Chapter 66 Disorders of Coagulation in the Neonate
Table 66-1 Neonatal Versus Adult Hemostasis
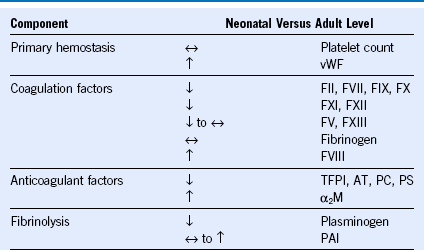
α2M, α2-Macroglobulin; AT, antithrombin; F, factor; PAI, plasminogen activator inhibitor; PC, protein C; PS, protein S; TFPI, tissue factor pathway inhibitor; vWF, von Willebrand factor.
Modified from Guzzetta NA, Miller BE: Principles of hemostasis in children: Models and maturation. Paediatr Anaesth 21:3, 2011.
Table 66-2 Reference Values (Ranges) for Common Coagulation Tests and Blood Coagulation Protein Levels by Age, Comparing Two Comprehensive Prospective Studies With Different Methodologies
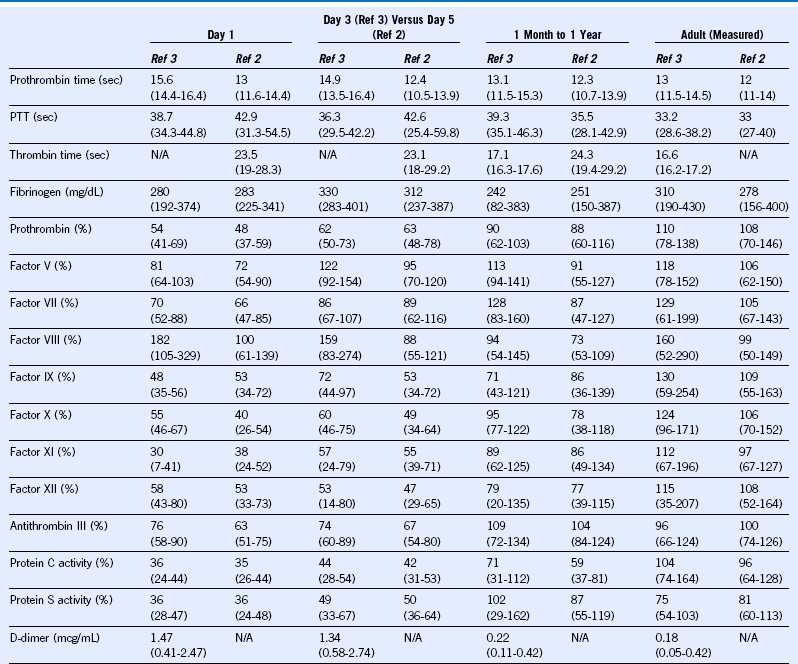
N/A, Not available; PTT, partial thromboplastin time.
Modified from Monagle P, Barnes C, Ignjatovic V, et al: Developmental haemostasis: Impact for clinical haemostasis laboratories. Thromb Haemost 95:362, 2006; and Andrew M, Paes B, Milner R, et al: Development of the human coagulation system in the full-term infant. Blood 70:165, 1987 (range inferred from published statistical documentation).
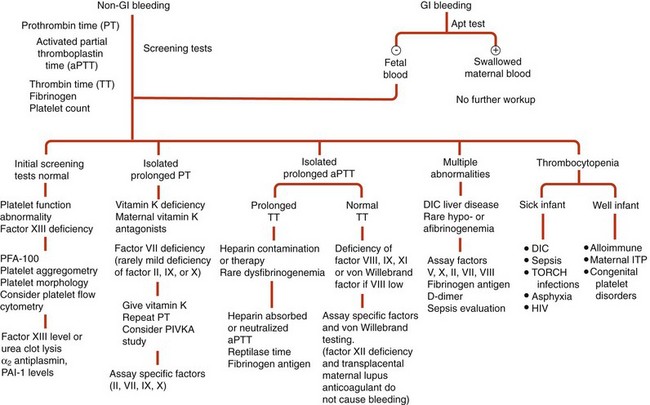
Figure 66-1 DIAGNOSTIC APPROACH TO THE BLEEDING NEONATE.
(Modified from Blanchette VS, Rand ML: Platelet disorders in newborn infants: diagnosis and management. Semin Perinatol 21:53, 1997.)
