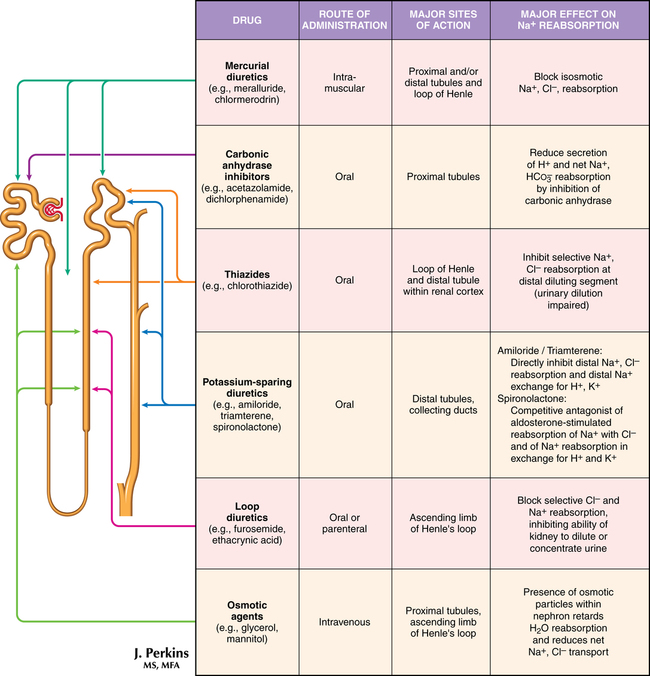
Diuretics
Drugs that increase the excretion of sodium and water through the kidneys, termed diuretics, are classified on the basis of their site (Figure 99-1) or mechanism of action in the nephron. Diuretics are the recommended drugs for initial treatment of hypertension and are used in a variety of relative fluid-overload conditions, including heart failure, renal disease, and liver cirrhosis. Despite the lack of evidence that diuretic therapy prevents acute renal injury or improves outcome following injury or that diuretics reduce morbidity or mortality risk when used in chronic heart failure, they do provide symptomatic relief from fluid-overload syndromes.