60
Anogenital Diseases
Introduction
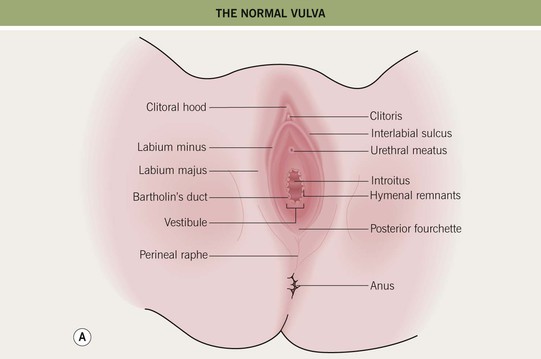
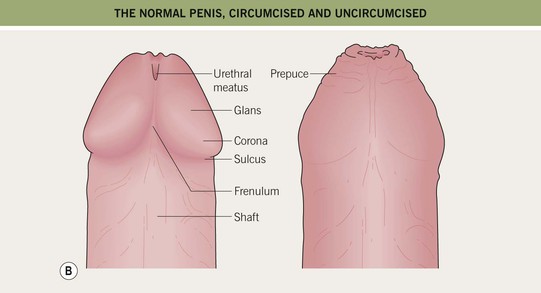
• The anatomy (Fig. 60.1), normal cutaneous findings, and benign lesions of the anogenital area (Table 60.1) should be appreciated before addressing diseases in this area.
Table 60.1
Normal findings and benign lesions of the anogenital region.
Papules in the anogenital region can also result from HPV infection, in particular condylomata acuminata and common warts (see Ch. 66).
| Common | Less Common |
| Epidermoid cysts | Fox-Fordyce disease |
| Open comedones | Syringomas |
| Pearly penile papules (see Fig. 95.7) | Idiopathic calcinosis of the scrotum |
| Vestibular papillomatosis | Urethral caruncle |
| Angiokeratomas (see Fig. 87.11) | Hidradenoma papilliferum |
| Seborrheic keratoses and acrochordons | |
| Melanocytic nevi and genital lentigines | |
| Free sebaceous glands |
• A number of systemic diseases affect the anogenital area (Table 60.2).
Table 60.2
Systemic diseases with associated anogenital cutaneous findings.

EM, erythema multiforme; SJS, Stevens–Johnson syndrome; TEN, toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Courtesy, Susan M. Cooper, MD, and Fenella Wojnarowska, MD.
• A number of dermatologic conditions affect the anogenital region, including inflammatory (Table 60.3; Figs. 60.2–60.6), bullous (Table 60.4; Fig. 60.7), infectious (Table 60.5; see Chapter 69), and premalignant and malignant (Table 60.6; Figs. 60.8–60.11) conditions.
Table 60.3
Inflammatory dermatologic disorders with anogenital features.
Porokeratosis ptychotropica is a rare disorder and can mimic anogenital dermatitis or inverse psoriasis.
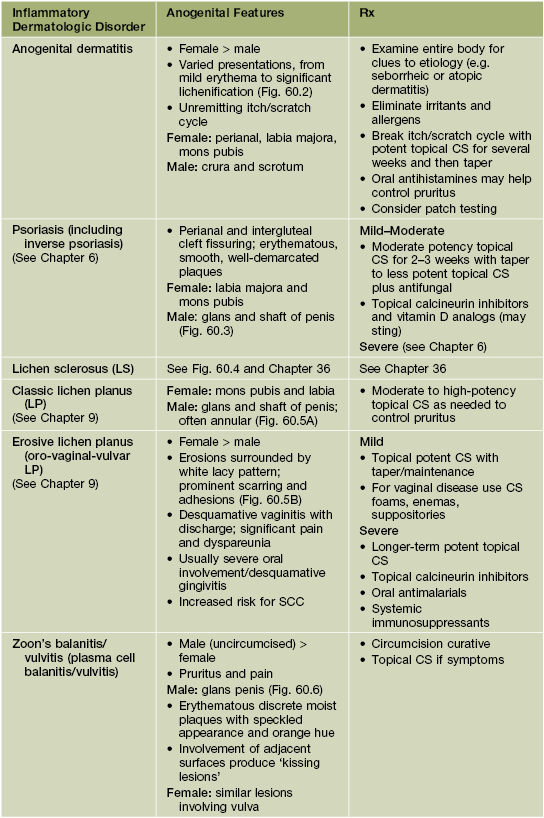
The DDx of these disorders includes the other entities listed in this table; consider infections, either primary or superimposed (see Table 60.5); less commonly bullous disorders (see Table 60.4); if nonhealing consider malignancy, most commonly SCC (see Table 60.6).
