Anesthesia in the patient with extreme obesity
General
< ?xml:namespace prefix = "mml" />
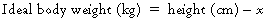
where x equals 105 for women and 100 for men. Body mass index (BMI) is a more relevant measure of height-weight relationships and is the currently accepted standard used to stratify obesity, although evidence has accumulated that the distribution of fat (central and intra-abdominal vs. peripheral) may best correlate with morbidity and mortality rates, recognizing that central intra-abdominal fat is a more metabolically active, proinflammatory substrate. BMI is calculated as body weight (in kilograms) divided by height (in meters) squared. The World Health Organization and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have defined levels of obesity (Table 163-1). Obesity can be further subdivided into morbid obesity (defined as a BMI >35 and <54.9) and super or extreme morbid obesity (BMI >55).
Table 163-1
Classification of Weight by Body Mass Index (BMI)
| Category | BMI (kg/m2) | Obesity Class |
| Underweight | <18.5 | |
| Normal weight | 18.5-24.9 | |
| Overweight | 25.0-29.9 | |
| Obesity | 30.0-34.9 | Obesity class I |
| 35.0-39.9 | Obesity class II | |
| Extreme obesity | ≥40 | Obesity class III |
Adapted from Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic. Geneva, Switzerland, World Health Organization; 1997. Report No. 894.
Physiology and pathophysiology of morbid obesity
Cardiovascular effects
Airway and pulmonary effects
As BMI exceeds 30 kg/m2, the risk of a patient having obstructive sleep apnea increases. This syndrome is due to the normal reduction in upper airway tone seen during stage 4 and rapid eye movement sleep. The excessive deposition of soft tissue in the upper airway in the obese individual accentuates this tendency and can result in periodic obstruction of the airway during sleep. Obstructive sleep apnea consists of both apneas and hypopneas and is best delineated via formal sleep evaluations with polysomnography. For more information on this topic, see Chapter 108, Obstructive Sleep Apnea.
Anesthesia for the morbidly obese patient
A routine general health examination, specifically focusing on cardiac, pulmonary, airway, and metabolic issues (Table 163-2), should be performed preoperatively.
Table 163-2
Preoperative Assessment of the Morbidly Obese Patient
| System | Assessment |
| Cardiovascular | Obtain baseline electrocardiogram |
| Assess BP control | |
| Examine for symptoms or evidence of right or left ventricular dysfunction | |
| Examine for presence of CAD | |
| Obtain appropriate guided studies of heart function (echocardiography) or CAD (noninvasive or invasive evaluation of coronary circulation) | |
| Ensure appropriate preoperative drug administration for any cardiovascular comorbid conditions | |
| Pulmonary | Assess exercise tolerance |
| Evaluate for symptoms or history of OSA | |
| Determine compliance with CPAP or BiPAP and ensure that patient brings personal CPAP device to hospital, if on therapy* | |
| Obtain baseline ABGs on room air | |
| Obtain PFTs if appropriate | |
| Airway | Perform a basic airway examination |
| Look for evidence of impaired oral or cervical ROM | |
| Determine Mallampati score and neck circumference | |
| Inquire about previous difficult mask airway or intubation | |
| Laboratory studies | Obtain electrolyte, blood glucose, and serum hemoglobin concentrations |
| Phlebotomize patients with a hemoglobin concentration >17 g/dL | |
| Gastrointestinal | Premedicate with metoclopramide, histamine H2 blocker, or PPI, as appropriate |
| Monitoring | Consider the needs for adequate intravenous access and BP monitoring |
| A central venous catheter may be needed to obtain reliable venous access | |
| BP cuffs should be of appropriate size (cuff bladder at least 75% of arm circumference) | |
| In some cases, the use of direct arterial monitoring may be more reliable or necessary | |
| Miscellaneous | Ensure that plans are made for the use of an appropriately sized OR bed that can accommodate the patient’s weight and size |
*Refer to the American Society of Anesthesiology’s Practice Guidelines for the Perioperative Management of Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. An updated report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Perioperative Management of Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Anesthesiology. 2013 Dec 16. [Epub ahead of print].
Intraoperative anesthetic techniques
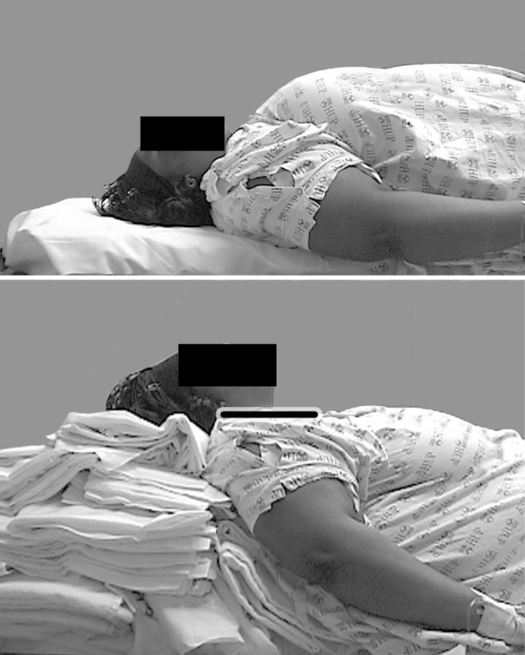
Modification of the anesthetic technique is necessary to minimize complications related to obesity. Because of physical limitations imposed by the patient’s girth, the anesthesia provider should ensure that proper “ramping” of the patient has been performed, such that the sternal notch is parallel to the angle of the mandible (Figure 163-1). This facilitates alignment of the intraoral axes for intubation. If a history of or major concerns regarding difficult intubation exist, awake fiberoptic intubation may be a reasonable option. Preoxygenation for 3 to 5 min with the patient in a mild reverse Trendelenburg position while using 10 cm H2O of continuous positive airway pressure plus 10 cm H2O of peak end-expiratory pressure with mask ventilation has been shown to significantly mitigate the initial drop in FRC on induction and to prolong time to desaturation. Appropriately sized oral and nasal airways should be available and used to maintain airway patency. An inability to use a mask should always be anticipated. The use of an intubating laryngeal mask airway can be highly effective in achieving successful airway maintenance when conventional mask techniques have failed.