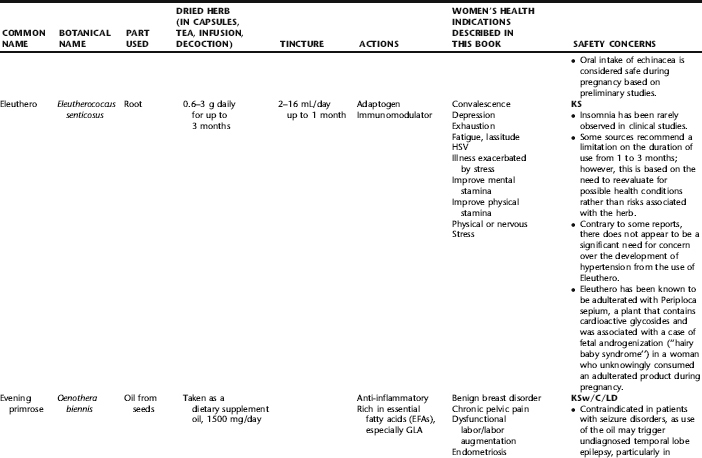
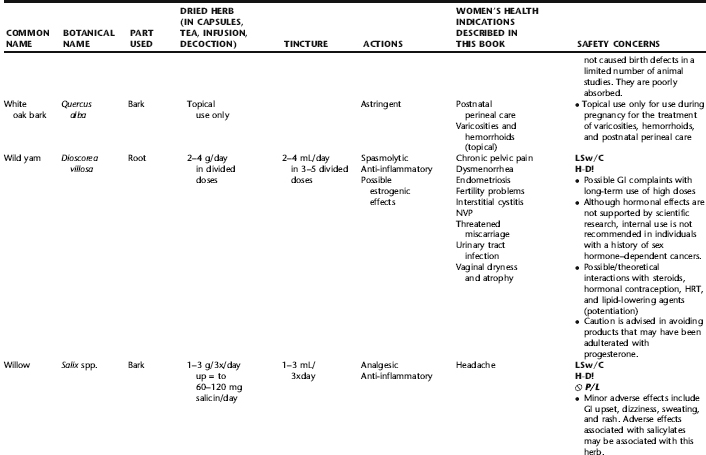
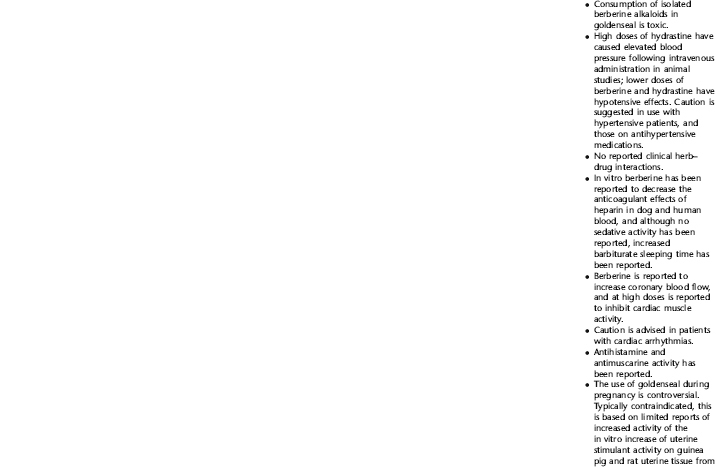WILD YAM
Botanical name: Dioscorea villosa
Synonyms: Colic root, rheumatism root
IN VITRO, ANIMAL, AND CLINICAL DATA
A 2001 double-blind placebo-controlled crossover study of the effects of a wild yam cream in 23 healthy women suffering from troublesome symptoms of menopause was conducted. After a 4-week baseline period, each woman was given active cream and matching placebo for 3 months in random order. Diaries were completed over the baseline period and for 1 week each month thereafter, and blood and saliva samples were collected at baseline and at 3 and 6 months, for measurement of lipids and hormones. The average age of the subjects was 53.3 *** 1.1 years and average time since last period 4.3 *** 0.9 years. At baseline, the average body mass index was 27.3 *** 0.8, cholesterol level 5.7 *** 0.2 mmol/L and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) level 74.2 5.1 IU/L; estradiol levels were undetectable in the majority of cases. After 3 months of treatment, no significant side effects were reported with either active treatment or placebo, and there were no