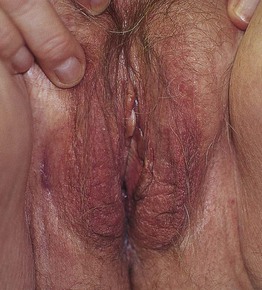
Fig. 60.2 Vulvar dermatitis. Lichenification is prominent. The underlying diagnosis was atopic dermatitis. Courtesy, Susan M. Cooper, MD, and Fenella Wojnarowska, MD.
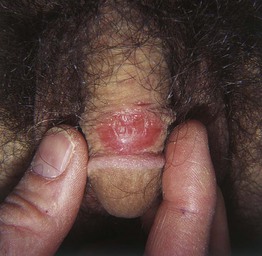
Fig. 60.3 Psoriasis of the penile shaft. Well-demarcated erythematous plaque with slight scale. Similar lesions can be seen in patients with reactive arthritis (formerly Reiter’s disease). Courtesy, Jean L. Bolognia, MD.
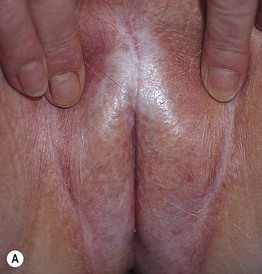
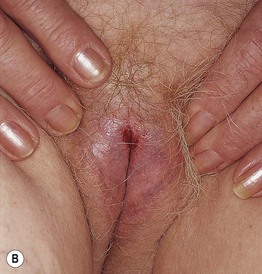
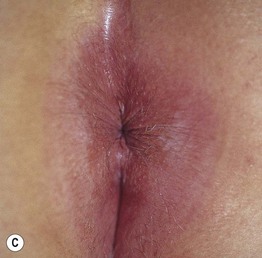
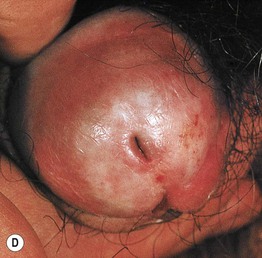
Fig. 60.4 Lichen sclerosus (LS). Typical involvement of the vulva demonstrating marked architectural change with the loss of the labia minora and midline fusion (A) and purpura (B). Perianal LS (C) and involvement of the penis (D) with an erythematous and hypopigmented plaque on the glans. A, Courtesy, Susan M. Cooper, MD, and Fenella Wojnarowska, MD; B, Courtesy, Kalman Watsky, MD. C, Courtesy, Susan M. Cooper, MD, and Fenella Wojnarowska, MD; D, Courtesy, Ronald P. Rapini, MD.
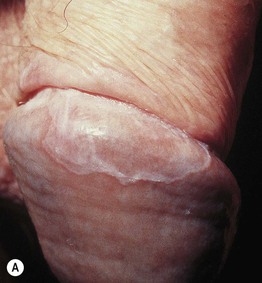
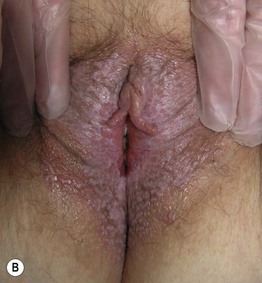
Fig. 60.5 Anogenital lichen planus. A Involvement of the penis with an annular band on the glans, a typical finding. B Erosive lichen planus of the vulva with fissures and an extensive white lacy pattern. A, Courtesy, R. Turner, MD; B, Courtesy, Susan M. Cooper, MD, and Fenella Wojnarowska, MD.
