Chapter 4 Aplastic Anemia
Table 4-1 Differential Diagnosis of Pancytopenia
| Pancytopenia With Hypocellular Bone Marrow |
|---|
| Pancytopenia With Cellular Bone Marrow |
| Hypocellular Bone Marrow ± Cytopenia |
*Pancytopenia in tuberculosis only rarely is associated with a hypocellular bone marrow at biopsy or autopsy. Marrow failure in the setting of tuberculosis is almost always fatal; exceptional patients probably had underlying myelodysplasia or acute leukemia.
Table 4-2 A Classification of Aplastic Anemia
Table 4-3 Classification of Drugs and Chemicals Associated With Aplastic Anemia
Table 4-4 Drugs Associated With Aplastic Anemia in the International Aplastic Anemia and Agranulocytosis Study*
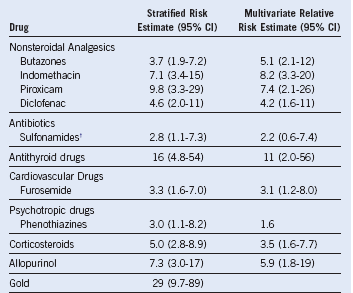
CI, Confidence interval.
† Other than trimethoprim–sulfonamide combination.
From Kaufman DW, Kelly JP, Levy M, et al: The drug etiology of agranulocytosis and aplastic anemia. New York, 1991, Oxford University Press.
Table 4-5 Clinical Presentation of Aplastic Anemia
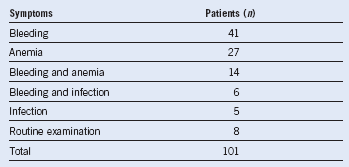
Adapted from Williams DM, Lynch RE, Cartwright GE: Drug induced aplastic anemia. Semin Hematol 10:195, 1973.
Table 4-6 Severity of Aplastic Anemia as Defined by Laboratory Studies
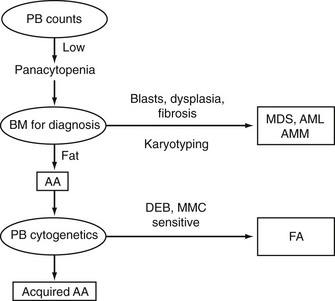
Diagnostic Algorithm in Aplastic Anemia
Table 4-7 Bone Marrow Morphologic Findings that Discriminate Myelodysplasia From Aplastic Anemia
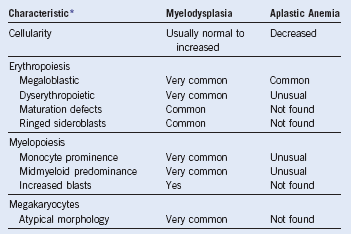
Adapted from Bagby GC: The preleukemic syndrome (hematopoietic dysplasia). In Shahidi NT, editor: Aplastic anemia and other bone marrow failure syndromes, New York, 1990, Springer-Verlag, p 199. Provides percentages for myelodysplasia.
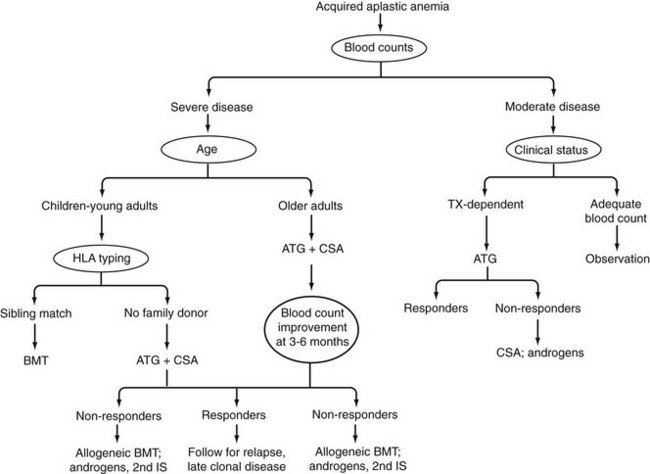
Treatment Algorithm in Aplastic Anemia
Table 4-8 Results of Matched Sibling Donor Allogeneic Marrow Transplantation for Aplastic Anemia
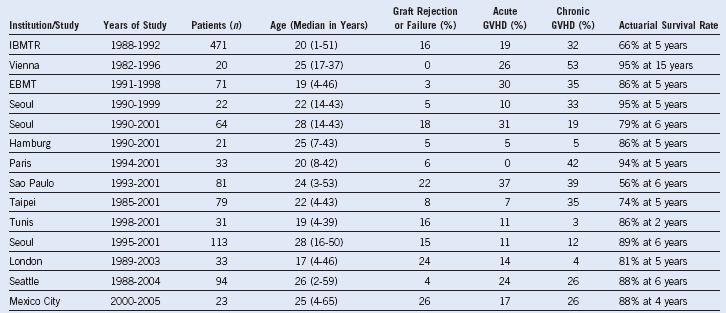
EBMT, European Group for Bone Marrow Transplant; GVHD, graft-versus-host disease; IBMTR; International Blood and Marrow Transplant Registry.