changes in weight, systolic or diastolic blood pressure, or levels of total serum cholesterol, triglyceride, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, FSH, glucose, estradiol, or serum or salivary progesterone. Symptom scores showed a minor effect of both placebo and active treatment on diurnal flushing number and severity and total non-flushing symptom scores, and on nocturnal sweating after placebo, but no statistical difference between placebo and active creams. A randomized, controlled trial of 13 menopausal women given two capsules three times daily for 3 months of an herbal combination containing wild yam root in doses lower than recommended, along with burdock root (Arctium lappa), licorice root (Glycyrrhiza glabra), motherwort (Leonurus cardiaca), and angelica root (Angelica archangelica) demonstrated statistically nonsignificant decreases in menopausal symptoms in the active treatment group. Diosgenin, a component of wild yam, has been shown in several studies to reduce total serum cholesterol levels, likely as a result of reduced intestinal cholesterol and an effect potentiated by taking the herb with vitamin C. No hormonal effects, including no changes in DHEA, estrogen, and progesterone levels, or FSH or LH levels, have been observed. In one study of ovariectomized mice receiving 20 to 40 mg/kg of diosgenin injected subcutaneously daily for 15 days, mammary gland epithelial stimulation was observed without progesteronic effects, however, the effects of oral wild yam on breast tissue have not been studied in animal or human trials.
RATINGS
Botanical Safety Handbook class 1: Herbs that can be safely consumed when used appropriately.
SAFETY INFORMATION: HERB–DRUG INTERACTIONS, TOXICITY, AND CONTRAINDICATIONS
Anecdotal reports state that large doses (amounts unspecified) may result in emesis. Positive interactions may be found in association with added benefits of lipid reduction when combined with lipid-lowering medications.
SUMMARY
Scientific data do not lend credibility to the popular use of wild yam as a hormonal precursor or supplement. There is no research into the traditional and contemporary use of this herb as an antispasmodic for the hollow viscera. The herb appears safe when used as recommended both internally and topically. Although no significant reports of adverse events in pregnancy and lactation are found in the literature, care should be taken when using any herbs in this context.