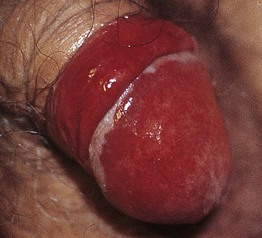
Fig. 60.6 Zoon’s balanitis. There are moist ‘kissing lesions’ on adjacent surfaces of the glans and prepuce. Courtesy, Susan M. Cooper, MD, and Fenella Wojnarowska, MD.
Table 60.4
Bullous dermatologic disorders with anogenital features.
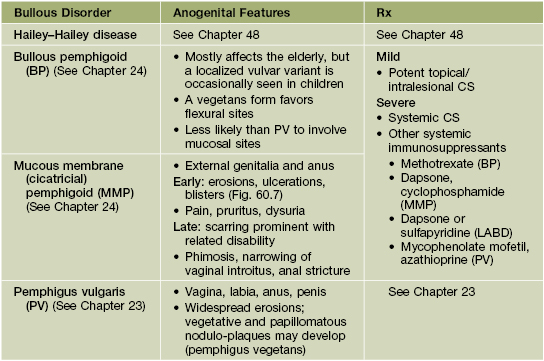
Acquired autoimmune bullous diseases are clinically difficult to differentiate from one another and require biopsies for H&E and DIF, as well as serum for IIF and/or ELISA.
MMP can be clinically indistinguishable from erosive lichen planus in the anogenital area.
The DDx (especially of PV) may include other causes of erosions (Table 60.7).
Other blistering disorders, including LABD (linear IgA bullous dermatosis), can occur in the genital area.
H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; DIF, direct immunofluorescence; IIF, indirect immunofluorescence.
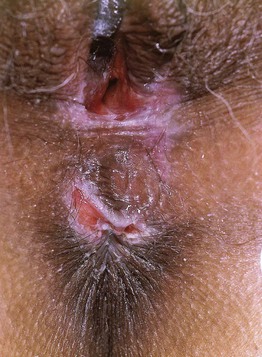
Fig. 60.7 Mucous membrane pemphigoid of the vulva. Ulcerations and scarring of the perianal area and perineum. Positive direct immunofluorescence with linear deposition of immunoreactants distinguished this from erosive lichen planus. Courtesy, Susan M. Cooper, MD, and Fenella Wojnarowska, MD.
Table 60.5
Infectious (nonvenereal) dermatologic disorders with anogenital features.
Condylomata acuminata and venereal diseases are covered in Chapters 66 and 69, respectively.
