists used in ophthalmology for refraction and their durations of action are given in Table 10-3.
TABLE 10–3 Pharmacokinetic Parameters for Muscarinic Receptor Antagonists used for Refraction
| Antagonist | Duration of Cycloplegia | Duration of Mydriasis |
|---|---|---|
| Atropine | 6-12 days | 7-10 days |
| Scopolamine | 3-7 days | 3-7 days |
| Homatropine | 1-3 days | 1-3 days |
| Cyclopentolate | 6 hr-1 day | 1 day |
| Tropicamide | 6 hr | 6 hr |
Gastrointestinal and Urinary Tracts
Muscarinic receptor antagonists are used to treat conditions characterized by excessive motility of the GI and urinary tracts. Oxybutynin and tolterodine are frequently used in the treatment of urge incontinence and overactive bladder, whereas dicyclomine and propantheline are often used in irritable bowel syndrome. The latter two antagonists are also sometimes used in the treatment of urinary incontinence. Propantheline and homatropine are quaternary ammonium compounds; consequently, their actions are limited to the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Oxybutynin, tolterodine, darifenacin, solifenacin, and trospium are relatively selective muscarinic receptor antagonists, acting at M2/M3 receptors, that are approved for the treatment of overactive bladder. These subtype-selective receptor antagonists relieve the symptoms of urgency, frequency, and incontinence and exhibit reduced inhibitory effect on salivation and GI motility.
Nonselective muscarinic receptor antagonists were occasionally used to inhibit gastric acid secretion in peptic ulcer disease but have now been supplanted by the histamine receptor antagonists and proton pump inhibitors (see Chapter 18). Pirenzepine, a selective M1 receptor antagonist that causes fewer side effects, is used in Europe to treat peptic ulcer disease but is not currently available in the United States.
COPD is characterized by a persistent narrowing of the airways and excessive vagal tone contributing to bronchoconstriction. Muscarinic receptor antagonists are useful in the treatment of COPD. The quaternary antagonists, ipratropium and tiotropium, are administered with the use of an inhaler (see Chapter 16). Because systemic absorption of these compounds by the lung is poor, their muscarinic receptor blocking effects are usually confined to the lung. Tiotropium has a much longer duration of action than ipratropium, but both ipratropium and tiotropium have little or no inhibitory effect on mucociliary clearance, unlike most other muscarinic receptor antagonists such as atropine, which typically inhibit this function.
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease characterized by skeletal muscle weakness. Many people afflicted with this disorder have circulating autoantibodies against the nicotinic cholinergic receptor at the neuromuscular junction, leading to reduced numbers of these receptors, which causes the weakness. Most cases of this disease are acquired (with an element of genetic predisposition), but there are also congenital myasthenia gravis cases. The ability of ChE inhibitors to amplify the effects of neuronally released ACh makes these drugs useful for temporarily restoring muscle strength in patients with myasthenia. ChE inhibitors are used alone in mild cases and in combination with immunosuppressants, including corticosteroids (e.g., prednisone) and other immunosuppressive drugs (azathioprine, cyclosporine, mycophenolate) and treatments (intravenous immune globulin [IVG] and plasmapheresis [removal and exchange of plasma to remove antibodies]) in more severe cases (see Chapter 6). Myasthenia gravis is also successfully treated surgically by removal of the thymus gland (thymectomy), because there is an abnormality of the thymus (hyperplasia or more rarely tumor) in the vast majority of cases that is associated with the autoimmune disease process.
Ganglionic blockers were developed initially for the treatment of hypertension, but better agents are now available (see Chapter 20). Because blockade of both sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia causes numerous side effects, ganglionic blockers are used only for treatment of hypertensive emergencies that occur during surgery or with an aortic aneurysm. Because of its quaternary ammonium structure, trimethaphan, which is used clinically, has effects only in the PNS. In addition, it selectively blocks nicotinic receptors at autonomic ganglia and not at the neuromuscular junction. Mecamylamine, a second ganglionic blocking drug, is rarely used and has both central and peripheral effects.
Miscellaneous Uses of Cholinesterase Inhibitors
ChE inhibitors are also used to rapidly reverse the neuromuscular blockade induced during surgery. Neuromuscular blocking agents are often administered as adjuncts during general anesthesia (see Chapter 12), and it is sometimes useful to rapidly reverse neuromuscular blockade after surgery. The reversible ChE inhibitors such as neostigmine and pyridostigmine are used to increase the availability of ACh, which competes with the competitive neuromuscular blockers and restores function at the neuromuscular junction, but these agents are not useful in reversing the depolarizing neuromuscular blockers. Atropine is often used in combination with the ChE inhibitor to counteract the muscarinic effects of ChE inhibition.
Pharmacovigilance: Clinical Problems, Side Effects, and Toxicity
ChE inhibitor poisoning is diagnosed on the basis of the signs and symptoms and the patient’s history. Diagnosis can be verified by plasma or erythrocyte ChE determinations, if time permits. Atropine is used to reverse the effects of ACh at muscarinic synapses and must be continually administered as long as ChE is inhibited. Organophosphorus irreversible ChE inhibitors phosphorylate a serine hydroxyl group in the active site of the enzyme (see Fig. 10-6) and results in excessive accumulation of ACh, which causes the toxicities. With many organophosporus ChE inhibitors, an additional reaction occurs called “aging.” Aging involves a chemical separation of a part of the alkyl or alkoxy portion of the ChE inhibitor molecule. The resultant complex is then resistant to spontaneous hydrolysis or reactivation. Oxime compounds such as 2-PAM can be used to reactivate the ChE and treat the adverse effects of organophosphorus ChE inhibitor poisoning. 2-PAM is a site-directed nucleophile that reacts with the phosphorylated-ChE complex to regenerate the free enzyme. It is important that the oxime is administered as soon after organophosphorus exposure as possible before the enzyme ages. 2-PAM is ineffective against the toxicity caused by carbamate inhibitors. In the United States only 2-PAM is available, and it is in a fixed combination with atropine in an injectable form known as ATNAA (Antidote Treatment-Nerve Agent, Auto-Injector). Considerable interest has been generated in administering reversible ChE inhibitors, such as pyridostigmine, prophylactically in battlefield situations where exposure to a nerve gas is possible, but the efficacy of this use is not clear. Benzodiazepines, including diazepam, are used to treat the convulsive seizures caused by ChE inhibitors. Supportive therapy is also important, including airway maintenance, ventilatory support, and O2 administration.
include an initial increase in blood pressure, followed by a decrease, weak pulse, and variable heart rate. Treatment of toxicity after oral ingestion includes gastric lavage or inducement of vomiting with syrup of ipecac. Support of respiration and maintenance of blood pressure are also important.
Anonymous. Drugs for some common eye disorders. Treat Guidel Med Lett. 2007;5:1-8.
Eglen RM. Muscarinic receptor subtypes in neuronal and non-neuronal cholinergic function. Auton Autacoid Pharmacol. 2006;26:219-233.
Gwilt CR, Donnelly LE, Rogers DF. The non-neuronal cholinergic system in the airways: An unappreciated regulatory role in pulmonary inflammation? Pharmacol Ther. 2007;115:208-222.
Hasin Y, Avidan N, Bercovich D, et al. Analysis of genetic polymorphisms in acetylcholinesterase as reflected in different populations. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2005;2:207-218.
Lawrence DT, Kirk MA. Chemical terrorism attacks: Update on antidotes. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2007;25(2):567-595.
Vernino S. Autoimmune and paraneoplastic channelopathies. Neurotherapeutics. 2007;4(2):305-314.