GVHD results are generally for grades II–IV and in patient at risk.
Only studies reporting ≥20 patients are tabulated.
In contrast to Table 4-1, response rates are not provided because, in surviving patients who do not experience primary graft rejection or secondary graft failure, full hematologic recovery with donor hematopoiesis is anticipated.
Table 4-9 Alternative Donor Stem Cell Transplantation for Severe Aplastic Anemia
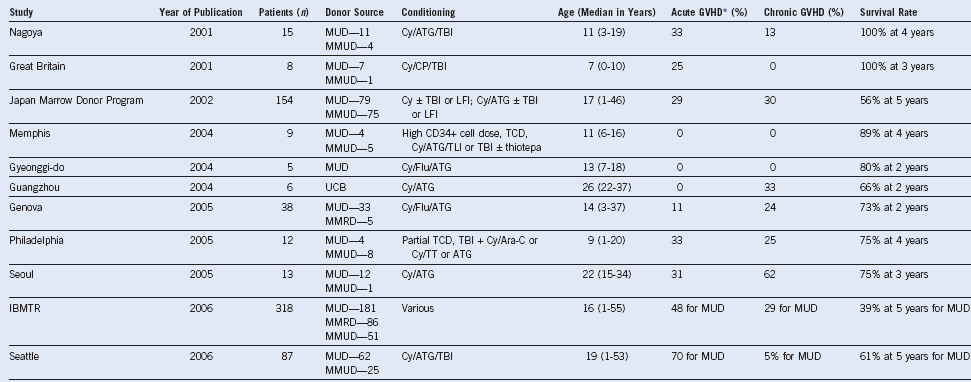
ATG, Anti-thymocyte globulin; CP, Campath; Cy, cyclophosphamide; Flu, fludarabine; GVHD, graft-versus-host disease; IBMTR, International Blood and Marrow Transplant Registry; LFI, limited field irradiation; MMRD, mismatched related donor; MMUD, mismatched unrelated donor; MUD, matched unrelated donor; TBI, total-body irradiation; TCD, T-cell depletion; TLI, total lymphoid irradiation; TT, thiotepa; UCB, umbilical cord blood.
Only studies reporting ≥5 patients are tabulated.
* GVHD results are generally for grades II-IV and in patient at risk.
Table 4-10 Intensive Immunosuppression in Severe Aplastic Anemia
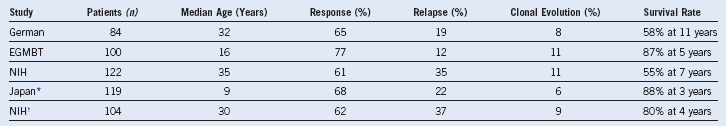
Only studies of more than 20 enrolled patients are tabulated. Responses to immunosuppressive therapy are usually partial; blood counts may not become normal, but transfusions are no longer required, and the neutrophil count is adequate to prevent infection. Relapse is usually responsive to further immunosuppressive therapies. Clonal evolution is to dysplastic bone marrow changes or cytogenetic abnormalities.
* With androgens and ± granulocyte colony-stimulating factor.