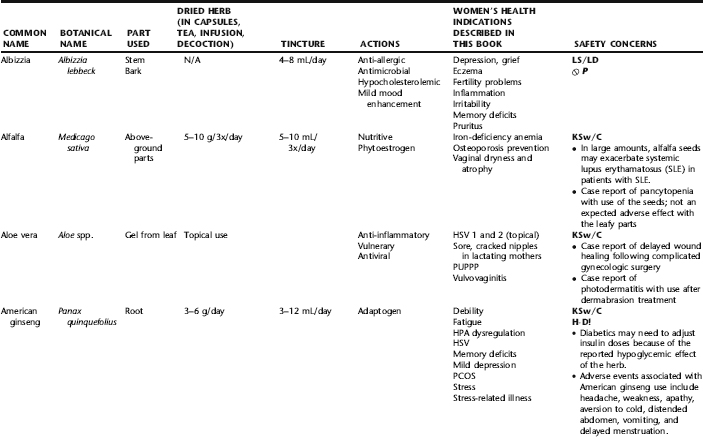
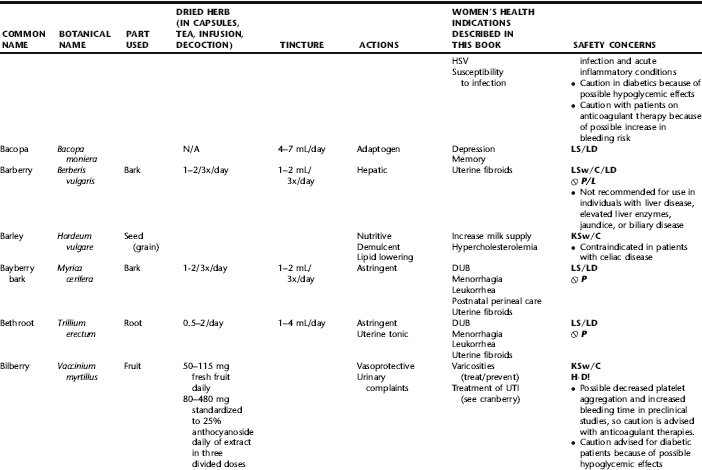
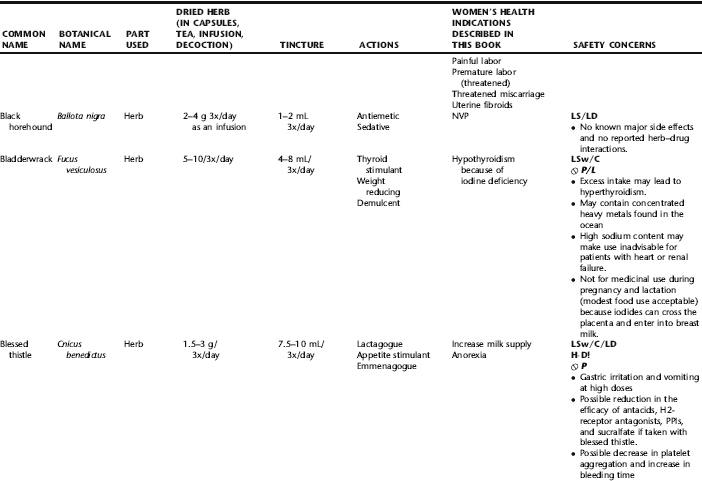
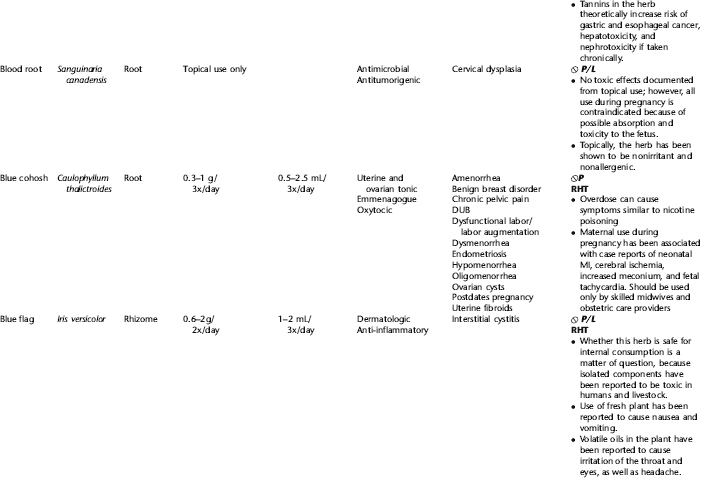
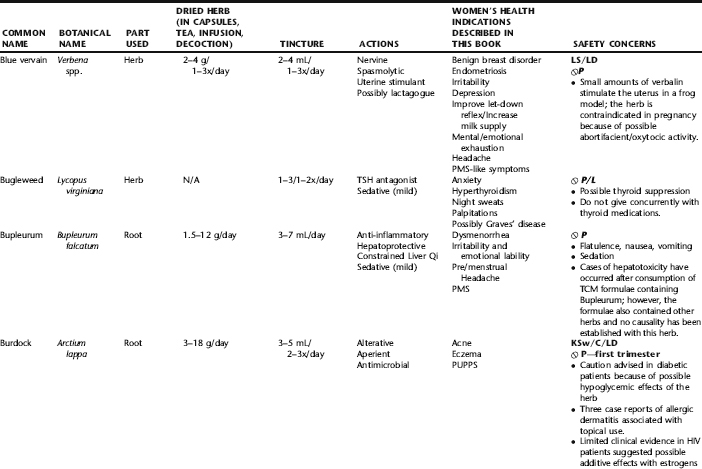
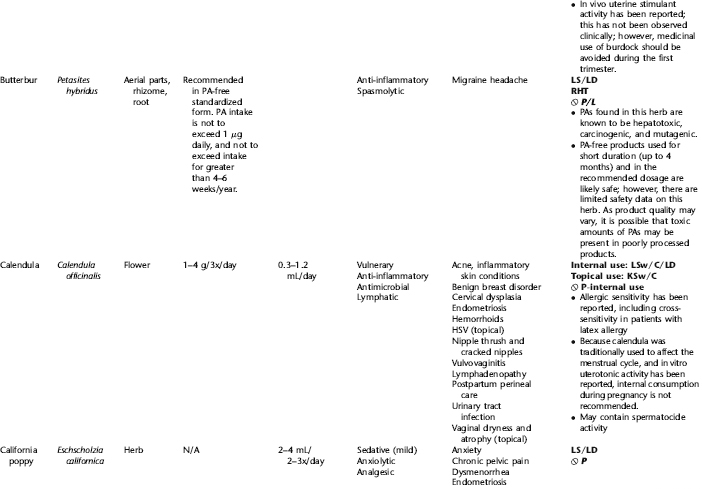
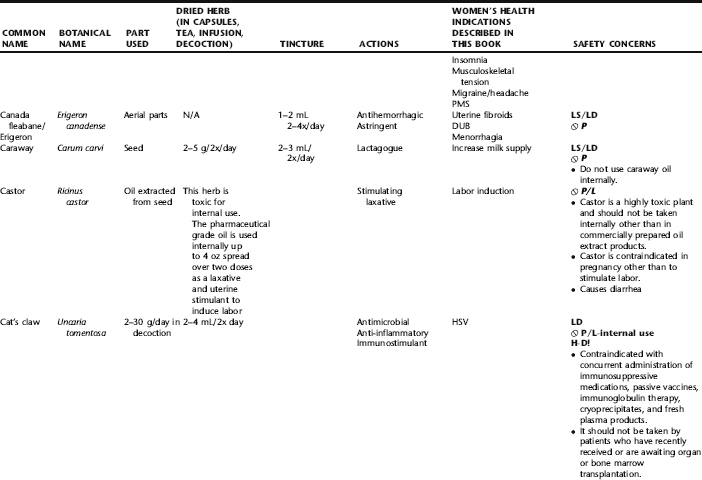
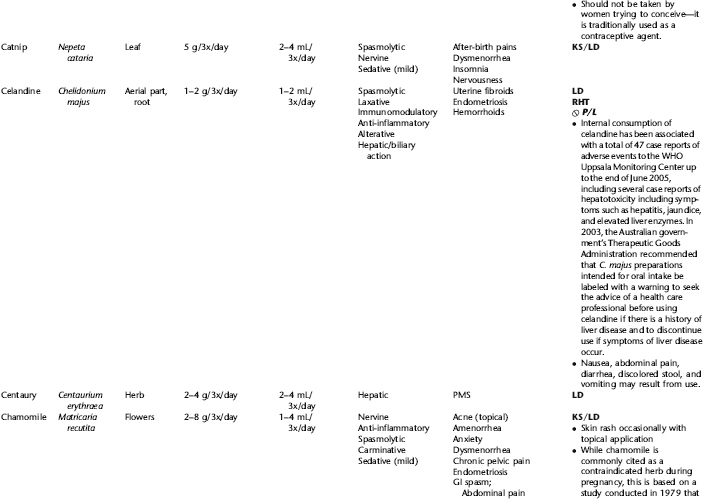
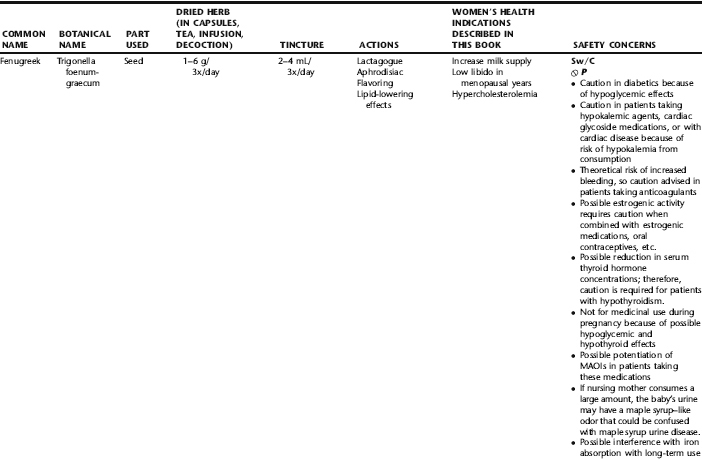
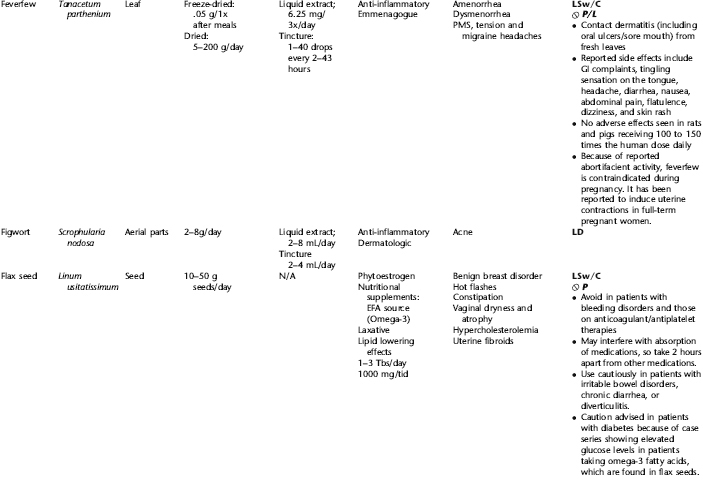
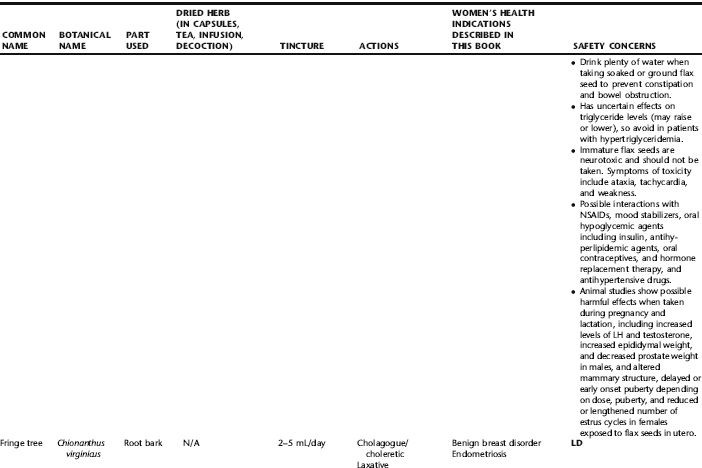
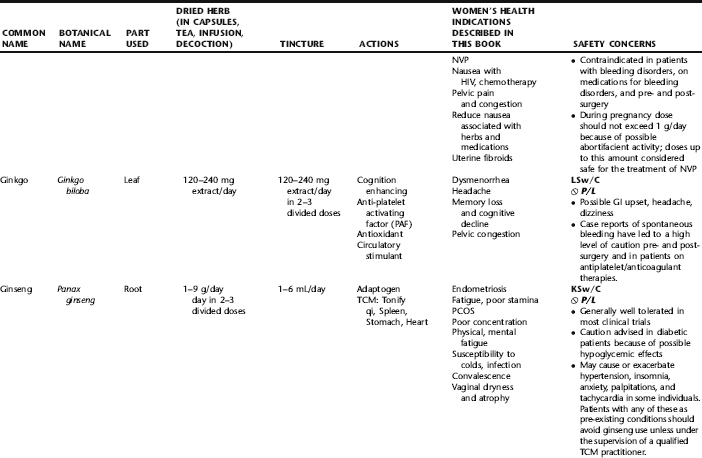
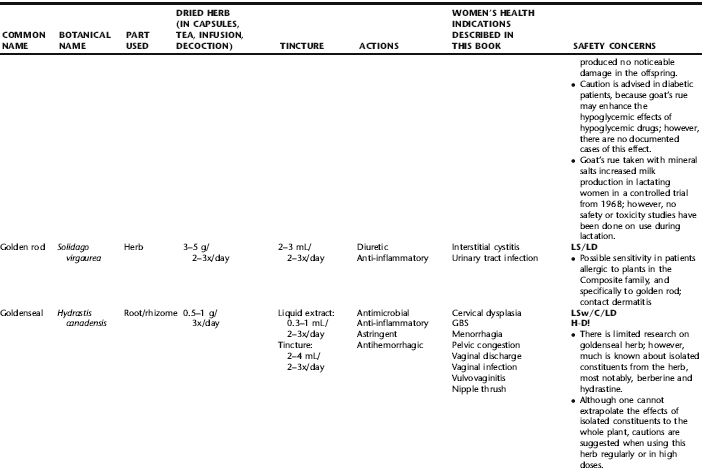
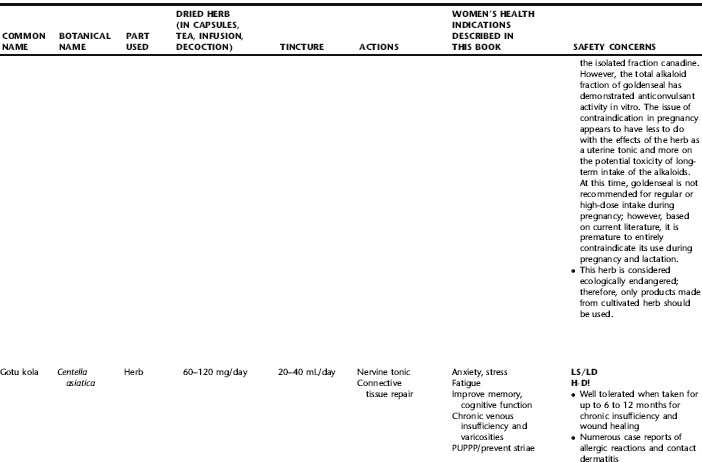
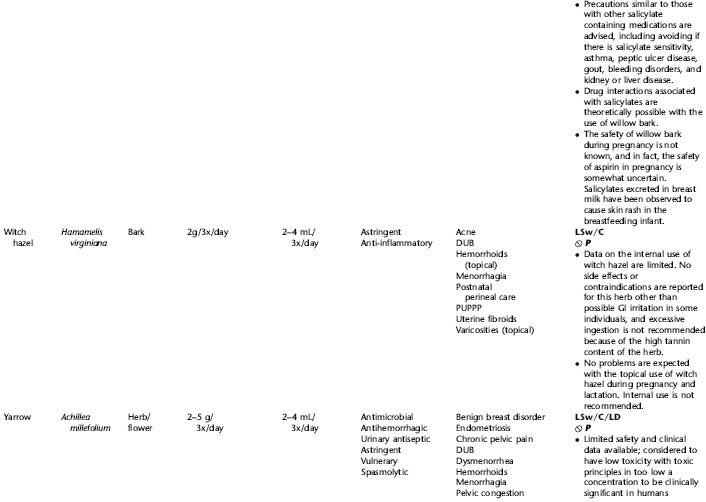
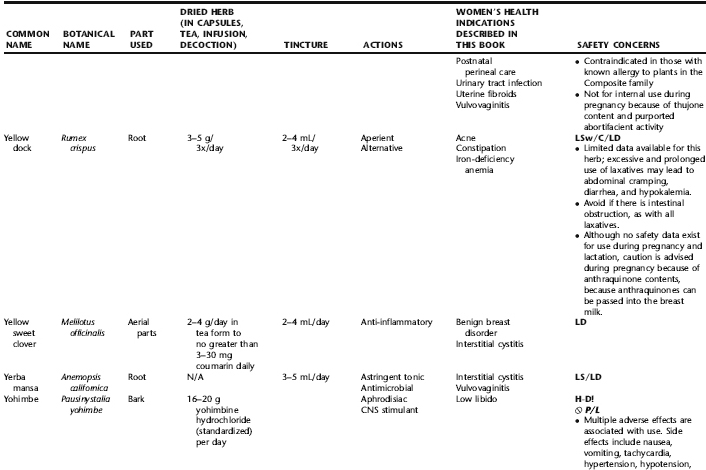
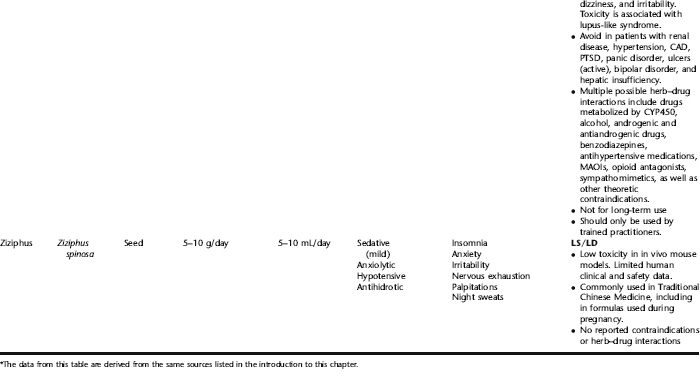
PLANT PROFILES: SUMMARY TABLE OF HERBS FOR WOMEN’S HEALTH
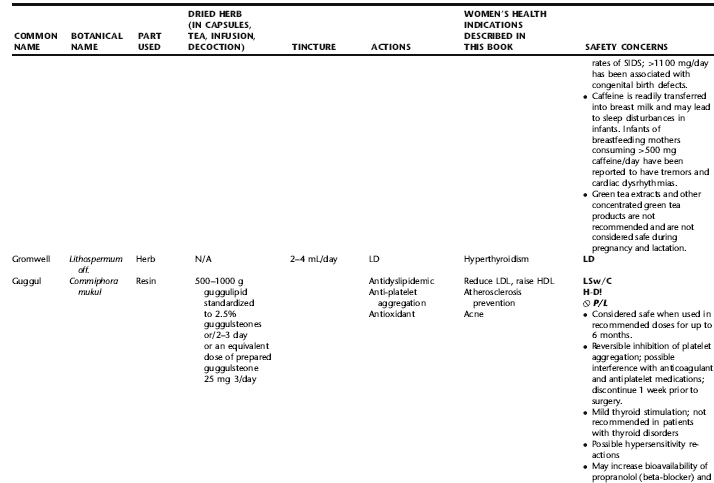
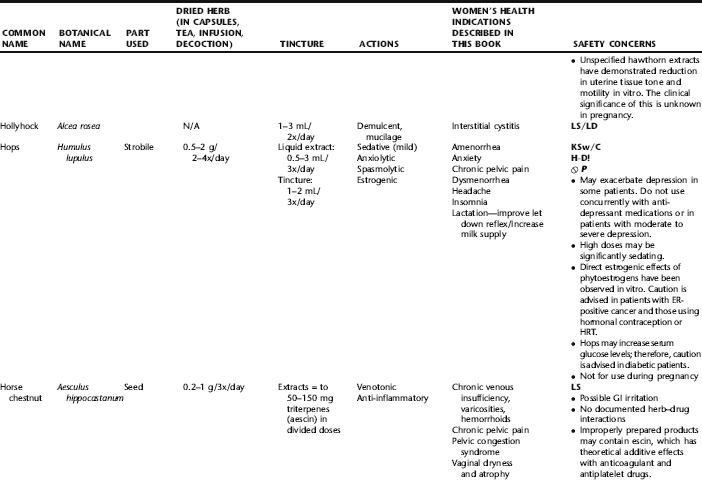
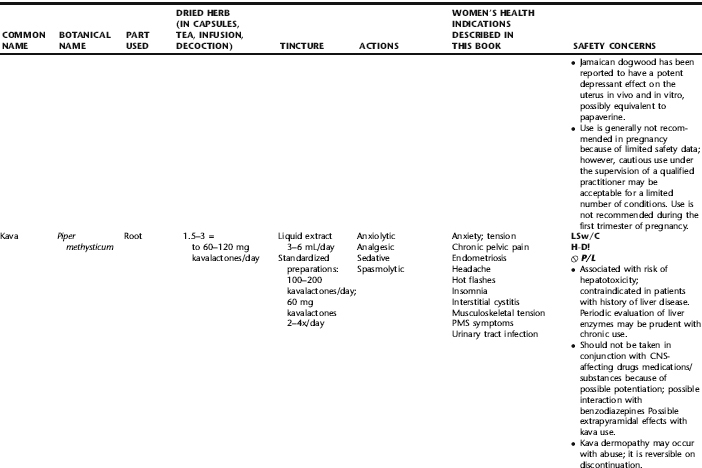
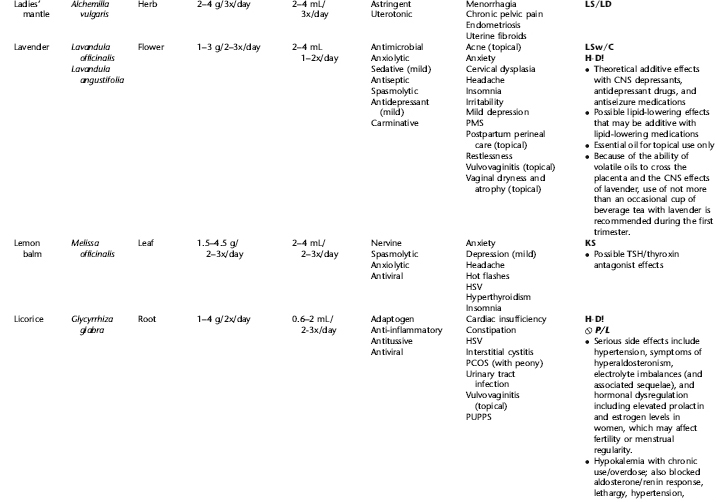
The following table provides a quick reference to dose, indications, and major safety issues for the pharmacopoeia of herbs for women’s health presented in this textbook. The table is not meant to be an exhaustive presentation of the scientific data for each