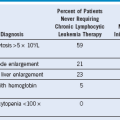
Table 66-3 Classification of Fetal and Neonatal Thrombocytopenia
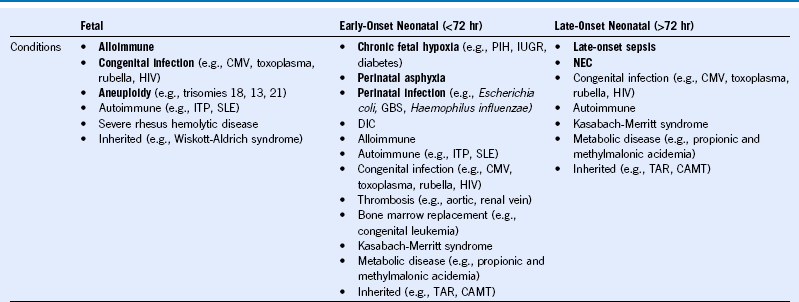
CAMT, Congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia; CMV, cytomegalovirus; DIC, disseminated intravascular coagulation; GBS, group B Streptococcus; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; ITP, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura; IUGR, intrauterine growth restriction; NEC, necrotizing enterocolitis; PIH, pregnancy-induced hypertension; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus, TAR, thrombocytopenia with absent radii. The most frequently occurring conditions are in bold.
Modified from Roberts I, Stanworth S, Murray NA: Thrombocytopenia in the neonate. Blood Rev 22:173, 2008.
Table 66-4 Syndromic, Genetic, and Acquired Causes of Neonatal Thrombocytopenia
| INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM |
| GENETIC MARROW FAILURE SYNDROMES |
| OTHER SYNDROMIC THROMBOCYTOPENIAS |
| ANEUPLOIDY |
| GENETIC MACROTHROMBOCYTOPENIAS |
| ACQUIRED MARROW DISORDERS |
Treatment of Neonatal Thrombosis
Enoxaparin
1.5 mg/kg subcutaneously every 12 hours (with normal renal function; round dose to nearest milligram; consider higher dose†)
Check anti-FXa level by peripheral venipuncture 4 to 6 hours after second or third dose; therapeutic goal, anti-FXa of 0.5 to 1 unit/mL (0.4 to 0.6 unit/mL if concurrent thrombocytopenia or other bleeding risk factor)
Purpura Fulminans
Concurrent heparin: UFH dose of 28 units/kg/hr with target anti-FXa of 0.3 to 0.7 units/mL; LMWH dose of 1.0 to 1.5 mg/kg every 12 hours with therapeutic target anti-FXa range of 0.5 to 1 units/mL and replacement with FFP or protein C concentrate
FFP: 10 to 20 mL/kg every 6 to 12 hours for purpura fulminans
Protein C concentrate for severe protein C deficiency: load with 100 to 120 units/kg, then 60 to 80 units/kg every 6 hours × three doses (goal protein C activity 100%). Once therapeutic anticoagulation is achieved, maintenance therapy with 45 to 60 units/kg every 6 to 12 hours (goal protein C activity >25%)
Tissue Plasminogen Activator Thrombolysis for Neonatal Thrombosis
Concurrent Heparin (UFH or Enoxaparin) Should be Considered at Prophylactic Dosing; UFH Preferred
Life- or limb-threatening thrombi: starting dose of 0.1 to 0.5 mg/kg/hr for up to 6 hours
If no response, consider increase by 0.1 mg/kg/hr increments to maximum 0.5 mg/kg/hr
Consider using fresh frozen plasma 10 mL/kg before thrombolytic therapy
Maintain fibrinogen greater than 100 mg/dL
Maintain platelet count above 100
Reversal of severe bleeding with aminocaproic acid at 100 mg/kg intravenously every 6 hours
Recommended Dosing for Transfusion in Neonatal Hemorrhage
PRBC: 10 to 15 mL/kg single-donor PRBC infused over 4 hours
Platelets*: 10 mL/kg raises platelet count by 75,000 (goal >50,000 if bleeding, >20,000 if not bleeding)
FFP: 10 to 20 mL/kg every 6 to 12 hours for purpura fulminans
Cryoprecipitate: 0.15 units/kg raises fibrinogen about 100 mg/dL (goal >150 mg/dL if bleeding, >50 mg/dL if not bleeding)
von Willebrand factor: 40 to 60 ristocetin cofactor units/kg of plasma-derived FVIII/vWF preparations
Factor VIII: for hemophilia A—50 units/kg load, then 25 units/kg every 12 hours; recombinant factor preferred (monitor FVIII)
Factor IX: for hemophilia B—80 to 100 units/kg daily; recombinant factor preferred (monitor FIX)
Factor VIIa: for severe factor VII deficiency—20 to 30 mcg/kg every 6 to 12 hours
FFP, Fresh frozen plasma; PRBC, packed red blood cells; vWF, von Willebrand factor.
*Expressed as percentage of normal level based on functional ATIII level.
†Malowany JI, Monagle P, Knoppert DC, et al: Enoxaparin for neonatal thrombosis: a call for a higher dose for neonates. Thromb Res 122:826, 2008.
*Volume limits transfusion of platelets by the “unit” in small neonates. Practices vary—follow institutional guidelines for volume dosing or volume reduction.