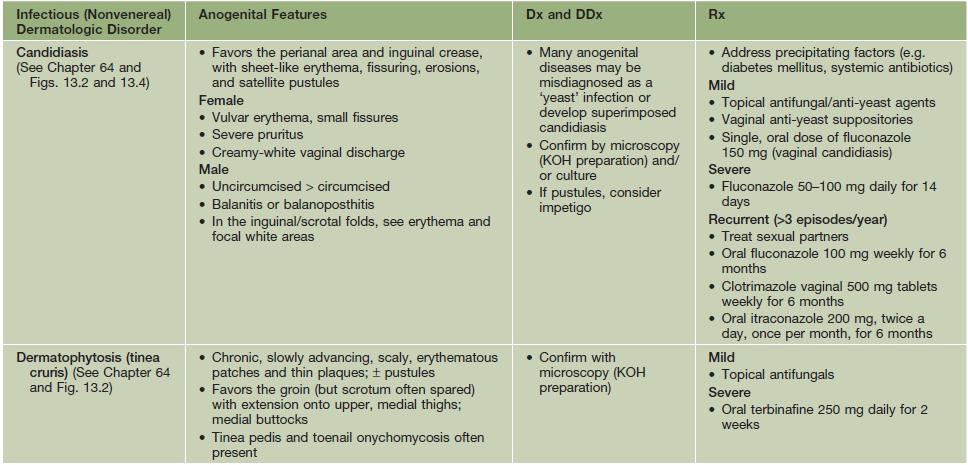
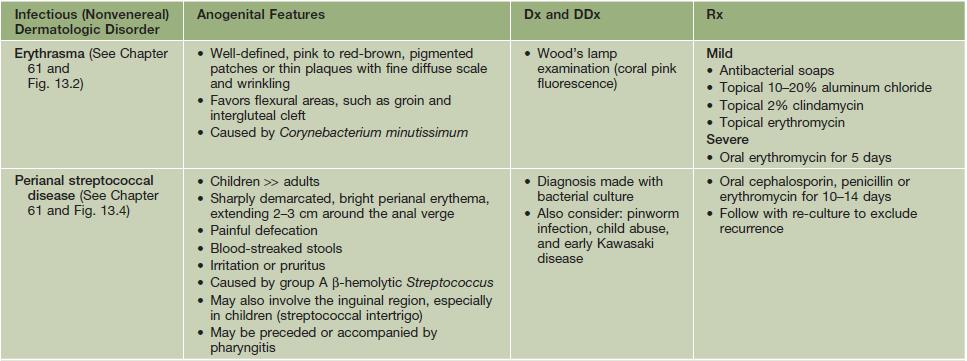
The DDx of these disorders includes the other entities listed in this table; they may be confused with the disorders listed in Tables 60.2 and 60.3 as well as superimposed upon them; topical medications can also lead to a superimposed contact dermatitis.
KOH, potassium hydroxide.
Table 60.6
Premalignant and malignant dermatologic disorders with anogenital features.
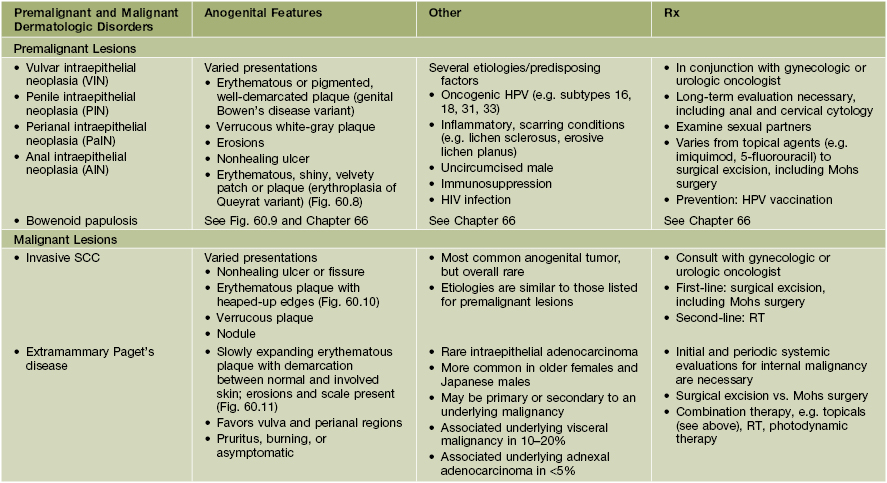
Multiple biopsies may be necessary to make a diagnosis.
The DDx of these disorders includes the other entities listed in this table and Table 60.2, as well as seborrheic keratosis, condyloma acuminata, NMSC, and amelanotic melanoma.
HPV, human papilloma virus; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; RT, radiotherapy.
Table 60.7
Causes of genital erosions.