herb; readers are encouraged to refer to the primary reference monographs and books from which this data was drawn. These resources were listed in the introduction to Part V: Plant Profiles. A great many herbs lack scientific research addressing clinical efficacy, mechanisms of action, and safety. Others have extensive research behind them. The data in this table does not attempt to address the scientific research for each herb; this is presented as relevant in the chapters within this textbook where the herb is mentioned in its clinical context. Only major safety issues are presented in the following. Allergic reactions, for example, are not addressed unless significant for a specific herb, as many individuals are allergic to plants in any number of families, for example, grasses, and thus may have a reaction to herbs in that family. Pregnancy data are listed only when specifically known to be safe or contraindicated. If not listed, it can be assumed that the data during pregnancy are not established due to lack of research. Readers are referred to Chapters 12 and 19 for specific information on the safety of specific herbs during the childbearing cycle. Many herb–drug interactions remain unknown, and the scientific literature is rife with examples of theoretical herb–drug interactions that may not have an actual clinical basis. Other interactions may, in fact, be positive, allowing the patient to use lower doses of potentially toxic medications, or helping patients to avoid the side effects of many commonly used medications. Nonetheless, caution and proper supervision are advised when taking herbs and pharmaceutical drugs simultaneously. Widely known contraindications or severe adverse effects that are well established are listed in bold. Practitioners will have to determine how to weigh single case reports on an individual basis.
KEY
The following abbreviations are intended to simplify use of the chart for readers:
KS: Known Safe: Known to be safe and well tolerated when used as recommended.
KSw/C: Known Safe with Cautions: Based on current information, this herb is considered generally safe and well tolerated, with no expected adverse effects when used within the recommended doses and duration and as indicated; however, there are cautions based on animal data or clinical reports of adverse effects, contraindications, or herb–drug interactions. A brief explanation of the adverse effects follows this abbreviation.
