Chapter 35 Diagnosis and Treatment of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma and Burkitt Lymphoma
Hepatitis B Prophylaxis and Therapy During Lymphoma Treatment
Table 35-1 Staging Evaluation for Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
| All Patients | As Clinically Indicated |
|---|---|
| History and physical examination | Other viral studies |
| CBC and chemistry (including LDH) | CT or MRI of the head |
| HIV and hepatitis B and C serology | Body PET scan |
| Chest radiograph | Additional imaging |
| CT scan of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis | CSF evaluation by cytology or flow cytometry |
| BM aspirate and biopsy | Other tests indicated by results of staging |
BM, Bone marrow; CBC, complete blood count; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; CT, computed tomography; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; PET, positron emission tomography.
Table 35-2 Ann Arbor Staging System for Lymphomas
| Stage* | Cotswold Modification of Arbor Classification |
|---|---|
| I | Involvement of a single LN region or lymphoid structure |
| II | Involvement of two or more LN regions on the same side of the diaphragm (the mediastinum is considered a single site, but the hilar LNs are considered bilaterally); the number of atomic sites should be indicated by a subscript (e.g., II3) |
| III | Involvement of LN regions on both sides of the diaphragm: III1 (with or without involvement of splenic hilar, celiac, or portal nodes) and III2 (with involvement of paraaortic, iliac, and mesenteric nodes |
| IV | Involvement of one or more extranodal sites in addition to a site for which the designation E has been used |
LN, Lymph node.
*All cases are subclassified to indicate the absence (A) or presence (B) of the systemic symptoms of significant fever (>38.0° C [100.4° F]), night sweats, and unexplained weight loss exceeding 10% of normal body weight within the previous 6 months. The clinical stage (CS) denotes the stage as determined by all diagnostic examinations and a single diagnostic biopsy only. In the Ann Arbor classification, the term pathologic stage (PS) is used if a second biopsy of any kind has been obtained, whether the result was negative or positive. In the Cotswold modification, the PS is determined by laparotomy; X designates bulky disease (widening of the mediastinum by more than one-third or the presence of a nodal mass >10 cm), and E designates involvement of a single extranodal site that is contiguous or proximal to the known nodal site.
Table 35-3 Revised International Prognostic Index (R-IPI)*
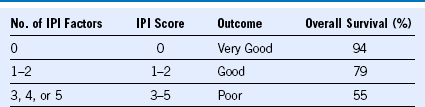
ECOG, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; IPI, International Prognostic Index; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase
From Sehn LH, Berry B, Chhanabhai M, et al: The revised International Prognostic Index is a better predictor of outcome than the standard IPI for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. Blood 109:1857, 2007.