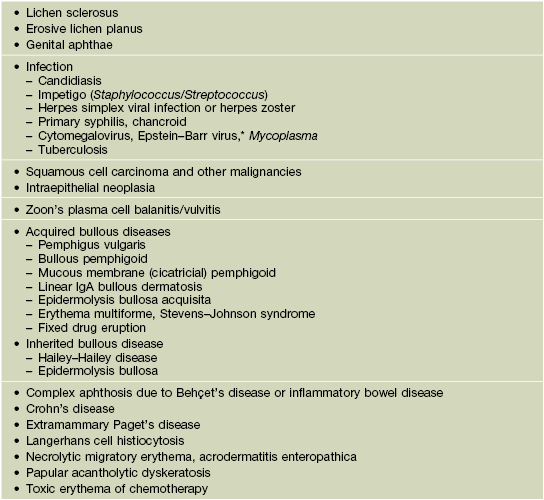
* Diagnosed via EBV IgM antibodies or PCR; favors female children and adolescents.
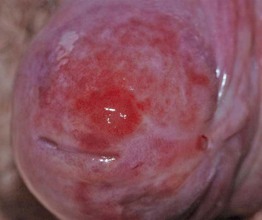
Fig. 60.8 Penile intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN). Persistent erythema not responding to topical steroids. Courtesy, R. Turner, MD.
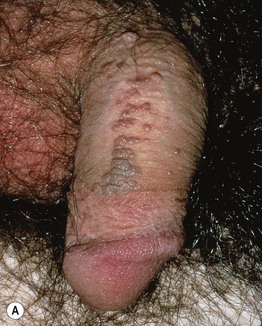
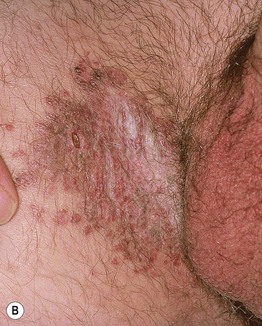
Fig. 60.9 Bowenoid papulosis variant of intraepithelial neoplasia. A Multiple red-brown to brown papules on the shaft of the penis. B Coalescence of red-brown to brown papules on the upper inner thigh. B, Courtesy, Robert Hartman, MD.
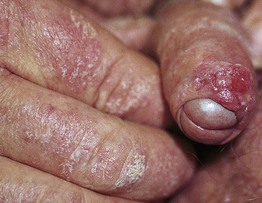
Fig. 60.10 Invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the foreskin. This patient with psoriasis had received PUVA therapy without genital protection. Courtesy, Susan M. Cooper, MD, and Fenella Wojnarowska, MD.
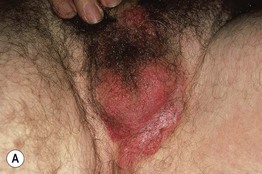
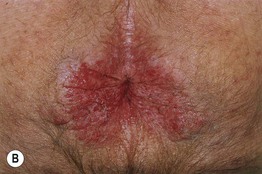
Fig. 60.11 Extramammary Paget’s disease. A Erythematous plaque with hydrated scale at the base of the scrotum. B Well-demarcated perianal plaque with both erosions and scale, giving rise to a ‘strawberries and cream’ appearance. B, Courtesy, Kalman Watsky, MD.
• Pain and pruritus can be the presenting symptoms in a wide variety of anogenital diseases (Figs. 60.12 and 60.13).
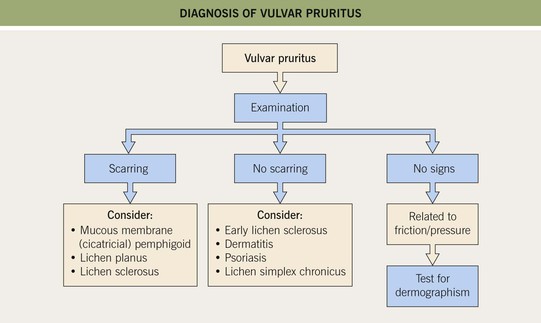
Fig. 60.12 The diagnosis of vulvar pruritus. Courtesy, Susan M. Cooper, MD, and Fenella Wojnarowska, MD.