LS: Likely Safe: Based on current information, no known contraindications or major adverse effects are expected; likely safe when used within recommended doses.
LSw/C: Known Safe with Cautions: Based on current information, this herb is considered generally safe and well tolerated, with no expected adverse effects when used within the recommended doses and duration and as indicated; however, the safety data on this herb are limited and there are cautions based on animal data or clinical reports of adverse effects, contraindications, or herb–drug interactions. A brief explanation of the adverse effects follows this abbreviation.
KS or LS/LD: Known Safe or Likely Safe/Limited Data: This designation is for herbs with a long history of traditional use and that are generally known to be well tolerated and without major contraindications, side effects, or expected interactions but for which no data are available in the resources used for this table.
LSP/L: Likely Safe During Pregnancy and Lactation: This rating is given to those herbs that are considered safe for use as a culinary herb in modest amounts, or when there is specific evidence of safety during pregnancy and/or lactation.
Ø P or ØP/L: Not for Use During Pregnancy/Not for Use During Pregnancy and Lactation: This is based on known contraindications due either to constituents that are present in the herb and may be harmful to the fetus or infant, or to known adverse effects in animals or human clinical reports. External use is exempted from this contraindication unless specified.
H-D!: Herb–Drug Interactions: This symbol appears if there is a known or highly suspected herb–drug interaction. Any herbs appearing with this symbol should be used under the supervision of a qualified health care provider. If a risk is theoretic, the word possible is included in the wording of the caution.
RHT: Reported Human Toxicity: This notation identifies an herb with important reported human toxicity when the whole plant is used as recommended. Commonly, hepatotoxicity is reported. Reports may be from case histories or trials. This notation does not imply causality but does suggest an added level of caution with use. Individuals considering use of an herb marked with RHT should consult a qualified health professional prior to taking the herb. Any herbs marked RHT should not be used internally during pregnancy.