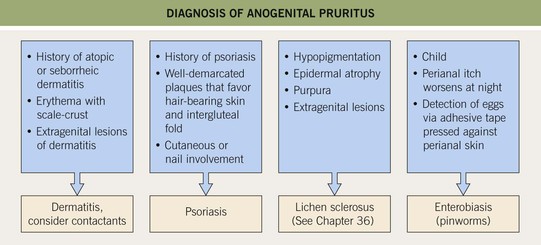
Fig. 60.13 The diagnosis of anogenital pruritus. Histologic evaluation may be required to confirm the clinical diagnosis (e.g. lichen sclerosus) or to exclude more unusual etiologies (e.g. extramammary Paget’s disease). Systemic contact dermatitis reactions in this region may also be very pruritic. Courtesy, Susan M. Cooper, MD, and Fenella Wojnarowska, MD.
• High-potency topical CS are generally avoided because of the increased risk for atrophy and striae, but they are used with confidence in certain situations (e.g. lichen sclerosus, erosive lichen planus) for periods of up to 12 weeks once to twice yearly.
Intraepithelial Neoplasia
• IN is further subdivided based on location: vulvar IN (VIN), penile IN (PIN), perianal IN (PaIN), and anal IN (AIN) (see Table 60.6), as well as the degree of atypia: 1, mild; 2, moderate; 3, severe.
• Bowenoid papulosis (BP) is a distinct clinical variant of IN that occurs in a younger (more sexually active) age group, is caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV subtypes 16 and 18), has a better prognosis, and sometimes spontaneously regresses (see Chapter 66).
Dysesthetic Genital Pain Syndromes
• Includes several regional pain syndromes in which clinical appearance of the involved anogenital region is normal despite the patient’s experience of debilitating pain (Fig. 60.14); associated depression is common.
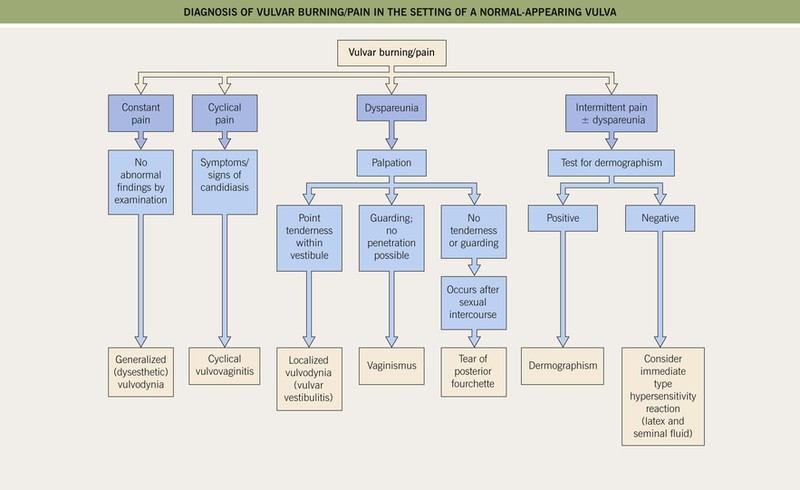
Fig. 60.14 The diagnosis of vulvar burning/pain in the setting of a normal-appearing vulva. Courtesy, Susan M. Cooper, MD, and Fenella Wojnarowska, MD.
• Rx: individualized and may include topical local anesthetics, oral tricyclic antidepressants, oral gabapentin, referral to a neurologist or specialized pain clinic (to exclude underlying neurologic disorder; see Chapter 4), acupuncture, or biofeedback.
For further information see Ch. 73. From Dermatology, Third Edition.